- Управление службами Windows с помощью PowerShell
- Основные командлеты PowerShell для управления службами Windows
- Остановка, запуск, приостановка и перезапуск служб из PowerShell
- Set-Service – изменение настроек службы Windows
- Создание и удаление служб Windows c помощью PowerShell
- Изменение учетной записи для запуска службы
- Set-Service
- Syntax
- Description
- Examples
- Example 1: Change a display name
- Example 2: Change the startup type of services
- Example 3: Change the description of a service
- Example 4: Start a service
- Example 5: Suspend a service
- Example 6: Stop a service
- Example 7: Stop a service on a remote system
- Example 8: Change credential of a service
- Example 9: Change the SecurityDescriptor of a service
- Parameters
- Inputs
- Outputs
- Notes
Управление службами Windows с помощью PowerShell
В Windows вы можете управлять службами не только из графической консоли services.msc или утилиты командной строки Sc.exe (первоначальна включалась в пакет ресурсов Resource Kit), но и с помощью PowerShell. В этой статье мы смотрим различные сценарии управления службами Windows с помощью PowerShell.
Основные командлеты PowerShell для управления службами Windows
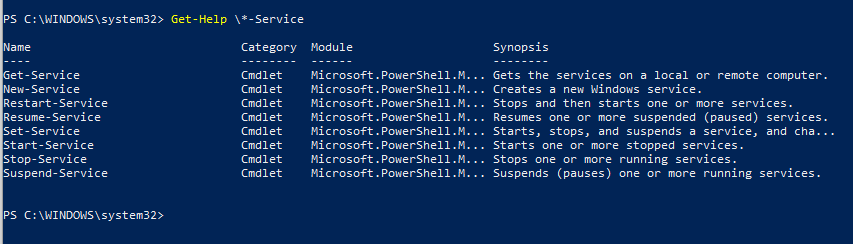
Существует восемь основных командлетов Service, предназначенных для просмотра состояния и управления службами Windows.
Чтобы получить весь список командлетов Service, введите команду:
- Get-Service — позволяет получить службы на локальном или удаленном компьютере, как запущенные, так и остановленные;
- New-Service – создать службу. Создает в реестре и базе данных служб новую запись для службы Windows;
- Restart-Service – перезапустить службу. Передает сообщение об перезапуске службы через Windows Service Controller
- Resume-Service – возобновить службы. Отсылает сообщение о возобновлении работы диспетчеру служб Windows;
- Set-Service — изменить параметры локальной или удаленной службы, включая состояние, описание, отображаемое имя и режим запуска. Этот командлет также можно использовать для запуска, остановки или приостановки службы;
- Start-Service – запустить службу;
- Stop-Service – остановить службу (отсылает сообщение об остановке диспетчеру служб Windows);
- Suspend-Service приостановить службу. Приостановленная служба по-прежнему выполняется, однако ее работа прекращается до возобновления работы службы, например с помощью командлета Resume-Service.
