- Windows Server Installation Guide
- Enable the Windows Subsystem for Linux
- Download a Linux distribution
- Extract and install a Linux distribution
- Running windows on ubuntu server
- 2. Requirements
- 3. Enable WSL
- 4. Install Ubuntu for Windows 10
- 5. Launch Ubuntu on Windows 10
- First launch
- 6. Getting help
- Ubuntu on WSL
- Deploying WSL at your company?
- Access the Linux terminal on Windows
- Develop cross-platform
- Manage IT infrastructure
- What you never thought was possible on Windows
- Editors
- Servers
- Development
- Shells
- Containers
- Scripting
- Network hardening
- Kubernetes
- Why WSL
- Easy to Use
- Security
- Enterprise support
- Install Ubuntu on Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL)
- Enable WSL on Windows 10
- Install Ubuntu
- Manually download Windows Subsystem for Linux distro packages
- Downloading distributions
- Downloading distros via the command line
- Download using PowerShell
- Download using curl
- Installing your distro
- Troubleshooting Windows Subsystem for Linux
- Search for any existing issues related to your problem
- Submit a bug report
- Submit a feature request
- Contribute to the docs
- Terminal or Command Line
- Common issues
- I’m on Windows 10 version 1903 and I still do not see options for WSL 2
- Error: 0x1bc when wsl —set-default-version 2
- Cannot access WSL files from Windows
- Can’t start WSL 2 distribution and only see ‘WSL 2’ in output
- command not found when executing windows .exe in linux
- «Error: 0x80370102 The virtual machine could not be started because a required feature is not installed.»
- Bash loses network connectivity once connected to a VPN
- Starting WSL or installing a distribution returns an error code
- Updating Bash on Ubuntu on Windows
- Apt-get upgrade errors
- «Error: 0x80040306» on installation
- «Error: 0x80040154» after Windows update
- Changing the display language
- Installation issues after Windows system restore
- No internet access in WSL
- Permission Denied error when using ping
- Bash is hung
- Check your build number
- Confirm WSL is enabled
- OpenSSH-Server connection issues
- «The referenced assembly could not be found.» when enabling the WSL optional feature
- Correct (SSH related) permission errors
- Running Windows commands fails inside a distribution
- Unable to boot after installing WSL 2
Windows Server Installation Guide
The Windows Subsystem for Linux is available for installation on Windows Server 2019 (version 1709) and later. This guide will walk through the steps of enabling WSL on your machine.
Enable the Windows Subsystem for Linux
Before you can run Linux distros on Windows, you must enable the «Windows Subsystem for Linux» optional feature and reboot.
Open PowerShell as Administrator and run:
