- Python on Windows FAQ¶
- How do I run a Python program under Windows?В¶
- How do I make Python scripts executable?В¶
- Why does Python sometimes take so long to start?В¶
- How do I make an executable from a Python script?В¶
- Is a *.pyd file the same as a DLL?В¶
- How can I embed Python into a Windows application?В¶
- How do I keep editors from inserting tabs into my Python source?В¶
- How do I check for a keypress without blocking?В¶
- Начало работы с Python в Windows для начинающих Get started using Python on Windows for beginners
- Настройка среды разработки Set up your development environment
- Установка Python Install Python
- Установка Visual Studio Code Install Visual Studio Code
- Установка Git (необязательно) Install Git (optional)
- Учебник по некоторым основам работы с Python (на примере Hello World) Hello World tutorial for some Python basics
- Учебник по использованию Python с VS Code (на примере Hello World) Hello World tutorial for using Python with VS Code
- Создание простой игры с помощью Pygame Create a simple game with Pygame
- Материалы для непрерывного обучения Resources for continued learning
- Онлайн-курсы для изучения Python Online courses for learning Python
- Работа с Python в VS Code Working with Python in VS Code
Python on Windows FAQ¶
How do I run a Python program under Windows?В¶
This is not necessarily a straightforward question. If you are already familiar with running programs from the Windows command line then everything will seem obvious; otherwise, you might need a little more guidance.
Unless you use some sort of integrated development environment, you will end up typing Windows commands into what is variously referred to as a “DOS window” or “Command prompt window”. Usually you can create such a window from your search bar by searching for cmd . You should be able to recognize when you have started such a window because you will see a Windows “command prompt”, which usually looks like this:
The letter may be different, and there might be other things after it, so you might just as easily see something like:
depending on how your computer has been set up and what else you have recently done with it. Once you have started such a window, you are well on the way to running Python programs.
You need to realize that your Python scripts have to be processed by another program called the Python interpreter. The interpreter reads your script, compiles it into bytecodes, and then executes the bytecodes to run your program. So, how do you arrange for the interpreter to handle your Python?
First, you need to make sure that your command window recognises the word “py” as an instruction to start the interpreter. If you have opened a command window, you should try entering the command py and hitting return:
You should then see something like:
You have started the interpreter in “interactive mode”. That means you can enter Python statements or expressions interactively and have them executed or evaluated while you wait. This is one of Python’s strongest features. Check it by entering a few expressions of your choice and seeing the results:
Many people use the interactive mode as a convenient yet highly programmable calculator. When you want to end your interactive Python session, call the exit() function or hold the Ctrl key down while you enter a Z , then hit the “ Enter ” key to get back to your Windows command prompt.
You may also find that you have a Start-menu entry such as Start ‣ Programs ‣ Python 3.x ‣ Python (command line) that results in you seeing the >>> prompt in a new window. If so, the window will disappear after you call the exit() function or enter the Ctrl-Z character; Windows is running a single “python” command in the window, and closes it when you terminate the interpreter.
Now that we know the py command is recognized, you can give your Python script to it. You’ll have to give either an absolute or a relative path to the Python script. Let’s say your Python script is located in your desktop and is named hello.py , and your command prompt is nicely opened in your home directory so you’re seeing something similar to:
So now you’ll ask the py command to give your script to Python by typing py followed by your script path:
How do I make Python scripts executable?В¶
On Windows, the standard Python installer already associates the .py extension with a file type (Python.File) and gives that file type an open command that runs the interpreter ( D:\Program Files\Python\python.exe «%1» %* ). This is enough to make scripts executable from the command prompt as вЂfoo.py’. If you’d rather be able to execute the script by simple typing вЂfoo’ with no extension you need to add .py to the PATHEXT environment variable.
Why does Python sometimes take so long to start?В¶
Usually Python starts very quickly on Windows, but occasionally there are bug reports that Python suddenly begins to take a long time to start up. This is made even more puzzling because Python will work fine on other Windows systems which appear to be configured identically.
The problem may be caused by a misconfiguration of virus checking software on the problem machine. Some virus scanners have been known to introduce startup overhead of two orders of magnitude when the scanner is configured to monitor all reads from the filesystem. Try checking the configuration of virus scanning software on your systems to ensure that they are indeed configured identically. McAfee, when configured to scan all file system read activity, is a particular offender.
How do I make an executable from a Python script?В¶
See cx_Freeze for a distutils extension that allows you to create console and GUI executables from Python code. py2exe, the most popular extension for building Python 2.x-based executables, does not yet support Python 3 but a version that does is in development.
