- Как настроить прокси в Linux
- Как настроить прокси в Linux
- В статье показано как настроить прокси в любой версии ОС Linux.
- Рассмотрим настройку переменных для использования прокси
- Тестирование работы
- How To Use Proxy Server To Access Internet at Shell Prompt With http_proxy Variable
- Set http_proxy shell variable on Linux/OS X/Unix bash shell
- How do I setup proxy variable for all users?
- A note about enabling proxy access to a specific user
- How do I use password protected proxy server using various command line options?
- How to set up proxy using http_proxy & https_proxy environment variable in Linux?
- What is Proxy Server?
- Check current proxy configuration status (https_proxy/https_proxy)
- Set up proxy server using http_proxy environment variable
- Set up proxy without username and password
- Set up proxy with username and password
- Set up proxy with domain, username and password
- Special character (@) handling
- Set up proxy permanently using /etc/environment
- Set up proxy permanently using /etc/profile.d
- How to configure proxy settings on Ubuntu 18.04
- Overview
- Ubuntu Desktop Network Settings
- Ubuntu Terminal Proxy Settings
- Single User Temporary Proxy Settings
- Single User Persistent Proxy Settings
- All Users
- Использование HTTP proxy и SOCKS в Linux
- curl: передача данных через proxy
- wget: закачка файлов через proxy
- ssh: доступ к серверам
- Соксификатор dante
- DNS запросы через proxy
Как настроить прокси в Linux
Как настроить прокси в Linux
В статье показано как настроить прокси в любой версии ОС Linux.
Прокси-сервер или proxy — в переводе с англ. «представитель» — сервер как комплекс программ в компьютерных сетях, позволяющий клиентам выполнять косвенные запросы к другим сетевым службам. В рамках данного материала прокси понимается сервер выполняющий доступ к глобальной сети интернет.
Проще всего для использования прокси в командной строке, но в зависимости от типа трафика, Вы можете определить переменные окружения http_proxy, https_proxy или ftp_proxy.
Практически все утилиты командой строки, такие как curl, wget, ssh, apt-get, ftp, wget, yum и прочие, используют данные переменные.
Рассмотрим настройку переменных для использования прокси
Используйте следующий синтаксис для настройки таких типов трафика как http, https и ftp из командной строки:
$ export ftp_proxy=»http://proxy-server:port»
$ export http_proxy=»http://proxy-server:port»
$ export https_proxy=»https://proxy-server:port»
Используйте следующий синтаксис, если прокси-сервер требует аутентификацию:
$ export http_proxy=»http://user:pass@proxy-server:port»
$ export https_proxy=»https://user:pass@proxy-server:port»
$ export ftp_proxy=»http://user:pass@proxy-server:port»
Если Ваш пароль содержит спец. символы, Вы должны заменить их на ASCII коды.
Например символ собаки «@», должен быть заменен на «%40» (т. е. p@ss = p%40ss).
Тестирование работы
Используйте следующую команду для проверки текущих переменных прокси:
$ env | grep -i proxy
Можно проверить работу прокси, узнав ваш внешний IP адрес из командной строки:
Источник
How To Use Proxy Server To Access Internet at Shell Prompt With http_proxy Variable
I ‘m behind a squid proxy server. How do I access internet via proxy server when I use wget, lynx and other utilities from a shell prompt on a Linux or Unix-like systems?
Linux and UNIX-like systems has environment variable called http_proxy. It allows you to connect text based session and/or applications via the proxy server. All you need is proxy server IP address (URL) and port values. This variable is almost used by all utilities such as elinks, lynx, wget, curl and others commands.
| Tutorial details | |
|---|---|
| Difficulty level | Easy |
| Root privileges | No |
| Requirements | Linux/Unix shell promot |
| Est. reading time | 2 mintues |
Set http_proxy shell variable on Linux/OS X/Unix bash shell
Type the following command to set proxy server:
$ export http_proxy=http://server-ip:port/
$ export http_proxy=http://127.0.0.1:3128/
$ export http_proxy=http://proxy-server.mycorp.com:3128/
If the proxy server requires a username and password then add these to the URL. For example, to include the username foo and the password bar:
$ export http_proxy=http://foo:bar@server-ip:port/
$ export http_proxy=http://foo:bar@127.0.0.1:3128/
$ export http_proxy=http://USERNAME:PASSWORD@proxy-server.mycorp.com:3128/
How do I setup proxy variable for all users?
To setup the proxy environment variable as a global variable, open /etc/profile file:
# vi /etc/profile
Add the following information:
export http_proxy=http://proxy-server.mycorp.com:3128/
OR
export http_proxy=http://USERNAME:PASSOWRD@proxy-server.mycorp.com:3128/
Save and close the file.
