- Сканирование сетевых портов в Linux – команда nmap
- Зачем нужна команда nmap?
- Синтаксис команды nmap и особенности её работы
- Использование nmap
- Заключение
- Linux / UNIX: Scanning network for open ports with nmap command
- nmap port scanning
- nmap TCP SYN (half-open) scanning
- nmap TCP FIN scanning
- nmap TCP Xmas tree scanning
- nmap TCP Null scanning
- nmap TCP Windows scanning
- nmap TCP RPC scanning
- nmap UDP scanning
- nmap remote software version scanning
- A note about Windows XP / 2003 / Vista version
- Top Port Scanners on Ubuntu Linux
- 1. Angry IP Scanner
- 4. Nmap — network mapper
- 3. pnscan
- 4. knocker
- 5 Best Free and Open Source Linux Port Scanners
- How to do a Port Scan in Linux
- TCP Scanning
- UDP Scanning
- Port Scanners
- Zenmap
- Netcat
- Unicornscan
- Conclusion
- About the author
- Usama Azad
Сканирование сетевых портов в Linux – команда nmap
Системы Linux и UNIX являются сетевыми операционными системами (ОС). Поэтому их эксплуатация неразрывно связана с администрированием и обслуживанием сетей. Независимо от сложности и масштабов сети необходимо проводить постоянный мониторинг окружения сети на предмет качества связи и соединений. А также для определения признаков или даже фактов вредительства в ней или несанкционированных атак. Одним из эффективных инструментов для выполнения подобных задач является команда nmap.
Зачем нужна команда nmap?
Основная задача команды nmap – сканирование сетевых портов указанных компьютеров для определения, какие из них используются (прослушиваются) программами-серверами. Для подавляющего числа сетевых демонов (служб) определены их стандартные порты по-умолчаню, которые они используют для своей работы. По этому признаку можно делать выводы, о том какие серверные программы запущены на том или ином компьютере в сети.
Также команда nmap – это самый доступный инструмент в руках злоумышленников для организации подготовки хакерской атаки на сеть. Ведь с помощью этой команды очень легко получить информацию, на основе которой можно судить о слабых и уязвимых местах в атакуемой системе.
Синтаксис команды nmap и особенности её работы
Команда nmap довольно проста в использовании и каким-то сложным синтаксисом не отличается:
Чего нельзя сказать о количестве, функциональности её ключей и неисчерпаемых возможностях их применения. Официальная документация, доступная на страницах man-руководства (команда man nmap), кроме того, что очень подробная (трудно встретить ещё подробнее), так ещё и имеет качественный перевод (локализации, в том числе и на русском языке) в большинстве Linux-дистрибутивов.
Не всегда утилита nmap предустановлена в системе, поэтому для её использования требуется установка соответствующего пакета, который обычно имеет имя nmap:
Или в Centos/Redhat
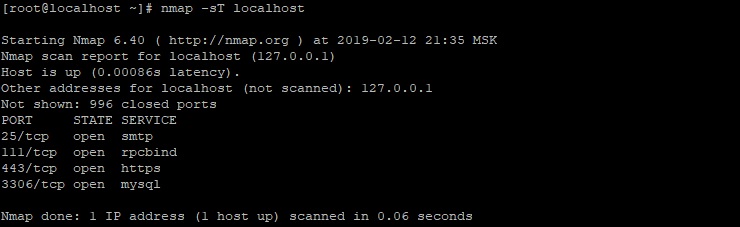
Столбец STATE показывает состояние порта: он может быть открыт (open), когда связан с использующими его службами (соединениями), закрыт (closed), когда порт не используется ни одним сервером. Также доступны состояния: unfiltered, когда nmap не смогла определить состояние порта. А также filtered – когда порт защищён (или заблокирован) брандмауэром.
Для задания хоста можно также использовать цифровую запись в виде IP-адреса. Отчёт из данного примера сформирован для самого обычного компьютера, для которого не была сконфигурирована какая-то защита. Как можно видеть, для прослушивания 80 и 443 портов для работы протоколов HTTP и HTTPS соответственно, запущен веб-сервер. Сервер баз данных (БД) MySQL также работает по стандартному порту.