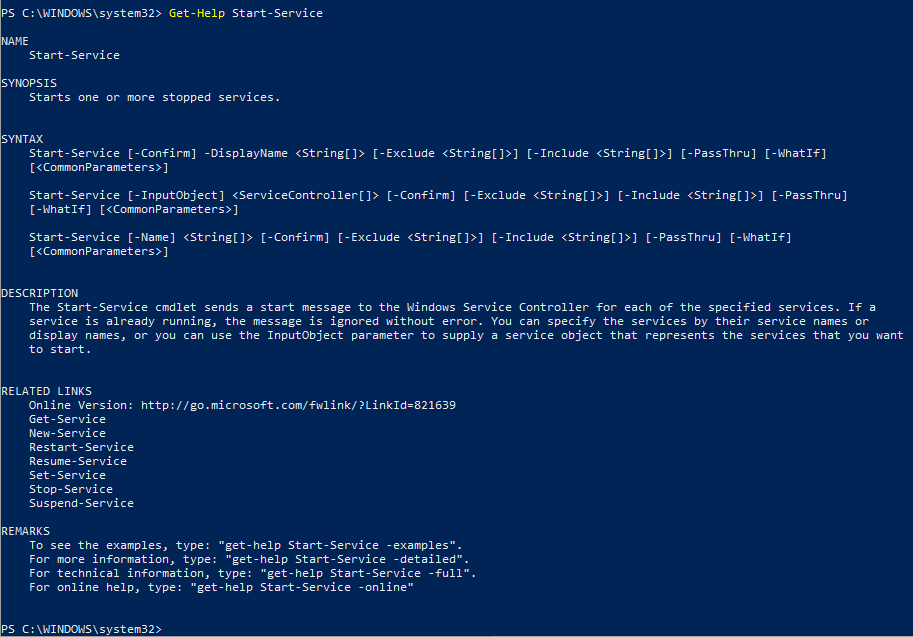
Получить подробное описание и примеры использования конкретного командлета можно через Get-help:
Get-Service: получаем список служб и их состояние
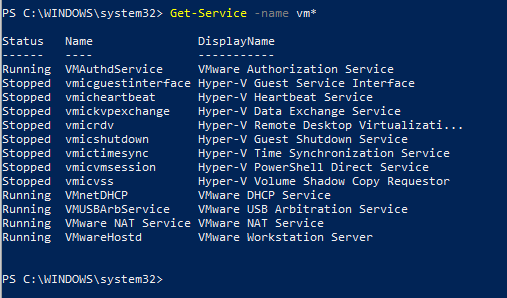
Получить список и состояние (Running/Stopped) службы на локальном или удаленном компьютере можно с помощью командлета Get-Service. Параметр -Name позволяет делать отбор по имени службы. Имя службы можно задать с использованием подстановочного символа *.
Если вы не знаете точное имя службы, есть возможность найти службы по отображаемому имени с помощью параметра –DisplayName. Можно использовать список значений и подстановочные знаки.
Командлет Get-Service можно использовать для получения состояния служб на удаленных компьютерах, указав параметр -ComputerName. Можно опросить статус службы сразу на множестве удаленных компьютеров, их имена нужно перечислить через запятую. Например, приведенная ниже команда получает состояние службы Spooler на удаленных компьютерах RM1 и RM2.
Get-Service spooler –ComputerName RM1,RM2
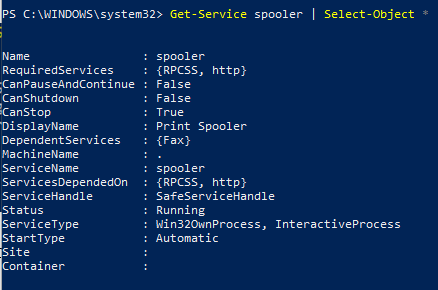
Вывести все свойства службы позволит командлет Select-Object:
Get-Service spooler | Select-Object *
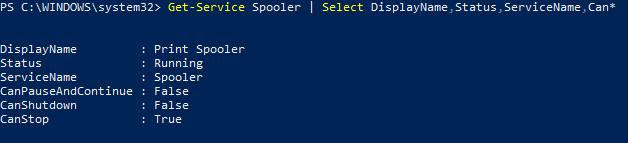
Командлет Select-Object позволит вывести определенные свойства службы. Например, нам нужно вывести имя, статус и доступные возможности службы Spooler:
Get-Service Spooler | Select DisplayName,Status,ServiceName,Can*
Командлет Get-Service имеет два параметра, которые позволяют получить зависимости служб:
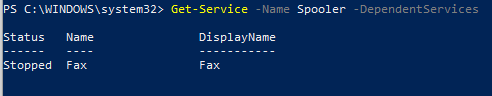
- Параметр -DependentServices позволяет вывести службы, которые зависят от данной службы;
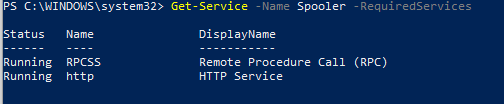
- Параметр -RequiredServices позволяет вывести службы, от которых зависит данная служба.
