- Отслеживание логов Linux в реальном времени
- Мониторинг лог-файлов командой tail
- Команда tailf
- tail -F. Если файл был переименован или удален
- Отслеживание нескольких лог-файлов одновременно
- Утилита multitail
- Linux Log Files Location And How Do I View Logs Files on Linux?
- How do I view log files on Linux?
- Common Linux log files names and usage
- Printing the Linux kernel ring buffer messages
- GUI tool to view log files on Linux
- A note about rsyslogd
- A note about systemd journal on modern Linux distros
- journalctl command examples
- See log by systemd unit or sevice
- Executable log
- Time ranges
- View log by user ID (UID) or PID
- Rverse output so that the newest entries are displayed first
- Show only Linux kernel messages
- Filter log files (grep like syntax)
- Summing up
Отслеживание логов Linux в реальном времени
При просмотре лог-файлов (файлов журналов) в Linux иногда бывает нужно мониторить новые записи в логах в реальном времени. То есть вы указываете, какой лог-файл (или файлы) вы хотите просматривать и в реальном времени отслеживаете новые записи в этом файле.
Мониторинг лог-файлов командой tail
Если выполнить команду tail ИмяФайла без каких-либо дополнительных аргументов, то будет выведено 10 последних строк файла, и команда завершит свою работу.
Для того, чтобы команда tail непрерывно выводила последние записи в файле, то есть, если в файле появились новые записи, то информация на экране обновлялась, используется опция -f :
tail -f ИмяЛогФайла
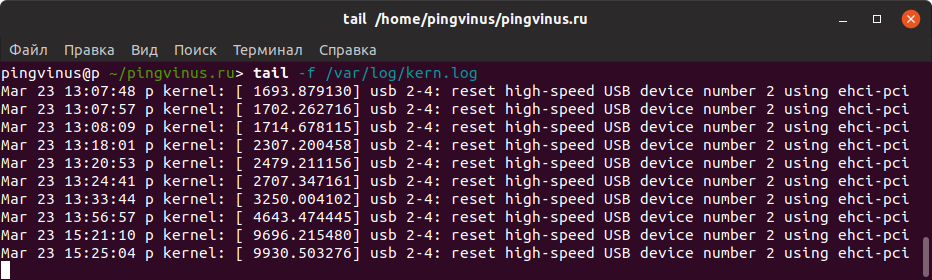
Выполним команду tail -f для вывода лог-файла /var/log/syslog
Так как используется опция -f , команда tail не завершает свою работу, а ожидает появления в лог-файле новых записей. Как только в лог-файл будут добавлены новые записи, они сразу же будут отображены в терминале.
Чтобы прервать выполнение команды, нажмите сочетание клавиш Ctrl+C
Команда tailf
Аналогом команды tail -f является команда tailf
Важным отличием команды tailf от tail -f является то, что tailf не обращается к файлу, когда он не изменяется. В следствии этого время доступа к файлу не обновляется и система не выполняет постоянный сброс файла на диск, когда файл не обновляется.
В описании команды tailf указывается на то, что ее удобно использовать для мониторинга файлов журналов на ноутбуках. Так как без надобности не происходит обращение к диску и сохраняется срок службы батареи.
tail -F. Если файл был переименован или удален
Обычно в Linux лог-файлы записываются не до бесконечности, иначе такой файл было бы очень неудобно в дальнейшем использовать. Вместо этого применяется так называемая ротация файлов. Когда лог-файл становится большим, то он либо удаляется, либо переименовывается (создается резервная копия файла), а дальнейшие сообщения начинают записываться в новый, пустой файл.
У команды tail есть две опции: -f и -F
- Если используется опция -f и происходит переименование, отслеживаемого файла, то команда tail продолжает отслеживать уже переименованный файл. Команда tail в данном случае привязывается к идентификатору (inode) файла.
- Если используется опция -F и происходит переименование, отслеживаемого файла, то команда tail определит это, и как только будет создан новый лог-файл (с тем именем, которое мы указали команде tail), команда tail начнет отслеживать этот новый файл.
Будем отслеживать лог-файл /var/log/apache2/error.log . Выполняем команду tail с опцией -F
Если система переместит (переименует) файл error.log в файл error.log.1 и создаст новый файл error.log , то наша команда tail продолжит отслеживать уже новый файл error.log
Если бы мы в этом примере использовали опцию -f , то команда tail продолжила бы отслеживать файл error.log.1 , который для нас уже неактуален при просмотре логов в реальном времени.
