How to Run Program from CMD (Command Prompt) Windows 10 [MiniTool News]
By Alisa | Follow | Last Updated June 10, 2020
Summary :
You can run a program or an exe file from Command Prompt. Check how to do it in this tutorial. MiniTool software, not only provides many useful computer solutions, but also provides users many useful computer software like data recovery program, disk partition manager, system backup and restore software, video editor, etc.
If you want to run program from CMD (Command Prompt) on Windows 10, you can check the detailed steps below.
How to Run a Program from CMD in Windows 10
You can only run the applications that are installed in Windows-created folders like Explorer in Command Prompt.
Step 1. Open Command Prompt in Windows 10
At first, you should open Command Prompt application on your Windows 10 computer. You can press Windows + R, type cmd, and press Enter to open normal Command Prompt or press Ctrl + Shift + Enter to open elevated Command Prompt on Windows 10.
Learn how to open a file/folder in Command Prompt (cmd) on Windows 10. Step-by-step guide is included.
Step 2. Run Program from CMD on Windows 10
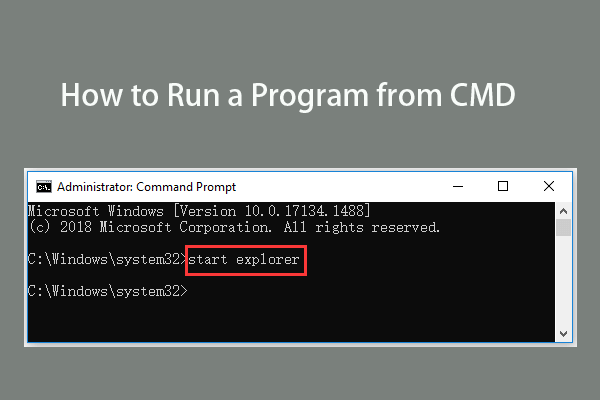
Next you can type start
command in Command Prompt window, and press Enter to open the target application in CMD. Replace the “program name” with the exact file’s system name of the program but not its shortcut name. For instance: start explorer.
The file’s system name of some common programs in Windows are as follows:
- Command Prompt: cmd
- File Explorer: explorer
- Task Manager: taskmgr
- Calculator: calc
- Notepad: notepad
- Paint: mspaint
- Windows Media Player: wmplayer
How to Run EXE in CMD on Windows 10
You can follow the instructions below to run an exe file in Command Prompt.
Step 1. Access Command Prompt window
You can follow the same operation above to open Command Prompt in Windows 10.
Step 2. Navigate to the folder of the target program
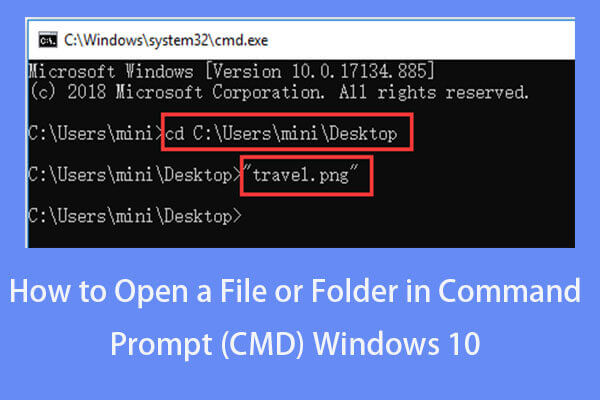
Next you can type cd command in Command Prompt window, and press Enter to navigate to the folder that contains the target exe application. Replace “file path” with the exact file path of the exe file.
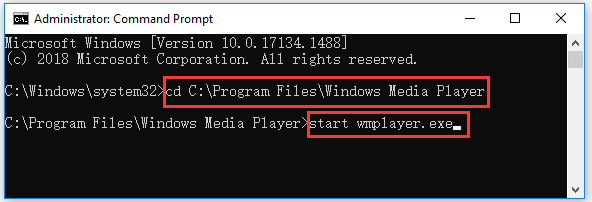
You can find the target program folder and click the address bar at the top of File Explorer window to copy the path of the program folder and paste it after cd command. For example, cd C:\Program Files\Windows Media Player.
Step 3. Run exe from CMD
After you are in the target program folder path, then you can type start after the selected file path in CMD, and press Enter to run the exe file in Command Prompt. Replace “filename.exe” with the target program name, e.g. start wmplayer.exe.
