- Как выполнять Linux-команды внутри Windows: официальный и сторонние способы
- Содержание
- WSL — официальная подсистема Linux внутри Windows
- CoreUtils — лёгкий инструмент для запуска базовых команд
- Cygwin — запуск команд и Bash-скриптов
- Running remotely Linux script from Windows and get execution result code
- Running a shell script through Cygwin on Windows
- 6 Answers 6
- Single script to run in both Windows batch and Linux Bash?
- 11 Answers 11
Как выполнять Linux-команды внутри Windows: официальный и сторонние способы
Под GNU/Linux-дистрибутивы создано огромное количество полезных и удобных инструментов и приложений для обычных пользователей и разработчиков. Далеко не всё из этого доступно на Windows, но, к счастью, для ОС от Microsoft есть решения, исправляющие эту проблему.
Содержание
WSL — официальная подсистема Linux внутри Windows
В Windows 10 существует крайне полезная вещь под названием Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL). Она позволяет использовать GNU/Linux-среду прямо в Windows и запускать не только команды, но и, например, Bash-скрипты. Для использования WSL необходимо следовать инструкции ниже.
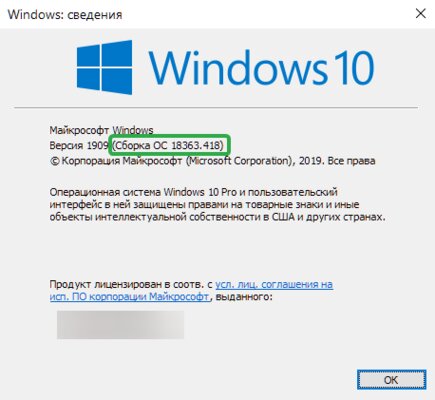
Шаг 1. Проверьте, подходит ли текущая версия Windows требованиям. Для этого нажмите сочетание клавиш Win+R, затем введите winver. Найдите строку «Сборка ОС» — она должна быть свежее версии 14316.
Шаг 2. Запустите стандартную утилиту PowerShell от имени администратора и введите в ней команду для включения WSL:
dism.exe /online /enable-feature /featurename:Microsoft-Windows-Subsystem-Linux /all /norestart
Шаг 3. Если версия Windows, определённая в первом пункте, свежее 18362, вы можете установить WSL 2, который в разы быстрее первой версии и обладает доработанным ядром. Введите команду ниже, если нужно установить WSL 2:
dism.exe /online /enable-feature /featurename:VirtualMachinePlatform /all /norestart
После этого скачайте и установите пакет обновления с официального сайта.
Шаг 4. Перезагрузите компьютер. Если была произведена установка WSL 2, введите в PowerShell от имени администратора следующую команду:
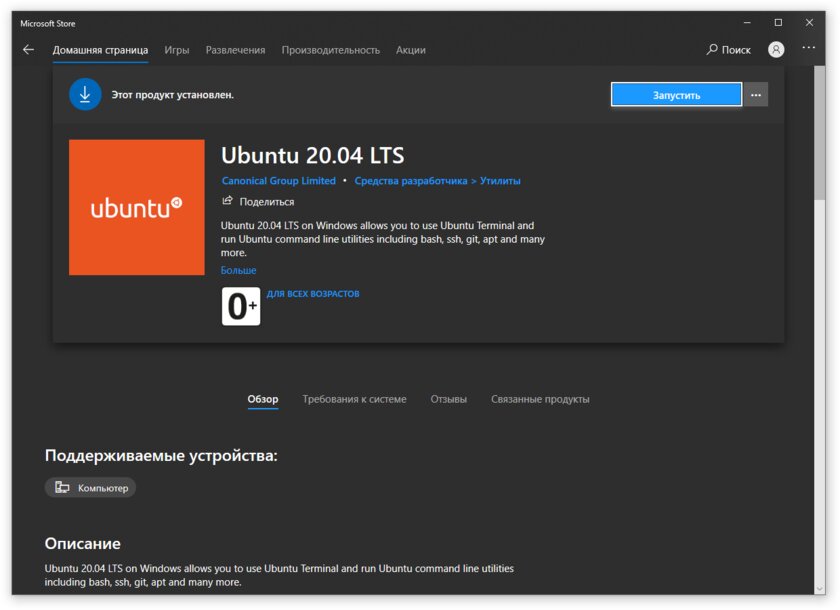
Шаг 5. После перезагрузки откройте фирменный магазин приложений Microsoft Store и найдите подходящий GNU/Linux-дистрибутив. Самым популярным является Ubuntu — вы можете установить любую версию из представленных в Microsoft Store.