Is a *.pyd file the same as a DLL?В¶
Yes, .pyd files are dll’s, but there are a few differences. If you have a DLL named foo.pyd , then it must have a function PyInit_foo() . You can then write Python “import foo”, and Python will search for foo.pyd (as well as foo.py, foo.pyc) and if it finds it, will attempt to call PyInit_foo() to initialize it. You do not link your .exe with foo.lib, as that would cause Windows to require the DLL to be present.
Note that the search path for foo.pyd is PYTHONPATH, not the same as the path that Windows uses to search for foo.dll. Also, foo.pyd need not be present to run your program, whereas if you linked your program with a dll, the dll is required. Of course, foo.pyd is required if you want to say import foo . In a DLL, linkage is declared in the source code with __declspec(dllexport) . In a .pyd, linkage is defined in a list of available functions.
How can I embed Python into a Windows application?В¶
Embedding the Python interpreter in a Windows app can be summarized as follows:
Do _not_ build Python into your .exe file directly. On Windows, Python must be a DLL to handle importing modules that are themselves DLL’s. (This is the first key undocumented fact.) Instead, link to python NN .dll ; it is typically installed in C:\Windows\System . NN is the Python version, a number such as “33” for Python 3.3.
You can link to Python in two different ways. Load-time linking means linking against python NN .lib , while run-time linking means linking against python NN .dll . (General note: python NN .lib is the so-called “import lib” corresponding to python NN .dll . It merely defines symbols for the linker.)
Run-time linking greatly simplifies link options; everything happens at run time. Your code must load python NN .dll using the Windows LoadLibraryEx() routine. The code must also use access routines and data in python NN .dll (that is, Python’s C API’s) using pointers obtained by the Windows GetProcAddress() routine. Macros can make using these pointers transparent to any C code that calls routines in Python’s C API.
Borland note: convert python NN .lib to OMF format using Coff2Omf.exe first.
If you use SWIG, it is easy to create a Python “extension module” that will make the app’s data and methods available to Python. SWIG will handle just about all the grungy details for you. The result is C code that you link into your .exe file (!) You do _not_ have to create a DLL file, and this also simplifies linking.
SWIG will create an init function (a C function) whose name depends on the name of the extension module. For example, if the name of the module is leo, the init function will be called initleo(). If you use SWIG shadow classes, as you should, the init function will be called initleoc(). This initializes a mostly hidden helper class used by the shadow class.
The reason you can link the C code in step 2 into your .exe file is that calling the initialization function is equivalent to importing the module into Python! (This is the second key undocumented fact.)
In short, you can use the following code to initialize the Python interpreter with your extension module.
There are two problems with Python’s C API which will become apparent if you use a compiler other than MSVC, the compiler used to build pythonNN.dll.
Problem 1: The so-called “Very High Level” functions that take FILE * arguments will not work in a multi-compiler environment because each compiler’s notion of a struct FILE will be different. From an implementation standpoint these are very _low_ level functions.
Problem 2: SWIG generates the following code when generating wrappers to void functions:
Alas, Py_None is a macro that expands to a reference to a complex data structure called _Py_NoneStruct inside pythonNN.dll. Again, this code will fail in a mult-compiler environment. Replace such code by:
It may be possible to use SWIG’s %typemap command to make the change automatically, though I have not been able to get this to work (I’m a complete SWIG newbie).
Using a Python shell script to put up a Python interpreter window from inside your Windows app is not a good idea; the resulting window will be independent of your app’s windowing system. Rather, you (or the wxPythonWindow class) should create a “native” interpreter window. It is easy to connect that window to the Python interpreter. You can redirect Python’s i/o to _any_ object that supports read and write, so all you need is a Python object (defined in your extension module) that contains read() and write() methods.
How do I keep editors from inserting tabs into my Python source?В¶
The FAQ does not recommend using tabs, and the Python style guide, PEP 8, recommends 4 spaces for distributed Python code; this is also the Emacs python-mode default.
Under any editor, mixing tabs and spaces is a bad idea. MSVC is no different in this respect, and is easily configured to use spaces: Take Tools ‣ Options ‣ Tabs , and for file type “Default” set “Tab size” and “Indent size” to 4, and select the “Insert spaces” radio button.
Python raises IndentationError or TabError if mixed tabs and spaces are causing problems in leading whitespace. You may also run the tabnanny module to check a directory tree in batch mode.
How do I check for a keypress without blocking?В¶
Use the msvcrt module. This is a standard Windows-specific extension module. It defines a function kbhit() which checks whether a keyboard hit is present, and getch() which gets one character without echoing it.
Начало работы с Python в Windows для начинающих Get started using Python on Windows for beginners
Это пошаговое руководство для начинающих работу с Python в Windows 10. The following is a step-by-step guide for beginners interested in learning Python using Windows 10.
