- System File Checker
- How to run SFC scannow in Windows 10
- How to use SFC scannow in Safe Mode
- Most common System File Checker/SFC scannow errors
- Use the System File Checker tool to repair missing or corrupted system files
- Run the System File Checker tool (SFC.exe)
- More Information
- CheckSystem¶
- Queries¶
- check_cpu¶
- Sample Commands¶
- Command-line Arguments¶
- Filter keywords¶
- check_memory¶
- Sample Commands¶
- Command-line Arguments¶
- Filter keywords¶
- check_network¶
- Command-line Arguments¶
- Filter keywords¶
- check_os_version¶
- Sample Commands¶
- Command-line Arguments¶
- Filter keywords¶
- check_pagefile¶
- Sample Commands¶
- Command-line Arguments¶
- Filter keywords¶
- check_pdh¶
- Sample Commands¶
- Command-line Arguments¶
- Filter keywords¶
- check_process¶
- Sample Commands¶
- Command-line Arguments¶
- Filter keywords¶
- check_service¶
- Sample Commands¶
- Command-line Arguments¶
- Filter keywords¶
- check_uptime¶
- Sample Commands¶
- Command-line Arguments¶
- Filter keywords¶
- checkcounter¶
- Command-line Arguments¶
- checkcpu¶
- Command-line Arguments¶
- checkmem¶
- Command-line Arguments¶
- checkprocstate¶
- Command-line Arguments¶
- checkservicestate¶
- Command-line Arguments¶
- checkuptime¶
- Command-line Arguments¶
- Configuration¶
- Windows system ¶
- Default buffer time ¶
- Disable automatic checks ¶
- PDH subsystem ¶
- PDH Counters ¶
- Legacy generic filters ¶
- Realtime cpu filters ¶
- Realtime memory filters ¶
- Realtime process filters ¶
System File Checker
- Download Restoro PC Repair Tool that comes with Patented Technologies (patent available here).
- Click Start Scan to find Windows issues that could be causing PC problems.
- Click Repair All to fix issues affecting your computer’s security and performance
- Restoro has been downloaded by 0 readers this month.
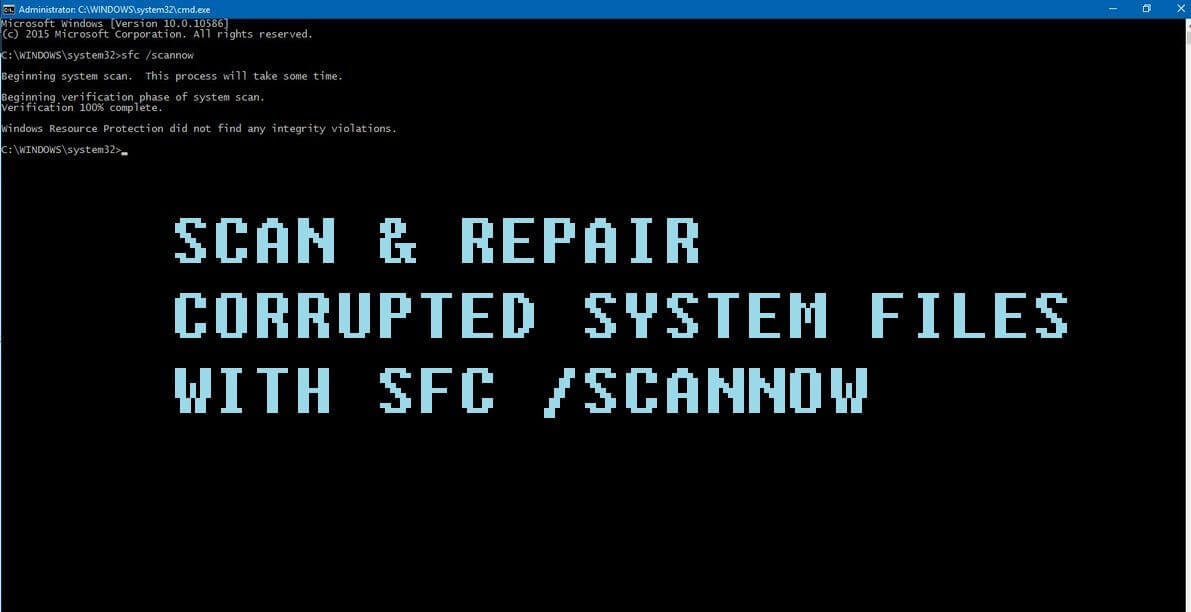
System File Checker (SFC) is a utility in Microsoft Windows that allows users to scan for and restore corruptions in Windows system files. This utility is available on all versions of Windows OS and is located in C:WindowsSystem32 folder.
This article will describe the following issues related to SFC tool:
The time required for SFC command scannow to repair important windows files is usually from 5 to 15 minutes.
How to run SFC scannow in Windows 10
The SFC might resolve many system errors, including blue screen issues. This is how you can run an SFC scan in Windows.
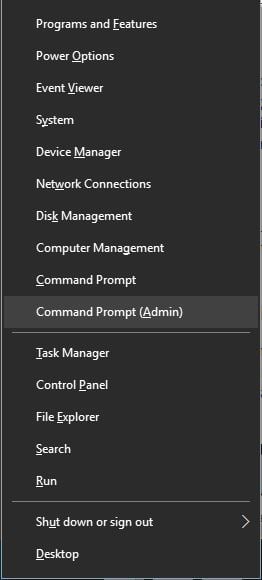
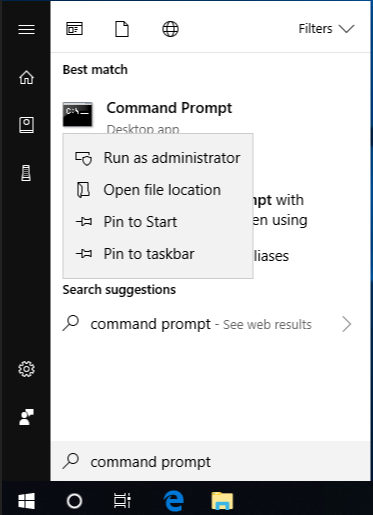
- Press the Windows key + X to open the main menu.
- Click Command Prompt (Admin) to open the Command Prompt as an administrator.
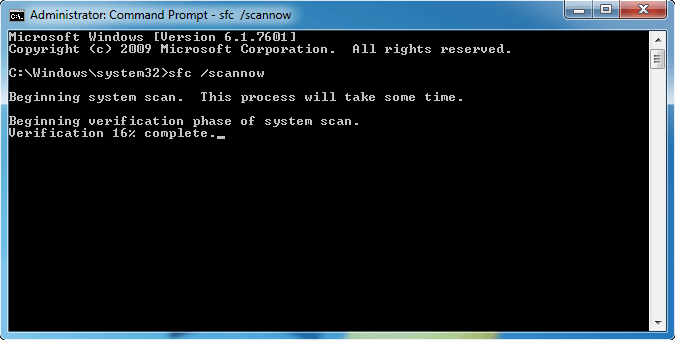
- When Command Prompt opens, enter sfc /scannow and press Enter.
- The repair process will now start. Don’t close Command Prompt or interrupt the repair process. The repair process can take a while, so wait patiently while it completes.
- When the SFC scan is complete, the Command Prompt might state, “Windows Resource Protection found corrupt files and successfully repaired them.” If that’s the case, restart Windows.
How to use SFC scannow in Safe Mode
When you cannot complete the SFC scan normally, you should initiate the same process from Safe Mode.
When the Windows 10 OS runs in Safe Mode all third-party apps, and the processes associated with such software will be stopped or deactivated.
Thus, if the SFC error was somehow related with a third party software, now you will be able to successfully perform the system scan.
Here is how you can reboot your device into Safe Mode right away:
- Launch the Run engine on your Windows 10 device: press the Win+R keyboard keys together.
- In the Run box type msconfig and click on OK.msconfig windows 10
- From System Configuration switch to Boot tab.
- Under Boot options select the Safe mode checkbox and also check Minimal from underneath.
- Click OK and Apply.reboot safe mode windows 10
- When prompted choose Restart.
- Now your device will be automatically restarted into Safe Mode.
- From there run the sfc /scannow command.
Most common System File Checker/SFC scannow errors
Although this process can automatically repair the most common Windows soft-related problems, in some situations, SFC itself might experience malfunctions.
Here are some of the most common issues that users reported:
Use the System File Checker tool to repair missing or corrupted system files
If some Windows functions aren’t working or Windows crashes, use the System File Checker to scan Windows and restore your files.
Though the steps below might look complicated at first glance, just follow them in order, step-by-step, and we’ll try to get you back on track.