A note about enabling proxy access to a specific user
To enable proxy access for a specific user, add the lines user shell profile. For the default bash shell, the profile is the file .bash_profile. For example, enable proxy access for a specifc user called vivek, type:
$ vi $HOME/.bash_profile
OR
# vi /home/vivek/.bash_profile
Append the following line:
export http_proxy=http://USERNAME:PASSOWRD@proxy-server.mycorp.com:3128/
Save and close the file.
- No ads and tracking
- In-depth guides for developers and sysadmins at Opensourceflare✨
- Join my Patreon to support independent content creators and start reading latest guides:
- How to set up Redis sentinel cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- How To Set Up SSH Keys With YubiKey as two-factor authentication (U2F/FIDO2)
- How to set up Mariadb Galera cluster on Ubuntu or Debian Linux
- A podman tutorial for beginners – part I (run Linux containers without Docker and in daemonless mode)
- How to protect Linux against rogue USB devices using USBGuard
Join Patreon ➔
How do I use password protected proxy server using various command line options?
You can simply use wget command as follows:
$ wget —proxy-user=USERNAME —proxy-password=PASSWORD http://path.to.domain.com/some.html
Lynx command has the following syntax:
$ lynx -pauth=USER:PASSWORD http://domain.com/path/html.file
Curl command has following syntax:
$ curl —proxy-user user:password http://url.com/
🐧 Get the latest tutorials on Linux, Open Source & DevOps via
Источник
How to set up proxy using http_proxy & https_proxy environment variable in Linux?
Table of Contents
In this article I will share the steps to set up proxy server using https_proxy and https_proxy environment variable.
What is Proxy Server?
A proxy server is a dedicated computer or a software system running on a computer that acts as an intermediary between an endpoint device, such as a computer, and another server from which a user or client is requesting a service. The proxy server may exist in the same machine as a firewall server or it may be on a separate server, which forwards requests through the firewall.
Check current proxy configuration status (https_proxy/https_proxy)
This variable will show if there is a proxy server configured on the system:
If these variables are empty it would mean that there are no proxy servers configured on the system level.
Set up proxy server using http_proxy environment variable
The http_proxy and https_proxy environment variable is used to specify proxy settings to client programs such as curl and wget .
Set up proxy without username and password
Execute the below command with valid SERVER_IP and PORT on the terminal. This will enable proxy configuration for the current session but these values will not be persistent across reboot.
Set up proxy with username and password
You can modify the earlier command to add the username and password value assuming a valid authentication is required to enable the proxy server configuration. But again this command will also enable proxy server for the current session only and will not be persistent across reboots.
Set up proxy with domain, username and password
Assuming you are also required to add domain detail while setting up proxy configuration on your system then use the below command
Special character (@) handling
With more complex and robust handling of special characters in username or password follow How to setup http or https proxy with special characters in username and password
When the username or password uses the @ symbol, add a backslash (\) before the @ — for example:
Set up proxy permanently using /etc/environment
Now as I have highlighted above the above commands will work only for the current active session but will not be available across reboots. So to make these changes persistent define the environment variables in /etc/environment file:
Set up proxy permanently using /etc/profile.d
For bash and sh users, add the export line given above into a new file called /etc/profile.d/http_proxy.sh file:
For csh and tcsh users, use the following command to set the http_proxy variable in a new file called /etc/profile.d/http_proxy.csh file:
The extension of these files determines which shell will read them. The commands are not interchangeable.
Lastly I hope the steps from the article to setup proxy using http_proxy and https_proxy environment variable in Linux was helpful. So, let me know your suggestions and feedback using the comment section.
Источник
How to configure proxy settings on Ubuntu 18.04
Overview
Proxies are commonly found on business networks, but they are increasingly becoming popular for personal use. The following tutorial will show you multiple ways of setting your proxy in Ubuntu 18.04, allowing you to browse the Internet with additional privacy.
This tutorial will cover the following three areas. Use the one the fits your needs.
Desktop: learn how to set your proxy settings from within the desktop.
Terminal: set environment variables for your proxy server when using a terminal or console.
All users: setting the proxy settings for all users on the system.
Ubuntu Desktop Network Settings
To configure your proxy settings in Ubuntu Desktop you need to access Network Settings. Within there you can set a number of parameters, including proxy settings for HTTP traffic, HTTPS traffic, and FTP traffic.
Equally as important as setting your Internet proxy settings is setting Ignore Hosts, to prevent local traffic from going through your proxy server.
