- Windows interoperability with Linux
- Run Linux tools from a Windows command line
- Mixing Linux and Windows commands
- Run Windows tools from Linux
- Share environment variables between Windows and WSL
- WSLENV flags
- Disable interoperability
- Earlier versions of Windows 10
- Как выполнять Linux-команды внутри Windows: официальный и сторонние способы
- Содержание
- WSL — официальная подсистема Linux внутри Windows
- CoreUtils — лёгкий инструмент для запуска базовых команд
- Cygwin — запуск команд и Bash-скриптов
Windows interoperability with Linux
The Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) is continuously improving integration between Windows and Linux. You can:
- Run Windows tools (ie. notepad.exe) from a Linux command line (ie. Ubuntu).
- Run Linux tools (ie. grep) from a Windows command line (ie. PowerShell).
- Share environment variables between Linux and Windows. (Build 17063+)
If you’re running Creators Update (Oct 2017, Build 16299) or Anniversary Update (Aug 2016, Build 14393), jump to the Earlier versions of Windows 10.
Run Linux tools from a Windows command line
Run Linux binaries from the Windows Command Prompt (CMD) or PowerShell using wsl (or wsl.exe ).
Binaries invoked in this way:
- Use the same working directory as the current CMD or PowerShell prompt.
- Run as the WSL default user.
- Have the same Windows administrative rights as the calling process and terminal.
The Linux command following wsl (or wsl.exe ) is handled like any command run in WSL. Things such as sudo, piping, and file redirection work.
Example using sudo to update your default Linux distribution:
Your default Linux distribution user name will be listed after running this command and you will be asked for your password. After entering your password correctly, your distribution will download updates.
Mixing Linux and Windows commands
Here are a few examples of mixing Linux and Windows commands using PowerShell.
To use the Linux command ls -la to list files and the PowerShell command findstr to filter the results for words containing «git», combine the commands:
To use the PowerShell command dir to list files and the Linux command grep to filter the results for words containing «git», combine the commands:
To use the Linux command ls -la to list files and the PowerShell command > out.txt to print that list to a text file named «out.txt», combine the commands:
The commands passed into wsl.exe are forwarded to the WSL process without modification. File paths must be specified in the WSL format.
To use the Linux command ls -la to list files in the /proc/cpuinfo Linux file system path, using PowerShell:
To use the Linux command ls -la to list files in the C:\Program Files Windows file system path, using PowerShell:
Run Windows tools from Linux
WSL can run Windows tools directly from the WSL command line using [tool-name].exe . For example, notepad.exe .
\’` as the file path.» Currently it I can just enter `notepad.exe foo.txt` and it seems to work fine, so explaining a situation where the file path is needed would be helpful. —>
Applications run this way have the following properties:
- Retain the working directory as the WSL command prompt (for the most part — exceptions are explained below).
- Have the same permission rights as the WSL process.
- Run as the active Windows user.
- Appear in the Windows Task Manager as if directly executed from the CMD prompt.
Windows executables run in WSL are handled similarly to native Linux executables — piping, redirects, and even backgrounding work as expected.
To run the Windows tool ipconfig.exe , use the Linux tool grep to filter the «IPv4» results, and use the Linux tool cut to remove the column fields, from a Linux distribution (for example, Ubuntu) enter:
Let’s try an example mixing Windows and Linux commands. Open your Linux distribution (ie. Ubuntu) and create a text file: touch foo.txt . Now use the Linux command ls -la to list the direct files and their creation details, plus the Windows PowerShell tool findstr.exe to filter the results so only your foo.txt file shows in the results:
Windows tools must include the file extension, match the file case, and be executable. Non-executables including batch scripts. CMD native commands like dir can be run with cmd.exe /C command.
For example, list the contents of your Windows files system C:\ directory, by entering:
Or use the ping command to send an echo request to the microsoft.com website:
Parameters are passed to the Windows binary unmodified. As an example, the following command will open C:\temp\foo.txt in notepad.exe :
This will also work:
Share environment variables between Windows and WSL
WSL and Windows share a special environment variable, WSLENV , created to bridge Windows and Linux distributions running on WSL.