Run the System File Checker tool (SFC.exe)
To do this, follow these steps:
Open an elevated command prompt. To do this, do the following as your appropriate:
If you are running Windows 10, Windows 8.1 or Windows 8, first run the inbox Deployment Image Servicing and Management (DISM) tool prior to running the System File Checker. (If you are running Windows 7 or Windows Vista, skip to Step 3.)
Type the following command, and then press Enter. It may take several minutes for the command operation to be completed.
DISM.exe /Online /Cleanup-image /Restorehealth
Important: When you run this command, DISM uses Windows Update to provide the files that are required to fix corruptions. However, if your Windows Update client is already broken, use a running Windows installation as the repair source, or use a Windows side-by-side folder from a network share or from a removable media, such as the Windows DVD, as the source of the files. To do this, run the following command instead:
DISM.exe /Online /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealth /Source: C:\RepairSource\Windows /LimitAccess
Note: Replace the C:\RepairSource\Windows placeholder with the location of your repair source. For more information about using the DISM tool to repair Windows, reference Repair a Windows Image.
At the command prompt, type the following command, and then press ENTER:
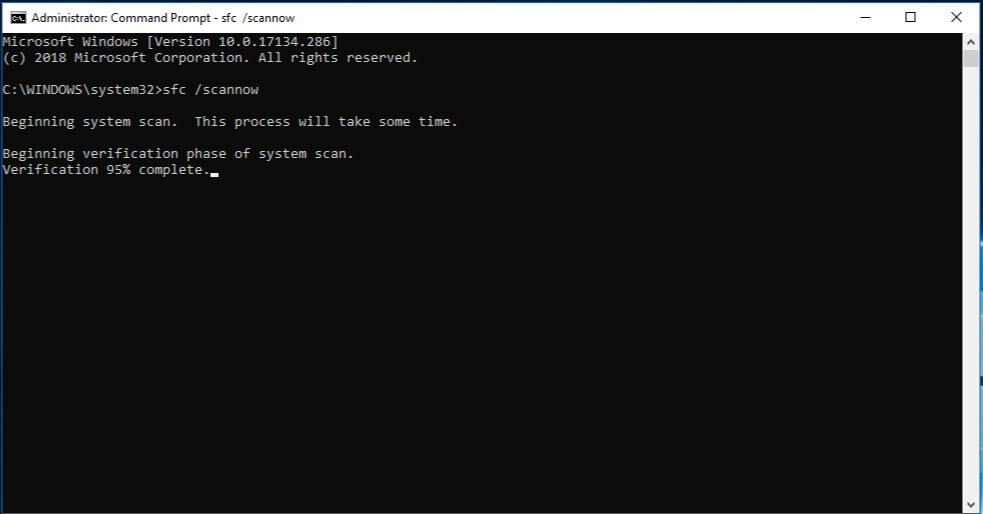
The sfc /scannow command will scan all protected system files, and replace corrupted files with a cached copy that is located in a compressed folder at %WinDir%\System32\dllcache.
The %WinDir% placeholder represents the Windows operating system folder. For example, C:\Windows.
Note Do not close this Command Prompt window until the verification is 100% complete. The scan results will be shown after this process is finished.
After the process is finished, you may receive one of the following messages:
Windows Resource Protection did not find any integrity violations.
This means that you do not have any missing or corrupted system files.
Windows Resource Protection could not perform the requested operation.
To resolve this problem, perform the System File Checker scan in safe mode, and make sure that the PendingDeletes and PendingRenames folders exist under %WinDir%\WinSxS\Temp.
Windows Resource Protection found corrupt files and successfully repaired them. Details are included in the CBS.Log %WinDir%\Logs\CBS\CBS.log.
To view the detail information about the system file scan and restoration, go to How to view details of the System File Checker process.
Windows Resource Protection found corrupt files but was unable to fix some of them. Details are included in the CBS.Log %WinDir%\Logs\CBS\CBS.log.
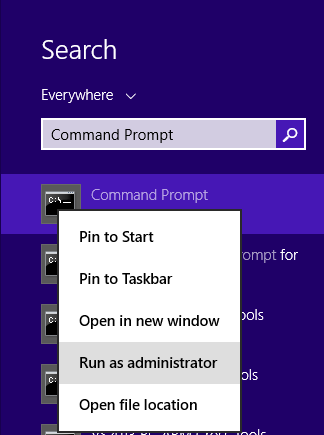
Swipe in from the right edge of the screen, and then tap Search. Or, if you are using a mouse, point to the lower-right corner of the screen, and then click Search. Type Command Prompt in the Search box, right-click Command Prompt, and then click Run as administrator. If you are prompted for an administrator password or for a confirmation, type the password, or click Allow.
To do this, click Start, type Command Prompt or cmd in the Search box, right-click Command Prompt, and then click Run as administrator. If you are prompted for an administrator password or for a confirmation, type the password, or click Allow.
More Information
To view the details that included in the CBS.Log file, you can copy the information to the Sfcdetails.txt file by using the Findstr command, and then view the details in the Sfcdetails.txt. To do this, follow these steps:
Open an elevated command prompt as described in the previous step 1.
At the command prompt, type the following command, and then press ENTER:
Note The Sfcdetails.txt file contains details from every time that the System File Checker tool has been run on the computer. The file includes information about files that were not repaired by the System File Checker tool. Verify the date and time entries to determine the problem files that were found the last time that you ran the System File Checker tool.
Open the Sfcdetails.txt file from your desktop.
The Sfcdetails.txt file uses the following format:
Date/Time SFC detail The following sample log file contains an entry for a file that could not be repaired: 2007-01-12 12:10:42, Info CSI 00000008 [SR] Cannot repair member file [l:34<17>]»Accessibility.dll» of Accessibility, Version = 6.0.6000.16386, pA = PROCESSOR_ARCHITECTURE_MSIL (8), Culture neutral, VersionScope neutral, PublicKeyToken =
How to manually replace a corrupted system file with a known good copy of the file
After you determine which system file was corrupted and could not be repaired through the detail information in the Sfcdetails.txt file, find where the corrupted file located, and then manually replace the corrupted file with a known good copy of the file. To do this, follow these steps:
Note You may be able to get a known good copy of the system file from another computer that is running the same version of Windows with your computer. You may perform a System File Checker process on that computer to make sure the system file that you intend to copy is a good copy.
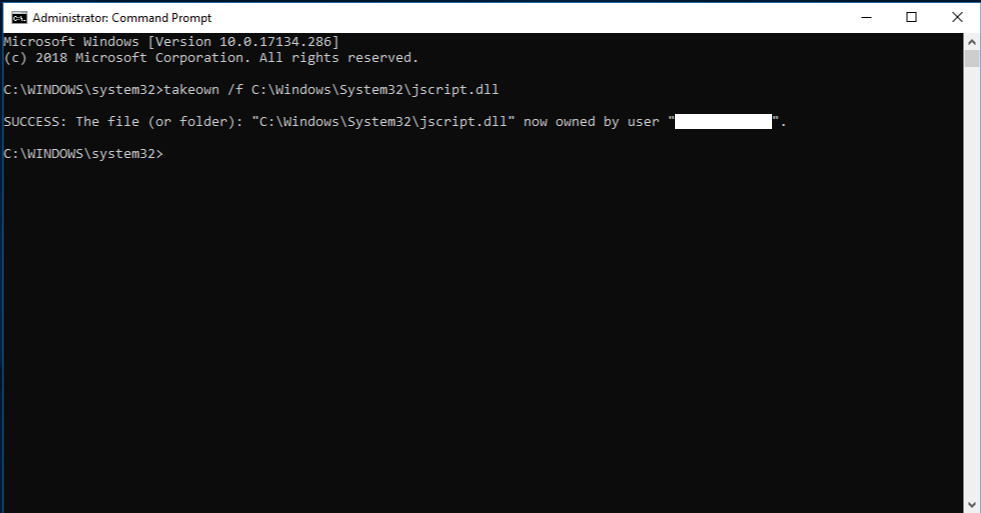
Take administrative ownership of the corrupted system file. To do this, at an elevated command prompt, copy and then paste (or type) the following command, and then press ENTER:
takeown /f Path_And_File_Name Note The Path_And_File_Name placeholder represents the path and the file name of the corrupted file. For example, type takeown /f C:\windows\system32\jscript.dll.