To set your proxy in Ubuntu Desktop, do the following:
- Open the Application launcher by clicking the “Show Applications” icon, located at the bottom of the left-hand quick application access bar.
- Type in ‘Settings’
- Click the ‘Settings’ icon.
- From the left-hand navigation, click the Network tab.
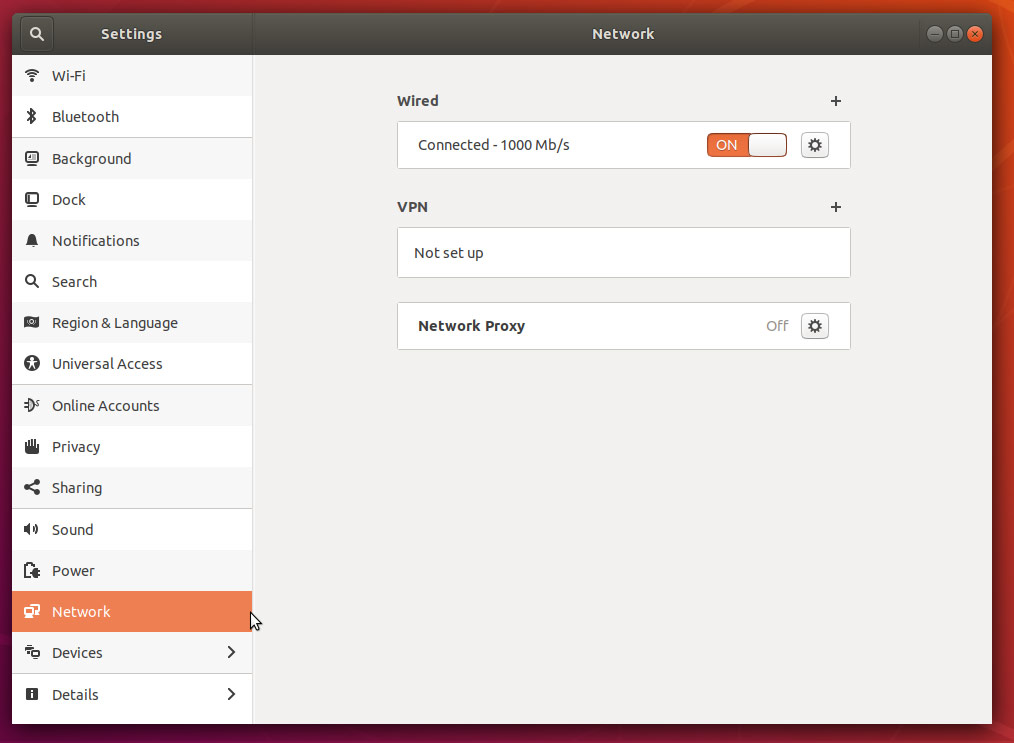
Click the cog icon near the Network Proxy label.
Network settings proxy icon
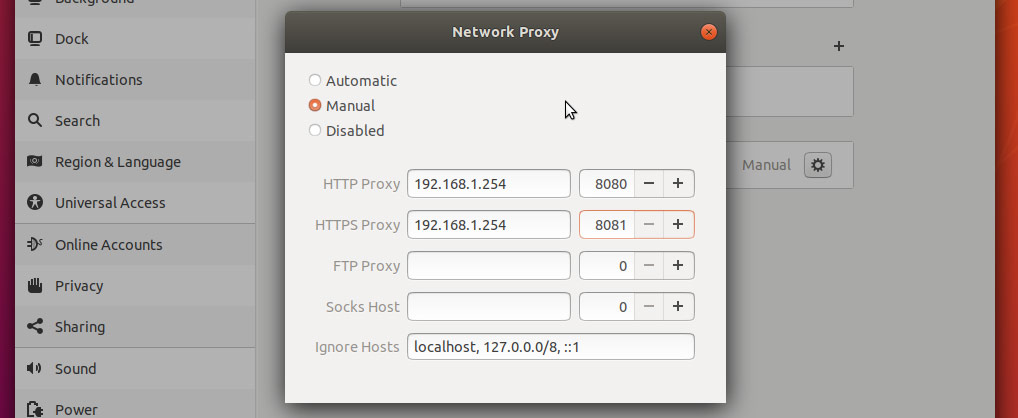
Ubuntu Terminal Proxy Settings
Like every Linux distribution, proxy settings can be set using environment variables. There are a number of variables available to use, ranging from HTTP traffic to FTP traffic.