Properties of WSLENV variable:
- It is shared; it exists in both Windows and WSL environments.
- It is a list of environment variables to share between Windows and WSL.
- It can format environment variables to work well in Windows and WSL.
- It can assist in the flow between WSL and Win32.
Prior to 17063, only Windows environment variable that WSL could access was PATH (so you could launch Win32 executables from under WSL). Starting in 17063, WSLENV begins being supported. WSLENV is case sensitive.
WSLENV flags
There are four flags available in WSLENV to influence how the environment variable is translated.
- /p — translates the path between WSL/Linux style paths and Win32 paths.
- /l — indicates the environment variable is a list of paths.
- /u — indicates that this environment variable should only be included when running WSL from Win32.
- /w — indicates that this environment variable should only be included when running Win32 from WSL.
Flags can be combined as needed.
Read more about WSLENV, including FAQs and examples of setting the value of WSLENV to a concatenation of other pre-defined environment vars, each suffixed with a slash followed by flags to specify how the value should be translated and passing variables with a script. This article also includes an example for setting up a dev environment with the Go programming language, configured to share a GOPATH between WSL and Win32.
Disable interoperability
Users may disable the ability to run Windows tools for a single WSL session by running the following command as root:
To re-enable Windows binaries, exit all WSL sessions and re-run bash.exe or run the following command as root:
Disabling interop will not persist between WSL sessions — interop will be enabled again when a new session is launched.
Earlier versions of Windows 10
There are several differences for the interoperability commands on earlier Windows 10 versions. If you’re running a Creators Update (Oct 2017, Build 16299), or Anniversary Update (Aug 2016, Build 14393) version of Windows 10, we recommend you update to the latest Windows version, but if that’s not possible, we have outlined some of the interop differences below.
- bash.exe has been replaced with wsl.exe .
- -c option for running a single command isn’t needed with wsl.exe .
- Windows path is included in the WSL $PATH .
- The process for disabling interop is unchanged.
Linux commands can be run from the Windows Command Prompt or from PowerShell, but for early Windows versions, you man need to use the bash command. For example:
Things such as input, piping, and file redirection work as expected.
The WSL commands passed into bash -c are forwarded to the WSL process without modification. File paths must be specified in the WSL format and care must be taken to escape relevant characters. Example:
When calling a Windows tool from a WSL distribution in an earlier version of Windows 10, you will need to specify the directory path. For example, from your WSL command line, enter:
In WSL, these executables are handled similar to native Linux executables. This means adding directories to the Linux path and piping between commands works as expected. For example:
Как выполнять Linux-команды внутри Windows: официальный и сторонние способы
Под GNU/Linux-дистрибутивы создано огромное количество полезных и удобных инструментов и приложений для обычных пользователей и разработчиков. Далеко не всё из этого доступно на Windows, но, к счастью, для ОС от Microsoft есть решения, исправляющие эту проблему.
Содержание
WSL — официальная подсистема Linux внутри Windows
В Windows 10 существует крайне полезная вещь под названием Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL). Она позволяет использовать GNU/Linux-среду прямо в Windows и запускать не только команды, но и, например, Bash-скрипты. Для использования WSL необходимо следовать инструкции ниже.
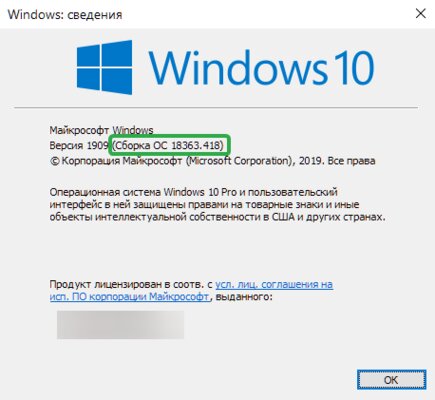
Шаг 1. Проверьте, подходит ли текущая версия Windows требованиям. Для этого нажмите сочетание клавиш Win+R, затем введите winver. Найдите строку «Сборка ОС» — она должна быть свежее версии 14316.