Отслеживание нескольких лог-файлов одновременно
Команда tail поддерживает отслеживание нескольких файлов одновременно. Для этого необходимо указать имена файлов через пробел.
Как только какой-либо из файлов меняется, на экран выводится имя этого файла и новые записи в нем.
Утилита multitail
Для одновременного отслеживания нескольких лог-файлов существует очень удобная утилита multitail
Она не просто выводит данные, а создает для каждого файла свое окно (область) и выводит данные в этом окне. С ее помощью очень удобно отслеживать сразу множество лог файлов и видеть их в одном окне терминала.
Утилиту multitail можно установить из штатных репозиториев вашего дистрибутива. Для установки выполните команду (выберите соответствующую команду для вашего дистрибутива):
Источник
Linux Log Files Location And How Do I View Logs Files on Linux?
I am a new Linux user. I would like to know where are the log files located under Debian/Ubuntu or CentOS/RHEL/Fedora Linux server? How do I open or view log files on Linux operating systems?
Almost all logfiles are located under /var/log directory and its sub-directories on Linux. You can change to this directory using the cd command. Of course, you need to be the root user to access log files on Linux or Unix-like operating systems. You can use the following commands to see the log files which are in text format:
| Tutorial details | |
|---|---|
| Difficulty level | Easy |
| Root privileges | Yes |
| Requirements | Linux terminal and GUI |
| Est. reading time | 4 minutes |
- less command
- more command
- cat command
- grep command
- tail command
- zcat command
- zgrep command
- zmore command
- dmesg command
- journalctl command
How do I view log files on Linux?
Open the Terminal or login as root user using ssh command. Go to /var/log directory using the following cd command:
# cd /var/log
To list files use the following ls command:
# ls
Sample outputs from RHEL 6.x server:
To view a common log file called /var/log/messages use any one of the following command:
# less /var/log/messages
# more -f /var/log/messages
# cat /var/log/messages
# tail -f /var/log/messages
# grep -i error /var/log/messages
Here is what I see:
Common Linux log files names and usage
- /var/log/messages : General message and system related stuff
- /var/log/auth.log : Authenication logs
- /var/log/kern.log : Kernel logs
- /var/log/cron.log : Crond logs (cron job)
- /var/log/maillog : Mail server logs
- /var/log/qmail/ : Qmail log directory (more files inside this directory)
- /var/log/httpd/ : Apache access and error logs directory
- /var/log/lighttpd/ : Lighttpd access and error logs directory
- /var/log/nginx/ : Nginx access and error logs directory
- /var/log/apt/ : Apt/apt-get command history and logs directory
- /var/log/boot.log : System boot log
- /var/log/mysqld.log : MySQL database server log file
- /var/log/secure or /var/log/auth.log : Authentication log
- /var/log/utmp or /var/log/wtmp : Login records file
- /var/log/yum.log or /var/log/dnf.log : Yum/Dnf command log file.
Printing the Linux kernel ring buffer messages
We use the dmesg command to examine or control the kernel ring buffer. The default action is to display all messages from the kernel ring buffer. For example:
sudo dmesg
sudo dmesg | grep ‘error’
sudo dmesg | grep -i -E ‘error|warn|failed’
sudo dmesg | more
Sample outputs:
GUI tool to view log files on Linux
System Log Viewer is a graphical, menu-driven viewer that you can use to view and monitor your system logs. This tool is only useful on your Linux powered laptop or desktop system. Most server do not have X Window system installed. You can start System Log Viewer in the following ways:
Click on System menu > Choose Administration > System Log:
Fig.01 Gnome log file viewer
Modern log viewer from Ubuntu desktop:
A note about rsyslogd
All of the above logs are generated using rsyslogd service. It is a system utility providing support for message logging. Support of both internet and unix domain sockets enables this utility to support both local and remote logging. You can view its config file by tying the following command:
# vi /etc/rsyslog.conf
# ls /etc/rsyslog.d/
In short /var/log is the location where you should find all Linux logs file. However, some applications such as httpd have a directory within /var/log/ for their own log files. You can rotate log file using logrotate software and monitor logs files using logwatch software.