Шаг 6. Как только установка завершится, найдите дистрибутив в меню «Пуск» и запустите его.
Шаг 7. Пройдите этап первоначальной настройки, введя имя нового пользователя и придумав пароль.
Шаг 8. Теперь различные GNU/Linux-команды можно выполнять, запустив дистрибутив, либо введя в командной строке wsl . Например, для просмотра всех файлов в текущей директории достаточно в командной строке выполнить wsl ls -a.
Обращу внимание на то, что путь к дискам в WSL отличается от такового в Windows. Вместо привычного C:/ используйте /mnt/c/. Также не забывайте про экранирование пробелов с помощью символа \ — это также пригодится при вводе путей к файлам.
Помимо выполнения базовых команд, с помощью WSL можно даже запускать приложения с графическим интерфейсом. Правда, рассчитывать на большое количество поддерживаемых подобных программ не стоит.
Шаг 1. Загрузите X-сервер и установите его.
Шаг 2. Запустите его с помощью ярлыка на рабочем столе. В открывшемся окне выберите вариант Multiple windows, затем Start no client. Завершите настройку кнопкой Finish.
Шаг 3. Откройте дистрибутив через меню Пуск и выполните команду export DISPLAY=:0
Шаг 4. Запустив приложение с графическим интерфейсом в WSL, вы увидите новое окно прямо в Windows.
CoreUtils — лёгкий инструмент для запуска базовых команд
Плюс данной утилиты — возможность запуска не только на Windows 10, но и на более старых версиях ОС. Кроме того, она легка и не занимает много места. Не обошлось без недостатков — программа скудна на функционал и не обновлялась очень давно. Она не только не умеет запускать скрипты и приложения с GUI, но и поддерживает лишь самые базовые GNU/Linux-команды. Установка CoreUtils весьма проста.
Шаг 1. Скачайте утилиту с официального сайта.
Шаг 2. Следуйте инструкциям установщика.
Шаг 3. Откройте «Панель управления», в разделе «Система и безопасность» выберите пункт «Система». На панели слева откройте «Дополнительные параметры системы». Нажмите кнопку «Переменные среды» и в открывшемся окне найдите область с заголовком «Системные переменные». В случае, когда там есть переменная Path, выберите её, нажмите «Изменить» и далее создайте новую строку. Содержимым этой строки должен быть путь к папке, который был указан при установке. Если вы ничего не меняли, то введите следующее:
Переменной Path нет? Тогда для начала создайте её кнопкой «Создать», затем в поле имени введите Path, а в поле значения — строку выше.
Шаг 4. Запустите командную строку и выполняйте команды прямо там.
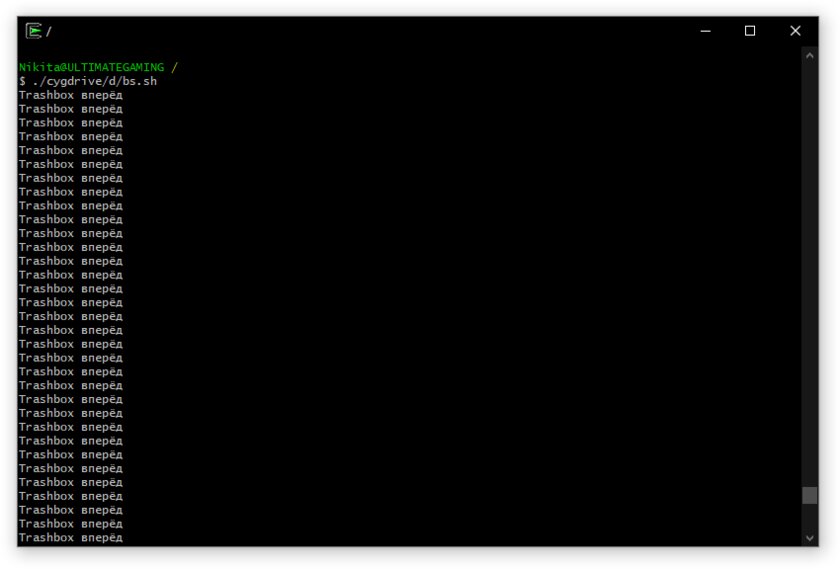
Cygwin — запуск команд и Bash-скриптов
Ещё одна утилита, схожая с CoreUtils, но обладающая более широким функционалом — в том числе и возможностью запуска скриптов. Из минусов — немалый вес и более сложная установка. Разумеется, не идёт ни в какое сравнение с максимально удобным WSL, но для базовых команд вполне подойдёт.