Шаг 2. Запустите стандартную утилиту PowerShell от имени администратора и введите в ней команду для включения WSL:
dism.exe /online /enable-feature /featurename:Microsoft-Windows-Subsystem-Linux /all /norestart
Шаг 3. Если версия Windows, определённая в первом пункте, свежее 18362, вы можете установить WSL 2, который в разы быстрее первой версии и обладает доработанным ядром. Введите команду ниже, если нужно установить WSL 2:
dism.exe /online /enable-feature /featurename:VirtualMachinePlatform /all /norestart
После этого скачайте и установите пакет обновления с официального сайта.
Шаг 4. Перезагрузите компьютер. Если была произведена установка WSL 2, введите в PowerShell от имени администратора следующую команду:
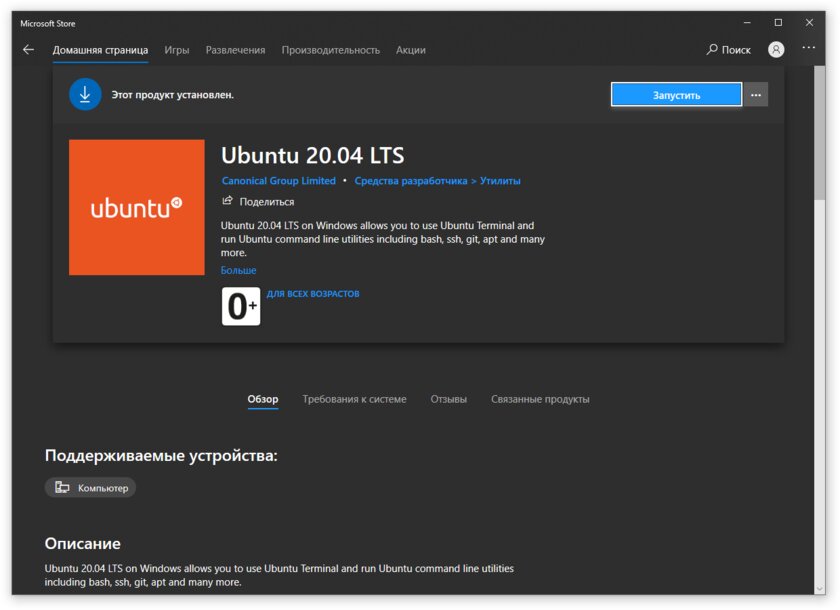
Шаг 5. После перезагрузки откройте фирменный магазин приложений Microsoft Store и найдите подходящий GNU/Linux-дистрибутив. Самым популярным является Ubuntu — вы можете установить любую версию из представленных в Microsoft Store.
Шаг 6. Как только установка завершится, найдите дистрибутив в меню «Пуск» и запустите его.
Шаг 7. Пройдите этап первоначальной настройки, введя имя нового пользователя и придумав пароль.
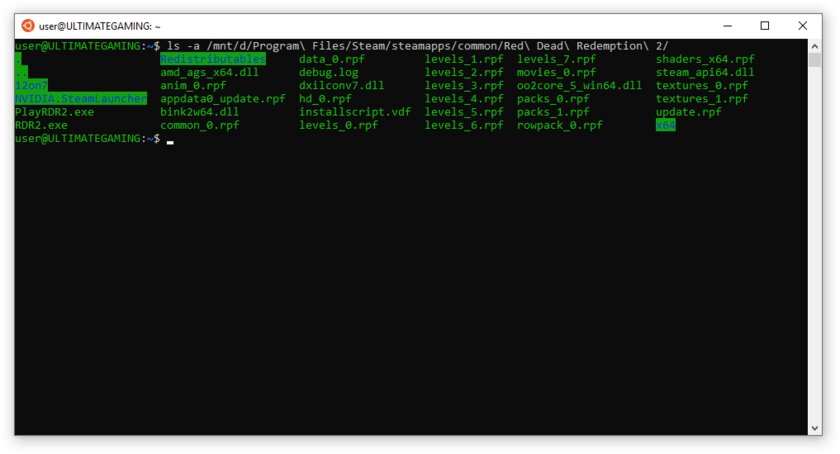
Шаг 8. Теперь различные GNU/Linux-команды можно выполнять, запустив дистрибутив, либо введя в командной строке wsl . Например, для просмотра всех файлов в текущей директории достаточно в командной строке выполнить wsl ls -a.