Настройка среды разработки Set up your development environment
Для начинающих, которые не знакомы с Python, рекомендуется установить Python из Microsoft Store. For beginners who are new to Python, we recommend you install Python from the Microsoft Store. При установке из Microsoft Store используется базовый интерпретатор Python3, но в дополнение к автоматическому обновлению также настраиваются параметры пути для текущего пользователя (без необходимости доступа администратора). Installing via the Microsoft Store uses the basic Python3 interpreter, but handles set up of your PATH settings for the current user (avoiding the need for admin access), in addition to providing automatic updates. Это особенно полезно, если вы работаете из среды образовательного учреждения или являетесь частью организации, которая ограничивает разрешения или административный доступ на компьютере. This is especially helpful if you are in an educational environment or a part of an organization that restricts permissions or administrative access on your machine.
Если вы используете Python в Windows для разработки веб-приложений, мы рекомендуем настроить среду разработки другим образом. If you are using Python on Windows for web development, we recommend a different set up for your development environment. Вместо установки непосредственно в Windows рекомендуется установить и использовать Python через подсистему Windows для Linux. Rather than installing directly on Windows, we recommend installing and using Python via the Windows Subsystem for Linux. Справочные сведения см. в следующих статьях: Начало работы с Python для разработки веб-приложений в Windows. For help, see: Get started using Python for web development on Windows. Если вы заинтересованы в автоматизации общих задач в операционной системе, ознакомьтесь с нашим руководством: Начало работы с Python в Windows для создания сценариев и автоматизации If you’re interested in automating common tasks on your operating system, see our guide: Get started using Python on Windows for scripting and automation. В некоторых сложных сценариях (например, при необходимости модификации или доступа к установленным файлам Python, создания копий двоичных файлов или непосредственного использования библиотек DLL Python) может потребоваться загрузить определенный выпуск Python непосредственно с сайта python.org или установить альтернативное средство, например Anaconda, Jython, PyPy, WinPython, IronPython и т. д. Мы рекомендуем это только в том случае, если вы более продвинутый программист на Python и у вас есть конкретная причина выбрать альтернативную реализацию. For some advanced scenarios (like needing to access/modify Python’s installed files, make copies of binaries, or use Python DLLs directly), you may want to consider downloading a specific Python release directly from python.org or consider installing an alternative, such as Anaconda, Jython, PyPy, WinPython, IronPython, etc. We only recommend this if you are a more advanced Python programmer with a specific reason for choosing an alternative implementation.
Установка Python Install Python
Чтобы установить Python с помощью Microsoft Store, сделайте следующее: To install Python using the Microsoft Store:
Перейдите в меню Пуск (значок Windows в нижнем левом углу), введите «Microsoft Store» и щелкните ссылку, чтобы открыть магазин. Go to your Start menu (lower left Windows icon), type «Microsoft Store», select the link to open the store.
Когда магазин откроется, выберите Поиск в верхнем правом меню и введите «Python». Once the store is open, select Search from the upper-right menu and enter «Python». Выберите «Python 3.9» из результатов в разделе приложений. Open «Python 3.9» from the results under Apps. Щелкните Получить. Select Get.
После того как Python завершит процесс загрузки и установки, откройте Windows PowerShell, используя меню Пуск (значок Windows в нижнем левом углу). Once Python has completed the downloading and installation process, open Windows PowerShell using the Start menu (lower left Windows icon). После открытия PowerShell введите Python —version , чтобы убедиться, что Python 3 установлен на компьютере. Once PowerShell is open, enter Python —version to confirm that Python3 has installed on your machine.
Установка Python из Microsoft Store содержит стандартный диспетчер пакетов pip. The Microsoft Store installation of Python includes pip, the standard package manager. Pip позволяет устанавливать дополнительные пакеты, которые не входят в стандартную библиотеку Python, и управлять ими. Pip allows you to install and manage additional packages that are not part of the Python standard library. Чтобы убедиться, что у вас есть pip, который можно использовать для установки пакетов и управления ими, введите pip —version . To confirm that you also have pip available to install and manage packages, enter pip —version .
Установка Visual Studio Code Install Visual Studio Code
При использовании VS Code в качестве текстового редактора или интегрированной среды разработки (IDE) вам доступны IntelliSense (помощь в завершении кода), анализ кода (помогает избежать ошибок в коде), поддержка отладки (помогает находить ошибки в коде после запуска), фрагменты кода (шаблоны для небольших повторно используемых блоков кода) и модульное тестирование (тестирование интерфейса кода с различными типами входных данных). By using VS Code as your text editor / integrated development environment (IDE), you can take advantage of IntelliSense (a code completion aid), Linting (helps avoid making errors in your code), Debug support (helps you find errors in your code after you run it), Code snippets (templates for small reusable code blocks), and Unit testing (testing your code’s interface with different types of input).