Шаг 1. Загрузите Cygwin и запустите установку.
Шаг 2. Выберите Install from Internet, укажите директории для установки и загрузки пакетов, а также любой подходящий сайт из списка для скачивания файлов.
Шаг 3. В процессе установки можете выбрать необходимые пакеты, либо сразу нажать «Далее», оставив базовый набор.
Шаг 4. Откройте «Панель управления», в разделе «Система и безопасность» выберите пункт «Система». На панели слева откройте «Дополнительные параметры системы». Нажмите кнопку «Переменные среды» и в открывшемся окне найдите область с заголовком «Системные переменные». В случае, когда там есть переменная Path, выберите её, нажмите «Изменить» и далее создайте новую строку. Содержимым этой строки должен быть путь к папке, который был указан при установке. Если вы ничего не меняли, то введите следующее:
Переменной Path нет? Тогда для начала создайте её кнопкой «Создать», затем в поле имени введите Path, а в поле значения — строку выше.
Шаг 5. Команды можно выполнять как через командную строку, так и через специальный терминал.
Шаг 6. Для удаления Cygwin достаточно удалить папку, в которую программа была установлена, а также (по желанию) значение из переменной Path по методу, обратному тому, что был описан в 4 шаге (не удаляйте саму переменную).
Running remotely Linux script from Windows and get execution result code
I have the current scenario to deal with: I have to schedule the backup of my company’s Linux-based server (under Suse Linux) with ARCServe R15 (installed on Windows 2003R2SP2). I know I have the ability in my backup software (ARCServe) to add pre/post execution scripts to my backup-jobs. If failure of the script, ARCServe would be specified NOT to run the backup-job, and if success, specified to be run. I have no problem with this.
The problem is, I want to make a windows script (to be launched by ARCServe) for executing a Linux script on the cluster: — If this Linux-script fails, I want my windows-script to fail, so my backup job in ARCServe wouldn’t run — If the Linux-script success, I want my windows-script to end normally with error code 0, so my ARCServe job would run normally. I’ve tried creating this batch file (let’s call it HPC.bat):
start /wait «C:\Program Files\PUTTY\plink.exe» -v -l root -i «C:\IST\admin\scripts\HPC\pri.ppk» [cluster_name] /appli/admin/backup_admin
If I manually launch this .bat by double-clicking on it, or launching it in a command prompt under Windows, it executes normally and then ends. If I make it being launched by ARCServe, the script seems never to end. My job stays in «waiting» status, it seems the execution code of the linux script isn’t returned to my batch file, and this one doesn’t close. In my mind, what’s happening is plink just opens the connection to the Linux, send the sript execution signal, and then close the connection, so the execution code can’t be returned to the batch. Am I right ?
Is what I want to do possible or am I trying something impossible to do ? So, do I have to proceed differently ? Do I have to use PUTTY or CygWin instead of plink ? Please, it’s giving me headaches .
Running a shell script through Cygwin on Windows
I have a bunch of shell scripts that used to run on a Linux machine. Now, we’ve switched over to Windows, and I need to run these scripts there. I have Cygwin installed, but is there a way to make the script run using Cygwin, but the call is made from Windows batch?
6 Answers 6
Sure. On my (pretty vanilla) Cygwin setup, bash is in c:\cygwin\bin so I can run a bash script (say testit.sh ) from a Windows batch file using a command like:
. which can be included in a .bat file as easily as it can be typed at the command line, and with the same effect.