Использование nmap
Если посмотреть на отчёт команды nmap для более защищённого узла, то он будет выглядеть примерно так:
Как можно видеть, на сканируемом узле (компьютере) скорее всего работает брандмауэр. Который блокирует все порты кроме тех, что отведены для работы почтового и веб- серверов. Таким образом, можно сделать вывод о том, что компьютер по указанному адресу настроен специально для работы с электронной почтой и обработкой HTTP-запросов.
Однако, одна из особенностей nmap заключается в том, что эту команду можно использовать в «хакерском» режиме. Другими словами она позволяет сканировать порты без установки реальных соединений. Это достигается путём использования неквитирующих пакетов, т. е. тех, которые похожи на имеющиеся в существующих соединениях. Но в ответ на такие пакеты можно получать пакеты диагностические. Т. е. получать информацию о соединении, при этом не быть «замеченным» брандмауэром или другим сетевым фильтром. Которые следят за «сканировщиками» портов.
Помимо всего прочего nmap умеет распознавать, какая ОС используется на проверяемом узле. Путём анализа некоторых особенностей, характерных для реализации стека TCP/IP для разных ОС. Для использования этой возможности существует ключ -O:
Как можно видеть, компьютер с IP-адресом 192.186.0.101 работает под управлением ОС Windows, предположительно Windows 7. Информация в отчёте довольно подробная, определён даже MAC-адрес сканируемого сетевого устройства.
Стоит рассмотреть некоторые примеры для команды nmap, которые могут пригодиться администраторам в их работе. Сканирование нескольких адресов:
Определение активных узлов в сети:
В этой команде используется формат записи, для обозначения подсети. В качестве параметров можно также указывать данные из файла:
Записи адресов в файле указываются также, как и в командной строке. И разделяться должны одним или несколькими пробелами или символами перевода строки. Для сканирования определённых портов:
или диапазона портов:
Сканирование всех портов:
Сканирование определённых типов портов (TCP или UDP):
Соответственно для указания UDP-портов следует указывать опцию -U. Для объединённого сканирования портов:
Для скрытого сканирования:
Сохранение результатов сканирования в файл:
Определить (с высокой степенью вероятности), работает ли на сканируемом узле брандмауэр или другой пакетный фильтр:
Определение только открытых портов:
Определение версии ОС, а также трассировки маршрутов:
Чтобы исключить из сканирования определённые адреса или подсети нужно использовать опцию —exclude:
Чтобы использовать для этой цели данные из файла, применяется опция —excludefile:
Заключение
Как можно видеть, nmap – это действительно мощный инструмент для мониторинга и анализа безопасности сетевого окружения. Следует также всегда помнить, что с помощью одной только команды nmap система или сеть могут быть досконально изучены «посторонними» или не совсем добросовестными людьми. Поэтому системные администраторы всегда должны учитывать этот фактор для обеспечения безопасности вверенных им систем.
Если вы нашли ошибку, пожалуйста, выделите фрагмент текста и нажмите Ctrl+Enter.
Источник
Linux / UNIX: Scanning network for open ports with nmap command
You can use nmap tool for this job. It is flexible in specifying targets. User can scan entire network or selected host or single server. Nmap is also useful to test your firewall rules. namp is metwork exploration tool and security / port scanner. According to nmap man page:
It is an open source tool for network exploration and security auditing. It was designed to rapidly scan large networks, although it works fine against single hosts. Nmap uses raw IP packets in novel ways to determine what hosts are available on the network, what services (application name and version) those hosts are offering, what operating systems (and OS versions) they are running, what type of packet filters/firewalls are in use, and dozens of other characteristics. While Nmap is commonly used for security audits, many systems and network administrators find it useful for routine tasks such as network inventory, managing service upgrade schedules, and monitoring host or service uptime.
nmap port scanning
TCP Connect scanning for localhost and network 192.168.0.0/24
# nmap -v -sT localhost
# nmap -v -sT 192.168.0.0/24
nmap TCP SYN (half-open) scanning
# nmap -v -sS localhost
# nmap -v -sS 192.168.0.0/24
nmap TCP FIN scanning
# nmap -v -sF localhost
# nmap -v -sF 192.168.0.0/24
nmap TCP Xmas tree scanning
Useful to see if firewall protecting against this kind of attack or not:
# nmap -v -sX localhost
# nmap -v -sX 192.168.0.0/24
nmap TCP Null scanning
Useful to see if firewall protecting against this kind attack or not:
# nmap -v -sN localhost
# nmap -v -sN 192.168.0.0/24
nmap TCP Windows scanning
# nmap -v -sW localhost
# nmap -v -sW 192.168.0.0/24
nmap TCP RPC scanning
Useful to find out RPC (such as portmap) services
# nmap -v -sR localhost
# nmap -v -sR 192.168.0.0/24
nmap UDP scanning
Useful to find out UDP ports
# nmap -v -O localhost
# nmap -v -O 192.168.0.0/24
nmap remote software version scanning
You can also find out what software version opening the port.
