- Устанавливаем в системе Linux время, дату и часовой пояс из командной строки или из Gnome | Используем ntp
- Set Time, Date Timezone in Linux from Command Line or Gnome | Use ntp
- Set Time/Date/Timezone in Ubuntu Linux
- Check Current Time
- Using the date command
- Using timedatectl command
- Changing Time
- using date command
- Change Date
- Create custom date format
- List/Change time zone
- Set the Local-rtc
- Check/Change CMOS Time
- Conclusion
- Команда date в Linux
- Синтаксис команды date
- Примеры использования date
- Выводы
Устанавливаем в системе Linux время, дату и часовой пояс из командной строки или из Gnome | Используем ntp
В системе Linux очень важно иметь правильное время и дату, поскольку от этого зависит многое. Причем неважно, используете ли вы систему Linux на своем персональном компьютере или у вас Linux-сервер. Серверные и системные часы должны указывать правильное время.
Аппаратные часы — это те часы, которые работают на вашем компьютере даже тогда, как питание компьютера отключено. Это возможно благодаря наличию в современных компьютерах литиевой батареи или батареи другого типа в более старых компьютерах.
Мы можем увидеть различие между аппаратными и системными часами
Вы увидите что-то вроде следующего:
Теперь проверьте системные часы
Вы увидите что-то вроде следующего:
Давайте установим аппаратные часы по местному времени:
Если вы хотите установить их на использование времени по Гринвичу (UTC):
Установка часового пояса
Чтобы в ваших системных часах установить часовой пояс, выполните следующее:
Правильно укажите ваш часовой пояс.
Автоматическая регулировка часов
Для того, чтобы ваша система могла автоматический регулировать время, вам нужно установить программу ntp . Получите ее из репозитария. После того, как она будет установлена, вы можете настроить ее следующим образом:
Отредактируйте файл /etc/ntpd.conf . Он будет выглядеть следующим образом:
Удостоверьтесь, что вы запустили демон, и сделайте так, чтобы он автоматически запускался при загрузке системы.
Для Arch Linux это: /etc/rc.d/ntpd start ; для Debian и производных систем: /etc/init.d/ntpd start
Обновление из командной строки времени по значению, получаемому с сервера времени
Вы можете обновлять время вручную без использования демона ntpdate
Вы получите что-то вроде следующего:
Бонус: Установка времени и даты в Gnome
Если вы используете Gnome, щелкните правой кнопкой мыши по изображению часов и выберите пункт настройки adjust, или в меню выберите пункт System > Administration > Time and Date (Система > Администрирование > Время и дата). Вам, возможно, будет предложено ввести пароль.
Источник
Set Time, Date Timezone in Linux from Command Line or Gnome | Use ntp
Written by Guillermo Garron
Date: 2012-04-19 15:55:00 00:00
To have the correct time and date in Linux is very important, a lot of things depends on it. It does not matter if you are using Linux to power your personal computer or you have a Linux server. The server and system clock needs to be on time.
Set date from the command line
Set time from the command line
Set time and date from the command line
Linux check date from command line
Will show you something like this:
Set hardware clock
The hardware clock is the clock that runs in you PC hardware even if you disconnect it from the main power supply. This is because it has a lithium battery in the modern computers and another type of battery in the old ones.
We’ll see differences between hardware clock and system clock
Will output something like this:
Now check the system clock
Will output something like this:
Let’s set the hardware clock to local time:
If you want to set it to UTC time use:
Set the timezone
To set the timezone of your system clock do the following:
Choose the right timezone for you.
Automatically adjust your computer clock
To have your system to automatically adjust time we need to install ntp . Get it from your repository. Once installed you can configure it this way:
Edit the file /etc/ntpd.conf . It will look like this:
Be sure to start the daemon, and to make it start automatically when the system boots.