VS Code также содержит встроенный терминал, который позволяет открывать командную строку Python с помощью командной строки Windows, PowerShell или любой другой, создавая простой рабочий процесс между редактором кода и командной строкой. VS Code also contains a built-in terminal that enables you to open a Python command line with Windows Command prompt, PowerShell, or whatever you prefer, establishing a seamless workflow between your code editor and command line.
Чтобы установить VS Code, скачайте VS Code для Windows: https://code.visualstudio.com. To install VS Code, download VS Code for Windows: https://code.visualstudio.com.
Установив VS Code, необходимо также установить расширение Python. Once VS Code has been installed, you must also install the Python extension. Для установки расширения Python можно выбрать ссылку на VS Code в Marketplace или открыть VS Code и выполнить поиск по фразе Python в меню расширений (Ctrl+Shift+X). To install the Python extension, you can select the VS Code Marketplace link or open VS Code and search for Python in the extensions menu (Ctrl+Shift+X).
Python — интерпретируемый язык, и для выполнения кода Python необходимо указать VS Code, какой интерпретатор нужно использовать. Python is an interpreted language, and in order to run Python code, you must tell VS Code which interpreter to use. Мы советуем использовать Python 3.7, если только у вас нет конкретной причины для выбора другой программы. We recommend sticking with Python 3.7 unless you have a specific reason for choosing something different. После установки расширения Python выберите интерпретатор Python 3, открыв палитру команд (CTRL+SHIFT+P), и начните вводить команду Python: Select Interpreter (Python: выбор интерпретатора) для поиска, а затем выберите появившуюся команду. Once you’ve installed the Python extension, select a Python 3 interpreter by opening the Command Palette (Ctrl+Shift+P), start typing the command Python: Select Interpreter to search, then select the command. Вы также можете использовать параметр Select Python Environment (Выбрать среду Python) в нижней строке состояния, если она доступна (возможно, уже отображается выбранный интерпретатор). You can also use the Select Python Environment option on the bottom Status Bar if available (it may already show a selected interpreter). Команда предоставляет список доступных интерпретаторов, которые VS Code может найти автоматически, включая виртуальные среды. The command presents a list of available interpreters that VS Code can find automatically, including virtual environments. Если нужный интерпретатор не отображается, перейдите к статье о настройке сред Python. If you don’t see the desired interpreter, see Configuring Python environments.
Чтобы открыть терминал в VS Code, выберите Просмотр > Терминал или используйте клавиши CTRL+` (символ обратного апострофа). To open the terminal in VS Code, select View > Terminal, or alternatively use the shortcut Ctrl+` (using the backtick character). Терминалом по умолчанию является PowerShell. The default terminal is PowerShell.
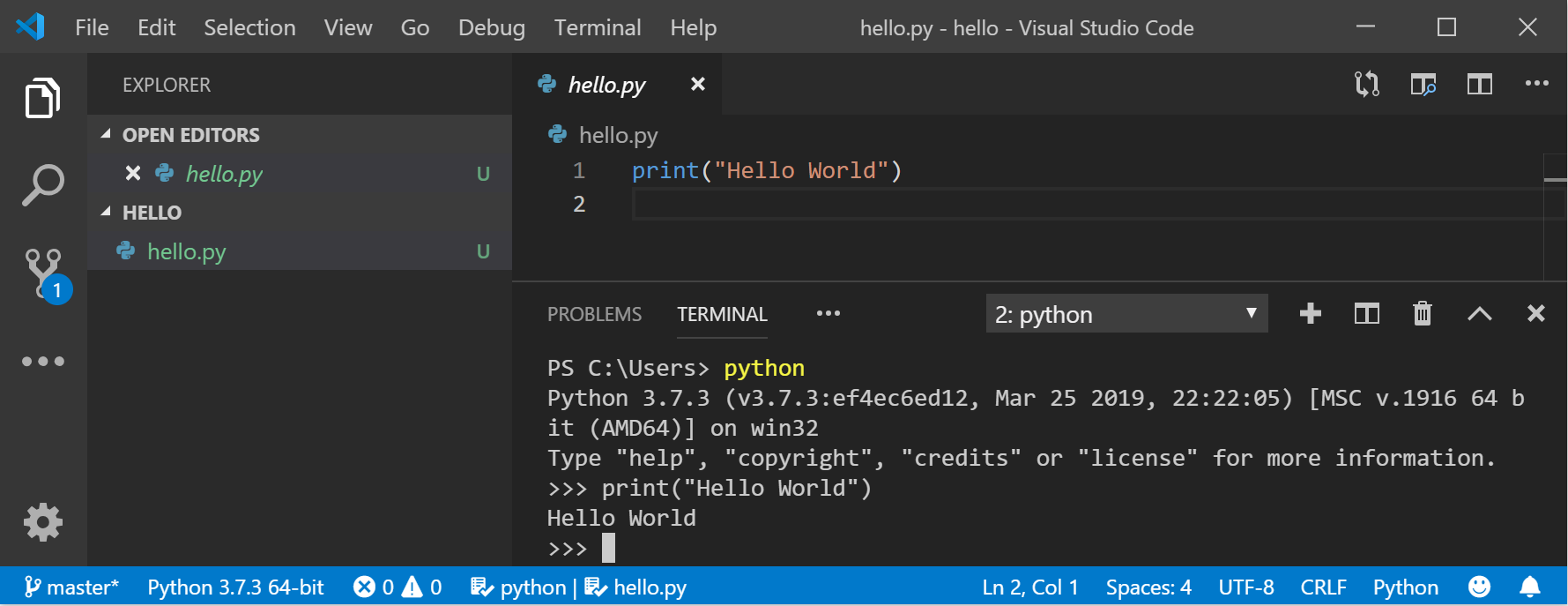
В окне терминала VS Code откройте Python, просто введя команду: python Inside your VS Code terminal, open Python by simply entering the command: python
Попробуйте использовать интерпретатор Python, введя: print(«Hello World») . Try the Python interpreter out by entering: print(«Hello World») . Python вернет фразу «Hello World». Python will return your statement «Hello World».
Установка Git (необязательно) Install Git (optional)
