Linux arp command
On Linux operating systems, the arp command manipulates or displays the kernel’s IPv4 network neighbour cache. It can add entries to the table, delete one, or display the current content.
ARP stands for Address Resolution Protocol, which is used to find the address of a network neighbor for a given IPv4 address.
Installing arp
Arp is part of the net-tools package. For example, on systems that use APT for package management, it can be installed with apt-get:
Syntax
Modes
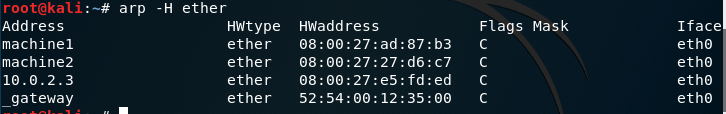
arp with no mode specifier prints the current content of the table. It is possible to limit the number of entries printed, by specifying a hardware address type, interface name or host address.
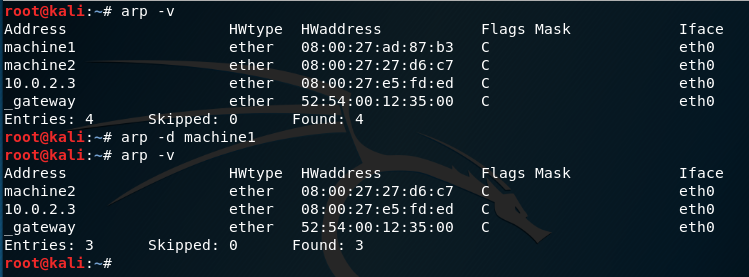
arp -d address deletes an ARP table entry. Root privilege is required to do this. The entry is found by IP address. If a hostname is given, it will be resolved before looking up the entry in the ARP table.
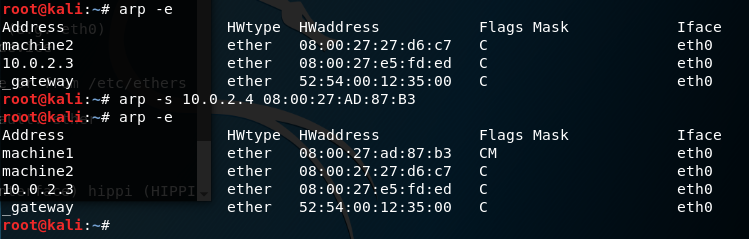
is used to set up a new table entry. The format of the hw_addr parameter is dependent on the hardware class, but for most classes one can assume that the usual presentation can be used. For the Ethernet class, this is 6 bytes in hexadecimal, separated by colons. When adding proxy arp entries (that is those with the publish («pub«) flag set a netmask may be specified to proxy arp for entire subnets. This is not good practice, but is supported by older kernels because it can be useful. If the temp flag is not supplied entries will be permanent stored into the ARP cache. To simplify setting up entries for one of your network interfaces, you can use the «arp -Ds address ifname» form. In that case the hardware address is taken from the interface with the specified name.