On Arch Linux is: /etc/rc.d/ntpd start on Debian and derivatives /etc/init.d/ntpd start
Update from the command line against a time server
You can update the clock manually, without the need of the daemon with ntpdate
You will get something like this:
Bonus: Set the time and Date on Gnome
If you are using Gnome right click on the clock and select adjust, or go to: System > Administration > Time and Date (You may be asked for root password)
You will see a window similar to this one:
If you enjoyed the article, please share it
Источник
Set Time/Date/Timezone in Ubuntu Linux
Time is an important aspect in Linux systems especially in critical services such as cron jobs. Having the correct time on the server ensures that the server operates in a healthy environment that consists of distributed systems and maintains accuracy in the workplace.
In this tutorial, we will focus on how to set time/date/time zone and to synchronize the server clock with your Ubuntu Linux machine.
Check Current Time
You can verify the current time and date using the date and the timedatectl commands. These linux commands can be executed straight from the terminal as a regular user or as a superuser. The commands are handy usefulness of the two commands is seen when you want to correct a wrong time from the command line.
Using the date command
Log in as a root user and use the command as follows
Output
You can also use the same command to check a date 2 days ago
Output
Using timedatectl command
Checking on the status of the time on your system as well as the present time settings, use the command timedatectl as shown
Changing Time
We use the timedatectl to change system time using the format HH:MM: SS. HH stands for the hour in 24-hour format, MM stands for minutes and SS for seconds.
Setting the time to 09:08:07 use the command as follows (using the timedatectl)
using date command
Changing time means all the system processes are running on the same clock putting the desktop and server at the same time. From the command line, use date command as follows
Where,
• 10: Hour (hh)
• 13: Minute (mm)
• 13: Second (ss)
To change the locale to either AM or PM use the %p in the following format.
Change Date
Generally, you want your system date and time is set automatically. If for some reason you have to change it manually using date command, we can use this command :
It will set your current date and time of your system into ‘January 25, 2014′ and ’09:17:00 AM’. Please note, that you must have root privilege to do this.
You can use timedatectl to set the time and the date respectively. The accepted format is ‘YYYY-MM-DD’, ‘YYYY’ represents the year, ‘MM’ the month in two digits and ‘DD’ for the day in two digits.
Changing the date to ’15 January 2019′, you should use the following command:
Create custom date format
To create custom date format, use a plus sign (+)
%D format follows Year/Month/Day format.
You can also put the day name if you want. Here are some examples :
List/Change time zone
Changing the time zone is crucial when you want to ensure that everything synchronizes with the Network Time Protocol. The first thing to do is to list all the region’s time zones using the list-time zones option or grep to make the command easy to understand
The above command will present a scrollable format.
Recommended timezone for servers is UTC as it doesn’t have daylight savings. If you know, the specific time zones set it using the name using the following command
To display timezone execute
Set the Local-rtc
The Real-time clock (RTC) which is also referred to as the hardware clock is independent of the operating system and continues to run even when the server is shut down.
Use the following command
In addition, the following command for the local time
Check/Change CMOS Time
The computer CMOS battery will automatically synchronize time with system clock as long as the CMOS is working correctly.
Use the hwclock command to check the CMOS date as follows
To synchronize the CMOS date with system date use the following format
Conclusion
To have the correct time for your Linux environment is critical because many operations depend on it. Such operations include logging events and cron jobs as well.
If you have any questions or feedback, feel free to leave a comment.
Источник
Команда date в Linux
Главное свойство утилит GNU/Linux — делать что-то одно, но эффективно. Яркий пример — команда date Linux, работающая с датой и временем. С её помощью можно извлекать любую дату в разнообразном формате, в том числе и рассчитывать прошлое и будущее время. Привилегированные пользователи могут перезаписывать системное время, используя её.
Утилита предустановлена во всех дистрибутивах GNU/Linux. В этой статье будут рассмотрены возможности date и способы применения этой команды.