Если вы планируете совместно работать над кодом Python с другими пользователями или размещать проект на сайте с открытым исходным кодом (например, GitHub), примите во внимание, что VS Code поддерживает управление версиями с помощью Git. If you plan to collaborate with others on your Python code, or host your project on an open-source site (like GitHub), VS Code supports version control with Git. Вкладка системы управления версиями в VS Code отслеживает все изменения и содержит общие команды Git (добавление, фиксация, принудительная отправка, извлечение) прямо в пользовательском интерфейсе. The Source Control tab in VS Code tracks all of your changes and has common Git commands (add, commit, push, pull) built right into the UI. Сначала необходимо установить Git для включения панели управления версиями. You first need to install Git to power the Source Control panel.
Скачайте и установите Git для Windows с веб-сайта git-scm. Download and install Git for Windows from the git-scm website.
В комплект входит мастер установки, который задает вам ряд вопросов о параметрах установки Git. An Install Wizard is included that will ask you a series of questions about settings for your Git installation. Рекомендуется использовать все параметры по умолчанию, если у вас нет конкретной причины изменить какой-либо из них. We recommend using all of the default settings, unless you have a specific reason for changing something.
Если вы никогда не использовали Git, обратитесь к руководствам по GitHub. Они помогут вам приступить к работе. If you’ve never worked with Git before, GitHub Guides can help you get started.
Учебник по некоторым основам работы с Python (на примере Hello World) Hello World tutorial for some Python basics
Python, согласно его создателю Гвидо ван Россуму, — это «язык программирования высокого уровня, и его основная философия проектирования — это удобочитаемость кода и синтаксис, позволяющий программистам выразить концепции в нескольких строках кода». Python, according to its creator Guido van Rossum, is a “high-level programming language, and its core design philosophy is all about code readability and a syntax which allows programmers to express concepts in a few lines of code.”
Python — интерпретируемый язык. Python is an interpreted language. В отличие от скомпилированных языков, в которых написанный код необходимо перевести в машинный код для выполнения процессором компьютера, код Python передается непосредственно интерпретатору и запускается напрямую. In contrast to compiled languages, in which the code you write needs to be translated into machine code in order to be run by your computer’s processor, Python code is passed straight to an interpreter and run directly. Просто введите код и запустите его. You just type in your code and run it. Попробуем сделать это! Let’s try it!
Откройте командную строку PowerShell и введите python , чтобы запустить интерпретатор Python 3. With your PowerShell command line open, enter python to run the Python 3 interpreter. (В некоторых инструкциях указано использовать команду py или python3 , которые также подойдут.) (Some instructions prefer to use the command py or python3 , these should also work). Если вы делаете все правильно, появится командная строка с тремя символами «больше, чем» (>>>). You will know that you’re successful because a >>> prompt with three greater-than symbols will display.
Существует несколько встроенных методов, позволяющих вносить изменения в строки в Python. There are several built-in methods that allow you to make modifications to strings in Python. Создайте переменную с помощью команды variable = ‘Hello World!’ . Create a variable, with: variable = ‘Hello World!’ . Нажмите клавишу ВВОД для создания новой строки. Press Enter for a new line.
