- Использование встроенного SSH клиента в Windows 10
- Установка клиента OpenSSH в Windows 10
- Как использовать SSH клиенте в Windows 10?
- SCP: копирование файлов из/в Windows через SSH
- Command Line SCP for Windows
- Related Posts
- 3 Responses to Command Line SCP for Windows
- Command-line Options
- Parameters
- Session
- Logging
- Console/scripting mode
- Operations
- Configuration
- Mass-modification of sites
- Private key conversion and modification
- Auxiliary
- Syntax
- Executables
Использование встроенного SSH клиента в Windows 10
В Windows 10 и Windows Server 2019 появился встроенный SSH клиент, который вы можете использовать для подключения к *Nix серверам, ESXi хостам и другим устройствам по защищенному протоколу, вместо Putty, MTPuTTY или других сторонних SSH клиентов. Встроенный SSH клиент Windows основан на порте OpenSSH и предустановлен в ОС, начиная с Windows 10 1809.
Установка клиента OpenSSH в Windows 10
Клиент OpenSSH входит в состав Features on Demand Windows 10 (как и RSAT). Клиент SSH установлен по умолчанию в Windows Server 2019 и Windows 10 1809 и более новых билдах.
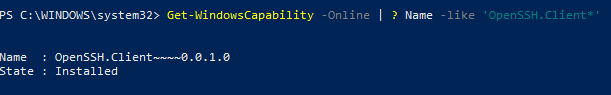
Проверьте, что SSH клиент установлен:
Get-WindowsCapability -Online | ? Name -like ‘OpenSSH.Client*’
В нашем примере клиент OpenSSH установлен (статус: State: Installed).
Если SSH клиент отсутствует (State: Not Present), его можно установить:
- С помощью команды PowerShell: Add-WindowsCapability -Online -Name OpenSSH.Client*
- С помощью DISM: dism /Online /Add-Capability /CapabilityName:OpenSSH.Client
0.0.1.0
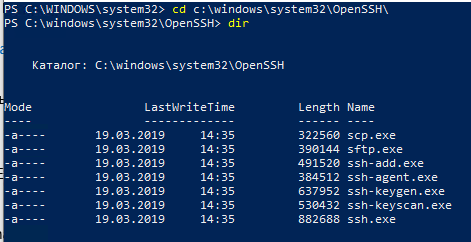
]Бинарные файлы OpenSSH находятся в каталоге c:\windows\system32\OpenSSH\.
- ssh.exe – это исполняемый файл клиента SSH;
- scp.exe – утилита для копирования файлов в SSH сессии;
- ssh-keygen.exe – утилита для генерации ключей аутентификации;
- ssh-agent.exe – используется для управления ключами;
- ssh-add.exe – добавление ключа в базу ssh-агента.
Как использовать SSH клиенте в Windows 10?
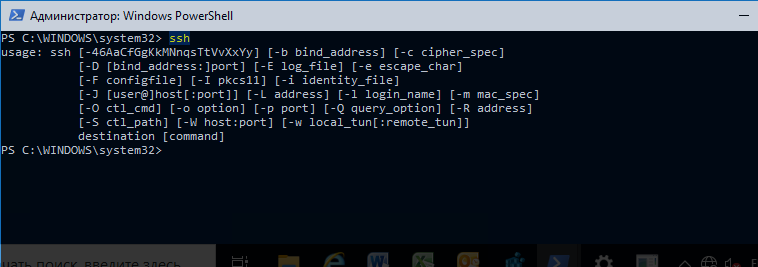
Чтобы запустить SSH клиент, запустите командную строку PowerShell или cmd.exe . Выведите доступные параметры и синтаксис утилиты ssh.exe, набрав команду:
ssh
usage: ssh [-46AaCfGgKkMNnqsTtVvXxYy] [-b bind_address] [-c cipher_spec]
[-D [bind_address:]port] [-E log_file] [-e escape_char]
[-F configfile] [-I pkcs11] [-i identity_file]
[-J [user@]host[:port]] [-L address] [-l login_name] [-m mac_spec]
[-O ctl_cmd] [-o option] [-p port] [-Q query_option] [-R address]
[-S ctl_path] [-W host:port] [-w local_tun[:remote_tun]]
destination [command]
Для подключения к удаленному серверу по SSH используется команда:
Если SSH сервер запущен на нестандартном порту, отличном от TCP/22, можно указать номер порта:
ssh username@host -p port
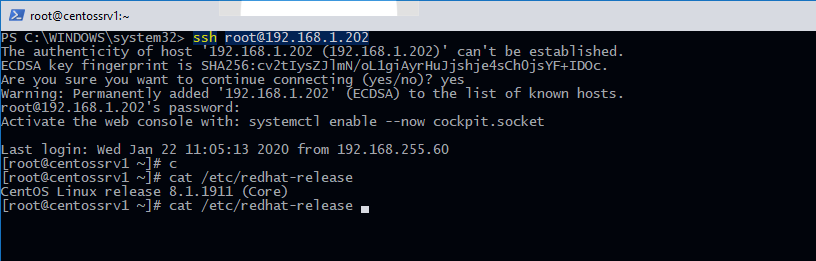
Например, чтобы подключиться к Linux хосту с IP адресом 192.168.1.202 под root, выполните:
При первом подключении появится запрос на добавление ключа хоста в доверенные, наберите yes -> Enter (при этом отпечаток ключа хоста добавляется в файл C:\Users\username\.ssh\known_hosts).