Синтаксис команды date
Программа может выполнятся от имени обычного пользователя. Стандартный синтаксис команды (квадратные скобки обозначают необязательное наличие):
date [ ОПЦИИ ] . [ +ФОРМАТ ]
Ниже представлена таблица с часто применяемыми опциями для date.
| Опция | Длинный вариант | Значение |
|---|---|---|
| -d STRING | —date=STRING | Вывод даты по указанной строке (например ‘yesterday’, ‘tomorrow’, ‘last monday’). |
| -I | —iso-8601[=FMT] | Вывод даты в формате ISO 8601. FMT по умолчанию содержит ‘date’. Также может содержать ‘hourse’, ‘minutes’, ‘seconds’, ‘ns’ для отображения соответствующих значений и часовой пояс относительно UTC рядом с датой. |
| —rfc-3339=FMT | Вывод даты в формате RFC 3339. FMT по умолчанию содержит ‘date’. Также может содержать ‘seconds’ и ‘ns’ для отображения секунд или наносекунд. | |
| -r FILE | —reference=FILE | Вывод даты последней модификации указанного файла в формате по умолчанию. |
| -u | —utc | Вывод UTC-даты |
Аргумент ФОРМАТ отвечает за форматирование вывода даты. Для его указания необходимо поставить знак «+» и написать нужную маску. Наиболее популярные форматы:
| Формат | Значение |
|---|---|
| %% | Знак процента |
| %a | День недели текущей локали в короткой форме («Чтв») |
| %A | День недели текущей локали в длинной форме («Четверг») |
| %b | Месяц года текущей локали в короткой форме в родительном падеже («янв») |