Выведите переменную с помощью команды print(variable) . Print your variable with: print(variable) . Отобразится текст «Hello World!». This will display the text «Hello World!».
Выясните, сколько символов используется для переменной строки, с помощью команды len(variable) . Find out the length, how many characters are used, of your string variable with: len(variable) . Будет показано, что используется 12 символов. This will display that there are 12 characters used. (Обратите внимание, что пробел учитывается как символ в общей длине.) (Note that the blank space it counted as a character in the total length.)
Преобразуйте строковую переменную в буквы верхнего регистра: variable.upper() . Convert your string variable to upper-case letters: variable.upper() . Теперь преобразуйте строковую переменную в буквы нижнего регистра: variable.lower() . Now convert your string variable to lower-case letters: variable.lower() .
Подсчитайте, сколько раз буква «l» используется в строковой переменной: variable.count(«l») . Count how many times the letter «l» is used in your string variable: variable.count(«l») .
Найдите определенный символ в вашей строковой переменной. Давайте найдем восклицательный знак с помощью команды variable.find(«!») . Search for a specific character in your string variable, let’s find the exclamation point, with: variable.find(«!») . Будет показано, что восклицательный знак находится в позиции 11 строки. This will display that the exclamation point is found in the 11th position character of the string.
Замените восклицательный знак на вопросительный знак: variable.replace(«!», «?») . Replace the exclamation point with a question mark: variable.replace(«!», «?») .
Чтобы выйти из Python, введите exit() , quit() или нажмите клавиши CTRL+Z. To exit Python, you can enter exit() , quit() , or select Ctrl-Z.
Надеемся, вам понравилось использовать некоторые из встроенных в Python методов модификации строк. Hope you had fun using some of Python’s built-in string modification methods. Теперь попробуйте создать файл программы Python и запустить его с помощью VS Code. Now try creating a Python program file and running it with VS Code.
Учебник по использованию Python с VS Code (на примере Hello World) Hello World tutorial for using Python with VS Code
Команда VS Code составила отличный учебник по началу работы с Python с пошаговым руководством по созданию программы Hello World с помощью Python, запуску программного файла, настройке и запуску отладчика, а также установке пакетов, таких как matplotlib и numpy, для создания графического изображения в виртуальной среде. The VS Code team has put together a great Getting Started with Python tutorial walking through how to create a Hello World program with Python, run the program file, configure and run the debugger, and install packages like matplotlib and numpy to create a graphical plot inside a virtual environment.
Откройте PowerShell и создайте пустую папку с именем hello, перейдите в эту папку и откройте ее в VS Code: Open PowerShell and create an empty folder called «hello», navigate into this folder, and open it in VS Code:
После открытия среды VS Code, где показана новая папка hello в левом окне обозревателя, откройте окно командной строки в нижней панели VS Code, нажав CTRL+` (символ обратного апострофа) или выбрав Просмотр > Терминал. Once VS Code opens, displaying your new hello folder in the left-side Explorer window, open a command line window in the bottom panel of VS Code by pressing Ctrl+` (using the backtick character) or selecting View > Terminal. После запуска VS Code в папке эта папка станет вашей рабочей областью. By starting VS Code in a folder, that folder becomes your «workspace». VS Code хранит параметры, относящиеся к этой рабочей области, в файле .vscode/settings.json. Они отделены от параметров пользователя, которые хранятся глобально. VS Code stores settings that are specific to that workspace in .vscode/settings.json, which are separate from user settings that are stored globally.
Продолжайте работу с учебником в документации для VS Code: Сведения о создании файла исходного кода для Hello World на Python. Continue the tutorial in the VS Code docs: Create a Python Hello World source code file.
Создание простой игры с помощью Pygame Create a simple game with Pygame
Pygame — это популярный пакет Python для создания игр, который позволяет учащимся изучать программирование увлекательным способом. Pygame is a popular Python package for writing games — encouraging students to learn programming while creating something fun. Pygame отображает графические изображения в новом окне, поэтому метод «только командной строки» WSL не подойдет. Pygame displays graphics in a new window, and so it will not work under the command-line-only approach of WSL. Но если вы установили Python с помощью Microsoft Store, как описано в этом учебнике, все получится. However, if you installed Python via the Microsoft Store as detailed in this tutorial, it will work fine.
После установки Python установите Pygame из командной строки (или терминала в VS Code), введя python -m pip install -U pygame —user . Once you have Python installed, install pygame from the command line (or the terminal from within VS Code) by typing python -m pip install -U pygame —user .