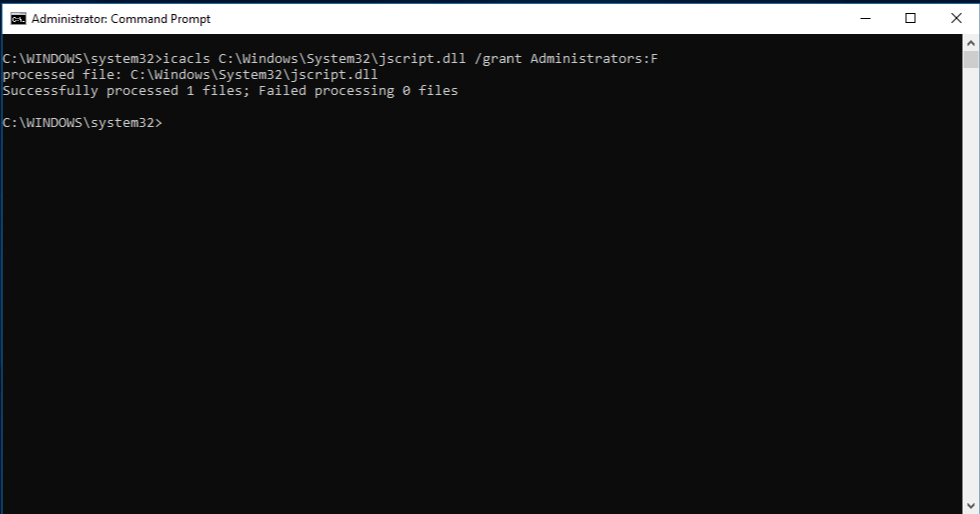
Grant administrators full access to the corrupted system file. To do this, copy and paste (or type) the following command, and then press ENTER:
icacls Path_And_File_Name /GRANT ADMINISTRATORS:F Note The Path_And_File_Name placeholder represents the path and the file name of the corrupted file. For example, type icacls C:\windows\system32\jscript.dll /grant administrators:F.
Replace the corrupted system file with a known good copy of the file. To do this, copy and paste (or type) the following command, and then press ENTER:
Copy Source_File Destination Note The Source_File placeholder represents the path and file name of the known good copy of the file on your computer, and the Destination placeholder represents the path and file name of the corrupted file. For example, type copy E:\temp\jscript.dll C:\windows\system32\jscript.dll.
If the steps above don’t work, you may need to reinstall Windows. For more info, see Windows 10 recovery options.
CheckSystem¶
Various system related checks, such as CPU load, process state, service state memory usage and PDH counters.
Queries¶
A quick reference for all available queries (check commands) in the CheckSystem module.
List of commands:
A list of all available queries (check commands)
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| check_cpu | Check that the load of the CPU(s) are within bounds. |
| check_memory | Check free/used memory on the system. |
| check_network | Check network interface status. |
| check_os_version | Check the version of the underlaying OS. |
| check_pagefile | Check the size of the system pagefile(s). |
| check_pdh | Check the value of a performance (PDH) counter on the local or remote system. |
| check_process | Check state/metrics of one or more of the processes running on the computer. |
| check_service | Check the state of one or more of the computer services. |
| check_uptime | Check time since last server re-boot. |
| checkcounter | Legacy version of check_pdh |
| checkcpu | Legacy version of check_cpu |
| checkmem | Legacy version of check_mem |
| checkprocstate | Legacy version of check_process |
| checkservicestate | Legacy version of check_service |
| checkuptime | Legacy version of check_uptime |
List of command aliases:
A list of all short hand aliases for queries (check commands)
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| check_counter | Alias for: :query: check_pdh |
check_cpu¶
Check that the load of the CPU(s) are within bounds.
The check_cpu command is a query based command which means it has a filter where you can use a filter expression with filter keywords to define which rows are relevant to the check. The filter is written using the filter query language and in it you can use various filter keywords to define the filtering logic. The filter keywords can also be used to create the bound expressions for the warning and critical which defines when a check returns warning or critical.
Sample Commands¶
To edit these sample please edit this page
Default check:
Checking all cores by adding filter=none (disabling the filter):
Adding kernel times to the check::
Default check via NRPE::
Command-line Arguments¶
| Option | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| filter | core = ‘total’ | Filter which marks interesting items. |
| warning | load > 80 | Filter which marks items which generates a warning state. |
| warn | Short alias for warning | |
| critical | load > 90 | Filter which marks items which generates a critical state. |
| crit | Short alias for critical. | |
| ok | Filter which marks items which generates an ok state. | |
| debug | N/A | Show debugging information in the log |
| show-all | N/A | Show details for all matches regardless of status (normally details are only showed for warnings and criticals). |
| empty-state | ignored | Return status to use when nothing matched filter. |
| perf-config | Performance data generation configuration | |
| escape-html | N/A | Escape any characters to prevent HTML encoding |
| help | N/A | Show help screen (this screen) |
| help-pb | N/A | Show help screen as a protocol buffer payload |
| show-default | N/A | Show default values for a given command |
| help-short | N/A | Show help screen (short format). |
| top-syntax | $| Top level syntax. | |
| ok-syntax | %(status): CPU load is ok. | ok syntax. |
| empty-syntax | Empty syntax. | |
| detail-syntax | $ | Detail level syntax. |
| perf-syntax | $ | Performance alias syntax. | |
| time | The time to check |
filter:
Filter which marks interesting items. Interesting items are items which will be included in the check. They do not denote warning or critical state instead it defines which items are relevant and you can remove unwanted items.
Default Value: core = ‘total’
warning:
Filter which marks items which generates a warning state. If anything matches this filter the return status will be escalated to warning.
Default Value: load > 80
critical:
Filter which marks items which generates a critical state. If anything matches this filter the return status will be escalated to critical.
Default Value: load > 90
Filter which marks items which generates an ok state. If anything matches this any previous state for this item will be reset to ok.
empty-state:
Return status to use when nothing matched filter. If no filter is specified this will never happen unless the file is empty.
Default Value: ignored
perf-config:
Performance data generation configuration TODO: obj ( key: value; key: value) obj (key:valuer;key:value)
top-syntax:
Top level syntax. Used to format the message to return can include text as well as special keywords which will include information from the checks. To add a keyword to the message you can use two syntaxes either $
ok-syntax:
ok syntax. DEPRECATED! This is the syntax for when an ok result is returned. This value will not be used if your syntax contains %(list) or %(count).
Default Value: %(status): CPU load is ok.
empty-syntax:
Empty syntax. DEPRECATED! This is the syntax for when nothing matches the filter.
detail-syntax:
Detail level syntax. Used to format each resulting item in the message. %(list) will be replaced with all the items formated by this syntax string in the top-syntax. To add a keyword to the message you can use two syntaxes either $
perf-syntax:
Performance alias syntax. This is the syntax for the base names of the performance data.
Filter keywords¶
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| core | The core to check (total or core ##) |
| core_id | The core to check (total or core_##) |
| count | Number of items matching the filter. Common option for all checks. |
| crit_count | Number of items matched the critical criteria. Common option for all checks. |
| crit_list | A list of all items which matched the critical criteria. Common option for all checks. |
| detail_list | A special list with critical, then warning and finally ok. Common option for all checks. |
| idle | The current idle load for a given core |
| kernel | The current kernel load for a given core |
| list | A list of all items which matched the filter. Common option for all checks. |
| load | The current load for a given core |
| ok_count | Number of items matched the ok criteria. Common option for all checks. |
| ok_list | A list of all items which matched the ok criteria. Common option for all checks. |
| problem_count | Number of items matched either warning or critical criteria. Common option for all checks. |
| problem_list | A list of all items which matched either the critical or the warning criteria. Common option for all checks. |
| status | The returned status (OK/WARN/CRIT/UNKNOWN). Common option for all checks. |
| time | The time frame to check |
| total | Total number of items. Common option for all checks. |
| warn_count | Number of items matched the warning criteria. Common option for all checks. |
| warn_list | A list of all items which matched the warning criteria. Common option for all checks. |
check_memory¶
Check free/used memory on the system.
Sample Commands¶
To edit these sample please edit this page
Default check:
Using –show-all to show the result:
Changing the return syntax to include more information::
Default check via NRPE::
Overriding the unit:
Most “byte” checks such as memory have an auto scaling feature which means values wqill go from 800M to 1.2G between checks. Some graphing systems does not honor the units in performance data in which case you can get unexpected large values (such as 800G). To remedy this you can lock the unit by adding perf-config=*(unit:G)
Command-line Arguments¶
| Option | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| filter | Filter which marks interesting items. | |
| warning | used > 80% | Filter which marks items which generates a warning state. |
| warn | Short alias for warning | |
| critical | used > 90% | Filter which marks items which generates a critical state. |
| crit | Short alias for critical. | |
| ok | Filter which marks items which generates an ok state. | |
| debug | N/A | Show debugging information in the log |
| show-all | N/A | Show details for all matches regardless of status (normally details are only showed for warnings and criticals). |
| empty-state | ignored | Return status to use when nothing matched filter. |
| perf-config | Performance data generation configuration | |
| escape-html | N/A | Escape any characters to prevent HTML encoding |
| help | N/A | Show help screen (this screen) |
| help-pb | N/A | Show help screen as a protocol buffer payload |
| show-default | N/A | Show default values for a given command |
| help-short | N/A | Show help screen (short format). |
| top-syntax | $| Top level syntax. | |
| ok-syntax | ok syntax. | |
| empty-syntax | Empty syntax. | |
| detail-syntax | $ | Detail level syntax. | |
| perf-syntax | $ | Performance alias syntax. |
| type | The type of memory to check (physical = Physical memory (RAM), committed = total memory (RAM+PAGE) |
filter:
Filter which marks interesting items. Interesting items are items which will be included in the check. They do not denote warning or critical state instead it defines which items are relevant and you can remove unwanted items.
warning:
Filter which marks items which generates a warning state. If anything matches this filter the return status will be escalated to warning.