| %B | Месяц года текущей локали в длинной форме в родительном падеже («января») |
| %c | Дата и время текущей локали без указания часового пояса |
| %С | Первые две цифры текущего года |
| %d | Числовой день месяца с ведущим нулём |
| %D | Дата в формате %m/%d/%y |
| %e | День месяца; аналог %_d |
| %F | Дата в формате %Y-%m-%d |
| %h | Аналог %b |
| %H | Часы (00..23) |
| %I | Часы (01..12) |
| %j | День года (001..366) |
| %m | Месяц (01..12) |
| %M | Минуты (00..59) |
| %n | Новая строка |
| %q | Квартал года |
| %S | Секунды (00..59) |
| %t | Знак табуляции |
| %T | Время в формате %H:%M:%S |
| %u | Числовой день недели; 1 — понедельник |
| %x | Дата в локальном формате |
| %X | Время в локальном формате |
| %Z | Аббревиатура временной зоны |
Примеры использования date
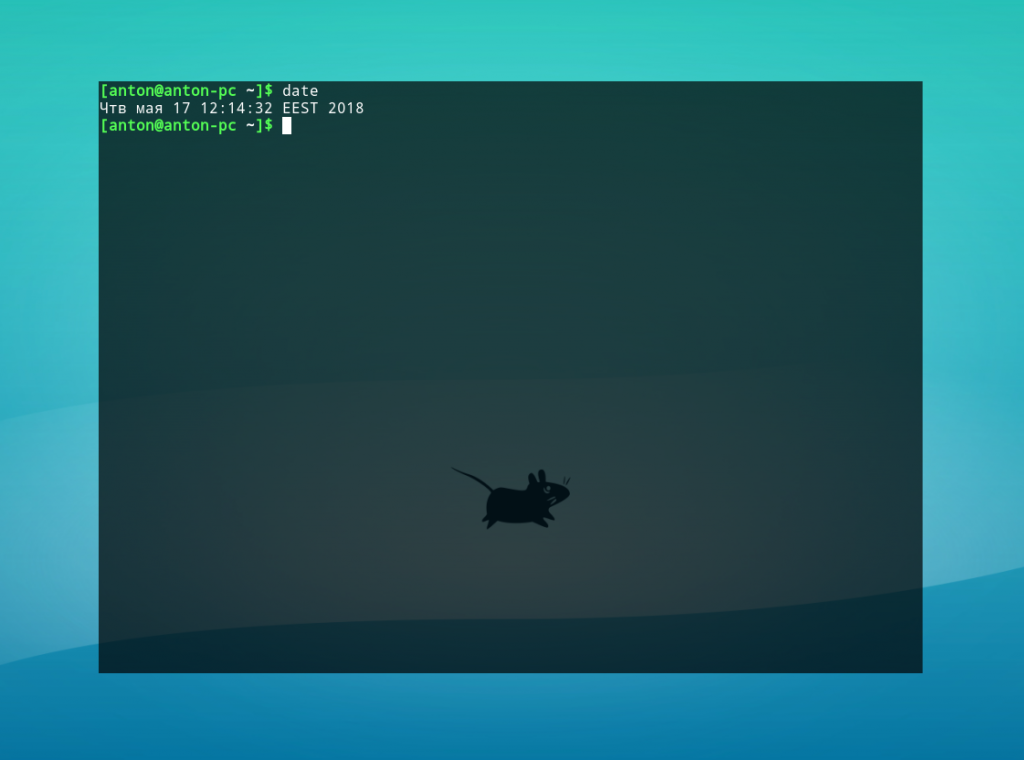
Введем команду без параметров.
Будет отображена текущая дата и время в соответствии с настройками локали системы.
Команда date без параметров по умолчанию применяет маску %a %b %d %X %Z. Поскольку все форматы должны быть переданы как один параметр (из-за принципа обработки данных командным интерпретатором Bash), пробелы между ними необходимо экранировать обратным слэшем (\) или взять в кавычки.
Особое внимание следует уделить параметру -d (—date). Его функциональность не слишком очевидна, но при этом наиболее обширна.
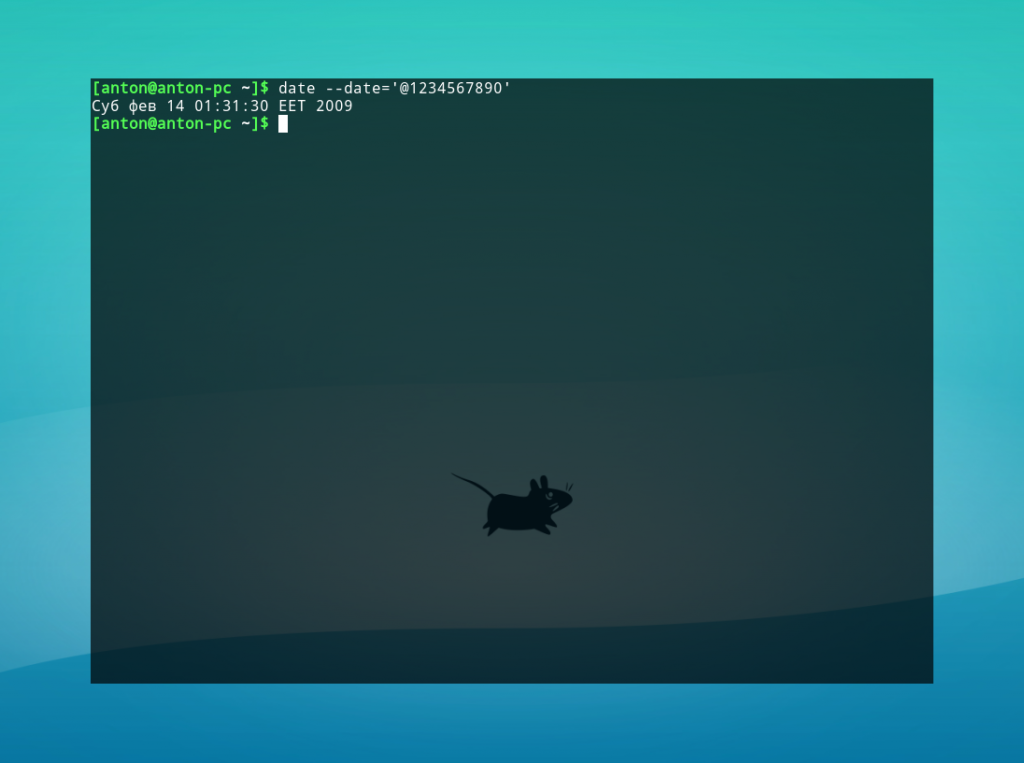
Пример 1. Вычисление даты по числу секунд, прошедших с 1 января 1970 года.