# nmap -v -sV localhost
# nmap -v -sV 192.168.0.0/24
- No ads and tracking
- In-depth guides for developers and sysadmins at Opensourceflare✨
- Join my Patreon to support independent content creators and start reading latest guides:
- How to set up Redis sentinel cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- How To Set Up SSH Keys With YubiKey as two-factor authentication (U2F/FIDO2)
- How to set up Mariadb Galera cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- A podman tutorial for beginners – part I (run Linux containers without Docker and in daemonless mode)
- How to protect Linux against rogue USB devices using USBGuard
Join Patreon ➔
A note about Windows XP / 2003 / Vista version
Windows user can find ipEye and IPSecScan utilities useful. Please note that Nmap also runes on Windows OS.
Read the man page of nmap for more information:
$ man nmap
Источник
Top Port Scanners on Ubuntu Linux
Here is a list of port scanners that work on Ubuntu/Linux.
1. Angry IP Scanner
Download and Install from http://www.angryip.org/
Fast and easy to use network scanner and port scanner.
To scan ports got to Tools > Preferences > Ports > Port Selection
Enter the ports you want to scan
Start the scan.
4. Nmap — network mapper
Install : sudo apt-get install nmap
Nmap is a utility for network exploration or security auditing. It supports ping scanning (determine which hosts are up), many port scanning techniques, version detection (determine service protocols and application versions listening behind ports), and TCP/IP fingerprinting (remote host OS or device identification). Nmap also offers flexible target and port specification, decoy/stealth scanning, sunRPC scanning, and more.
nmap also has with an easy to use GUI frontends :
1. zenmap
Install : sudo apt-get install zenmap
http://nmap.org/zenmap/
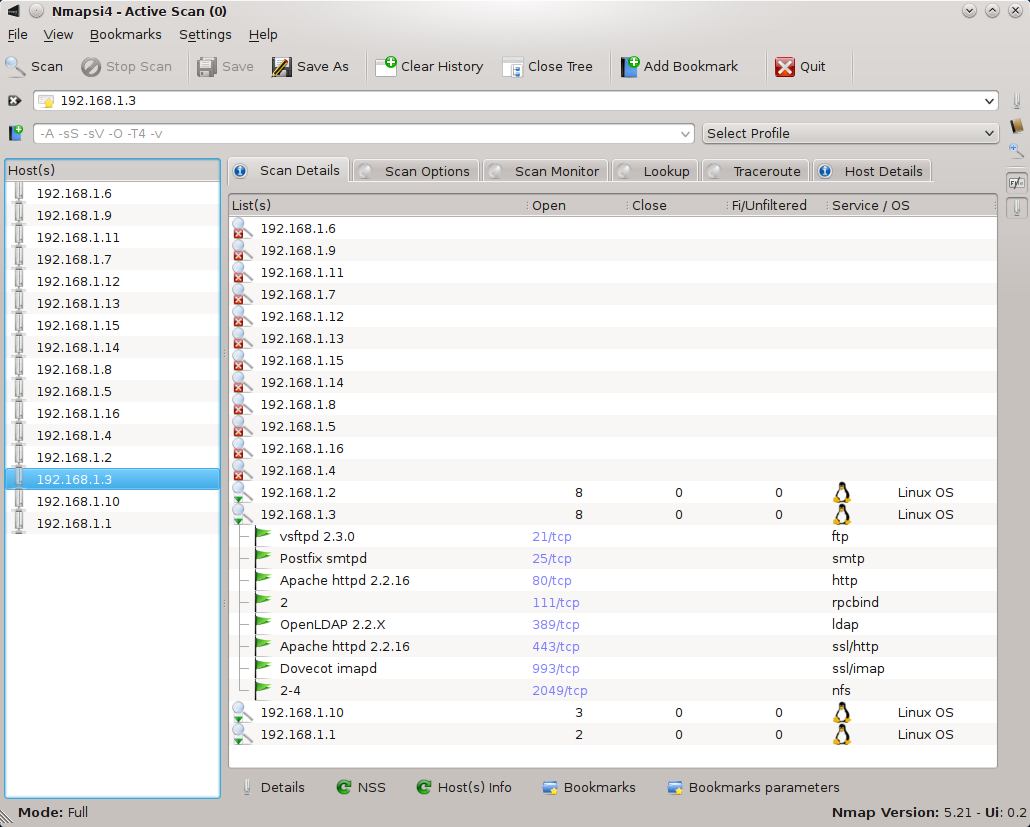
2. Nmapsi4
Install : sudo apt-get install nmapsi4
http://www.nmapsi4.org/
3. Umit
Install : sudo apt-get install umit
http://www.umitproject.org/
3. pnscan
Install : sudo apt-get install pnscan
Pnscan is a multi threaded port scanner that can scan a large network very quickly. If does not have all the features that nmap have but is much faster.