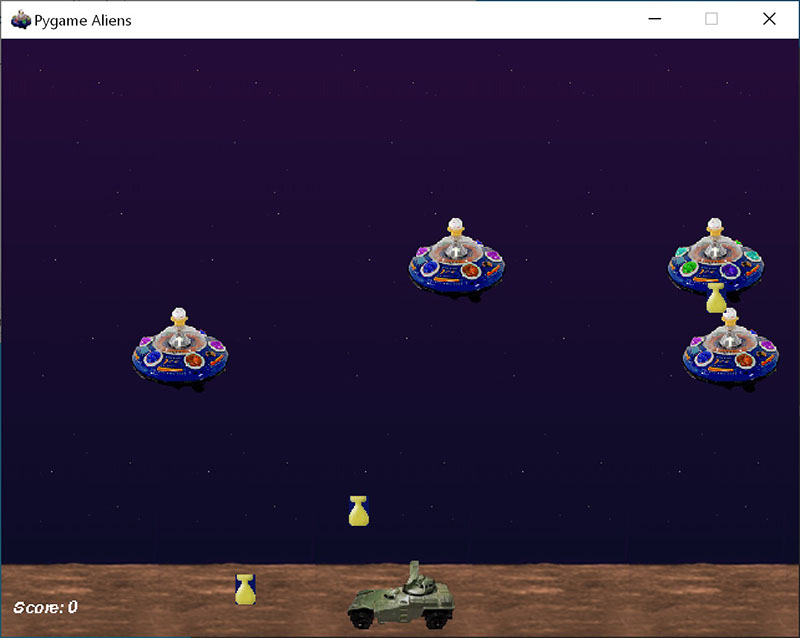
Протестируйте установку, запустив пример игры: python -m pygame.examples.aliens Test the installation by running a sample game : python -m pygame.examples.aliens
Если все в порядке, откроется окно игры. All being well, the game will open a window. По завершении игры закройте окно. Close the window when you are done playing.
Вот как начать написание кода собственной игры: Here’s how to start writing your own game.
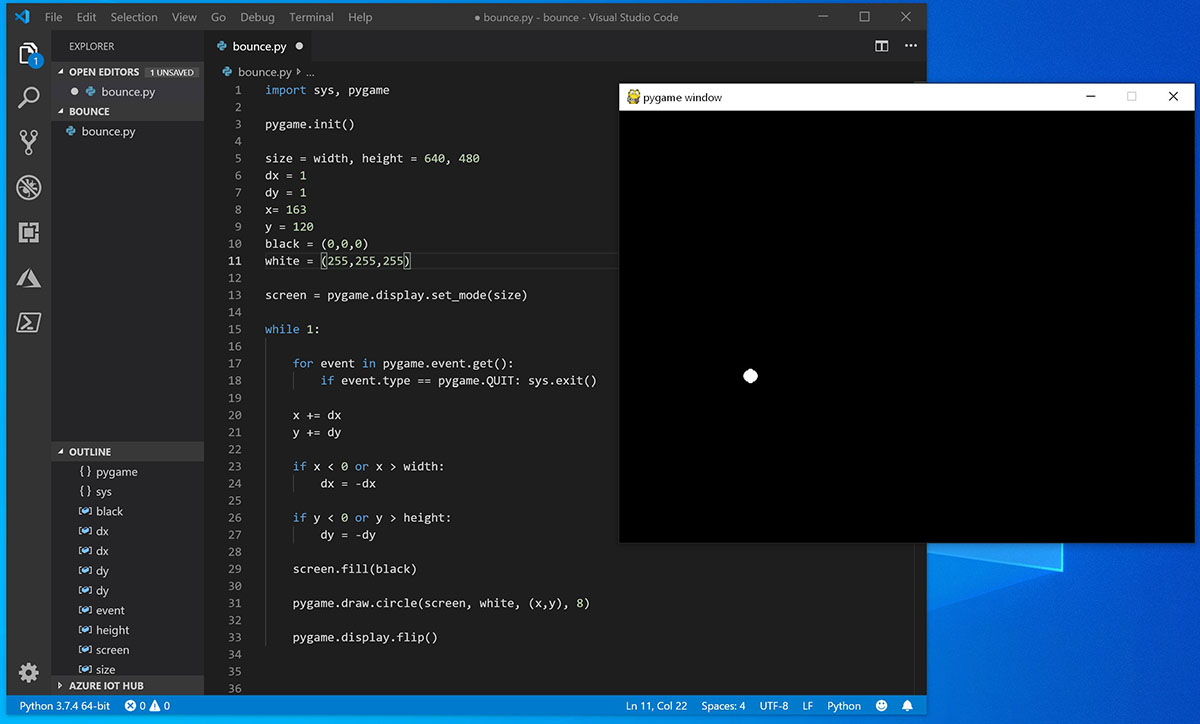
Откройте PowerShell (или командную строку Windows) и создайте пустую папку с именем bounce. Open PowerShell (or Windows Command Prompt) and create an empty folder called «bounce». Перейдите к этой папке и создайте файл с именем bounce.py. Navigate to this folder and create a file named «bounce.py». Откройте папку в VS Code: Open the folder in VS Code:
С помощью VS Code введите следующий код Python (или скопируйте и вставьте его): Using VS Code, enter the following Python code (or copy and paste it):
Сохраните его как: bounce.py . Save it as: bounce.py .