Default Value: used > 80%
critical:
Filter which marks items which generates a critical state. If anything matches this filter the return status will be escalated to critical.
Default Value: used > 90%
Filter which marks items which generates an ok state. If anything matches this any previous state for this item will be reset to ok.
empty-state:
Return status to use when nothing matched filter. If no filter is specified this will never happen unless the file is empty.
Default Value: ignored
perf-config:
Performance data generation configuration TODO: obj ( key: value; key: value) obj (key:valuer;key:value)
top-syntax:
Top level syntax. Used to format the message to return can include text as well as special keywords which will include information from the checks. To add a keyword to the message you can use two syntaxes either $
ok-syntax:
ok syntax. DEPRECATED! This is the syntax for when an ok result is returned. This value will not be used if your syntax contains %(list) or %(count).
empty-syntax:
Empty syntax. DEPRECATED! This is the syntax for when nothing matches the filter.
detail-syntax:
Detail level syntax. Used to format each resulting item in the message. %(list) will be replaced with all the items formated by this syntax string in the top-syntax. To add a keyword to the message you can use two syntaxes either $
perf-syntax:
Performance alias syntax. This is the syntax for the base names of the performance data.
Filter keywords¶
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| count | Number of items matching the filter. Common option for all checks. |
| crit_count | Number of items matched the critical criteria. Common option for all checks. |
| crit_list | A list of all items which matched the critical criteria. Common option for all checks. |
| detail_list | A special list with critical, then warning and finally ok. Common option for all checks. |
| free | Free memory in bytes (g,m,k,b) or percentages % |
| free_pct | % free memory |
| list | A list of all items which matched the filter. Common option for all checks. |
| ok_count | Number of items matched the ok criteria. Common option for all checks. |
| ok_list | A list of all items which matched the ok criteria. Common option for all checks. |
| problem_count | Number of items matched either warning or critical criteria. Common option for all checks. |
| problem_list | A list of all items which matched either the critical or the warning criteria. Common option for all checks. |
| size | Total size of memory |
| status | The returned status (OK/WARN/CRIT/UNKNOWN). Common option for all checks. |
| total | Total number of items. Common option for all checks. |
| type | The type of memory to check |
| used | Used memory in bytes (g,m,k,b) or percentages % |
| used_pct | % used memory |
| warn_count | Number of items matched the warning criteria. Common option for all checks. |
| warn_list | A list of all items which matched the warning criteria. Common option for all checks. |
check_network¶
Check network interface status.
Command-line Arguments¶
| Option | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| filter | Filter which marks interesting items. | |
| warning | total > 10000 | Filter which marks items which generates a warning state. |
| warn | Short alias for warning | |
| critical | total > 100000 | Filter which marks items which generates a critical state. |
| crit | Short alias for critical. | |
| ok | Filter which marks items which generates an ok state. | |
| debug | N/A | Show debugging information in the log |
| show-all | N/A | Show details for all matches regardless of status (normally details are only showed for warnings and criticals). |
| empty-state | critical | Return status to use when nothing matched filter. |
| perf-config | Performance data generation configuration | |
| escape-html | N/A | Escape any characters to prevent HTML encoding |
| help | N/A | Show help screen (this screen) |
| help-pb | N/A | Show help screen as a protocol buffer payload |
| show-default | N/A | Show default values for a given command |
| help-short | N/A | Show help screen (short format). |
| top-syntax | $| Top level syntax. | |
| ok-syntax | %(status): Network interfaces seem ok. | ok syntax. |
| empty-syntax | Empty syntax. | |
| detail-syntax | $ |
critical:
Filter which marks items which generates a critical state. If anything matches this filter the return status will be escalated to critical.
Default Value: total > 100000
Filter which marks items which generates an ok state. If anything matches this any previous state for this item will be reset to ok.
empty-state:
Return status to use when nothing matched filter. If no filter is specified this will never happen unless the file is empty.
Default Value: critical
perf-config:
Performance data generation configuration TODO: obj ( key: value; key: value) obj (key:valuer;key:value)
top-syntax:
Top level syntax. Used to format the message to return can include text as well as special keywords which will include information from the checks. To add a keyword to the message you can use two syntaxes either $
ok-syntax:
ok syntax. DEPRECATED! This is the syntax for when an ok result is returned. This value will not be used if your syntax contains %(list) or %(count).
Default Value: %(status): Network interfaces seem ok.
empty-syntax:
Empty syntax. DEPRECATED! This is the syntax for when nothing matches the filter.
detail-syntax:
Detail level syntax. Used to format each resulting item in the message. %(list) will be replaced with all the items formated by this syntax string in the top-syntax. To add a keyword to the message you can use two syntaxes either $
perf-syntax:
Performance alias syntax. This is the syntax for the base names of the performance data.
Filter keywords¶
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| MAC | The MAC address |
| count | Number of items matching the filter. Common option for all checks. |
| crit_count | Number of items matched the critical criteria. Common option for all checks. |
| crit_list | A list of all items which matched the critical criteria. Common option for all checks. |
| detail_list | A special list with critical, then warning and finally ok. Common option for all checks. |
| enabled | True if the network interface is enabled |
| list | A list of all items which matched the filter. Common option for all checks. |
| name | Network interface name |
| net_connection_id | Network connection id |
| ok_count | Number of items matched the ok criteria. Common option for all checks. |
| ok_list | A list of all items which matched the ok criteria. Common option for all checks. |
| problem_count | Number of items matched either warning or critical criteria. Common option for all checks. |
| problem_list | A list of all items which matched either the critical or the warning criteria. Common option for all checks. |
| received | Bytes received per second |
| sent | Bytes sent per second |
| speed | The network interface speed |
| status | The returned status (OK/WARN/CRIT/UNKNOWN). Common option for all checks. |
| total | Total number of items. Common option for all checks. |
| warn_count | Number of items matched the warning criteria. Common option for all checks. |
| warn_list | A list of all items which matched the warning criteria. Common option for all checks. |
check_os_version¶
Check the version of the underlaying OS.
Sample Commands¶
To edit these sample please edit this page
Default check:
Making sure the OS version is Windows 8:
Default check via NRPE:
Command-line Arguments¶
| Option | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| filter | Filter which marks interesting items. | |
| warning | version characters to prevent HTML encoding | |
| help | N/A | Show help screen (this screen) |
| help-pb | N/A | Show help screen as a protocol buffer payload |
| show-default | N/A | Show default values for a given command |
| help-short | N/A | Show help screen (short format). |
| top-syntax | $| Top level syntax. | |
| ok-syntax | ok syntax. | |
| empty-syntax | Empty syntax. | |
| detail-syntax | $ | Detail level syntax. |
| perf-syntax | version | Performance alias syntax. |
filter:
Filter which marks interesting items. Interesting items are items which will be included in the check. They do not denote warning or critical state instead it defines which items are relevant and you can remove unwanted items.
warning:
Filter which marks items which generates a warning state. If anything matches this filter the return status will be escalated to warning.
Default Value: version
critical:
Filter which marks items which generates a critical state. If anything matches this filter the return status will be escalated to critical.
Default Value: version
Filter which marks items which generates an ok state. If anything matches this any previous state for this item will be reset to ok.
empty-state:
Return status to use when nothing matched filter. If no filter is specified this will never happen unless the file is empty.
Default Value: ignored
perf-config:
Performance data generation configuration TODO: obj ( key: value; key: value) obj (key:valuer;key:value)
top-syntax:
Top level syntax. Used to format the message to return can include text as well as special keywords which will include information from the checks. To add a keyword to the message you can use two syntaxes either $
ok-syntax:
ok syntax. DEPRECATED! This is the syntax for when an ok result is returned. This value will not be used if your syntax contains %(list) or %(count).
empty-syntax:
Empty syntax. DEPRECATED! This is the syntax for when nothing matches the filter.
detail-syntax:
Detail level syntax. Used to format each resulting item in the message. %(list) will be replaced with all the items formated by this syntax string in the top-syntax. To add a keyword to the message you can use two syntaxes either $
perf-syntax:
Performance alias syntax. This is the syntax for the base names of the performance data.
