- Find Specific Files in Windows Explorer with These Search Tips
- Locating Images using Parameters
- www.makeuseof.com
- Follow MUO
- 7 Search Tips to Find What You’re Looking for in Windows 10
- 1. Search Using First Letters
- 2. Add Search to the Taskbar
- 3. Use Filters to Narrow Your Search
- 4. Quick Calculations
- 5. Customize Where Windows Searches
- 6. Search Within File Explorer
- 7. Use Third-party Applications
- Search and Conquer
- Subscribe To Our Newsletter
- One More Step…!
- Fix problems in Windows Search
- Check for updates
- Run the Search and Indexing troubleshooter
- Restart Windows Search or your device
- Reset Windows Search
- Windows 10, version 1809 and earlier
- Windows 10, version 1903 and later
- Help us improve Search in Windows 10
Find Specific Files in Windows Explorer with These Search Tips
Even if you can’t remember its name
Ever lost a file on your PC and just can’t track it down? With the search tips in this article, you’ll be able to find specific files in Windows file explorer, even if you can’t remember the exact name or location.
The more information you know about the file you are looking for the better. You’ll be able to use search parameters like file size, created date, file type, and more by using the tips listed below.
For reference, before we begin, all of the tips listed in this article will be making use of the search function found at the top right of Windows file Explorer.
Hopefully by the time you’ve read all of the tips in this article, you’ll have found a solution to track down your files.
Also, check out my other post on searching Windows using third-party tools or via the command line. Also, in order for all the searches below to work faster, you should have search indexing enabled in Windows.
Locating Images using Parameters
First let’s take a look at the options you have available for tracking down specific images. Below we have a number of tips exclusive for images on your PC.
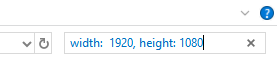
If you know the dimensions of the image, you can type in width: x, height: x. Simply replace ‘x’ with the exact dimensions.
If you don’t know the exact dimensions, but you know it’s within a certain limit, you can instead use the following search parameters:
- Width: >x for files over a specific width
- Width: x for files over a specific height
- Height: ’ to look for files made before or after specific dates, respectively. An example has been provided below.
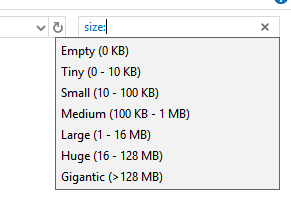
If you know the rough file size, you can use the ‘size:’ command to filter out results. You can use the following quick commands for certain sizes:
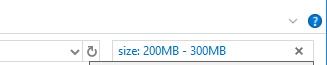
Using these commands is great for smaller files, but for files that are larger than 128MB, you should use a search range. For example, if you know that a file is between 200MB and 300MB, you can use the command: ‘size: 500MB – 800MB’. This will only show the files that are between that range.
Thanks for taking a look at our advanced Windows Explorer file search tips. Remember that you can combine any combination of these search filters in a single search.
If, for example, you are looking for a .png file that is over 1000 pixels wide and you know it was created before the 20th of February 2018, you can use this command: ‘type: .png, width: >1000, date:
Ollie stumbled upon writing online whilst participating in a mobile network forum back in 2011. Since then, he has developed an incredible passion for writing about all sorts of tech from smartphones, PC hardware, software, and everything in between. Read Ollie’s Full Bio
www.makeuseof.com
Follow MUO
7 Search Tips to Find What You’re Looking for in Windows 10
Are you using Windows 10 search to its full extent? We will show you how to customize where Windows searches, handy search parameters, and other shortcuts. Our search tips will turn you into a search wizard.
The search within Windows 10 is incredibly powerful, but you might not be using it to its full extent. We’re here to show you all the tips and tricks surrounding search, meaning you can hunt down what you need much more efficiently.
Whether it’s adjusting where Windows scans when you search, using handy parameters to limit your search, or just typing as few letters as possible, the advice herein will turn you into a searching wizard.
If you’ve got your own search tip to share, please be sure to let us know in the comments section below.
1. Search Using First Letters
If you’re searching for a program or file with a long name, you probably already know you don’t need to type it in its entirety. Once a match has been found, the result will be displayed. But you can take this one step further to reduce your keystrokes to the bare minimum.
To find something that is made up of multiple words, just type the first letter of each word and put a space between each letter. For example, Google Chrome can be found by typing g c, Windows Media Player can be found with w m p, and so on.