Download a Linux distribution
Follow these instructions to download your favorite Linux distribution.
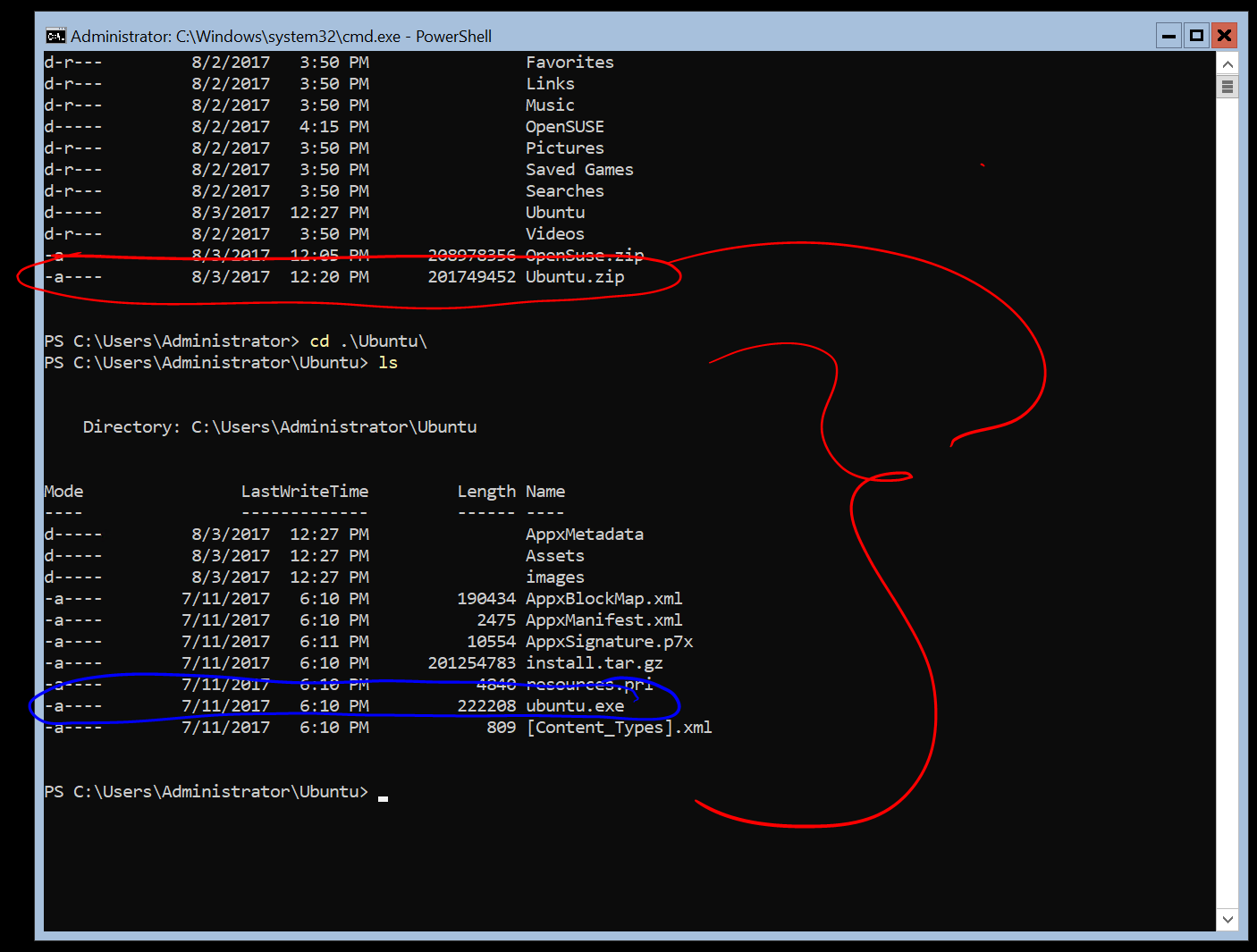
Extract and install a Linux distribution
Now that you’ve downloaded a Linux distribution, in order to extract its contents and manually install, follow these steps:
Extract the .appx package’s contents, using PowerShell:
Run the distribution launcher application in the target folder. The launcher is typically named .exe (for example, ubuntu.exe ).
Installation failed with error 0x8007007e: If you receive this error, then your system doesn’t support WSL. Ensure that you’re running Windows build 16215 or later. Check your build. Also check to confirm that WSL is enabled and your computer was restarted after the feature was enabled.
3.Add your distro path to the Windows environment PATH ( C:\Users\Administrator\Ubuntu in this example), using PowerShell:
You can now launch your distribution from any path by typing .exe . For example: ubuntu.exe .
Now that it is installed, you must initialize your new distribution instance before using it.
Running windows on ubuntu server
Switch language: EN | ES
The wonderful Ubuntu terminal is freely available for Windows 10.
As any Linux user knows, it’s the command line terminal where the magic happens. It’s perfect for file management, development, remote administration and a thousand other tasks.
The Ubuntu terminal for Windows has many of the same features you’ll find using the terminal on Ubuntu:
- Unrivalled breadth of packages, updates and security features
- Bash, Z-Shell, Korn and other shell environments without virtual machines or dual-booting
- Run native tools such as SSH, git, apt and dpkg directly from your Windows computer
- A huge community of friendly, approachable users
Originally authored by Graham Morrison.
2. Requirements
You will need a x86 PC running Windows 10.
Windows 10 needs to be updated to include the Windows 10 Fall Creators update, released October 2017. This update includes the Windows Subsystem for Linux which is needed to run the Ubuntu terminal.
3. Enable WSL
To enable WSL 1 on Windows 10 Fall Creators update and newer run the following in PowerShell as Administrator:
To enable WSL 2 on Windows 10 May 2020 update and newer run the following in PowerShell as Administrator:
and then restart Windows 10.
4. Install Ubuntu for Windows 10
Ubuntu can be installed from the Microsoft Store:
- Use the Start menu to launch the Microsoft Store application or click here.
- Search for Ubuntu and select the first result, ‘Ubuntu’, published by Canonical Group Limited.
- Click on the Install button.
Ubuntu will be downloaded and installed automatically. Progress will be reported within the Microsoft Store application.