A note about systemd journal on modern Linux distros
systemd-journald is a system service on modern Linux distro that comes with systemd. It collects and stores logging data. In addition, it creates and maintains structured, indexed journals based on logging information received from various sources such as Linux Kernel log messages via kmsg. Therefore, we need to use the journalctl command to query the contents of the systemd-journald.
journalctl command examples
Without any arguments, all collected logs are shown unfiltered as follows:
journalctl
View all boot messages:
journalctl -b
Want to see kernel logs from previous boot? Try:
journalctl -k -b -1
See log by systemd unit or sevice
Display a live log display from a system service apache.service or nginx.service:
journalctl -f -u apache
journalctl -f -u nginx
The -u switch can be used multiple time to save typing at the CLI. For example:
journalctl -f -u apache.service -u php-cgi.service -u mysqld.service
We can follow log in real time. Like tail -f /var/log/nginx/foo.log :
journalctl -u mysqld.service -f
journalctl -u nginx.service -f
journalctl -f
Only display last 10 log entries:
journalctl -n 10 -u nginx.service
Executable log
See all logs generated by the D-Bus or app executable
journalctl /usr/bin/dbus-daemon
journalctl /usr/local/bin/app
Time ranges
We can see logs created using time ranges. For instnace:
journalctl —since «30 min ago»
journalctl —since «1 hour ago»
journalctl —since «1 days ago»
# The date and time format is YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS
# So we can do
journalctl —since «2020-06-06»
journalctl —since «2020-06-06 10:42:00»
journalctl —since «2020-06-04 10:42:00» —until «2020-06-07 10:42:00»
View log by user ID (UID) or PID
See log for user ID # 300
sudo journalctl _UID=300
View log for PID # 4242
sudo journalctl _PID=4242
- No ads and tracking
- In-depth guides for developers and sysadmins at Opensourceflare✨
- Join my Patreon to support independent content creators and start reading latest guides:
- How to set up Redis sentinel cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- How To Set Up SSH Keys With YubiKey as two-factor authentication (U2F/FIDO2)
- How to set up Mariadb Galera cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- A podman tutorial for beginners – part I (run Linux containers without Docker and in daemonless mode)
- How to protect Linux against rogue USB devices using USBGuard
Join Patreon ➔
Rverse output so that the newest entries are displayed first
Try:
journalctl -r
journalctl -r -u apache.service
Show only Linux kernel messages
journalctl -k
journalctl —-dmesg
Filter log files (grep like syntax)
We can filter output to entries where the MESSAGE= field matches the specified regular expression. PERL-compatible regular expressions are used. For instance:
journalctl -k -g PATTERN
journalctl -u mysqld.service -g PATTERN
journalctl -u nginx.service -g ‘error’
journalctl -k -g failed
Click to enlarge
Summing up
You learned about various log files and showed them on Linux using CLI and GUI options. See man pages for more info using the help command or info command/man command:
man cat
man grep
man less
man more
man journalctl
🐧 Get the latest tutorials on Linux, Open Source & DevOps via
| Category | List of Unix and Linux commands |
|---|---|
| Documentation | help • mandb • man • pinfo |
| Disk space analyzers | df • duf • ncdu • pydf |
| File Management | cat • cp • less • mkdir • more • tree |
| Firewall | Alpine Awall • CentOS 8 • OpenSUSE • RHEL 8 • Ubuntu 16.04 • Ubuntu 18.04 • Ubuntu 20.04 |
| Linux Desktop Apps | Skype • Spotify • VLC 3 |
| Modern utilities | bat • exa |
| Network Utilities | NetHogs • dig • host • ip • nmap |
| OpenVPN | CentOS 7 • CentOS 8 • Debian 10 • Debian 8/9 • Ubuntu 18.04 • Ubuntu 20.04 |
| Package Manager | apk • apt |
| Processes Management | bg • chroot • cron • disown • fg • glances • gtop • jobs • killall • kill • pidof • pstree • pwdx • time • vtop |
| Searching | ag • grep • whereis • which |
| Shell builtins | compgen • echo • printf |
| Text processing | cut • rev |
| User Information | groups • id • lastcomm • last • lid/libuser-lid • logname • members • users • whoami • who • w |
| WireGuard VPN | Alpine • CentOS 8 • Debian 10 • Firewall • Ubuntu 20.04 |
Comments on this entry are closed.
Very informative. Helped me 🙂 thumbs up
Very nice, thanks a lot
Can u help me how to redirect the /var/log/messages to email.
DNS server if any clients query log will stores /var/log/messages files i need to send those lof files in ip wise daily or weekly.
how shell i do it.
it is possible using mutt coomand and mail -s command just write a script and put in crontab it is working
I had an automatic reboot system in my server linux and I don´t find any evidence about the cause that could produce that.