Затем появится запрос пароля указанной учетной записи, укажите пароль root, после чего должна открытся консоль удаленного Linux сервера (в моем примере на удаленном сервере установлен CentOS 8).
Если вы используете SSH аутентификацию по RSA ключам (см. пример с настройкой SSH аутентификации по ключам в Windows), вы можете указать путь к файлу с закрытым ключом в клиенте SSH так:
ssh root@192.168.1.92 -i «C:\Users\username\.ssh\id_rsa»
Также вы можете добавить ваш закрытый ключ в SSH-Agent. Сначала нужно включить службу ssh-agent и настроить ее автозапуск:
set-service ssh-agent StartupType ‘Automatic’
Start-Service ssh-agent
Добавим ваш закрытый ключ в базу ssh-agent:
Теперь вы можете подключиться к серверу по SSH без указания пути к RSA ключу, он будет использоваться автоматически. Пароль для подключения не запрашивается (если только вы не защитили ваш RSA ключ отдельным паролем):
Еще несколько полезных аргументов SSH:
- -C – сжимать трафик между клиентом и сервером (полезно на медленных и нестабильных подключениях);
- -v – вывод подробной информации обо всех действия клиента ssh;
- -R / -L – можно использовать для проброса портов через SSH туннель.
SCP: копирование файлов из/в Windows через SSH
С помощью утилиты scp.exe, которая входит в состав пакета клиента SSH, вы можете скопировать файл с вашего компьютера на SSH сервер:
scp.exe «E:\ISO\CentOS-8.1.1911-x86_64.iso» root@192.168.1.202:/home
Можно рекурсивно скопировать все содержимое каталога:
scp -r E:\ISO\ root@192.168.1.202:/home
И наоборот, вы можете скопировать файл с удаленного сервера на ваш компьютер:
scp.exe root@192.168.1.202:/home/CentOS-8.1.1911-x86_64.iso e:\tmp
Итак, теперь вы можете прямо из Windows 10 подключаться к SSH серверам, копировать файлы с помощью scp без установки сторонних приложений и утилит.
Command Line SCP for Windows
I do not use FTP, and you shouldn’t use it either. Sending your password and files over the tubes in plaintext form might have been ok in the 80’s but nowadays it’s just asking for trouble. I use scp for all my file transfer operations.
Now, as every self respecting geek I have cygwin installed on every windows box I use. But sometimes going through cygwin is an overkill. For example if I simply want to process and upload 1 small file to a remote machine I really shouldn’t have to install cygwin environment just to get access to command line scp version. I should be able to do this from an ordinary batch script.
This is where PuTTY comes into play. But wait, you say, PuTTY is a graphical SSH client for windows. What does it have to do with SCP? To that, I answer: “Very good question, voice in my head. Let me explain…”
If you go to to the official PuTTY download page and scroll down you will see a link to pscp.exe. What is that? It is exactly what I’m talking about here. A command line scp client for windows.
Just download it, rename it to scp.exe, stick it somewhere in your path and you are ready to go. It works almost the same like the real thing with few little exceptions. But it is great tool for automated upload scripts.
scp, windows, secure copy, ftp, putty, scp clients[/tags]
Related Posts
3 Responses to Command Line SCP for Windows
Some of my customers want to transfer files through a gui, so I support WinSCP (http://www.winscp.net/). It will use the sftp or scp method behind the scenes. Best of all, it also will use pageant for the ssh-agent! WinSCP is the missing piece from PuTTY!