Default Value: version
Filter keywords¶
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| build | Build version number |
| count | Number of items matching the filter. Common option for all checks. |
| crit_count | Number of items matched the critical criteria. Common option for all checks. |
| crit_list | A list of all items which matched the critical criteria. Common option for all checks. |
| detail_list | A special list with critical, then warning and finally ok. Common option for all checks. |
| list | A list of all items which matched the filter. Common option for all checks. |
| major | Major version number |
| minor | Minor version number |
| ok_count | Number of items matched the ok criteria. Common option for all checks. |
| ok_list | A list of all items which matched the ok criteria. Common option for all checks. |
| problem_count | Number of items matched either warning or critical criteria. Common option for all checks. |
| problem_list | A list of all items which matched either the critical or the warning criteria. Common option for all checks. |
| status | The returned status (OK/WARN/CRIT/UNKNOWN). Common option for all checks. |
| suite | Which suites are installed on the machine (Microsoft BackOffice, Web Edition, Compute Cluster Edition, Datacenter Edition, Enterprise Edition, Embedded, Home Edition, Remote Desktop Support, Small Business Server, Storage Server, Terminal Services, Home Server) |
| total | Total number of items. Common option for all checks. |
| version | The system version |
| warn_count | Number of items matched the warning criteria. Common option for all checks. |
| warn_list | A list of all items which matched the warning criteria. Common option for all checks. |
check_pagefile¶
Check the size of the system pagefile(s).
Sample Commands¶
To edit these sample please edit this page
Default options:
Only showing the total amount of pagefile usage::
Getting help on avalible options::
Command-line Arguments¶
| Option | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| filter | Filter which marks interesting items. | |
| warning | used > 60% | Filter which marks items which generates a warning state. |
| warn | Short alias for warning | |
| critical | used > 80% | Filter which marks items which generates a critical state. |
| crit | Short alias for critical. | |
| ok | Filter which marks items which generates an ok state. | |
| debug | N/A | Show debugging information in the log |
| show-all | N/A | Show details for all matches regardless of status (normally details are only showed for warnings and criticals). |
| empty-state | ignored | Return status to use when nothing matched filter. |
| perf-config | Performance data generation configuration | |
| escape-html | N/A | Escape any characters to prevent HTML encoding |
| help | N/A | Show help screen (this screen) |
| help-pb | N/A | Show help screen as a protocol buffer payload |
| show-default | N/A | Show default values for a given command |
| help-short | N/A | Show help screen (short format). |
| top-syntax | $| Top level syntax. | |
| ok-syntax | ok syntax. | |
| empty-syntax | Empty syntax. | |
| detail-syntax | $ | Detail level syntax. |
| perf-syntax | $ | Performance alias syntax. |
filter:
Filter which marks interesting items. Interesting items are items which will be included in the check. They do not denote warning or critical state instead it defines which items are relevant and you can remove unwanted items.
warning:
Filter which marks items which generates a warning state. If anything matches this filter the return status will be escalated to warning.
Default Value: used > 60%
critical:
Filter which marks items which generates a critical state. If anything matches this filter the return status will be escalated to critical.
Default Value: used > 80%
Filter which marks items which generates an ok state. If anything matches this any previous state for this item will be reset to ok.
empty-state:
Return status to use when nothing matched filter. If no filter is specified this will never happen unless the file is empty.
Default Value: ignored
perf-config:
Performance data generation configuration TODO: obj ( key: value; key: value) obj (key:valuer;key:value)
top-syntax:
Top level syntax. Used to format the message to return can include text as well as special keywords which will include information from the checks. To add a keyword to the message you can use two syntaxes either $
ok-syntax:
ok syntax. DEPRECATED! This is the syntax for when an ok result is returned. This value will not be used if your syntax contains %(list) or %(count).
empty-syntax:
Empty syntax. DEPRECATED! This is the syntax for when nothing matches the filter.
detail-syntax:
Detail level syntax. Used to format each resulting item in the message. %(list) will be replaced with all the items formated by this syntax string in the top-syntax. To add a keyword to the message you can use two syntaxes either $
perf-syntax:
Performance alias syntax. This is the syntax for the base names of the performance data.
Filter keywords¶
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| count | Number of items matching the filter. Common option for all checks. |
| crit_count | Number of items matched the critical criteria. Common option for all checks. |
| crit_list | A list of all items which matched the critical criteria. Common option for all checks. |
| detail_list | A special list with critical, then warning and finally ok. Common option for all checks. |
| free | Free memory in bytes (g,m,k,b) or percentages % |
| free_pct | % free memory |
| list | A list of all items which matched the filter. Common option for all checks. |
| name | The name of the page file (location) |
| ok_count | Number of items matched the ok criteria. Common option for all checks. |
| ok_list | A list of all items which matched the ok criteria. Common option for all checks. |
| problem_count | Number of items matched either warning or critical criteria. Common option for all checks. |
| problem_list | A list of all items which matched either the critical or the warning criteria. Common option for all checks. |
| size | Total size of pagefile |
| status | The returned status (OK/WARN/CRIT/UNKNOWN). Common option for all checks. |
| total | Total number of items. Common option for all checks. |
| used | Used memory in bytes (g,m,k,b) or percentages % |
| used_pct | % used memory |
| warn_count | Number of items matched the warning criteria. Common option for all checks. |
| warn_list | A list of all items which matched the warning criteria. Common option for all checks. |
check_pdh¶
Check the value of a performance (PDH) counter on the local or remote system. The counters can also be added and polled periodcally to get average values. Performance Log Users group membership is required to check performance counters.
Sample Commands¶
To edit these sample please edit this page
п»їChecking specific Counter (\System\System Up Time):
Using the expand index to check for translated counters::
Checking translated counters without expanding indexes::
Checking large values using the type=large keyword::
Using real-time checks to check avergae values over time.
Here we configure a counter to be checked at regular intervals and the value is added to a rrd buffer. The configuration from nsclient.ini::
Then we can check the value (current snapshot)::
To check averages from the same counter we need to specify the time option::
Checking all instances of a given counter::
Command-line Arguments¶
| Option | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| filter | Filter which marks interesting items. | |
| warning | Filter which marks items which generates a warning state. | |
| warn | Short alias for warning | |
| critical | Filter which marks items which generates a critical state. | |
| crit | Short alias for critical. | |
| ok | Filter which marks items which generates an ok state. | |
| debug | N/A | Show debugging information in the log |
| show-all | N/A | Show details for all matches regardless of status (normally details are only showed for warnings and criticals). |
| empty-state | unknown | Return status to use when nothing matched filter. |
| perf-config | Performance data generation configuration | |
| escape-html | N/A | Escape any characters to prevent HTML encoding |
| help | N/A | Show help screen (this screen) |
| help-pb | N/A | Show help screen as a protocol buffer payload |
| show-default | N/A | Show default values for a given command |
| help-short | N/A | Show help screen (short format). |
| top-syntax | $| Top level syntax. | |
| ok-syntax | ok syntax. | |
| empty-syntax | Empty syntax. | |
| detail-syntax | $ | Detail level syntax. | |
| perf-syntax | $ | Performance alias syntax. |
| counter | Performance counter to check | |
| expand-index | N/A | Expand indexes in counter strings |
| instances | N/A | Expand wildcards and fetch all instances |
| reload | N/A | Reload counters on errors (useful to check counters which are not added at boot) |
| averages | N/A | Check average values (ie. wait for 1 second to collecting two samples) |
| time | Timeframe to use for named rrd counters | |
| flags | Extra flags to configure the counter (nocap100, 1000, noscale) | |
| type | large | Format of value (double, long, large) |
| ignore-errors | N/A | If we should ignore errors when checking counters, for instance missing counters or invalid counters will return 0 instead of errors |
filter:
Filter which marks interesting items. Interesting items are items which will be included in the check. They do not denote warning or critical state instead it defines which items are relevant and you can remove unwanted items.
warning:
Filter which marks items which generates a warning state. If anything matches this filter the return status will be escalated to warning.
critical:
Filter which marks items which generates a critical state. If anything matches this filter the return status will be escalated to critical.
Filter which marks items which generates an ok state. If anything matches this any previous state for this item will be reset to ok.
empty-state:
Return status to use when nothing matched filter. If no filter is specified this will never happen unless the file is empty.