Приведенная ниже команда выводит службы, необходимые для запуска службе Spooler:
Get-Service –Name Spooler -RequiredServices
Следующая команда выводит службы, которые зависят от службы Spooler:
Get-Service –Name Spooler -DependentServices
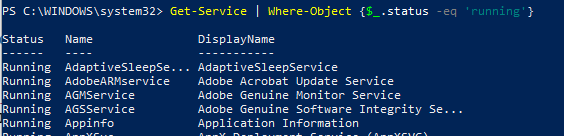
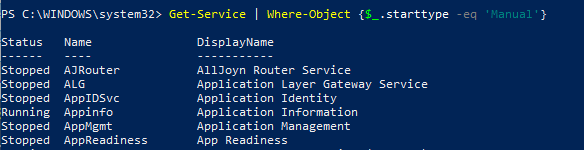
При необходимости найти службы с определенным состоянием или параметрами, используйте командлет Where-Object. Например, получим список запущенных служб со статусом Running:
Для вывода служб с типом запуска Manual, выполните команду
Проверить, что в системе имеется указанная служба:
if (Get-Service «ServiceTest» -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue)
<
Write-host «ServiceTest exists»
>
Остановка, запуск, приостановка и перезапуск служб из PowerShell
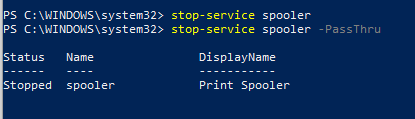
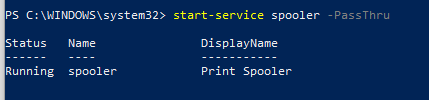
Остановить службу можно с помощью командлета Stop-Service. Чтобы остановить службу печати, выполните команду:
Stop-Service -Name spooler
Командлет Stop-Service не выводит никаких данных после выполнения. Чтобы увидеть результат выполнения команды, используйте параметр -PassThru.
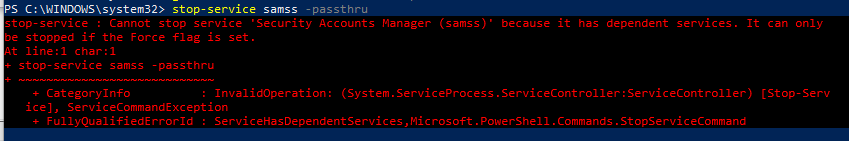
Обратите внимание, что не каждую службу можно остановить. Если есть зависимые службы, то получите ошибку
Для принудительной остановки используйте параметр –Force. Вы должны помнить, что остановятся также все зависимые службы:
Stop-Service samss –Force -Passthru
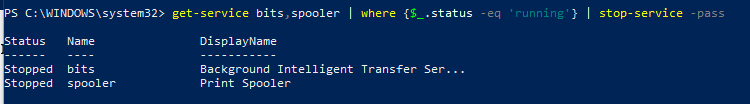
Следующая команда остановит перечисленные службы (bits,spooler) со статусом ”Running”:
get-service bits,spooler | where <$_.status -eq 'running'>| stop-service –passthru
Командлет Start-Service запускает остановленные службы:
Start-Service -Name spooler -PassThru
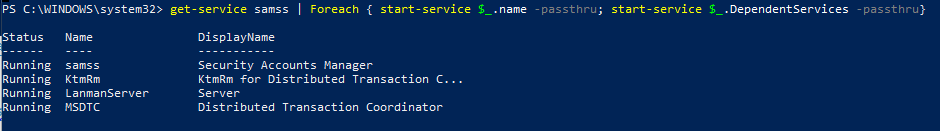
Служба не запустится, если есть остановленные зависимые службы. Чтобы их найти и включить:
get-service samss | Foreach
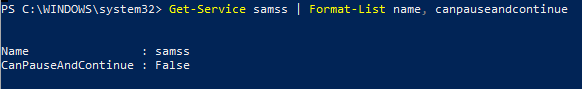
Командлет Suspend-Service может приостанавливать службы, допускающие временную приостановку и возобновление. Для получения сведений о возможности временной приостановки конкретной службы используйте командлет Get-Service со свойством «CanPauseAndContinue«.