4. knocker
Install : sudo apt-get install knocker
A Tech Enthusiast, Blogger, Linux Fan and a Software Developer. Writes about Computer hardware, Linux and Open Source software and coding in Python, Php and Javascript. He can be reached at [email protected] .
Источник
5 Best Free and Open Source Linux Port Scanners
A port scanner is a utility which probes a server or host to verify if the virtual ports of a system are open or closed. Ports allow different applications on the same computer to share network resources simultaneously.
Computers that are connected to a local area network or internet run many different services that listen at well-known (and not so well-known) port numbers. Port numbers range from 0 to 65535, with port numbers from 0 to 1023 considered to be the well-known ports. These include ports reserved for the File Transfer Protocol (FTP), Secure Shell (SSH), telnet, Domain Name System (DNS), Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) used in the World Wide Web, Network News Transfer Protocol (NNTP), to name a few. Port numbers from 1024 to 49151 are known as registered ports, and the range from 49152 to 65535 are allocated to dynamic or private ports.
Port scanning is a popular technique used by attackers to find services that they may be able to compromise. A port scan assists the attacker in finding which ports are available. The scan sends a message to each port, with the response indicating whether the port is used and can therefore be probed further for weaknesses. There are a variety of different forms of scanning which include TCP, SYN, UDP, ACK, Window, and FIN scanning.
However, port scanning has many legitimate uses such as network inventory and the verification of the security of a network. Port scanners therefore represent an important tool for users and system administrators to verify the security policies of their computers and network.
Linux has a good range of port scanners that help administrators identify and rectify weaknesses in a system. To provide an insight into the software that is available, we have compiled a list of 5 of our favorite port scanners. Hopefully, there will be something of interest here for administrators or users that want to scan computers and services that are running on a network. We give our strongest recommendation to Nmap, an indispensable utility to gather information about remote computers.
Let’s explore the 5 port scanners at hand. For each application we have compiled its own portal page, a full description with an in-depth analysis of its features, screenshots, together with links to relevant resources.
Источник
How to do a Port Scan in Linux
TCP Scanning
TCP is stateful protocol because it maintains the state of connections. TCP connection involves a three-way handshaking of Server socket and client-side socket. While a server-socket is listening, the client sends a SYN and then Server responds back with SYN-ACK. Client then, sends ACK to complete the handshake for the connection
To scan for a TCP open port, a scanner sends a SYN packet to the server. If SYN-ACK is sent back, then the port is open. And if server doesn’t complete the handshake and responds with an RST then the port is closed.
UDP Scanning
UDP on the other hand, is a stateless protocol and doesn’t maintain the state of connection. It also doesn’t involve three-way handshake.
To scan for a UDP port, a UDP scanner sends a UDP packet to the port. If that port is closed, an ICMP packet is generated and sent back to the origin. If this doesn’t happen, that means port is open.
UDP port scanning is often unreliable because ICMP packets are dropped by firewalls, generating false positives for port scanners.
Port Scanners
Now that we’ve looked at how port scanning works, we can move forward to different port scanners and their functionality.