Запустите его в терминале PowerShell, введя: python bounce.py . From the PowerShell terminal, run it by entering: python bounce.py .
Попробуйте изменить некоторые из чисел, чтобы увидеть, как они влияют на прыгающий шарик. Try adjusting some of the numbers to see what effect they have on your bouncing ball.
Дополнительные сведения о создании игр с помощью Pygame см. на сайте pygame.org. Read more about writing games with pygame at pygame.org.
Материалы для непрерывного обучения Resources for continued learning
Мы рекомендуем использовать следующие ресурсы, чтобы продолжить изучение разработки на Python в Windows. We recommend the following resources to support you in continuing to learn about Python development on Windows.
Онлайн-курсы для изучения Python Online courses for learning Python
Введение в Python на Microsoft Learn. Попробуйте интерактивную платформу Microsoft Learn и получите навыки выполнения этого модуля, охватывающего основы написания базового кода Python, объявления переменных и работы с входными и выходными данными консоли. Introduction to Python on Microsoft Learn: Try the interactive Microsoft Learn platform and earn experience points for completing this module covering the basics on how to write basic Python code, declare variables, and work with console input and output. Интерактивная среда песочницы предоставляет эту отличную возможность начать пользователям, у которых еще не настроена среда разработки Python. The interactive sandbox environment makes this a great place to start for folks who don’t have their Python development environment set up yet.
Python на Pluralsight: 8 курсов, 29 часов. Схема обучения Python на Pluralsight предлагает онлайн-курсы, охватывающие различные темы, связанные с Python, включая средство для измерения навыков и поиска пробелов в знаниях. Python on Pluralsight: 8 Courses, 29 Hours: The Python learning path on Pluralsight offers online courses covering a variety of topics related to Python, including a tool to measure your skill and find your gaps.
Учебники на сайте LearnPython.org. Приступите к изучению Python без необходимости дополнительной установки или настройки с помощью этих бесплатных интерактивных учебников по Python от DataCamp. LearnPython.org Tutorials: Get started on learning Python without needing to install or set anything up with these free interactive Python tutorials from the folks at DataCamp.
Учебники на сайте Python.org. Предоставляют читателям неформальное описание основных понятий и функций языка и системы Python. The Python.org Tutorials: Introduces the reader informally to the basic concepts and features of the Python language and system.
Изучение Python на сайте Lynda.com. Основные сведения о Python. Learning Python on Lynda.com: A basic introduction to Python.
Работа с Python в VS Code Working with Python in VS Code
Редактирование Python в VS Code. Узнайте больше о том, как воспользоваться преимуществами автозаполнения VS Code и поддержкой IntelliSense для Python, включая их настройку или отключение. Editing Python in VS Code: Learn more about how to take advantage of VS Code’s autocomplete and IntelliSense support for Python, including how to customize their behavior. or just turn them off.
Анализ кода Python. Анализ кода — это процесс запуска программы, которая будет анализировать код на наличие возможных ошибок. Linting Python: Linting is the process of running a program that will analyse code for potential errors. Узнайте о различных формах поддержки анализа кода VS Code для Python и о том, как выполнить его настройку. Learn about the different forms of linting support VS Code provides for Python and how to set it up.
Отладка Python. Отладка — это процесс обнаружения и удаления ошибок из компьютерной программы. Debugging Python: Debugging is the process of identifying and removing errors from a computer program. В статье по этой ссылке описывается инициализация и настройка отладки для Python с помощью VS Code, установка и проверка точек останова, присоединение локального скрипта, выполнение отладки для различных типов приложений или на удаленном компьютере, а также некоторые основные способы устранения неполадок. This article covers how to initialize and configure debugging for Python with VS Code, how to set and validate breakpoints, attach a local script, perform debugging for different app types or on a remote computer, and some basic troubleshooting.
Модульное тестирование Python. В статье по этой ссылке содержатся некоторые основные сведения о модульном тестировании, включении платформы тестирования, создании и выполнении тестов, отладке тестов и параметрах конфигурации теста, а также приведено пошаговое руководство с примером. Unit testing Python: Covers some background explaining what unit testing means, an example walkthrough, enabling a test framework, creating and running your tests, debugging tests, and test configuration settings.