5. Launch Ubuntu on Windows 10
Ubuntu can now be launched in the same way as any other Windows 10 application, such as searching for and selecting Ubuntu in the Start menu.
First launch
When launched for the first time, Ubuntu will inform you that it’s ‘Installing’ and you’ll need to wait a few moments.
When complete, you’ll be asked for a username and password specific to your Ubuntu installation. These don’t need to be the same as your Windows 10 credentials. With this step complete, you’ll find yourself at the Ubuntu bash command line.
Congratulations! You have successfully installed and activated the Ubuntu terminal on Windows 10. You now have all the power of the command line at your fingertips.
6. Getting help
If you need some guidance getting started with the Ubuntu terminal, take a look at the community documentation, and if you get stuck, help is always at hand:
Ubuntu on WSL
Install a complete Ubuntu terminal environment in minutes on Windows 10 with Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL).
Access the Linux terminal on Windows, develop cross-platform applications, and manage IT infrastructure without leaving Windows.
Deploying WSL at your company?
We help companies achieve a seamless integration with their WSL deployments. Contact us to learn more about how we support enterprises on the Windows Subsystem for Linux.
Access the Linux terminal on Windows
In seconds, be able to access the Linux terminal and run Linux applications and workflows on your Windows machine.
Develop cross-platform
Build and debug Linux applications with Windows tools like Visual Studio Code, Visual Studio, and JetBrains IDEs before deploying to the cloud.
Manage IT infrastructure
From the same workstation, manage mixed Linux and Windows infrastructure both on-prem and across public clouds.
What you never thought was possible on Windows
Editors
Run your choice of Linux text editors, including vim, emacs, and nano
Servers
Spin up Node.js, install your dependencies with npm, and start testing your web app
Development
Install compilers and libraries from the Ubuntu repository, maintained by Canonical
Shells
Use your choice of Linux shells, such as bash, zsh and fish
Containers
Work with LXD and Docker containers on Windows
Scripting
Automate Linux and Windows tasks with advanced bash scripting
Network hardening
Leverage Linux security tools to test and harden your network
Crunch big numbers with tools for R and Python
Kubernetes
Build, test, and deploy Kubernetes clusters on Windows
Why WSL
Easy to Use
Ubuntu is intuitive, user-friendly, and offers the flexibility for customizations when operating within WSL.
Security
Achieve the same first-class, out-of-the-box, compliant security that is synonymous with Ubuntu. With long-term support releases, you’ll have five years of security patches and updates.
Enterprise support
Ubuntu is certified on WSL through close collaboration with Microsoft. Enterprise support is provided for Ubuntu from Azure to Windows workstations creating a seamless operating environment.
Install Ubuntu on Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL)
Enable WSL on Windows 10
Open PowerShell as Administrator:
Type the following command to enable WSL 1:
Type the following command to enable WSL 2:
Restart your computer.
After restarting, download and install the WSL 2 Linux kernel from Microsoft for your device architecture:
- x86_64 for Intel and AMD devices
- arm64 for Snapdragon and other ARM devices
Finally, it is recommended to set WSL 2 as the default WSL environment.
Open PowerShell as Administrator as above and type the following command:
Install Ubuntu
Download Ubuntu for WSL from the Microsoft Store.
Manually download Windows Subsystem for Linux distro packages
There are several scenarios in which you may not be able (or want) to, install WSL Linux distros via the Microsoft Store. Specifically, you may be running a Windows Server or Long-Term Servicing (LTSC) desktop OS SKU that doesn’t support Microsoft Store, or your corporate network policies and/or admins to not permit Microsoft Store usage in your environment.
In these cases, while WSL itself is available, how do you download and install Linux distros in WSL if you can’t access the store?
Note: Command-line shell environments including Cmd, PowerShell, and Linux/WSL distros are not permitted to run on Windows 10 S Mode. This restriction exists in order to ensure the integrity and safety goals that S Mode delivers: Read this post for more information.
Downloading distributions
If the Microsoft Store app is not available, you can download and manually install Linux distros by clicking these links:
This will cause the .appx packages to download to a folder of your choosing. Follow the installation instructions to install your downloaded distro(s).
Downloading distros via the command line
If you prefer, you can also download your preferred distro(s) via the command line:
Download using PowerShell
To download distros using PowerShell, use the Invoke-WebRequest cmdlet. Here’s a sample instruction to download Ubuntu 16.04.