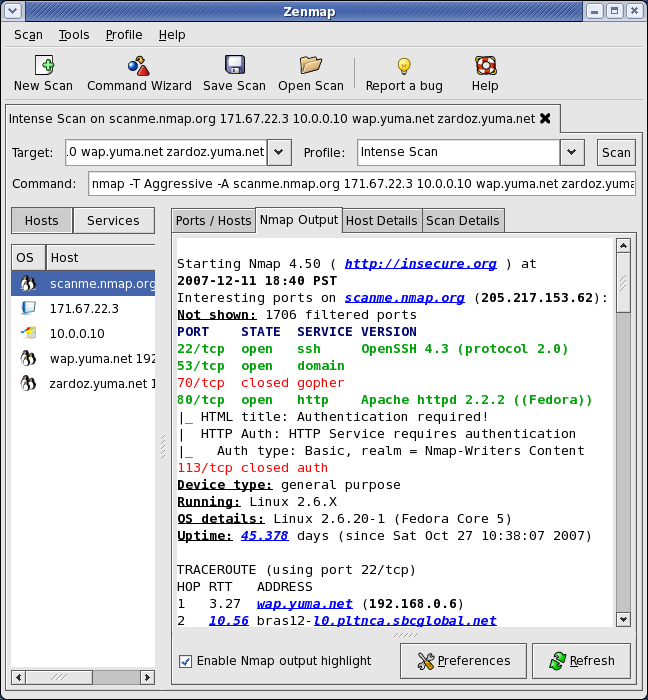
Nmap is the most versatile and comprehensive port scanner available till now. It can do everything from port scanning to fingerprinting Operating systems and vulnerability scanning. Nmap has both CLI and GUI interfaces, the GUI is called Zenmap. It has a lot of varying options to do quick and effective scans. Here’s how to install Nmap in Linux.
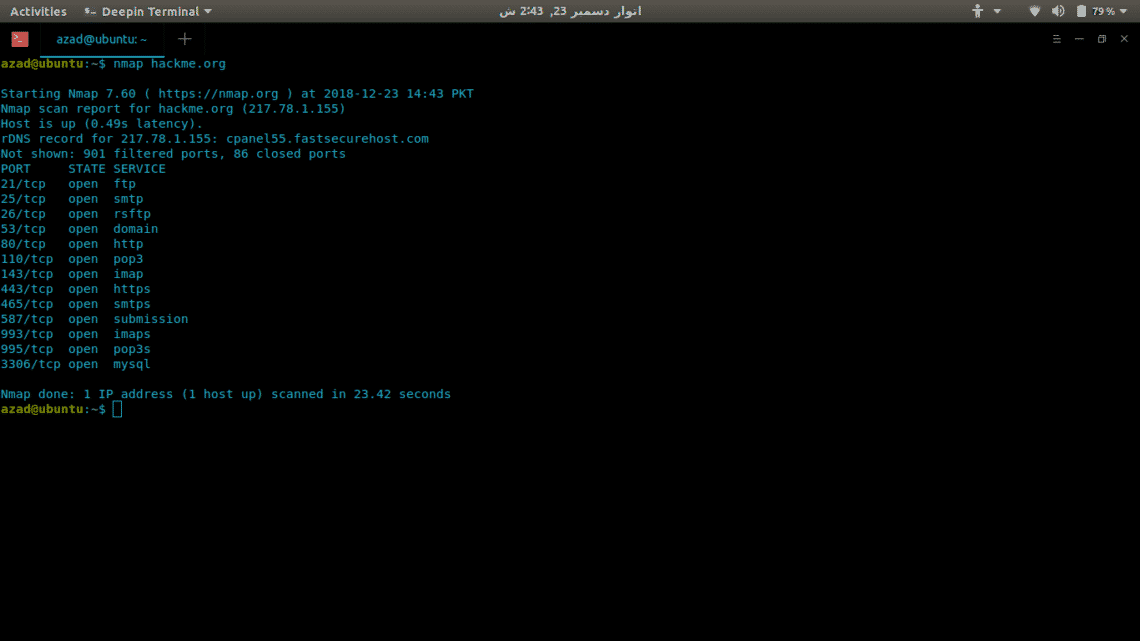
Now we’ll use Nmap to scan a server (hackme.org) for open ports and to list services available on those ports, its really easy. Just type nmap and the server address.
To scan for UDP ports, include -sU option with sudo because it requires root privileges.