Options
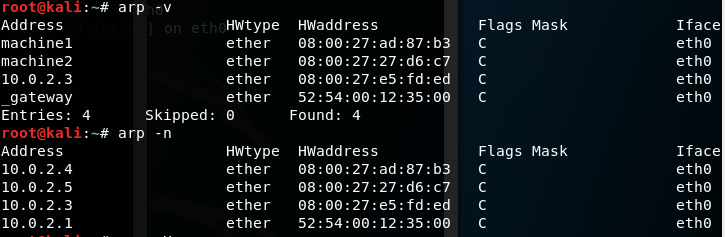
| -v, —verbose | Display information verbosely. |
| -n, —numeric | shows numerical addresses instead of trying to determine symbolic host, port or user names. |
| -H type, —hw-Type type | When setting or reading the ARP cache, this optional parameter tells arp which class of entries it should check. The default value of this parameter is ether (i.e., hardware code 0x01 for IEEE 802.3 10 Mbps Ethernet). Other values might include network technologies such as ARCnet (arcnet), PROnet (pronet), AX.25 (ax25) and NET/ROM (netrom). |
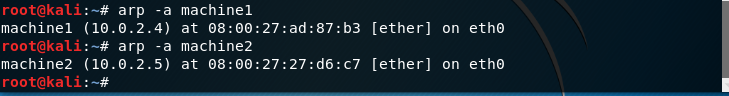
| -a [hostname], —all [hostname] | Displays the entries of the specified hosts. If the hostname parameter is not used, all entries display. Hostnames are displayed using alternate BSD-style output format (with no fixed columns). |
| -d hostname, —delete hostname | Remove any entry for the specified host. This can be used if the indicated host is brought down, for example. |
| -D, —use-device | Instead of a hw_addr, the given argument is the name of an interface. arp uses the MAC address of that interface for the table entry. This is usually the best option to set up a proxy ARP entry to yourself. |
| -e | Shows entries in default (Linux) style. |
| -i If, —device If | Select an interface. When dumping the ARP cache, only entries matching the specified interface will be printed. When setting a permanent or temp ARP entry this interface will be associated with the entry; if this option is not used, the kernel will guess based on the routing table. For pub entries, the specified interface is the interface on which ARP requests will be answered. NOTE: This has to be different from the interface that the IP datagrams will be routed. NOTE: As of kernel 2.2.0 it is no longer possible to set an ARP entry for an entire subnet. Linux instead does automagic proxy arp when a route exists and it is forwarding. Also, the dontpub option that is available for delete and set operations cannot be used with 2.4 and newer kernels. |
| -s hostname hw_addr, —set hostname | Manually create an ARP address mapping entry for host hostname with hardware address set to hw_addr class, but for most classes one can assume that the usual presentation can be used. For the Ethernet class, this is 6 bytes in hexadecimal, separated by colons. When adding proxy arp entries (that is those with the publish flag set) a netmask may be specified to proxy arp for entire subnets. This is not good practice, but is supported by older kernels because it can be useful. If the temp flag is not supplied entries will be permanent stored into the ARP cache. NOTE: As of kernel 2.2.0 it is no longer possible to set an ARP entry for an entire subnet. Linux instead does automagic proxy arp when a route exists and it is forwarding. |
| -f file name, —file file name | Similar to the -s option, only this time the address info is taken from file file name set up. The name of the data file is very often /etc/ethers, but this is not official. If no file name is specified /etc/ethers is used as default. The format of the file is simple; it only contains ASCII text lines with a hostname, and a hardware address separated by whitespace. Additionally, the pub, temp and netmask flags can be used. |
Notes
In all places where a hostname is expected, one can also enter an IP address in dotted-decimal notation.
As a special case for compatibility, the order of the hostname and the hardware address can be exchanged.
Each complete entry in the ARP cache will be marked with the C flag. Permanent entries are marked with M and published entries have the P flag.
Examples
Display network card and Ethernet connectivity.
Related commands
ifconfig — View or modify the configuration of network interfaces.
ip — Display and manipulate information about routing, devices, policy routing and tunnels.
netstat — Print information about network connections, routing tables, and more.
route — Display and manipulate the IP routing table.
Источник
Команда arp в Linux с примерами
Команда arp управляет системным ARP-кэшем. Это также позволяет полный дамп кэша ARP. ARP обозначает протокол разрешения адресов. Основной функцией этого протокола является преобразование IP-адреса системы в ее mac-адрес, и, следовательно, он работает между уровнем 2 (уровень канала передачи данных) и уровнем 3 (уровень сети).
Синтаксис:
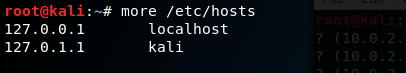
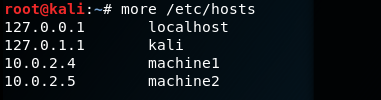
Пример: Здесь мы создали две машины с именем machine1 и machine2 с IP — адресом 10.0.2.4 и 10.0.2.5
- Скриншот хостов перед добавлением
Файл хостов после добавления машин
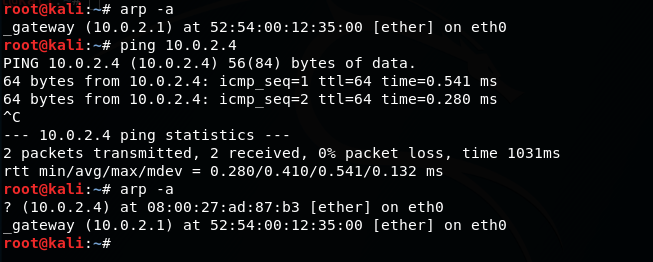
Теперь проверяю arp для всех
Параметры:
- -v, –verbose: эта опция отображает подробную информацию.