Yeah, winscp is a great tool. In fact there are many GUI applications that will do ssh, scp or both on windows. I just needed something that can be silently called from a batch file without any need for user interaction (eg. as part of a login script).
Thanks for this – I didn’t know you could just use that small putty executable there for this – and I’ve always wanted scp on my Windows machines. So this, . this was GREAT! 🙂
Command-line Options
Parameters
Parameters for winscp.exe executable:
Session
The first syntax opens the site. To open site, stored in folder, use path syntax “folder/site”. You can also open workspace or all sites in site folder.
The second creates the session specified by session URL and optionally by initial remote path. If the remote path is not ended by slash ( / ), it is treated as path to file (or even directory) that should be downloaded.
The parameter /sessionname specifies a custom name of the session to be used instead of the automatically generated name in a format username@hostname or to override the name of the saved site.
If there’s already idle WinSCP instance running, the session(s) opens in the existing instance. To force session open in new instance of WinSCP, use /newinstance parameter.
The parameter /privatekey specifies a local path to an SSH private key file. If the key file is encrypted, use the /passphrase to specify its passphrase.
You can use the parameters /username and /password as an alternative way to specify the credentials. The credentials are normally part of the session URL. Using these switches has the advantage of not needing to URL-encode special characters. This feature is available only in the latest beta release.
The parameter /clientcert specifies a local path to FTPS or WebDAVS TLS/SSL client certificate. If the certificate is encrypted, use the /passphrase to specify its passphrase.
When a FTPS or WebDAVS server TLS/SSL certificate is not trusted (typically a self-signed certificate), use the parameter /certificate to specify the fingerprint of the untrusted certificate. It makes WinSCP trust the certificate. Several alternative fingerprints can be separated by a semicolon.
The parameter /passive enables a passive ( =on ) or an active ( =off ) transfer mode (FTP protocol only).
The parameters /implicit , and /explicit enable respective method of invoking FTPS.
The parameter /timeout specifies server response timeout.
The parameter /rawsettings allows configuring any site settings using raw format as in an INI file. E.g. to enable an SSH compression and an agent forwarding, use /rawsettings Compression=1 AgentFwd=1 . The parameter must come after the session URL (if any).
When using scripting, use the open command (and its switches) instead.
Logging
With /log parameter you may turn on session logging to file specified by local path.
Use parameter /loglevel to change logging level. The value can be in range -1 … 2 (for Reduced, Normal, Debug 1 and Debug 2 logging levels respectively). Append additional * to enable password logging (e.g. /loglevel=2* ).1
Use parameter /logsize to configure log file size limit and log file rotation. Specify maximum size in bytes, optionally with K , M or G units. Optionally you can limit number of archived log files using count* prefix. For example /logsize=5*10M will limit log file size to 10 MB and will allow up to 5 archived logs.
With /xmllog parameter you may turn on XML logging to file specified by local path.2 In either path you can use the same patterns as in the logging preferences.
Use parameter /xmlgroups along with /xmllog , to group all XML log elements belonging to the same command under parent group element.
Console/scripting mode
Parameter /console executes WinSCP in console (scripting) mode. Note that when using winscp.com , the console mode is implicit, so using /console parameter is redundant.
To run batch script either pass script file using /script parameter or specify the commands directly on command line using /command . In the latter case each following parameter is treated as single command. See syntax section and examples below for details how to deal with spaces and double-quotes.
If both /script and /command parameters are used, commands from script file are executed first. When the last command is not exit , regular non-batch mode follows.
Use parameter /parameter to specify list of arguments to be passed to script. It is recommended to escape the arguments with // switch.
With winscp.exe , if /console parameter is not used along with /script or /command , the script/command is executed without visual feedback (window).
Use the parameter /stdout to enable streaming files to the standard output. When the parameter is used, the get command will stream the downloaded file(s) to the standard output, when — is used as a download target. By default (or with the binary flag), the files are streamed unmodified. With the chunked flag, the files are individually encoded using Chunked transfer encoding, what allows separating contents of multiple streamed files. When the parameter is used, all console output that would normally be printed to the standard output is redirected to the error output. This feature is available only in the latest beta release.
Use the parameter /stdin to enable streaming files from the standard input. When the parameter is used, the put command will stream the standard input to the remote server, when — is used as an upload source. Implies /nointeractiveinput . This feature is available only in the latest beta release.
Use parameter /nointeractiveinput , when feeding commands to winscp.com using standard input, to make sure prompts for anything other than commands (such as password prompts) are cancelled. Also prevents error message popping up when fatal error occurs while starting WinSCP. When combined with /xmllog the fatal error is recorded in the XML log.