Bottom Line
This post introduces how to run a program or exe file from CMD on Windows 10. Hope it helps.
If you need a free data recovery software to recover deleted/lost files from Windows 10 computer or other storage devices, you can try MiniTool Power Data Recovery.
MiniTool Power Data Recovery is a Windows data recovery program that allows you to recover data from PC, external hard drive HDD or SSD, USB drive, SD card, memory card, and more. It is very simple to use and 100% clean.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR
Position: Columnist
Alisa is a professional English editor with 4-year experience. She loves writing and focuses on sharing detailed solutions and thoughts for computer problems, data recovery & backup, digital gadgets, tech news, etc. Through her articles, users can always easily get related problems solved and find what they want. In spare time, she likes basketball, badminton, tennis, cycling, running, and singing. She is very funny and energetic in life, and always brings friends lots of laughs.
Useful Run Commands Every Windows User Should Know
A quick-and-easy keyboard-only way to run Windows’ wealth of tools is through the “Run” command. If you know the corresponding Run command of a tool or task, then you know the quickest way to access said tool or task.
The following is a list of our favorite Run commands to help you be more productive.
Note: Press Win + R on your keyboard to open the Run dialog box, and enter any of the below commands to access the respective tool.
List of Run Commands
1. services.msc – When you enter “services.msc” and press the Enter button, it will open the Windows Services app where you can easily start, stop and configure other settings for each and every service individually. It’s quite helpful when you want to toggle a service.
2. mstsc – Entering “mstsc” into the Run dialog box opens the Remote Desktop Connection app which allows you to connect to another Windows computers over the local network or through the Internet. This helps you use the host computer as your own.
3. msinfo32 – If you want to quickly get your system information, then the “msinfo32” command is the way to go. At a glance it will display all the system details including the hardware resources and software environment.
4. sdclt – This command opens the Backup and Restore window that allows you to quickly set a backup schedule or restore any of your previous backups.
5. compmgmt.msc – The Computer Management app is where you can access almost all the advanced Windows modules like Event Viewer, Shared Folder, System Tools, etc.
6. cleanmgr – This command allows you to open the Windows Disk Cleanup utility. Once opened, simply select the drive your want to clean up and click the “OK” button.
7. eventvwr.msc – Windows Event Viewer is where Windows stores all the monitoring and troubleshooting messages. You can use this command to quickly access the Event Viewer application.
8. control – Every Windows user knows a thing or two about the Windows Control Panel, and using this command you can quickly access the Control Panel with some stumbling around.
9. mmc – Microsoft Management Console (MMC) is an advanced Windows module that is mainly aimed at system administrators and power users, as it sports all the tools required for configuring and monitoring a Windows system.
10. resmon – Whenever you want to check how your system resources are being utilized, simply use this Run command, and it displays everything from your CPU to Dist to Network.
11. \ – This is one of the lesser-known Run commands. Just enter the backslash into the Run dialog box, and it will open up the C drive. It is one of the quickest ways to access the C drive.
12. . – This is yet another lesser-known Run command. When executed, it opens the current user’s home folder which hosts all the other local folders like the Downloads, Documents, Desktop, Pictures, etc.
13. .. – When you execute these two dots in the Run dialog box, it will open up the Users folder which is located directly in the C drive.
14. calc – If you want to quickly open the built-in Windows calculator app, typing calc in the Run dialog box is the easiest way to do it.
15. cmd – Even Windows users have to deal with the command line sometimes. With this command you can quickly open the command prompt without administrator privileges.
16. powershell – If the command prompt is too old for you, then you may want to try PowerShell. Just type this command in the Run dialog box, and you will have your PowerShell opened without administrator privileges.
17. netplwiz – The general user accounts option is available through the Control Panel, but if you want to mess with the advanced user account options, then use this command to open the Advanced User Accounts window. If you want to deal with the Authorization Manager, then use the Run command azman.msc .
18. gpedit.msc – Group Policy Editor in Windows allows you to set and edit different Windows policies of a local or remote computer. Since Group Policy Editor is an advanced tool, it is buried deep inside Windows, and this Run command is the easiest way to access it.
19. lusrmgr.msc – Using this command, you can open the Local Users and Groups Manager where you can edit several properties of all the users and groups.