2. Add Search to the Taskbar
You can open the Start menu and type straight away to begin searching. However, you can also add a dedicated search icon or bar to your Taskbar. To do so, right click an empty space on the Taskbar, hover on Search and then select Show search icon or Show search box.
If you don’t see the ability to add the search box, it means your Taskbar isn’t tall enough to support it. To rectify this, right click an empty Taskbar space again and select Properties. In the new window, untick Use small taskbar buttons and then click OK.
3. Use Filters to Narrow Your Search
When searching in the Start menu or search box, you can use filters to quickly narrow down to the type of file that you’re seeking. You have many different filtering options. All you need to do is input the filter term, followed by a colon, directly before your search terms. The available filters are apps, settings, files, folders, photos, videos, music, and web.
For example, if you wanted to find a document about animals then you’d search files:animals. If you were more interested in websites on the topic then you’d search web:animals.
4. Quick Calculations
Sure, Windows has a built-in calculator, but did you know that you can use the search to perform some quick calculations? For this you’ll need to have searching the web enabled. Access the search, then go to Settings and turn Search online and include web results to On.
Now you can type calculations into the search bar and it’ll display the sum right there. Of course, it’s not suitable if you’re trying to do advanced mathematics, but it’s incredibly handy for speedy working out of simple calculations.
5. Customize Where Windows Searches
By default, Windows will have a number of locations that it will scan when you perform a search. If you want to include or exclude particular locations from search, that’s simple. First, do a system search for indexing options and select the relevant result. Here you will see all locations that are indexed, meaning those which are searched.
To change these, click Modify. You can then navigate through the folder trees and tick those locations you wish to search. For example, you may wish to include an external hard drive. Once done, click OK.
Back on the Indexing Options window, you can also include or exclude particular file types. For this, click Advanced and then switch to the File Types tab. Again, make your selections with a tick, then click OK.
Excluding large folder paths and limiting your file types may speed up the search function, but your mileage will depend on just how many items you’ve got indexed. Frankly, I’ve found Windows 10’s searching to be lightning fast.
6. Search Within File Explorer
You can also search from within File Explorer by using the search box that appears in the top right. You can navigate to This PC if you want to search your whole system, but you can search straight from whichever folder you like. Just input your search term and the results will display.
After searching, you’ll be able to make use of the Search tab on the ribbon. From here you can filter your results using the dropdowns like Date modified, Type, and Size. If you want to quickly filter in and out of indexed locations, use the Advanced options dropdown. You can use Save search to create a Smart Folder, which we cover in our guide to setting up Windows smart folders.
To filter your searches within the search box itself, you’ll need to use parameters. You can discover these in our Windows search tricks guide, but those most handy include type, modified, and size. Use these with a colon, followed by your search term. For example, type:music, modified:last year and size:large.
7. Use Third-party Applications
If Windows 10’s built-in search just isn’t cutting the mustard, you might want to explore third-party applications. Many of the countless alternatives are free. We’ve rounded up the best in the past, so check out our awesome alternatives to Windows search. Alternatively, see those search programs we recommend judged on speed.
If you’re after some instant recommendations, Everything is a good choice due to how simple and lightweight it is. If you need something a bit more advanced, like one that will search the contents of your files rather than just the metadata, then check out Agent Ransack. This program will look inside your files, find the search term, and tell you where it appears within the file.
Search and Conquer
It’d be remiss not to mention Cortana, the personal assistant within Windows 10. If you really want to limit how much you type to perform a search, you can ask Cortana to find stuff for you using your voice! Be sure to discover which apps support Cortana to get the ultimate use out of it.
Armed with all these tips, now you can go forth and conquer all your searches. Whether you adjust your indexing options, make use of parameters, or just use a third-party program, you’ll be able to find what you need in a bang.
What tips can you share to help us all perform better searches? Do you think Windows 10 is missing any vital search features?
It’s called Drawfest, and it hopes to celebrate the growth of anime-art-related content and bring artists together.
Joe was born with a keyboard in his hands and immediately started writing about technology. He has a BA (Hons) in Business and is now a full-time freelance writer who enjoys making tech simple for everyone.
Subscribe To Our Newsletter
Join our newsletter for tech tips, reviews, free ebooks, and exclusive deals!
One More Step…!
Please confirm your email address in the email we just sent you.
Fix problems in Windows Search
If Windows Search is unresponsive or the search results don’t appear as expected, try any of the following solutions in this article.