Get-Service samss | Format-List name, canpauseandcontinue
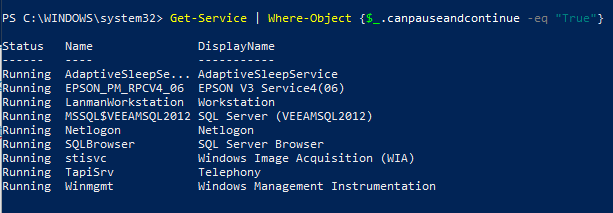
Чтобы отобразить список всех служб, работа которых может быть приостановлена, введите команду:
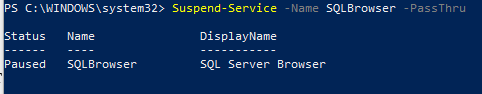
Приостановим службу SQLBrowser:
Suspend-Service -Name SQLBrowser
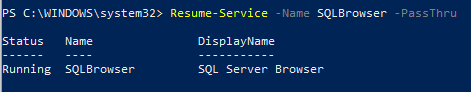
Для возобновления работы приостановленной службы служит командлет Resume-service:
Resume-Service -Name SQLBrowser
Следующая команда возобновляет работу всех приостановленных служб:
get-service | where-object <$_.Status -eq "Paused">| resume-service
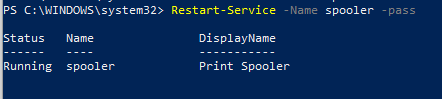
Командлет Restart-Service перезапускает службу:
Restart-Service -Name spooler
Эта команда запускает все остановленные сетевые службы компьютера:
get-service net* | where-object <$_.Status -eq "Stopped">| restart-service
Параметр —ComputerName у этих командлетов отсутствует, но их можно выполнить на удаленном компьютере с помощью командлета Invoke-Command или через пайп:
Например, чтобы перезапустите очередь печати на удаленном компьютере RM1, выполните команду:
Get-Service Spooler -ComputerName RM1 | Start-Service
Set-Service – изменение настроек службы Windows
Командлет Set-Service позволяет изменить параметры или настройки служб на локальном или удаленном компьютере. Так как состояние службы является свойством, этот командлет можно использовать для запуска, остановки и приостановки службы. Командлет Set-Service имеет параметр -StartupType, позволяющий изменять тип запуска службы.
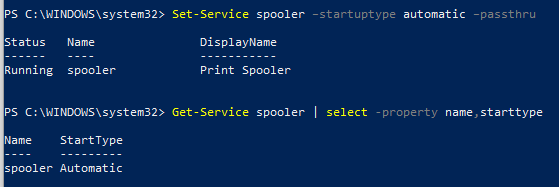
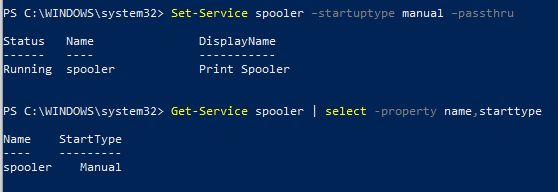
Изменим тип запуска службы spooler на автоматический:
Set-Service spooler –startuptype automatic –passthru
Можно перевести службу на ручной (manual) запуск:
Set-Service spooler –startuptype manual –passthru
Создание и удаление служб Windows c помощью PowerShell
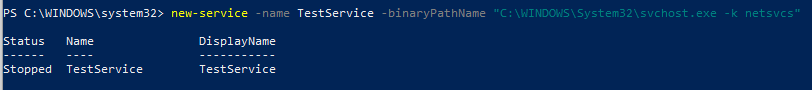
New-Service – командлет для создания новой службы в Windows. Для новой службы требуется указать имя и исполняемый файл (вы можете запустить PowerShell скрипт как службу Windows).