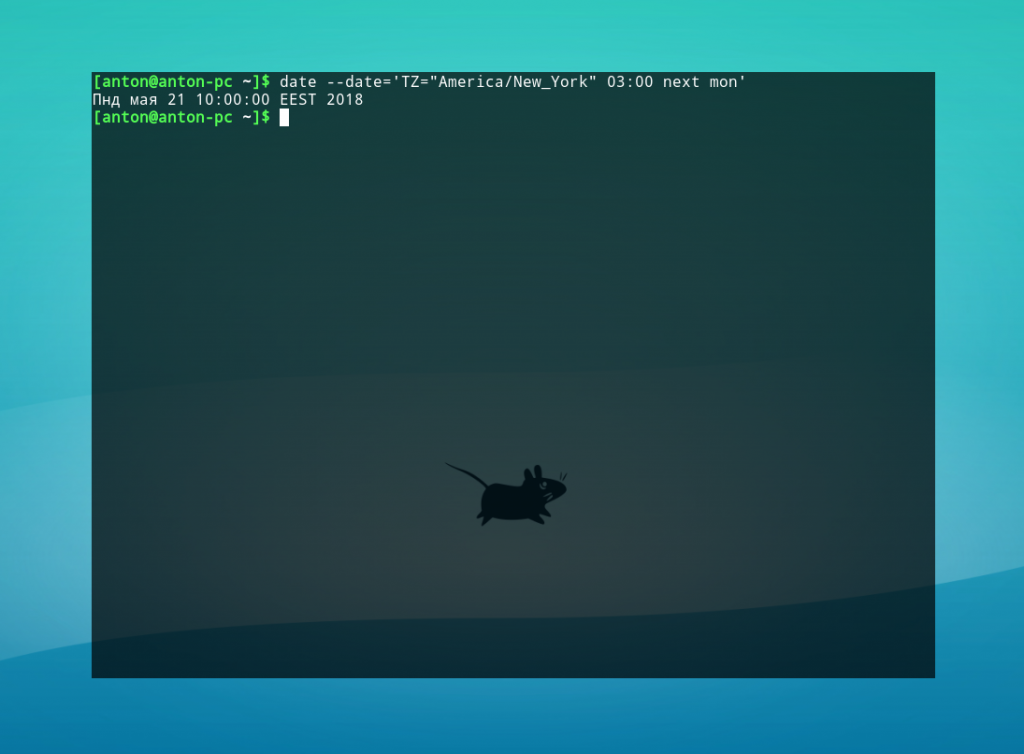
Пример 2. Вычисление даты и времени следующего понедельника при указании часового пояса Нью-Йорка в 03:00.
date —date=’TZ=»America/New_York» 03:00 next mon’
Обратите внимание: указывать название дня недели или месяца можно в любом регистре, в короткой или длинной форме. Параметры next и last обозначают следующий и прошедший, соответственно, ближайшие дни недели.
Пример 3. Если текущий день месяца — последний, сформировать отчет о занятости дискового пространства корневого и домашнего каталога в файл report.
#!/bin/bash
if [[ $(date —date=’next day’ +%d) = ’01’ ]]; then
df -h / /home > report
Такой скрипт можно использовать для автоматизации работы с помощью демона crontab или anacron.
Выводы
Команда date Linux является эффективным инструментом работы с датой и временем, с широкой возможностью их расчёта для прошедших или будущих показателей. Также она применяется в написании сценариев в командном интерпретаторе Bash.
Источник