If you’re running Windows 10 May 2019 Update (version 1903) or later versions and Windows can detect a problem, we’ll run the Search troubleshooter automatically. This troubleshooter will reset Windows Search back to the default experience. View your troubleshooter history under Settings > Update & Security > Troubleshoot > View History. Follow the steps below if your issue is still not resolved.
Original product version: В Windows 10 — all editions
Original KB number: В 4520146
Check for updates
Windows 10 lets you choose when and how to get the latest updates to keep your device running smoothly and securely. To manage your options and see any available updates, select the Start button, and then go to Settings > Update & Security > Windows Update > Check for updates. Install any available updates, and then restart your computer if the updates require it.
For more information, see Update Windows 10.
Run the Search and Indexing troubleshooter
Your PC automatically indexes content to deliver faster search results. Learn more about Search indexing in Windows 10.
Use the Windows Search and Indexing troubleshooter to try to fix any problems that may arise. To use the troubleshooter, follow these steps:
- Select Start, then select Settings.
- In Windows Settings, select Update & Security >Troubleshoot. Under Find and fix other problems, select Search and Indexing.
- Run the troubleshooter, and select any problems that apply. Windows will try to detect and solve them.
You can also use a command prompt to open the troubleshooter. Press Windows logo key+R, enter cmd in the Open box, and then select OK. At the command prompt, run the following command:
Restart Windows Search or your device
End the SearchUI process to restart Windows Search by following these steps:
- Press Ctrl+Alt+Delete, and select Task Manager.
- In the Task Manager window, select the Details tab.
- In the Name column, right-click SearchUI.exe, and then select End task.
- When you’re prompted to end SearchUI.exe, select End process.
The Windows Search process will automatically restart the next time that you search.
If this solution doesn’t fix your problem, try restarting your device. Restarting will also install any pending updates.
You may want to bookmark this page before you restart.
Reset Windows Search
Try resetting Windows Search by using the method that’s appropriate for your version of Windows.
To determine which version of Windows your device is running, follow these steps:
Select Start > Settings > System > About.
Under Windows specifications, check which version of Windows your device is running.
Resetting Windows Search does not affect your files. However, it may temporarily affect the relevance of search results.
Windows 10, version 1809 and earlier
If the Windows 10 October 2018 Update or an earlier update is installed, reset Cortana to reset Windows Search by following these steps:
- Select Start, right-click Cortana, select More, and then select App settings.
- In the Cortana settings, select Reset.
Windows 10, version 1903 and later
If the Windows 10 May 2019 Update or a later update is installed, use Windows PowerShell to reset Windows Search by following these steps:
You must have administrator permissions to run this script.
Download the ResetWindowsSearchBox.ps1 script from the Reset Windows Search PowerShell script, and save the file to a local folder.
Right-click the file that you saved, and select Run with PowerShell.
If you’re asked the following question, select Yes.
Do you want to allow this app to make changes to your device?
The PowerShell script resets the Windows Search feature. When the word Done appears, close the PowerShell window.
If you receive the following error message:
Cannot be loaded because running scripts is disabled on this system
enter the following command on the command line of the PowerShell window, and then press Enter:
The current policy appears in the window. For example, you might see Restricted. We recommend that you note this value because you’ll have to use it later.
Enter the following command on the command line of the PowerShell window, and then press Enter:
You’ll receive a warning message that explains the security risks of an execution policy change. Press Y, and then press Enter to accept the change.
To learn more about PowerShell execution policies, see About Execution Policies.
After the policy change is completed, close the window, and then repeat steps 2-4. However, when the Done message appears this time, DON’T close the PowerShell window. Instead, press any key to continue.
Revert to your previous PowerShell execution policy setting. Enter the following command on the command line of the PowerShell window, press the Spacebar, enter the policy value that you noted in step 5, and then press Enter:
For example, if the policy that you noted in step 5 was Restricted, the command would resemble the following one:
You’ll receive a warning message that explains the security risks of an execution policy change. Press Y, and then press Enter to accept the change and revert to your previous policy setting.
Close the PowerShell window.
If your organization has disabled the ability to run scripts, contact your administrator for help.
Help us improve Search in Windows 10
If the previous suggestions don’t fix the problem, let us know by sending feedback in the Feedback Hub. Provide details, such as a description of the problem, screenshots, log files, and any other information that might be helpful. In the Feedback Hub, select the appropriate category and subcategory. In this case, submit your feedback in the Cortana and Search category.