Can you explain me where I have to looking for logs of error that guide me to find automatic reboot cause?.
Regards,
Gonzalo R.
your permissions. you can set it so a remote user can shut down the server. change permissions on shutdown or search your distributions forum and post if you do not find an answer in there or in google.
some distributions are setup that way by default, which is kind of annoying. Means if anyone logs in remotely in any way, they can turn you off or reboot you. NOT FUNNY. I hope you have a firewall and have it enabled.
where can i find the AT command logs. how to find out when the last time AT command run.
Use atq for last time at commands run
and check the logs
by using grep error /var/log/messages
and also check the by using atd
Thank you very much.
Chandra You can do this by opening a terminal and typing #cd /var/log/ and may view the files in the directory by typing #ls . You may view the log by typing #vi /var/log/messages .
I can see a lot of the following error in my system and I cannot understand what it means, can yu shed somelight on it
Feb 22 04:40:00 msuic3 msu6_6: ciMonitor 3 of 131 registered tasks Failed!
It’s a fruitful information…
Thanks a lot vivek
I want classify logs and store it in a database. Into what categories can/should I classify them.
Thank you,
Sparrow
Hi there Linux users, I have bean trying to in stall Debian Lenny beta 2-i386 in a raid 0 con fig, on my p/c
the hard ware is all set up for raid 0, I am having difficulty with the configuration of the partitons, boot sector, file type, the “type of file allocation table” to install. I have bean trying to track down the
var/log, but I cant find that, the location was “http://192.2.2/var/log/partman_choose_partitiion_o.png
I have bean using pure dyne live CD to help me ,but I still was not able to look at the “/var/logs,
invariable I think I need expert help. thank you in advance
this is a reply to my last message , I have given up on trying to install Linux on a virtual raid 0 system, so I ended up installing win 98 se with a new web browser OPERA and it runs like a hot dam, by far this is my most complex P/C to date, in one respect by the things it can do, the open source community has truly bean a liberator for me , not to mention Debian lenny -57-i386 1.iso I know this is old hat by computer standards , I was having problems trying to install NDISWRAPPER on an i386 architecture , and it did not help when my PC was hacked and I was effectively locked out of my p/c, no thanks to VLUG in Victoria but thats a “Hole” different story, I ended up installing ndiswrapper with a new O/S on a network complete with a bunch of other computers , I am currently working on a new black project , but that is top secret .
I have a basic account in linux of my intitue. How can i know all the login sessions done in my account ,their timing etc… an i also know any ftp or ssh done in my account.
it will tell you when, what ip address, time in and out , and for how long
Thanks. I have a question: does Linux record the software installation process? For example I use apt to install some software in Debian but I would like to know where it puts the files. Can it be found in log file?
i have smb server and i want to know the logs of each and every folder those who access please help its very urgent…..
pls go to /var/log/messages file there you will find your all logs of smb server
thanks, it helped me
how can we check online redo log file is full or empty?
Which command use to routed logs in linux
thanks, it helped me a lot. To know about log files this is very helpful…
Someone desintalled an application on my Linux server ( Control_M) – What log file should I search for that – and find out who is doing it?
Hi,
I am new to Linux, Can u pls any one of u tell me how to copy files using “rcp” from the remote location and what r da min requirements to my system.
[1] What log files in /var/logs can we safely delete to free up hard-disk space?
[2] System reports “Disk-Controller Failure” then which log files in /var/logs should we check?
or some other log files?
hi, i am having webserver in linux and mail server in windows.
in our websites we have contuct us page from that we are not able to get any email.
Can anyone help me in this reg
Let me know which linux distribution is used , and the web server having public domain ?
Dear naresh,
there is coomand –
#rsync -r Ipaddress :location of data
example :
#rsync -r192.168.0.18 :/root/slides
cite:
# cd /var/logs
# tail -f /var/log/messages
logs/log? Looks like a typo.
Trace of runtime activities in UNIX
I’ve taken a project to work upon tracing of runtime activities on unix system
into a log file. Like, to implement a program which will show the log of everything
happened in past, including many requirements, like applications i used (with the time of access),
kind of files/directories i opened, closed, created, deleted(with the time), etc.
Please suggest me something to do it in a better way.
How can i archive all the log files in redhat enterprise linux5?
Your help would be really appreciated.
Thanks
I’m confused what does the following command do :
sudo cat /var/log/messages | grep err | -d” -f5
Источник