Default Value: unknown
perf-config:
Performance data generation configuration TODO: obj ( key: value; key: value) obj (key:valuer;key:value)
top-syntax:
Top level syntax. Used to format the message to return can include text as well as special keywords which will include information from the checks. To add a keyword to the message you can use two syntaxes either $
ok-syntax:
ok syntax. DEPRECATED! This is the syntax for when an ok result is returned. This value will not be used if your syntax contains %(list) or %(count).
empty-syntax:
Empty syntax. DEPRECATED! This is the syntax for when nothing matches the filter.
detail-syntax:
Detail level syntax. Used to format each resulting item in the message. %(list) will be replaced with all the items formated by this syntax string in the top-syntax. To add a keyword to the message you can use two syntaxes either $
perf-syntax:
Performance alias syntax. This is the syntax for the base names of the performance data.
Format of value (double, long, large)
Default Value: large
Filter keywords¶
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| alias | The counter alias |
| count | Number of items matching the filter. Common option for all checks. |
| counter | The counter name |
| crit_count | Number of items matched the critical criteria. Common option for all checks. |
| crit_list | A list of all items which matched the critical criteria. Common option for all checks. |
| detail_list | A special list with critical, then warning and finally ok. Common option for all checks. |
| list | A list of all items which matched the filter. Common option for all checks. |
| ok_count | Number of items matched the ok criteria. Common option for all checks. |
| ok_list | A list of all items which matched the ok criteria. Common option for all checks. |
| problem_count | Number of items matched either warning or critical criteria. Common option for all checks. |
| problem_list | A list of all items which matched either the critical or the warning criteria. Common option for all checks. |
| status | The returned status (OK/WARN/CRIT/UNKNOWN). Common option for all checks. |
| time | The time for rrd checks |
| total | Total number of items. Common option for all checks. |
| value | The counter value (either float or int) |
| value_f | The counter value (force float value) |
| value_i | The counter value (force int value) |
| warn_count | Number of items matched the warning criteria. Common option for all checks. |
| warn_list | A list of all items which matched the warning criteria. Common option for all checks. |
check_process¶
Check state/metrics of one or more of the processes running on the computer.
Sample Commands¶
To edit these sample please edit this page
Default check:
Default check via NRPE::
Check that specific process are running::
Check memory footprint from specific processes::
Extend the syntax to display the attributes we are interested in::
List all processes which use more then 200m virtual memory Default check via NRPE::
Command-line Arguments¶
| Option | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| filter | state != ‘unreadable’ | Filter which marks interesting items. |
| warning | state not in (‘started’) | Filter which marks items which generates a warning state. |
| warn | Short alias for warning | |
| critical | state = ‘stopped’, count = 0 | Filter which marks items which generates a critical state. |
| crit | Short alias for critical. | |
| ok | Filter which marks items which generates an ok state. | |
| debug | N/A | Show debugging information in the log |
| show-all | N/A | Show details for all matches regardless of status (normally details are only showed for warnings and criticals). |
| empty-state | unknown | Return status to use when nothing matched filter. |
| perf-config | Performance data generation configuration | |
| escape-html | N/A | Escape any characters to prevent HTML encoding |
| help | N/A | Show help screen (this screen) |
| help-pb | N/A | Show help screen as a protocol buffer payload |
| show-default | N/A | Show default values for a given command |
| help-short | N/A | Show help screen (short format). |
| top-syntax | $| Top level syntax. | |
| ok-syntax | %(status): all processes are ok. | ok syntax. |
| empty-syntax | UNKNOWN: No processes found | Empty syntax. |
| detail-syntax | $| Detail level syntax. | |
| perf-syntax | $ | Performance alias syntax. |
| process | The service to check, set this to * to check all services | |
| scan-info | If all process metrics should be fetched (otherwise only status is fetched) | |
| scan-16bit | If 16bit processes should be included | |
| delta | Calculate delta over one elapsed second. | |
| scan-unreadable | If unreadable processes should be included (will not have information) | |
| total | N/A | Include the total of all matching files |
filter:
Filter which marks interesting items. Interesting items are items which will be included in the check. They do not denote warning or critical state instead it defines which items are relevant and you can remove unwanted items.
Default Value: state != ‘unreadable’
warning:
Filter which marks items which generates a warning state. If anything matches this filter the return status will be escalated to warning.
Default Value: state not in (‘started’)
critical:
Filter which marks items which generates a critical state. If anything matches this filter the return status will be escalated to critical.
Default Value: state = ‘stopped’, count = 0
Filter which marks items which generates an ok state. If anything matches this any previous state for this item will be reset to ok.
empty-state:
Return status to use when nothing matched filter. If no filter is specified this will never happen unless the file is empty.
Default Value: unknown
perf-config:
Performance data generation configuration TODO: obj ( key: value; key: value) obj (key:valuer;key:value)
top-syntax:
Top level syntax. Used to format the message to return can include text as well as special keywords which will include information from the checks. To add a keyword to the message you can use two syntaxes either $
ok-syntax:
ok syntax. DEPRECATED! This is the syntax for when an ok result is returned. This value will not be used if your syntax contains %(list) or %(count).
Default Value: %(status): all processes are ok.
empty-syntax:
Empty syntax. DEPRECATED! This is the syntax for when nothing matches the filter.
Default Value: UNKNOWN: No processes found
detail-syntax:
Detail level syntax. Used to format each resulting item in the message. %(list) will be replaced with all the items formated by this syntax string in the top-syntax. To add a keyword to the message you can use two syntaxes either $
perf-syntax:
Performance alias syntax. This is the syntax for the base names of the performance data.
delta:
Calculate delta over one elapsed second. This call will measure values and then sleep for 2 second and then measure again calculating deltas.
Filter keywords¶
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| command_line | Command line of process (not always available) |
| count | Number of items matching the filter. Common option for all checks. |
| creation | Creation time |
| crit_count | Number of items matched the critical criteria. Common option for all checks. |
| crit_list | A list of all items which matched the critical criteria. Common option for all checks. |
| detail_list | A special list with critical, then warning and finally ok. Common option for all checks. |
| error | Any error messages associated with fetching info |
| exe | The name of the executable |
| filename | Name of process (with path) |
| gdi_handles | Number of handles |
| handles | Number of handles |
| hung | Process is hung |
| kernel | Kernel time in seconds |
| legacy_state | Get process status (for legacy use via check_nt only) |
| list | A list of all items which matched the filter. Common option for all checks. |
| new | Process is new (can inly be used for real-time filters) |
| ok_count | Number of items matched the ok criteria. Common option for all checks. |
| ok_list | A list of all items which matched the ok criteria. Common option for all checks. |
| page_fault | Page fault count |
| pagefile | Peak page file use in bytes |
| peak_pagefile | Page file usage in bytes |
| peak_virtual | Peak virtual size in bytes |
| peak_working_set | Peak working set in bytes |
| pid | Process id |
| problem_count | Number of items matched either warning or critical criteria. Common option for all checks. |
| problem_list | A list of all items which matched either the critical or the warning criteria. Common option for all checks. |
| started | Process is started |
| state | The current state (started, stopped hung) |
| status | The returned status (OK/WARN/CRIT/UNKNOWN). Common option for all checks. |
| stopped | Process is stopped |
| time | User-kernel time in seconds |
| total | Total number of items. Common option for all checks. |
| user | User time in seconds |
| user_handles | Number of handles |
| virtual | Virtual size in bytes |
| warn_count | Number of items matched the warning criteria. Common option for all checks. |
| warn_list | A list of all items which matched the warning criteria. Common option for all checks. |
| working_set | Working set in bytes |
check_service¶
Check the state of one or more of the computer services.
Sample Commands¶
To edit these sample please edit this page
Default check:
Excluding services using exclude::
Show all service by changing the syntax::
Excluding services using the filter::
Exclude versus filter::
You can use both exclude and filter to exclude services the befnefit of exclude is that it is faster with the obvious drawback that it only works on the service name. The upside to filters are that they are richer in terms of functionality i.e. substring matching (as below).