В примере создадим новую службу с именем TestService.
new-service -name TestService -binaryPathName «C:\WINDOWS\System32\svchost.exe -k netsvcs»
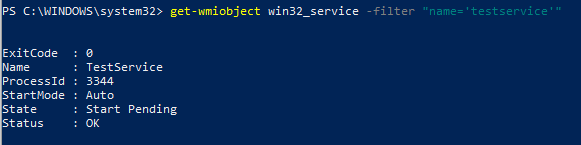
С помощью параметра Get-WmiObject получим информацию о режиме запуска и описание службы
get-wmiobject win32_service -filter «name=’testservice'»
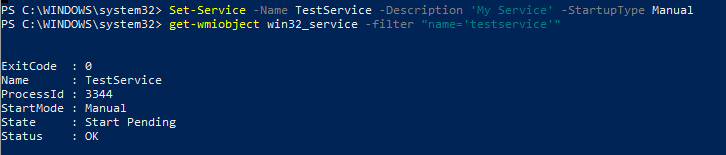
Изменить параметры новой службы можно командой
Set-Service -Name TestService -Description ‘My Service’ -StartupType Manual
Чтобы удалить службу используйте команду
(Get-WmiObject win32_service -Filter ″name=′TestService′″).delete()
Изменение учетной записи для запуска службы
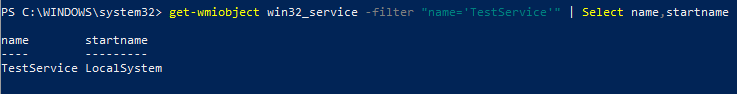
Вы можете изменить учетную запись, из-под которой запускается служба. Получим имя учетной записи, которая используется для запуска службы TestService
get-wmiobject win32_service -filter «name=’TestService'» | Select name,startname
Для изменения имени и пароля учетной записи выполняем команды.
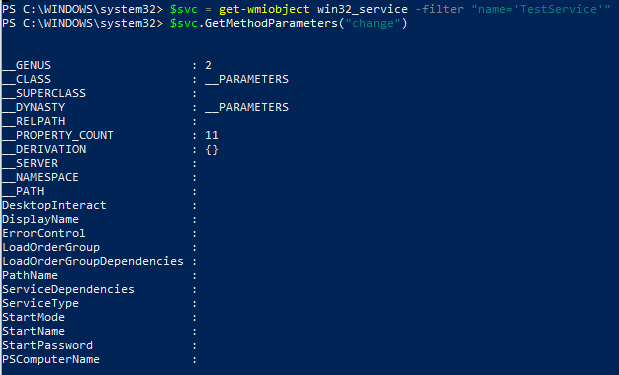
$svc = get-wmiobject win32_service -filter «name=’TestService'»
$svc.GetMethodParameters(«change»)
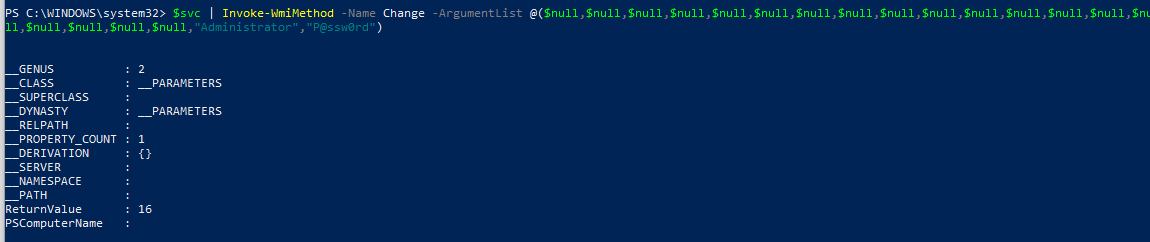
В результате получаем список параметров метода Change(). Считаем на каком месте находятся параметры StartName и StartPassword – 20 и 21 место соответственно.
$svc | Invoke-WmiMethod -Name Change –ArgumentList @ ($null,$null,$null,$null,$null,$null,$null, $null,$null,$null,$null,$null,$null,$null,$null,$null, $null,$null,$null,»Administrator»,»P@ssw0rd»)
Либо вы можете указать имя gMSA аккаунта. Пароль при этом не указывается.
Как видите, PowerShell позволяет легко управлять службами Windows. Можно создавать, останавливать, запускать и возобновлять службы, менять их свойства. Большинство командлетов позволяют управлять службами на удаленных компьютерах.