There are a lot of other options available in Nmap such as:
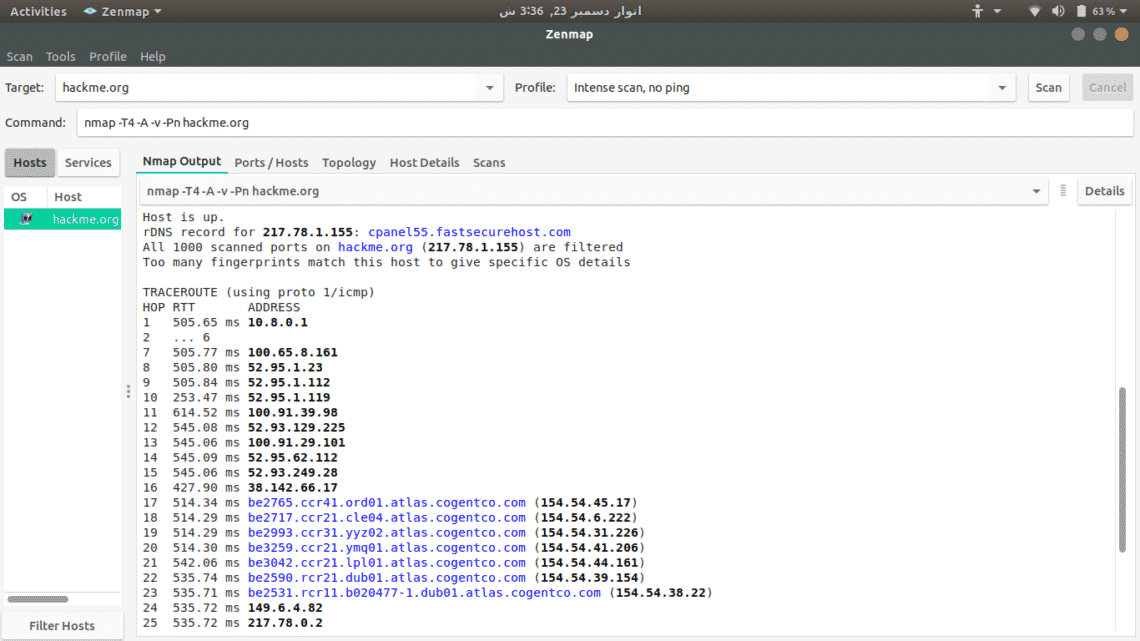
Zenmap
Zenmap is a GUI interface of Nmap for click-kiddies so that you won’t have to remember its commands. To install it, type
To scan a server, just type its address and select from available scan options.
Netcat
Netcat is a raw TCP and UDP port writer which can also be used as a port scanner. It uses connect scan that’s why it is not so fast like Network Mapper. To install it, type
$ sudo apt install netcat-traditional -y
To check for an open port, write
$ nc -z -v hackme.org 80
. snip.
hackme.org [ 217.78.1.155 ] 80 ( http ) open
To scan for a range of ports, type
$ nc -z -nv 127.0.0.1 20 — 80
( UNKNOWN ) [ 127.0.0.1 ] 80 ( http ) open
( UNKNOWN ) [ 127.0.0.1 ] 22 ( ssh ) open
Unicornscan
Unicornscan is a comprehensive and fast port scanner, built for vulnerability researchers. Unlike Network Mapper, it uses its own User-land Distributed TCP/IP stack. It has a lot of features that Nmap doesn’t, some of them are given,
- Asynchronous stateless TCP scanning with all variations of TCP Flags.
- Asynchronous stateless TCP banner grabbing
- Asynchronous protocol specific UDP Scanning (sending enough of a signature to elicit a response).
- Active and Passive remote OS, application, and component identification by analyzing responses.
- PCAP file logging and filtering
- Relational database output
- Custom module support
- Customized data-set views
To install Unicornscan, type
$ sudo apt-get install unicornscan -y
To run a scan, write
$ sudo us 127.0.0.1
TCP open ftp [ 21 ] from 127.0.0.1 ttl 128
TCP open smtp [ 25 ] from 127.0.0.1 ttl 128
TCP open http [ 80 ] from 127.0.0.1 ttl 128
. snip.
Conclusion
Ports scanners come in handy whether you are a DevOp, Gamer or a Hacker. There is no real comparison between these scanners, none of them is perfect, each of them has its benefits and drawbacks. It completely depends upon your requirements and how you use them.
About the author
Usama Azad
A security enthusiast who loves Terminal and Open Source. My area of expertise is Python, Linux (Debian), Bash, Penetration testing, and Firewalls. I’m born and raised in Wazirabad, Pakistan and currently doing Undergraduation from National University of Science and Technology (NUST). On Twitter i go by @UsamaAzad14
Источник