If the download is taking a long time, turn off the progress bar by setting $ProgressPreference = ‘SilentlyContinue’
Download using curl
Windows 10 Spring 2018 Update (or later) includes the popular curl command-line utility with which you can invoke web requests (i.e. HTTP GET, POST, PUT, etc. commands) from the command line. You can use curl.exe to download the above distros:
In the above example, curl.exe is executed (not just curl ) to ensure that, in PowerShell, the real curl executable is invoked, not the PowerShell curl alias for Invoke-WebRequest
Note: Using curl might be preferable if you have to invoke/script download steps using Cmd shell and/or .bat / .cmd scripts.
Installing your distro
If you’re using Windows 10 you can install your distro with PowerShell. Simply navigate to folder containing the distro downloaded from above, and in that directory run the following command where app_name is the name of your distro .appx file.
If you are using Windows server, or run into problems running the command above you can find the alternate install instructions on the Windows Server documentation page to install the .appx file by changing it to a zip file.
Once your distribution is installed, follow the normal instructions to * Update from WSL 1 to WSL 2 or create a new user account and password.
Troubleshooting Windows Subsystem for Linux
For support with issues related to WSL, please see our WSL product repo on GitHub.
Search for any existing issues related to your problem
For technical issues, use the product repo.
For issues related to the contents of this documentation, use the docs repo.
Submit a bug report
For bugs related to WSL functions or features, file an issue in the product repo: https://github.com/Microsoft/wsl/issues
Submit a feature request
To request a new feature related to WSL functionality or compatibility, file an issue in the product repo.
Contribute to the docs
To contribute to the WSL documentation, submit a pull request in the docs repo: https://github.com/MicrosoftDocs/wsl/issues
Terminal or Command Line
Lastly, if your issue is related to the Windows Terminal, Windows Console, or the command-line UI, use the Windows terminal repo: https://github.com/microsoft/terminal
Common issues
I’m on Windows 10 version 1903 and I still do not see options for WSL 2
This is likely because your machine has not yet taken the backport for WSL 2. The simplest way to resolve this is by going to Windows Settings and clicking ‘Check for Updates’ to install the latest updates on your system. See the full instructions on taking the backport.
If you hit ‘Check for Updates’ and still do not receive the update you can install KB KB4566116 manually.
Error: 0x1bc when wsl —set-default-version 2
This may happen when ‘Display Language’ or ‘System Locale’ setting is not English.
The actual error for 0x1bc is:
For more information, please refer to issue 5749
Cannot access WSL files from Windows
A 9p protocol file server provides the service on the Linux side to allow Windows to access the Linux file system. If you cannot access WSL using \\wsl$ on Windows, it could be because 9P did not start correctly.
To check this, you can check the start up logs using: dmesg |grep 9p , and this will show you any errors. A successfull output looks like the following:
Please see this Github thread for further discussion on this issue.
Can’t start WSL 2 distribution and only see ‘WSL 2’ in output
If your display language is not English, then it is possible you are seeing a truncated version of an error text.
To resolve this issue, please visit https://aka.ms/wsl2kernel and install the kernel manually by following the directions on that doc page.
command not found when executing windows .exe in linux
Users can run Windows executables like notepad.exe directly from Linux. Sometimes, you may hit «command not found» like below:
If there are no win32 paths in your $PATH, interop isn’t going to find the .exe. You can verify it by running echo $PATH in Linux. It’s expected that you will see a win32 path (for example, /mnt/c/Windows) in the output. If you can’t see any Windows paths then most likely your PATH is being overwritten by your Linux shell.
Here is a an example that /etc/profile on Debian contributed to the problem:
The correct way on Debian is to remove above lines. You may also append $PATH during the assignment like below, but this lead to some other problems with WSL and VSCode..
For more information, see issue 5296 and issue 5779.
«Error: 0x80370102 The virtual machine could not be started because a required feature is not installed.»
Please enable the Virtual Machine Platform Windows feature and ensure virtualization is enabled in the BIOS.
If your machine is a VM, please enable nested virtualization manually. Launch powershell with admin, and run:
Please follow guidelines from your PC’s manufacturer on how to enable virtualization. In general, this can involve using the system BIOS to ensure that these features are enabled on your CPU. Instructions for this process can vary from machine to machine, please see this article from Bleeping Computer for an example.
Restart your machine after enabling the Virtual Machine Platform optional component.