One more thing — if You edited the shell script in some Windows text editor, which produces the \r\n line-endings, cygwin’s bash wouldn’t accept those \r . Just run dos2unix testit.sh before executing the script:
If you have access to the Notepad++ editor on Windows there is a feature that allows you to easily get around this problem:
- Open the file that’s giving the error in Notepad++.
- Go under the «Edit» Menu and choose «EOL Conversion»
- There is an option there for «UNIX/OSX Format.» Choose that option.
- Re-save the file.
I did this and it solved my problems.
Hope this helps!
Just wanted to add that you can do this to apply dos2unix fix for all files under a directory, as it saved me heaps of time when we had to ‘fix’ a bunch of our scripts.
I’d do it as a comment to Roman’s answer, but I don’t have access to commenting yet.
The existing answers all seem to run this script in a DOS console window.
This may be acceptable, but for example means that colour codes (changing text colour) don’t work but instead get printed out as they are:
I found this solution some time ago, so I’m not sure whether mintty.exe is a standard Cygwin utility or whether you have to run the setup program to get it, but I run like this:
. this causes the script to run in a Cygwin BASH console instead of a Windows DOS console.
If you don’t mind always including .sh on the script file name, then you can keep the same script for Cygwin and Unix (Macbook).
To illustrate:
1. Always include .sh to your script file name, e.g., test1.sh
2. test1.sh looks like the following as an example:
#!/bin/bash echo ‘$0 = ‘ $0 echo ‘$1 = ‘ $1 filepath=$1 3. On Windows with Cygwin, you type «test1.sh» to run
4. On a Unix, you also type «test1.sh» to run
Note: On Windows, you need to use the file explorer to do following once:
1. Open the file explorer
2. Right-click on a file with .sh extension, like test1.sh
3. Open with. -> Select sh.exe
After this, your Windows 10 remembers to execute all .sh files with sh.exe.
Note: Using this method, you do not need to prepend your script file name with bash to run
Single script to run in both Windows batch and Linux Bash?
Is it possible to write a single script file which executes in both Windows (treated as .bat) and Linux (via Bash)?
I know the basic syntax of both, but didn’t figure out. It could probably exploit some Bash’s obscure syntax or some Windows batch processor glitch.
The command to execute may be just a single line to execute other script.
The motivation is to have just a single application boot command for both Windows and Linux.
Update: The need for system’s «native» shell script is that it needs to pick the right interpreter version, conform to certain well-known environment variables etc. Installing additional environments like CygWin is not preferable — I’d like to keep the concept «download & run».
The only other language to consider for Windows is Windows Scripting Host — WSH, which is preset by default since 98.
11 Answers 11
What I have done is use cmd’s label syntax as comment marker. The label character, a colon ( : ), is equivalent to true in most POSIXish shells. If you immediately follow the label character by another character which can’t be used in a GOTO , then commenting your cmd script should not affect your cmd code.
The hack is to put lines of code after the character sequence “ :; ”. If you’re writing mostly one-liner scripts or, as may be the case, can write one line of sh for many lines of cmd , the following might be fine. Don’t forget that any use of $? must be before your next colon : because : resets $? to 0.
A very contrived example of guarding $? :
Another idea for skipping over cmd code is to use heredocs so that sh treats the cmd code as an unused string and cmd interprets it. In this case, we make sure that our heredoc’s delimiter is both quoted (to stop sh from doing any sort of interpretation on its contents when running with sh ) and starts with : so that cmd skips over it like any other line starting with : .
Depending on your needs or coding style, interlacing cmd and sh code may or may not make sense. Using heredocs is one method to perform such interlacing. This could, however, be extended with the GOTO technique:
Universal comments, of course, can be done with the character sequence : # or :;# . The space or semicolon are necessary because sh considers # to be part of a command name if it is not the first character of an identifier. For example, you might want to write universal comments in the first lines of your file before using the GOTO method to split your code. Then you can inform your reader of why your script is written so oddly:
Thus, some ideas and ways to accomplish sh and cmd -compatible scripts without serious side effects as far as I know (and without having cmd output ‘#’ is not recognized as an internal or external command, operable program or batch file. ).