Excluding nfoo service with exclude:
Excluding nscp2 with substring like mathcing filter:
Default check via NRPE::
Check that a service is not started::
Command-line Arguments¶
| Option | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| filter | Filter which marks interesting items. | |
| warning | not state_is_perfect() | Filter which marks items which generates a warning state. |
| warn | Short alias for warning | |
| critical | not state_is_ok() | Filter which marks items which generates a critical state. |
| crit | Short alias for critical. | |
| ok | Filter which marks items which generates an ok state. | |
| debug | N/A | Show debugging information in the log |
| show-all | N/A | Show details for all matches regardless of status (normally details are only showed for warnings and criticals). |
| empty-state | unknown | Return status to use when nothing matched filter. |
| perf-config | Performance data generation configuration | |
| escape-html | N/A | Escape any characters to prevent HTML encoding |
| help | N/A | Show help screen (this screen) |
| help-pb | N/A | Show help screen as a protocol buffer payload |
| show-default | N/A | Show default values for a given command |
| help-short | N/A | Show help screen (short format). |
| top-syntax | $ | Top level syntax. |
| ok-syntax | %(status): All %(count) service(s) are ok. | ok syntax. |
| empty-syntax | %(status): No services found | Empty syntax. |
| detail-syntax | $ | Detail level syntax. |
| perf-syntax | $ | Performance alias syntax. |
| computer | The name of the remote computer to check | |
| service | The service to check, set this to * to check all services | |
| exclude | A list of services to ignore (mainly usefull in combination with service=*) | |
| type | service | The types of services to enumerate available types are driver, file-system-driver, kernel-driver, service, service-own-process, service-share-process |
| state | all | The types of services to enumerate available states are active, inactive or all |
| only-essential | N/A | Set filter to classification = ‘essential’ |
| only-ignored | N/A | Set filter to classification = ‘ignored’ |
| only-role | N/A | Set filter to classification = ‘role’ |
| only-supporting | N/A | Set filter to classification = ‘supporting’ |
| only-system | N/A | Set filter to classification = ‘system’ |
| only-user | N/A | Set filter to classification = ‘user’ |
filter:
Filter which marks interesting items. Interesting items are items which will be included in the check. They do not denote warning or critical state instead it defines which items are relevant and you can remove unwanted items.
warning:
Filter which marks items which generates a warning state. If anything matches this filter the return status will be escalated to warning.
Default Value: not state_is_perfect()
critical:
Filter which marks items which generates a critical state. If anything matches this filter the return status will be escalated to critical.
Default Value: not state_is_ok()
Filter which marks items which generates an ok state. If anything matches this any previous state for this item will be reset to ok.
empty-state:
Return status to use when nothing matched filter. If no filter is specified this will never happen unless the file is empty.
Default Value: unknown
perf-config:
Performance data generation configuration TODO: obj ( key: value; key: value) obj (key:valuer;key:value)
top-syntax:
Top level syntax. Used to format the message to return can include text as well as special keywords which will include information from the checks. To add a keyword to the message you can use two syntaxes either $
ok-syntax:
ok syntax. DEPRECATED! This is the syntax for when an ok result is returned. This value will not be used if your syntax contains %(list) or %(count).
Default Value: %(status): All %(count) service(s) are ok.
empty-syntax:
Empty syntax. DEPRECATED! This is the syntax for when nothing matches the filter.
Default Value: %(status): No services found
detail-syntax:
Detail level syntax. Used to format each resulting item in the message. %(list) will be replaced with all the items formated by this syntax string in the top-syntax. To add a keyword to the message you can use two syntaxes either $
perf-syntax:
Performance alias syntax. This is the syntax for the base names of the performance data.
The types of services to enumerate available types are driver, file-system-driver, kernel-driver, service, service-own-process, service-share-process
Default Value: service
state:
The types of services to enumerate available states are active, inactive or all
Default Value: all
Filter keywords¶
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| classification | Get classification |
| count | Number of items matching the filter. Common option for all checks. |
| crit_count | Number of items matched the critical criteria. Common option for all checks. |
| crit_list | A list of all items which matched the critical criteria. Common option for all checks. |
| delayed | If the service is delayed |
| desc | Service description |
| detail_list | A special list with critical, then warning and finally ok. Common option for all checks. |
| is_trigger | If the service is has associated triggers |
| legacy_state | Get legacy state (deprecated and only used by check_nt) |
| list | A list of all items which matched the filter. Common option for all checks. |
| name | Service name |
| ok_count | Number of items matched the ok criteria. Common option for all checks. |
| ok_list | A list of all items which matched the ok criteria. Common option for all checks. |
| pid | Process id |
| problem_count | Number of items matched either warning or critical criteria. Common option for all checks. |
| problem_list | A list of all items which matched either the critical or the warning criteria. Common option for all checks. |
| start_type | The configured start type () |
| state | The current state () |
| state_is_ok() | Check if the state is ok, i.e. all running services are runningelayed services are allowed to be stopped) |
| state_is_perfect() | Check if the state is ok, i.e. all running services are running |
| status | The returned status (OK/WARN/CRIT/UNKNOWN). Common option for all checks. |
| total | Total number of items. Common option for all checks. |
| triggers | The number of associated triggers for this service |
| warn_count | Number of items matched the warning criteria. Common option for all checks. |
| warn_list | A list of all items which matched the warning criteria. Common option for all checks. |
check_uptime¶
Check time since last server re-boot.
Sample Commands¶
To edit these sample please edit this page
Default check:
Adding warning and critical thresholds::
Default check via NRPE::
Command-line Arguments¶
| Option | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| filter | Filter which marks interesting items. | |
| warning | uptime characters to prevent HTML encoding | |
| help | N/A | Show help screen (this screen) |
| help-pb | N/A | Show help screen as a protocol buffer payload |
| show-default | N/A | Show default values for a given command |
| help-short | N/A | Show help screen (short format). |
| top-syntax | $| Top level syntax. | |
| ok-syntax | ok syntax. | |
| empty-syntax | Empty syntax. | |
| detail-syntax | uptime: $ | Detail level syntax. |
| perf-syntax | uptime | Performance alias syntax. |
filter:
Filter which marks interesting items. Interesting items are items which will be included in the check. They do not denote warning or critical state instead it defines which items are relevant and you can remove unwanted items.
warning:
Filter which marks items which generates a warning state. If anything matches this filter the return status will be escalated to warning.
Default Value: uptime
critical:
Filter which marks items which generates a critical state. If anything matches this filter the return status will be escalated to critical.
Default Value: uptime
Filter which marks items which generates an ok state. If anything matches this any previous state for this item will be reset to ok.
empty-state:
Return status to use when nothing matched filter. If no filter is specified this will never happen unless the file is empty.
Default Value: ignored
perf-config:
Performance data generation configuration TODO: obj ( key: value; key: value) obj (key:valuer;key:value)
top-syntax:
Top level syntax. Used to format the message to return can include text as well as special keywords which will include information from the checks. To add a keyword to the message you can use two syntaxes either $
ok-syntax:
ok syntax. DEPRECATED! This is the syntax for when an ok result is returned. This value will not be used if your syntax contains %(list) or %(count).
empty-syntax:
Empty syntax. DEPRECATED! This is the syntax for when nothing matches the filter.
detail-syntax:
Detail level syntax. Used to format each resulting item in the message. %(list) will be replaced with all the items formated by this syntax string in the top-syntax. To add a keyword to the message you can use two syntaxes either $
Default Value: uptime: $
perf-syntax:
Performance alias syntax. This is the syntax for the base names of the performance data.
Default Value: uptime
Filter keywords¶
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| boot | System boot time |
| count | Number of items matching the filter. Common option for all checks. |
| crit_count | Number of items matched the critical criteria. Common option for all checks. |
| crit_list | A list of all items which matched the critical criteria. Common option for all checks. |
| detail_list | A special list with critical, then warning and finally ok. Common option for all checks. |
| list | A list of all items which matched the filter. Common option for all checks. |
| ok_count | Number of items matched the ok criteria. Common option for all checks. |
| ok_list | A list of all items which matched the ok criteria. Common option for all checks. |
| problem_count | Number of items matched either warning or critical criteria. Common option for all checks. |
| problem_list | A list of all items which matched either the critical or the warning criteria. Common option for all checks. |
| status | The returned status (OK/WARN/CRIT/UNKNOWN). Common option for all checks. |
| total | Total number of items. Common option for all checks. |
| uptime | Time since last boot |
| warn_count | Number of items matched the warning criteria. Common option for all checks. |
| warn_list | A list of all items which matched the warning criteria. Common option for all checks. |
checkcounter¶
Legacy version of check_pdh
Command-line Arguments¶
| Option | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| help | N/A | Show help screen (this screen) |
| help-pb | N/A | Show help screen as a protocol buffer payload |
| show-default | N/A | Show default values for a given command |
| help-short | N/A | Show help screen (short format). |
| Counter | The time to check | |
| ShowAll | short | Configures display format (if set shows all items not only failures, if set to long shows all cores). |
| MaxWarn | Maximum value before a warning is returned. | |
| MaxCrit | Maximum value before a critical is returned. | |
| MinWarn | Minimum value before a warning is returned. | |
| MinCrit | Minimum value before a critical is returned. |
ShowAll:
Configures display format (if set shows all items not only failures, if set to long shows all cores).