- -n, –numeric: эта опция показывает числовые адреса вместо символических имен хостов, портов или пользователей.
-H тип, -hw-тип, -t тип: сообщает arp, какой класс записей следует проверять. Значением по умолчанию является эфир. Список возможных типов оборудования (которые поддерживают ARP): пепел (Ash), эфир (Ethernet), ax25 (AMPR AX.25), netrom (AMPR NET / ROM), роза (AMPR ROSE), arcnet (ARCnet), dlci ( Frame Relay DLCI), fddi (Fibre Distributed Data Interface), hippi (HIPPI), irda (IrLAP), x25 (универсальный X.25), eui64 (универсальный EUI-64).
-a [hostname] –all: эта опция используется для отображения записей указанного хоста. Если ничего не пропущено, все записи будут отображаться.
-d hostname, –delete hostname: удаляет любую запись для указанного хоста. Если какой-либо хост не работает, нет необходимости сохранять его запись в кэше arp, поэтому эта команда используется для явного удаления этих записей пользователем.
-D, –use-device: использовать аппаратный адрес данного интерфейса.
Примечание. Это должно отличаться от интерфейса, на который будут перенаправляться дейтаграммы IP.
-s имя хоста hw_address: вручную создать запись сопоставления адресов ARP для имени хоста хоста с его mac-адресом как hw_address.
-f имя файла: работает так же, как и -s, но вместо того, чтобы давать записи вручную, он получает запись из файла, заданного в качестве параметра.
Некоторые полезные флаги:
- -C: Полная запись.
- -М: постоянная запись.
- -P: Опубликованная запись.
Некоторые полезные файлы, связанные с этими данными:
- / Proc / нетто / агр
- / и т.д. / сети
- / И т.д. / хосты /
- / и т.д. / простые эфиры
Источник
Проверка ARP-таблиц
Аргумент hostname может быть как именем, так и IP адресом в стандарте dotted quad.
Это показывает Ethernet-адреса vlager , vstout и vale .
При использовании опции -t Вы увидите информацию только о том типе аппаратных средств, который укажете. Это могут быть: ether , ax25 или pronet для Ethernet 10Mbps, AMPR AX.25 и IEEE 802.5 token ring, соответственно.
Опция -s используется, чтобы добавить Ethernet-адрес хоста к ARP-таблицам. Аргумент hwaddr определяет адрес аппаратных средств, который по умолчанию предполагается Ethernet-адресом, указанным как шесть шестнадцатиричных байт, разделяемых двоеточиями. Вы можете также устанавливать адреса для других типов аппаратных средств, используя опцию -t .
Одна из проблем, которая может потребовать, чтобы Вы вручную добавили IP-адрес к ARP-таблице, это когда по некоторым причинам ARP-запросы для удаленного хоста не доходят, например, когда есть сбой ARP-драйвера, или имеется другой хост в сети, который ошибочно опознает себя с IP-адресом другого хоста. Твердая установка IP-адреса в ARP-таблице также является мерой защиты себя от хостов в Вашем Ethernet, которые прикидываются кем-то другим.
Вызов arp с использованием ключа -d удаляет все ARP-записи, касающиеся данного хоста. Это может быть необходимо, чтобы вынудить интерфейс повторно получить Ethernet-адрес для данного IP. Это полезно, когда переконфигурированная система имеет неправильную ARP-информацию.
Опция -s может также использоваться, чтобы создать proxy ARP. Это специальная техника когда хост, скажем, gate действует как gateway для другого хоста, назовем его fnord , делая вид, что оба адреса относятся к тому же самому хосту, а именно, gate . Это делается так: на gate создается ARP-запись о fnord , которая указывает на его собственный Ethernet-интерфейс. Теперь, когда хост посылает ARP-запрос о fnord , gate будет возвращать ответ, содержащий собственный Ethernet-адрес. Спрашивающий хост будет посылать все пакеты gate , который перенаправит их к fnord .