Set-Service
Starts, stops, and suspends a service, and changes its properties.
Syntax
Description
The Set-Service cmdlet changes the properties of a service such as the Status, Description, DisplayName, and StartupType. Set-Service can start, stop, suspend, or pause a service. To identify a service, enter its service name or submit a service object. Or, send a service name or service object down the pipeline to Set-Service .
Examples
Example 1: Change a display name
In this example, a service’s display name is changed. To view the original display name, use Get-Service .
Set-Service uses the Name parameter to specify the service’s name, LanmanWorkstation. The DisplayName parameter specifies the new display name, LanMan Workstation.
Example 2: Change the startup type of services
This example shows how to change a service’s startup type.
Set-Service uses the Name parameter to specify the service’s name, BITS. The StartupType parameter sets the service to Automatic.
Get-Service uses the Name parameter to specify the BITS service and sends the object down the pipeline. Select-Object uses the Property parameter to display the BITS service’s status.
Example 3: Change the description of a service
This example changes the BITS service’s description and displays the result.
The Get-CimInstance cmdlet is used because it returns a Win32_Service object that includes the service’s Description.
Get-CimInstance sends the object down the pipeline to Format-List and displays the service’s name and description. For comparison purposes, the command is run before and after the description is updated.
Set-Service uses the Name parameter to specify the BITS service. The Description parameter specifies the updated text for the services’ description.
Example 4: Start a service
In this example, a service is started.
Set-Service uses the Name parameter to specify the service, WinRM. The Status parameter uses the value Running to start the service. The PassThru parameter outputs a ServiceController object that displays the results.
Example 5: Suspend a service
This example uses the pipeline to pause to service.
Get-Service uses the Name parameter to specify the Schedule service, and sends the object down the pipeline. Set-Service uses the Status parameter to set the service to Paused.
Example 6: Stop a service
This example uses a variable to stop a service.
Get-Service uses the Name parameter to specify the service, Schedule. The object is stored in the variable, $S . Set-Service uses the InputObject parameter and specifies the object stored $S . The Status parameter sets the service to Stopped.
Example 7: Stop a service on a remote system
This example stops a service on a remote computer. For more information, see Invoke-Command.
Get-Credential prompts for a username and password, and stores the credentials in the $Cred variable. Get-Service uses the Name parameter to specify the Schedule service. The object is stored in the variable, $S .
Invoke-Command uses the ComputerName parameter to specify a remote computer. The Credential parameter uses the $Cred variable to sign on to the computer. The ScriptBlock calls Set-Service . The InputObject parameter specifies the service object stored $S . The Status parameter sets the service to Stopped.
Example 8: Change credential of a service
This example changes the credentials that are used to manage a service.
Get-Credential prompts for a username and password, and stores the credentials in the $credential variable. Set-Service uses the Name parameter to specify the Schedule service. The Credential parameter uses the $credential variable and updates the Schedule service.
Example 9: Change the SecurityDescriptor of a service
This example changes a service’s SecurityDescriptor.
The SecurityDescriptor is stored in the $SDDL variable. Set-Service uses the Name parameter to specify the BITS service. The SecurityDescriptorSddl parameter uses $SDDL to change the SecurityDescriptor for the BITS service.
Parameters
Prompts you for confirmation before running Set-Service .
| Type: | SwitchParameter |
| Aliases: | cf |
| Position: | Named |
| Default value: | False |
| Accept pipeline input: | False |
| Accept wildcard characters: | False |
Specifies the account used by the service as the Service Logon Account.
Type a user name, such as User01 or Domain01\User01, or enter a PSCredential object, such as one generated by the Get-Credential cmdlet. If you type a user name, this cmdlet prompts you for a password.
Credentials are stored in a PSCredential object and the password is stored as a SecureString.
For more information about SecureString data protection, see How secure is SecureString?.
This parameter was introduced in PowerShell 6.0.
| Type: | PSCredential |
| Position: | Named |
| Default value: | None |
| Accept pipeline input: | False |
| Accept wildcard characters: | False |
Specifies a new description for the service.