Default Value: short
checkcpu¶
Legacy version of check_cpu
Command-line Arguments¶
| Option | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| help | N/A | Show help screen (this screen) |
| help-pb | N/A | Show help screen as a protocol buffer payload |
| show-default | N/A | Show default values for a given command |
| help-short | N/A | Show help screen (short format). |
| time | The time to check | |
| ShowAll | short | Configures display format (if set shows all items not only failures, if set to long shows all cores). |
| MaxWarn | Maximum value before a warning is returned. | |
| MaxCrit | Maximum value before a critical is returned. | |
| MinWarn | Minimum value before a warning is returned. | |
| MinCrit | Minimum value before a critical is returned. | |
| warn | Maximum value before a warning is returned. | |
| crit | Maximum value before a critical is returned. |
ShowAll:
Configures display format (if set shows all items not only failures, if set to long shows all cores).
Default Value: short
checkmem¶
Legacy version of check_mem
Command-line Arguments¶
| Option | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| help | N/A | Show help screen (this screen) |
| help-pb | N/A | Show help screen as a protocol buffer payload |
| show-default | N/A | Show default values for a given command |
| help-short | N/A | Show help screen (short format). |
| type | The types to check | |
| ShowAll | short | Configures display format (if set shows all items not only failures, if set to long shows all cores). |
| MaxWarn | Maximum value before a warning is returned. | |
| MaxCrit | Maximum value before a critical is returned. | |
| MinWarn | Minimum value before a warning is returned. | |
| MinCrit | Minimum value before a critical is returned. | |
| warn | Maximum value before a warning is returned. | |
| crit | Maximum value before a critical is returned. |
ShowAll:
Configures display format (if set shows all items not only failures, if set to long shows all cores).
Default Value: short
checkprocstate¶
Legacy version of check_process
Command-line Arguments¶
| Option | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| help | N/A | Show help screen (this screen) |
| help-pb | N/A | Show help screen as a protocol buffer payload |
| show-default | N/A | Show default values for a given command |
| help-short | N/A | Show help screen (short format). |
| ShowAll | short | Configures display format (if set shows all items not only failures, if set to long shows all cores). |
| MaxWarnCount | Maximum value before a warning is returned. | |
| MaxCritCount | Maximum value before a critical is returned. | |
| MinWarnCount | Minimum value before a warning is returned. | |
| MinCritCount | Minimum value before a critical is returned. |
ShowAll:
Configures display format (if set shows all items not only failures, if set to long shows all cores).
Default Value: short
checkservicestate¶
Legacy version of check_service
Command-line Arguments¶
| Option | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| help | N/A | Show help screen (this screen) |
| help-pb | N/A | Show help screen as a protocol buffer payload |
| show-default | N/A | Show default values for a given command |
| help-short | N/A | Show help screen (short format). |
| CheckAll | true | Check all services. |
| exclude | Exclude services | |
| ShowAll | short | Configures display format (if set shows all items not only failures, if set to long shows all cores). |
CheckAll:
Check all services.
Default Value: true
ShowAll:
Configures display format (if set shows all items not only failures, if set to long shows all cores).
Default Value: short
checkuptime¶
Legacy version of check_uptime
Command-line Arguments¶
| Option | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| help | N/A | Show help screen (this screen) |
| help-pb | N/A | Show help screen as a protocol buffer payload |
| show-default | N/A | Show default values for a given command |
| help-short | N/A | Show help screen (short format). |
| ShowAll | short | Configures display format (if set shows all items not only failures, if set to long shows all cores). |
| MaxWarn | Maximum value before a warning is returned. | |
| MaxCrit | Maximum value before a critical is returned. | |
| MinWarn | Minimum value before a warning is returned. | |
| MinCrit | Minimum value before a critical is returned. | |
| warn | Maximum value before a warning is returned. | |
| crit | Maximum value before a critical is returned. |
ShowAll:
Configures display format (if set shows all items not only failures, if set to long shows all cores).
Default Value: short
Configuration¶
| Path / Section | Description |
|---|---|
| /settings/system/windows | Windows system |
| /settings/system/windows/counters | PDH Counters |
| /settings/system/windows/real-time/checks | Legacy generic filters |
| /settings/system/windows/real-time/cpu | Realtime cpu filters |
| /settings/system/windows/real-time/memory | Realtime memory filters |
| /settings/system/windows/real-time/process | Realtime process filters |
Windows system ¶
Section for system checks and system settings
| Key | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| default buffer length | 1h | Default buffer time |
| disable | Disable automatic checks | |
| subsystem | default | PDH subsystem |
Default buffer time ¶
Used to define the default size of range buffer checks (ie. CPU).
| Key | Description |
|---|---|
| Path: | /settings/system/windows |
| Key: | default buffer length |
| Default value: | 1h |
| Used by: | CheckSystem |
Sample:
Disable automatic checks ¶
A comma separated list of checks to disable in the collector: cpu,handles,network,metrics,pdh. Please note disabling these will mean part of NSClient++ will no longer function as expected.
| Key | Description |
|---|---|
| Path: | /settings/system/windows |
| Key: | disable |
| Advanced: | Yes (means it is not commonly used) |
| Default value: | N/A |
| Used by: | CheckSystem |
Sample:
PDH subsystem ¶
Set which pdh subsystem to use. Currently default and thread-safe are supported where thread-safe is slower but required if you have some problematic counters.
| Key | Description |
|---|---|
| Path: | /settings/system/windows |
| Key: | subsystem |
| Advanced: | Yes (means it is not commonly used) |
| Default value: | default |
| Used by: | CheckSystem |
Sample:
PDH Counters ¶
Add counters to check
This is a section of objects. This means that you will create objects below this point by adding sections which all look the same.
Keys:
| Key | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| alias | ALIAS | |
| buffer size | BUFFER SIZE | |
| collection strategy | COLLECTION STRATEGY | |
| counter | COUNTER | |
| flags | FLAGS | |
| instances | Interpret instances | |
| is template | false | IS TEMPLATE |
| parent | default | PARENT |
| type | COUNTER TYPE |
Sample:
Known instances:
Legacy generic filters ¶
A set of filters to use in real-time mode
This is a section of objects. This means that you will create objects below this point by adding sections which all look the same.
Keys:
| Key | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| check | cpu | TYPE OF CHECK |
| command | COMMAND NAME | |
| critical | CRITICAL FILTER | |
| debug | DEBUG | |
| destination | DESTINATION | |
| detail syntax | SYNTAX | |
| empty message | eventlog found no records | EMPTY MESSAGE |
| escape html | ESCAPE HTML | |
| filter | FILTER | |
| maximum age | 5m | MAGIMUM AGE |
| ok | OK FILTER | |
| ok syntax | SYNTAX | |
| perf config | PERF CONFIG | |
| severity | SEVERITY | |
| silent period | false | Silent period |
| source id | SOURCE ID | |
| target | DESTINATION | |
| target id | TARGET ID | |
| time | TIME | |
| times | FILES | |
| top syntax | SYNTAX | |
| warning | WARNING FILTER |
Sample:
Realtime cpu filters ¶
A set of filters to use in real-time mode
This is a section of objects. This means that you will create objects below this point by adding sections which all look the same.
Keys:
| Key | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| command | COMMAND NAME | |
| critical | CRITICAL FILTER | |
| debug | DEBUG | |
| destination | DESTINATION | |
| detail syntax | SYNTAX | |
| empty message | eventlog found no records | EMPTY MESSAGE |
| escape html | ESCAPE HTML | |
| filter | FILTER | |
| maximum age | 5m | MAGIMUM AGE |
| ok | OK FILTER | |
| ok syntax | SYNTAX | |
| perf config | PERF CONFIG | |
| severity | SEVERITY | |
| silent period | false | Silent period |
| source id | SOURCE ID | |
| target | DESTINATION | |
| target id | TARGET ID | |
| time | TIME | |
| top syntax | SYNTAX | |
| warning | WARNING FILTER |
Sample:
Realtime memory filters ¶
A set of filters to use in real-time mode
This is a section of objects. This means that you will create objects below this point by adding sections which all look the same.
Keys:
| Key | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| command | COMMAND NAME | |
| critical | CRITICAL FILTER | |
| debug | DEBUG | |
| destination | DESTINATION | |
| detail syntax | SYNTAX | |
| empty message | eventlog found no records | EMPTY MESSAGE |
| escape html | ESCAPE HTML | |
| filter | FILTER | |
| maximum age | 5m | MAGIMUM AGE |
| ok | OK FILTER | |
| ok syntax | SYNTAX | |
| perf config | PERF CONFIG | |
| severity | SEVERITY | |
| silent period | false | Silent period |
| source id | SOURCE ID | |
| target | DESTINATION | |
| target id | TARGET ID | |
| top syntax | SYNTAX | |
| type | MEMORY TYPE | |
| warning | WARNING FILTER |
Sample:
Realtime process filters ¶
A set of filters to use in real-time mode
This is a section of objects. This means that you will create objects below this point by adding sections which all look the same.