Обращу внимание на то, что путь к дискам в WSL отличается от такового в Windows. Вместо привычного C:/ используйте /mnt/c/. Также не забывайте про экранирование пробелов с помощью символа \ — это также пригодится при вводе путей к файлам.
Помимо выполнения базовых команд, с помощью WSL можно даже запускать приложения с графическим интерфейсом. Правда, рассчитывать на большое количество поддерживаемых подобных программ не стоит.
Шаг 1. Загрузите X-сервер и установите его.
Шаг 2. Запустите его с помощью ярлыка на рабочем столе. В открывшемся окне выберите вариант Multiple windows, затем Start no client. Завершите настройку кнопкой Finish.
Шаг 3. Откройте дистрибутив через меню Пуск и выполните команду export DISPLAY=:0
Шаг 4. Запустив приложение с графическим интерфейсом в WSL, вы увидите новое окно прямо в Windows.
CoreUtils — лёгкий инструмент для запуска базовых команд
Плюс данной утилиты — возможность запуска не только на Windows 10, но и на более старых версиях ОС. Кроме того, она легка и не занимает много места. Не обошлось без недостатков — программа скудна на функционал и не обновлялась очень давно. Она не только не умеет запускать скрипты и приложения с GUI, но и поддерживает лишь самые базовые GNU/Linux-команды. Установка CoreUtils весьма проста.
Шаг 1. Скачайте утилиту с официального сайта.
Шаг 2. Следуйте инструкциям установщика.
Шаг 3. Откройте «Панель управления», в разделе «Система и безопасность» выберите пункт «Система». На панели слева откройте «Дополнительные параметры системы». Нажмите кнопку «Переменные среды» и в открывшемся окне найдите область с заголовком «Системные переменные». В случае, когда там есть переменная Path, выберите её, нажмите «Изменить» и далее создайте новую строку. Содержимым этой строки должен быть путь к папке, который был указан при установке. Если вы ничего не меняли, то введите следующее:
Переменной Path нет? Тогда для начала создайте её кнопкой «Создать», затем в поле имени введите Path, а в поле значения — строку выше.
Шаг 4. Запустите командную строку и выполняйте команды прямо там.
Cygwin — запуск команд и Bash-скриптов
Ещё одна утилита, схожая с CoreUtils, но обладающая более широким функционалом — в том числе и возможностью запуска скриптов. Из минусов — немалый вес и более сложная установка. Разумеется, не идёт ни в какое сравнение с максимально удобным WSL, но для базовых команд вполне подойдёт.
Шаг 1. Загрузите Cygwin и запустите установку.
Шаг 2. Выберите Install from Internet, укажите директории для установки и загрузки пакетов, а также любой подходящий сайт из списка для скачивания файлов.
Шаг 3. В процессе установки можете выбрать необходимые пакеты, либо сразу нажать «Далее», оставив базовый набор.
Шаг 4. Откройте «Панель управления», в разделе «Система и безопасность» выберите пункт «Система». На панели слева откройте «Дополнительные параметры системы». Нажмите кнопку «Переменные среды» и в открывшемся окне найдите область с заголовком «Системные переменные». В случае, когда там есть переменная Path, выберите её, нажмите «Изменить» и далее создайте новую строку. Содержимым этой строки должен быть путь к папке, который был указан при установке. Если вы ничего не меняли, то введите следующее:
Переменной Path нет? Тогда для начала создайте её кнопкой «Создать», затем в поле имени введите Path, а в поле значения — строку выше.
Шаг 5. Команды можно выполнять как через командную строку, так и через специальный терминал.
Шаг 6. Для удаления Cygwin достаточно удалить папку, в которую программа была установлена, а также (по желанию) значение из переменной Path по методу, обратному тому, что был описан в 4 шаге (не удаляйте саму переменную).