Bash loses network connectivity once connected to a VPN
If after connecting to a VPN on Windows, bash loses network connectivity, try this workaround from within bash. This workaround will allow you to manually override the DNS resolution through /etc/resolv.conf .
- Take a note of the DNS server of the VPN from doing ipconfig.exe /all
- Make a copy of the existing resolv.conf sudo cp /etc/resolv.conf /etc/resolv.conf.new
- Unlink the current resolv.conf sudo unlink /etc/resolv.conf
- sudo mv /etc/resolv.conf.new /etc/resolv.conf
- Open /etc/resolv.conf and
a. Delete the first line from the file, which says «# This file was automatically generated by WSL. To stop automatic generation of this file, remove this line.».
b. Add the DNS entry from (1) above as the very first entry in the list of DNS servers.
c. Close the file.
Once you have disconnected the VPN, you will have to revert the changes to /etc/resolv.conf . To do this, do:
- cd /etc
- sudo mv resolv.conf resolv.conf.new
- sudo ln -s ../run/resolvconf/resolv.conf resolv.conf
Starting WSL or installing a distribution returns an error code
Follow these instructions to collect detailed logs and file an issue on our GitHub.
Updating Bash on Ubuntu on Windows
There are two components of Bash on Ubuntu on Windows that can require updating.
The Windows Subsystem for Linux
Upgrading this portion of Bash on Ubuntu on Windows will enable any new fixes outlines in the release notes. Ensure that you are subscribed to the Windows Insider Program and that your build is up to date. For finer grain control including resetting your Ubuntu instance check out the command reference page.
The Ubuntu user binaries
Upgrading this portion of Bash on Ubuntu on Windows will install any updates to the Ubuntu user binaries including applications that you have installed via apt-get. To update run the following commands in Bash:
Apt-get upgrade errors
Some packages use features that we haven’t implemented yet. udev , for example, isn’t supported yet and causes several apt-get upgrade errors.
To fix issues related to udev , follow the following steps:
Write the following to /usr/sbin/policy-rc.d and save your changes.
Add execute permissions to /usr/sbin/policy-rc.d :
Run the following commands:
«Error: 0x80040306» on installation
This has to do with the fact that we do not support legacy console. To turn off legacy console:
- Open cmd.exe
- Right click title bar -> Properties -> Uncheck Use legacy console
- Click OK
«Error: 0x80040154» after Windows update
The Windows Subsystem for Linux feature may be disabled during a Windows update. If this happens the Windows feature must be re-enabled. Instructions for enabling the Windows Subsystem for Linux can be found in the Installation Guide.
Changing the display language
WSL install will try to automatically change the Ubuntu locale to match the locale of your Windows install. If you do not want this behavior you can run this command to change the Ubuntu locale after install completes. You will have to relaunch bash.exe for this change to take effect.
The below example changes to locale to en-US:
Installation issues after Windows system restore
- Delete the %windir%\System32\Tasks\Microsoft\Windows\Windows Subsystem for Linux folder.
Note: Do not do this if your optional feature is fully installed and working. - Enable the WSL optional feature (if not already)
- Reboot
- lxrun /uninstall /full
- Install bash
No internet access in WSL
Some users have reported issues with specific firewall applications blocking internet access in WSL. The firewalls reported are:
- Kaspersky
- AVG
- Avast
- Symantec Endpoint Protection
In some cases turning off the firewall allows for access. In some cases simply having the firewall installed looks to block access.
Permission Denied error when using ping
For Windows Anniversary Update, version 1607, administrator privileges in Windows are required to run ping in WSL. To run ping, run Bash on Ubuntu on Windows as an administrator, or run bash.exe from a CMD/PowerShell prompt with administrator privileges.
For later versions of Windows, Build 14926+, administrator privileges are no longer required.
Bash is hung
If while working with bash, you find that bash is hung (or deadlocked) and not responding to inputs, help us diagnose the issue by collecting and reporting a memory dump. Note that these steps will crash your system. Do not do this if you are not comfortable with that or save your work prior to doing this.
To collect a memory dump
Change the memory dump type to «complete memory dump». While changing the dump type, take a note of your current type.
Use the steps to configure crash using keyboard control.
Repro the hang or deadlock.
Crash the system using the key sequence from (2).
The system will crash and collect the memory dump.
Once the system reboots, report the memory.dmp to secure@microsoft.com. The default location of the dump file is %SystemRoot%\memory.dmp or C:\Windows\memory.dmp if C: is the system drive. In the email, note that the dump is for the WSL or Bash on Windows team.