Эта схема может быть необходима, например, когда Вы хотите работать с fnord с DOS-машины с нестандартным TCP, которое плохо работает с маршрутизацией. Когда Вы используете proxy ARP, DOS-машине будет казаться, что fnord находится в локальной подсети, так что ей не требуется что-либо знать относительно маршрутов и gateway.
Другое очень полезное применение proxy ARP, когда один из Ваших хостов действует как gateway к некоторому другому хосту только временно, например, по телефону. В предыдущем примере мы уже столкнулись с laptop vlite , который был связан с vlager через PLIP-связь только в небольшом промежутке времени. Конечно, это будет работать только, если адрес хоста, для которого Вы хотите обеспечить proxy ARP, находится в той же самой IP-подсети, что и Ваш gateway. Например, vstout мог бы быть proxy ARP для любого хоста из подсети Brewery ( 172.16.1.0 ), но не для хоста из подсети Winery ( 172.16.2.0 ).
Требуемые действия для обеспечения proxy ARP для fnord приведены ниже. Конечно, Ethernet-адрес должен быть от gate :
Источник
arp command in Linux with examples
arp command manipulates the System’s ARP cache. It also allows a complete dump of the ARP cache. ARP stands for Address Resolution Protocol. The primary function of this protocol is to resolve the IP address of a system to its mac address, and hence it works between level 2(Data link layer) and level 3(Network layer).
Syntax:
Example: Here we created two machines with name machine1 and machine2 with IP address 10.0.2.4 and 10.0.2.5
- Screenshot of hosts before adding
Addition of host
Hosts file after adding machines
Now checking arp for all
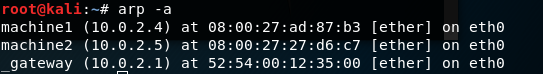
Options:
- -v, –verbose: This option shows the verbose information.
- -n, –numeric: This option shows numerical addresses instead of symbolic host, port or usernames.
-H type, –hw-type type, -t type: This tells arp which class of entries it should check for. Default value is ether. List of possible hardware types(which support ARP) are ash(Ash), ether(Ethernet), ax25(AMPR AX.25), netrom (AMPR NET/ROM), rose (AMPR ROSE), arcnet (ARCnet), dlci (Frame Relay DLCI), fddi (Fiber Distributed Data Interface), hippi (HIPPI), irda (IrLAP), x25 (generic X.25), eui64 (Generic EUI-64).
-a [hostname] –all: This option is used for showing entries of the specified host. If nothing is passed all entries will be displayed.
-d hostname, –delete hostname: Removes any entry for the specified host. If any host is down, there is no need of keeeping its entry in arp cache so this command is used to delete those entries explicitly by the user.
-D, –use-device: Use the given interface’s hardware address.
Note: This has to be different from the interface to which the IP datagrams will be routed.
-s hostename hw_address: Manually create an ARP address mapping entry for the host hostname with its mac address as hw_address.
-f filename: Works same as -s but instead of giving the entries manually, it takes entry from the file given as parameter.
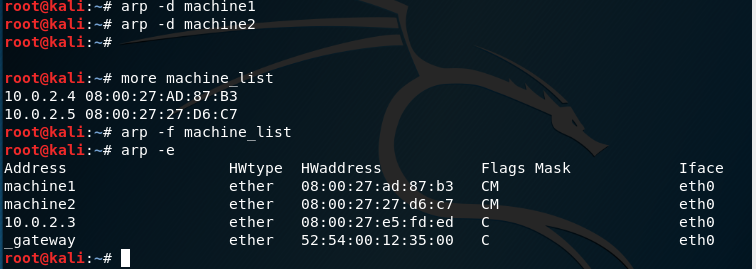
Some useful flags are:
- -C: Complete entry.
- -M: Permanent entry.
- -P: Published entry.
Some useful file related to these data are:
- /proc/net/arp
- /etc/networks
- /etc/hosts/
- /etc/ethers
Источник