20. mrt – Every month Windows releases a newer version of Microsoft Windows Malicious Software Removal Tool through the Windows Update. This free tool helps you in cleaning some of the most popular malicious software from your Windows computer. This tool runs silently in the background, but if you want to run it manually, then use this Run command.
21. ncpa.cpl – Being an Internet user means that you have to deal with occasional (if not daily) network problems, and one way to troubleshoot your network connection is by accessing your Network Adapters. To access all your Network Adapters, you can use this Run command.
22. perfmon.msc – If you want to monitor the performance of your Windows computer and effects of the programs you run, running Performance Monitor will provide ample data. You can access the Performance Monitor using this command.
23. powercfg.cpl – Windows hosts a wide range of power options to deal with your computer’s power usage, and you can access all those Power Options using this command.
24. appwiz.cpl – Using this command you can quickly access the Programs and Features window where you can quickly uninstall your installed programs.
25. devmgmt.msc – Windows Device Manager is where you can manage all your hardware devices, and you can use this Run command to quickly access it. Alternatively, you can also use the command “hdwwiz.cpl.”
26. regedit – Regedit Run command can be used to access the Windows Registry, which is a hierarchical database that hosts all the configurations and settings of an operating system and the installed programs.
27. msconfig – Windows System Configuration is where you can edit different things like the boot options, startup options, services, etc. You can use this Run command to access the System Configuration window.
28. sysdm.cpl – If you ever want to access the System Properties window, then using this Run command opens it right up.
29. firewall.cpl – If you want to manage or configure your Windows firewall, then you can use this Run command to quickly access the Firewall window.
30. wuapp – Last but not least, you can use this command to check, manage and configure all your Windows update settings.
More Run Commands
Can’t get enough of the Run command? Here we have compiled a big list of all the Run commands available in Windows.
| Task Name | Run Command |
|---|---|
| About Windows | winver |
| Add a Device | devicepairingwizard |
| Add Hardware Wizard | hdwwiz |
| Advanced User Accounts | netplwiz |
| Authorization Manager | azman |
| Backup and Restore | sdclt |
| Bluetooth File Transfer | fsquirt |
| Calculator | calc |
| Certificates | certmgr |
| Change Computer Performance Settings | systempropertiesperformance |
| Change Data Execution Prevention Settings | systempropertiesdataexecutionprevention |
| Change Printer Settings | printui |
| Character Map | charmap |
| ClearType Tuner | cttune |
| Color Management | colorcpl |
| Command Prompt | cmd |
| Component Services | comexp |
| Component Services | dcomcnfg |
| Computer Management | compmgmt |
| Computer Management | compmgmtlauncher |
| Connect to a Network Projector | netproj |
| Connect to a Projector | displayswitch |
| Control Panel | control |
| Create A Shared Folder Wizard | shrpubw |
| Create a System Repair Disc | recdisc |
| Credential Backup and Restore Wizard | credwiz |
| Data Execution Prevention | systempropertiesdataexecutionprevention |
| Default Location | locationnotifications |
| Device Manager | devmgmt |
| Device Pairing Wizard | devicepairingwizard |
| Diagnostics Troubleshooting Wizard | msdt |
| Digitizer Calibration Tool | tabcal |
| DirectX Diagnostic Tool | dxdiag |
| Disk Cleanup | cleanmgr |
| Disk Defragmenter | dfrgui |
| Disk Management | diskmgmt |
| Display | dpiscaling |
| Display Color Calibration | dccw |
| Display Switch | displayswitch |
| DPAPI Key Migration Wizard | dpapimig |
| Driver Verifier Manager | verifier |
| Ease of Access Center | utilman |
| Encrypting File System Wizard | rekeywiz |
| Event Viewer | eventvwr |
| Fax Cover Page Editor | fxscover |
| File Signature Verification | sigverif |
| Getting Started | gettingstarted |
| IExpress Wizard | iexpress |
| Import to Windows Contacts | wabmig* |
| iSCSI Initiator Configuration Tool | iscsicpl |