Proxy settings can be either persistent by setting them in your profile, or non-persistent by setting them from the shell session.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| http_proxy | Proxy server for HTTP Traffic. |
| https_proxy | Proxy server for HTTPS traffic |
| ftp_proxy | Proxy server for FTP traffic |
| no_proxy | Patterns for IP addresses or domain names that shouldn’t use the proxy |
The value for every proxy setting, except for no_proxy, uses the same template. They all require a hostname, but you may optionally specify a proxy server port and your user credentials if required to do so. For example:
Single User Temporary Proxy Settings
You may not always want to force Internet traffic through a proxy. Sometimes you need to override existing settings, and you can do this safely by setting the proxy environment variables from the command line.
The following will set a proxy for HTTP and HTTPS, while preventing local traffic from going through the proxy. Our example proxy server endpoint is my.proxy.server:8080 for HTTP traffic and my.proxy.server:8081 for HTTPS.
- Open a Terminal window where you need proxy access.
- Set and export the HTTP_PROXY variable.
- Set and export the HTTPS_PROXY variable.
- Set and export the NO_PROXY variable to prevent local traffic from being sent to the proxy.
Single User Persistent Proxy Settings
- Open your bash profile file into a text editor.
- Add the following lines, modifying them to match your environment.
- Save your settings.
- The proxy settings will be applied the next time you start a session, by logging into the server or opening a new Terminal window from a Desktop.
- To force apply your new proxy settings in the current Terminal session, execute the source command against your bash profile.
All Users
You will need administrative rights to perform this task. All versions of Ubuntu and Debian have a file called /etc/environment. Within this file, we can set global variables and other such things.
Similar to how you set proxy settings for your own local proxy, we’ll be adding the environment variables to this file. The variables will be set when a new user session is created, which is to say when you log in next.
- Using an administrator account, open /etc/environment into a text editor.
- Add the following lines, modifying them to fit your environment. Username and password may be omitted, if not required.
For example, if you do not need to enter a username or password, and your proxy server is my.proxyserver.net at port 8080, and you do not want local traffic going through the proxy, you would enter the following:
Источник
Использование HTTP proxy и SOCKS в Linux
В Linux существует много полезных консольных команд, которые при необходимости хотелось бы запустить через proxy. Некоторые приложения имеют встроенную поддержку proxy, а некоторые нет. Далее описано как пользоваться востребованными утилитами через proxy, даже теми, которые этой поддержки не имеют.
curl: передача данных через proxy
curl имеет полноценную поддержку как HTTP proxy так и SOCKS.
Для тестирования возможно использовать proxy сервера из бесплатных списков (socks — sockslist.net, и HTTP proxy — proxyhttp.net). Проверка IP адреса будет производиться с помощью ресурса check-host.net
Часть параметров curl можно записать в файл
С помощью time и curl также можно замерить время отклика сервера:
Результат будет выглядеть так:
wget: закачка файлов через proxy
wget имеет встроенную поддержку proxy. Недостаток лишь в том, что только поддержку HTTP proxy. Для использования совместно с SOCKS рекомендуется использовать соксификатор dante.
Чтобы все время не указывать —proxy-user и —proxy-password можно их прописать в файл
ssh: доступ к серверам
Для доступа к серверам через ssh и proxy также лучше использовать соксификатор dante.
Соксификатор dante
С помощью socksify можно направить через proxy почти любое приложение, не только консольное.
Чтобы все время не вводить данные о proxy можно создать файл /etc/socks.conf
Пример для SOCKS:
Пример для HTTP proxy с авторизацией:
А также экспортировать переменные SOCKS_USERNAME и SOCKS_PASSWORD, если для SOCKS или HTTP proxy требуется авторизация:
DNS запросы через proxy
Часто требуется чтобы и преобразование имен происходило через proxy. Если использовать dante, то запрос на преобразование имен идет и через proxy, и через именной сервер указанный в /etc/resolv.conf . Понять почему же идет два одинаковых запроса вместо одного не удалось. Поэтому можно предложить два варианта:
1) Закомментировать именные сервера в файле /etc/resolv.conf, чтобы преобразование имен шло только через proxy. Это отразится на всей системе.
2) Изменить /etc/resolv.conf и выставить именные сервера необходимой страны, или просто отличные от серверов провайдера. Например установить сервера Google:
Чтобы данные не были перезаписаны именными серверами провайдера (при переподключении), можно запретить обновление списка именных серверов сетевому менеджеру (NetworkManager/wicd) или DHCP-клиенту (спасибо ergil за корректировку).
Или воспользоваться «грубым» методом — запрещением изменения файла /etc/resolv.conf:
Если есть какие-то дополнения, пожалуйста, напишите, это будет полезно узнать и применить.
Источник