The service description appears in Computer Management, Services. The Description isn’t a property of the Get-Service ServiceController object. To see the service description, use Get-CimInstance that returns a Win32_Service object that represents the service.
| Type: | String |
| Position: | Named |
| Default value: | None |
| Accept pipeline input: | False |
| Accept wildcard characters: | False |
Specifies a new display name for the service.
| Type: | String |
| Aliases: | DN |
| Position: | Named |
| Default value: | None |
| Accept pipeline input: | False |
| Accept wildcard characters: | False |
Specifies the Stop mode of the service. This parameter only works when -Status Stopped is used. If enabled, Set-Service stops the dependent services before the target service is stopped. By default, exceptions are raised when other running services depend on the target service.
| Type: | SwitchParameter |
| Position: | Named |
| Default value: | False |
| Accept pipeline input: | False |
| Accept wildcard characters: | False |
Specifies a ServiceController object that represents the service to change. Enter a variable that contains the object, or type a command or expression that gets the object, such as a Get-Service command. You can use the pipeline to send a service object to Set-Service .
| Type: | ServiceController |
| Position: | 0 |
| Default value: | None |
| Accept pipeline input: | True |
| Accept wildcard characters: | False |
Specifies the service name of the service to be changed. Wildcard characters aren’t permitted. You can use the pipeline to send a service name to Set-Service .
| Type: | String |
| Aliases: | ServiceName, SN |
| Position: | 0 |
| Default value: | None |
| Accept pipeline input: | True |
| Accept wildcard characters: | False |
Returns a ServiceController object that represents the services that were changed. By default, Set-Service doesn’t generate any output.
| Type: | SwitchParameter |
| Position: | Named |
| Default value: | False |
| Accept pipeline input: | False |
| Accept wildcard characters: | False |
Specifies the SecurityDescriptor for the service in Sddl format.
| Type: | String |
| Aliases: | sd |
| Position: | Named |
| Default value: | None |
| Accept pipeline input: | False |
| Accept wildcard characters: | False |
Specifies the start mode of the service.
The acceptable values for this parameter are as follows:
- Automatic — The service is started or was started by the operating system, at system start-up. If an automatically started service depends on a manually started service, the manually started service is also started automatically at system startup.
- AutomaticDelayedStart — Starts shortly after the system boots.
- Disabled — The service is disabled and cannot be started by a user or application.
- InvalidValue — Has no effect. The cmdlet does not return an error but the StartupType of the service is not changed.
- Manual — The service is started only manually, by a user, using the Service Control Manager, or by an application.
| Type: | Microsoft.PowerShell.Commands.ServiceStartupType |
| Aliases: | StartMode, SM, ST, StartType |
| Accepted values: | Automatic, AutomaticDelayedStart, Disabled, InvalidValue, Manual |
| Position: | Named |
| Default value: | None |
| Accept pipeline input: | False |
| Accept wildcard characters: | False |
Specifies the status for the service.
The acceptable values for this parameter are as follows:
- Paused. Suspends the service.
- Running. Starts the service.
- Stopped. Stops the service.
| Type: | String |
| Accepted values: | Paused, Running, Stopped |
| Position: | Named |
| Default value: | None |
| Accept pipeline input: | False |
| Accept wildcard characters: | False |
Shows what would happen if Set-Service runs. The cmdlet isn’t run.
| Type: | SwitchParameter |
| Aliases: | wi |
| Position: | Named |
| Default value: | False |
| Accept pipeline input: | False |
| Accept wildcard characters: | False |
Inputs
System.ServiceProcess.ServiceController, System.String
You can use the pipeline to send a service object or a string that contains a service name to Set-Service .
Outputs
By default, Set-Service doesn’t return any objects. Use the PassThru parameter to output a ServiceController object.
Notes
This cmdlet is only available on Windows platforms.
Set-Service requires elevated permissions. Use the Run as administrator option.
Set-Service can only control services when the current user has permissions to manage services. If a command doesn’t work correctly, you might not have the required permissions.
To find a service’s service name or display name, use Get-Service . The service names are in the Name column and the display names are in the DisplayName column.