Restore the memory dump type to the original setting.
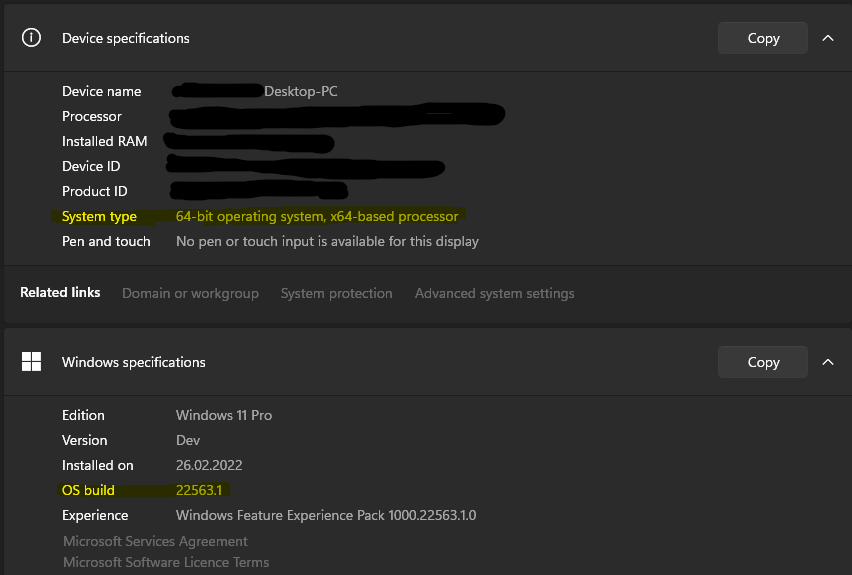
Check your build number
To find your PC’s architecture and Windows build number, open
Settings > System > About
Look for the OS Build and System Type fields.
To find your Windows Server build number, run the following in PowerShell:
Confirm WSL is enabled
You can confirm that the Windows Subsystem for Linux is enabled by running the following in PowerShell:
OpenSSH-Server connection issues
Trying to connect your SSH server is failed with the following error: «Connection closed by 127.0.0.1 port 22».
Make sure your OpenSSH Server is running:
Stop the sshd service and start sshd in debug mode:
Check the startup logs and make sure HostKeys are available and you don’t see log messages such as:
If you do see such messages and the keys are missing under /etc/ssh/ , you will have to regenerate the keys or just purge&install openssh-server:
«The referenced assembly could not be found.» when enabling the WSL optional feature
This error is related to being in a bad install state. Please complete the following steps to try and fix this issue:
If you are running the enable WSL feature command from PowerShell, try using the GUI instead by opening the start menu, searching for ‘Turn Windows features on or off’ and then in the list select ‘Windows Subsystem for Linux’ which will install the optional component.
Update your version of Windows by going to Settings, Updates, and clicking ‘Check for Updates’
If both of those fail and you need to access WSL please consider upgrading in place by reinstalling Windows 10 using installation media and selecting ‘Keep Everything’ to ensure your apps and files are preserved. You can find instructions on how to do so at the Reinstall Windows 10 page.
Correct (SSH related) permission errors
If you’re seeing this error:
To fix this, append the following to the the /etc/wsl.conf file:
Please note that adding this command will include metadata and modify the file permissions on the Windows files seen from WSL. Please see the File System Permissions for more information.
Running Windows commands fails inside a distribution
Some distributions available in Microsoft Store are yet not fully compatible to run Windows commands in Terminal out of the box. If you get an error -bash: powershell.exe: command not found running powershell.exe /c start . or any other Windows command, you can resolve it following these steps:
- In your WSL distribution run echo $PATH .
If it does not include: /mnt/c/Windows/system32 something is redefining the standard PATH variable. - Check profile settings with cat /etc/profile .
If it contains assignment of the PATH variable, edit the file to comment out PATH assignment block with a # character. - Check if wsl.conf is present cat /etc/wsl.conf and make sure it does not contain appendWindowsPath=false , otherwise comment it out.
- Restart distribution by typing wsl -t followed by distribution name or run wsl —shutdown either in cmd or PowerShell.
Unable to boot after installing WSL 2
We are aware of an issue affecting users where they are unable to boot after installing WSL 2. While we fully diagnose those issue, users have reported that changing the buffer size or installing the right drivers can help address this. Please view this Github issue to see the latest updates on this issue.