| iSCSI Initiator Properties | iscsicpl |
| Language Pack Installer | lpksetup |
| Local Group Policy Editor | gpedit |
| Local Security Policy | secpol |
| Local Users and Groups | lusrmgr |
| Location Activity | locationnotifications |
| Magnifier | magnify |
| Malicious Software Removal Tool | mrt |
| Manage Your File Encryption Certificates | rekeywiz |
| Math Input Panel | mip* |
| Microsoft Management Console | mmc |
| Microsoft Support Diagnostic Tool | msdt |
| NAP Client Configuration | napclcfg |
| Narrator | narrator |
| New Scan Wizard | wiaacmgr |
| Notepad | notepad |
| ODBC Data Source Administrator | odbcad32 |
| ODBC Driver Configuration | odbcconf |
| On-Screen Keyboard | osk |
| Paint | mspaint |
| Performance Monitor | perfmon |
| Performance Options | systempropertiesperformance |
| Phone Dialer | dialer |
| Presentation Settings | presentationsettings |
| Print Management | printmanagement |
| Printer Migration | printbrmui |
| Printer User Interface | printui |
| Private Character Editor | eudcedit |
| Problem Steps Recorder | psr |
| Protected Content Migration | dpapimig |
| Registry Editor | regedit |
| Remote Access Phonebook | rasphone |
| Remote Desktop Connection | mstsc |
| Resource Monitor | resmon |
| Resultant Set of Policy | rsop |
| Securing the Windows Account Database | syskey |
| Services | services |
| Set Program Access and Computer Defaults | computerdefaults |
| Share Creation Wizard | shrpubw |
| Shared Folders | fsmgmt |
| Snipping Tool | snippingtool |
| Sound Recorder | soundrecorder |
| SQL Server Client Network Utility | cliconfg |
| Sticky Notes | stikynot |
| Stored User Names and Passwords | credwiz |
| Sync Center | mobsync |
| System Configuration | msconfig |
| System Configuration Editor | sysedit (This command doesn’t work in the 64-bit version of Windows.) |
| System Information | msinfo32 |
| System Properties (Advanced Tab) | systempropertiesadvanced |
| System Properties (Computer Name Tab) | systempropertiescomputername |
| System Properties (Hardware Tab) | systempropertieshardware |
| System Properties (Remote Tab) | systempropertiesremote |
| System Properties (System Protection Tab) | systempropertiesprotection |
| System Restore | rstrui |
| Tablet PC Input Panel | tabtip* |
| Task Manager | taskmgr |
| Task Scheduler | taskschd |
| Trusted Platform Module (TPM) Management | tpm |
| User Account Control Settings | useraccountcontrolsettings |
| Utility Manager | utilman |
| Version Reporter Applet | winver |
| Volume Mixer | sndvol |
| Windows Activation Client | slui |
| Windows Anytime Upgrade Results | windowsanytimeupgraderesults |
| Windows Contacts | wab* |
| Windows Disc Image Burning Tool | isoburn |
| Windows DVD Maker | dvdmaker* |
| Windows Easy Transfer | migwiz* |
| Windows Explorer | explorer |
| Windows Fax and Scan | wfs |
| Windows Features | optionalfeatures |
| Windows Firewall with Advanced Security | wf |
| Windows Help and Support | winhlp32 |
| Windows Journal | journal* |
| Windows Media Player | wmplayer* |
| Windows Memory Diagnostic Scheduler | mdsched |
| Windows Mobility Center | mblctr |
| Windows Picture Acquisition Wizard | wiaacmgr |
| Windows PowerShell | powershell* |
| Windows PowerShell ISE | powershell_ise* |
| Windows Remote Assistance | msra |
| Windows Repair Disc | recdisc |
| Windows Script Host | wscript |
| Windows Update | wuapp |
| Windows Update Standalone Installer | wusa |
| WMI Management | wmimgmt |
| WMI Tester | wbemtest |
| WordPad | write |
| XPS Viewer | xpsrchvw |
| Access Screen Resolution page | desk.cpl |
| Access Mouse properties | main.cpl |
| Access Windows Action Center | wscui.cpl |
| Access Network Adapters | ncpa.cpl |
| Access Power Option | powercfg.cpl |
| Access the Programs and Features Window | appwiz.cpl |
| Access the System Properties | sysdm.cpl |
| Access the Windows Firewall | firewall.cpl |
| *You cannot run these commands from a command prompt or the search box. |
As you can see, the Windows Run command is one of the best utilities you can find in Windows. Besides the commands shared above that first come to mind, there are many other commands to access different parts of Windows. So if you think that we missed any of your favorite Run commands, do share them in the comments below.