Operations
The following parameters can be used to create a shortcut that initiates operation in GUI mode. They are not intended for automation, for that see scripting.
Use /edit to open a remote file in WinSCP internal editor.
Use /browse to select the specified file in (both) file panel(s). The switch can also be used together with a file URL for the same effect, overriding the default download action.
With /synchronize or /keepuptodate parameter WinSCP performs Synchronize or Keep remote directory up to date commands respectively on the specified session and directories. A dialog to set options is displayed first.
With /upload parameter WinSCP uploads specified files to initial remote directory of session.3 A dialog to set options is displayed first.
Use /defaults parameter along with /upload , /synchronize or /keepuptodate to skip the settings dialog and start the operation straight away with default settings. Alternatively you can specify a number of seconds, to actually show the settings dialogs, but have them automatically submit after the specified time elapses.
Use the /refresh parameter to reload remote panel of all running instances of WinSCP. If a session is specified on command-line, only instances that have that session as active are refreshed. If a path is specified after the /refresh , only that directory is refreshed.
It is recommended to escape the arguments with // switch.
Configuration
With /ini parameter you may specify local path to configuration INI file. It effectively disables using registry as configuration storage. If the file does not exist, default configuration will be used and the file will be created.
Use nul instead of path to force WinSCP start with its default configuration and not save the configuration on exit.
With /rawconfig parameter you can set any configuration settings using raw format as in an INI file. E.g. to configure an external IP address use /rawconfig Interface\ExternalIpAddress=198.51.100.10 . The parameter must come after a session URL (if any). The configuration set this way is preserved.
With /rawtransfersettings you can set any transfer settings using raw format as in an INI file. E.g. to enable preserving of directory timestamps, use /rawtransfersettings PreserveTimeDirs=1 . The configuration set this way is preserved. In scripting, it is better to use -rawtransfersettings switch of individual scripting commands, like get , put , etc.
Mass-modification of sites
Use /batchsettings to mass-modify stored sites. The first argument is a mask to select sites to modify. Use a syntax of basic file masks. You can also use path mask to select sites based on their folders. The other arguments define new values for site settings. Use the same syntax as for /rawsettings .
For example to configure a proxy for all sites in a “clients” folder, use:
Private key conversion and modification
Use the /keygen switch to convert private keys from other formats to a PuTTY .ppk format or to change their passphrase or comment.
A parameter after the /keygen switch specifies a path to an input private key file. The input key can be in OpenSSH or ssh.com format (when converting the key to the PuTTY format) or in the PuTTY format (when changing a key passphrase or comment).
When converting the key from other format, you need to specify an output key path using the /output switch. When modifying a PuTTY key, the existing file is overwritten, if /output is not specified.
Use /changepassphrase switch to change the key passphrase.
Use /comment switch to change the key comment.
For example, to convert key mykey.pem from OpenSSH format to mykey.ppk in PuTTY format and set its comment:
To change the passphrase of existing mykey.ppk :
For a compatibility with *nix puttygen , the -o , -P and -C switches are understood as aliases to /output , /changepassphrase and /comment respectively. So, for features supported by WinSCP, you can use the same arguments as for puttygen , just prefixed with /keygen :
Auxiliary
When run with /update parameter, WinSCP only checks for its updates.
The parameter /info lists the supported SSH and TLS/SSL algorithms.
Parameter /help shows usage (overview similar to this).
Syntax
Command-line parameters that include space(s) must be surrounded by double-quotes:
To use the double-quote as a literal, use two double-quotes sequentially. For example, the /command expects that each script command is surrounded by double quotes, so that it is passed as a single command-line argument. In addition, any script command argument that includes spaces is expected to be surrounded by double-quotes within the command (see doubling double-quotes):
When executing such command from PowerShell, you additionally have to escape the doubled inner double-quotes with ` (backtick) to prevent PowerShell from interpreting them on its own:4
To debug the quoting, enable session logging on level Debug 1 ( /loglevel=1 ). The log will show how WinSCP understands your command-line.
An argument that begins with a slash is considered a switch. To pass a parameter that itself starts with the slash in its syntax (i.e. a remote path like /root ), use the special switch // (two slashes) before the argument. The switch // denotes that all following arguments are not switches. Example:
Executables
Learn about two WinSCP executables, winscp.exe and winscp.com .
If you are going to run WinSCP from command-line often, you may wish to add WinSCP installation directory to search path.