- Узнаём данные S.M.A.R.T. в Linux. Контроль состояния HDD или SSD
- S.M.A.R.T.
- Contents
- Smartmontools
- smartctl
- Run a test
- View test results
- Generate table with attributes of all disks
- smartd
- daemon management
- Define the devices to monitor
- Notifying potential problems
- Power management
- Schedule self-tests
- Alert on temperature changes
- Complete smartd.conf example
- Console applications
- LINUX — Жизнь в консоли ЕСТЬ.
- Главное меню
- Последние статьи
- Счетчики
- SMART. Смотрим состояние жесткого диска.
- S.M.A.R.T. (англ. Self-Monitoring, Analysis and Reporting Technology) —
- А теперь немного о параметрах, выводимых программой.
- Критичные атрибуты:
- Некритичные атрибуты:
Узнаём данные S.M.A.R.T. в Linux. Контроль состояния HDD или SSD
Дата добавления: 07 июля 2012
S.M.A.R.T. (Self-Monitoring, Analisys and Reporting Technology) — это технология, предоставляющая пользователю различные данные о текущем состоянии жесткого диска или твердотельного накопителя. Анализируя данные S.M.A.R.T., пользователь может оценить состояние своих накопителей и решить, требуют ли они замены или ещё смогут работать долго и без сбоев.
Консольный способ: smartmontools
Узнать данные S.M.A.R.T. в чистом виде нам поможет утилита под названием smartmontools .
Приведем пример установки для дистрибутивов на основе Debian:
Количество атрибутов может отличаться в зависимости от модели диска.
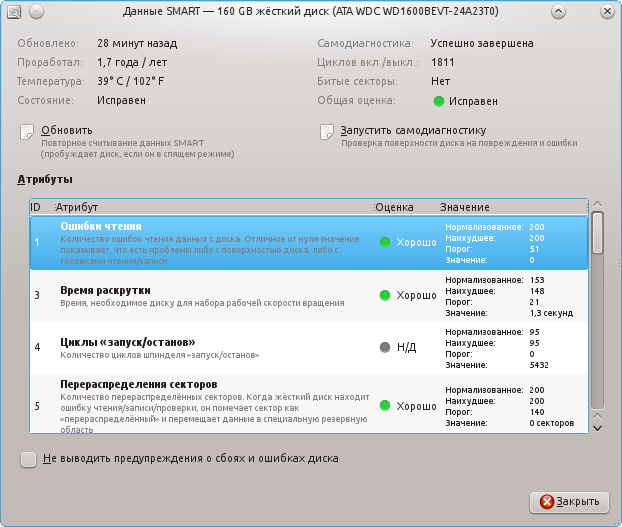
В этой таблице нам нужно смотреть на значение поля RAW_VALUE для нужного атрибута. Именно оно показывает текущее значение атрибута.
Наиболее важные показатели:
Raw_Read_Error_Rate — количество ошибок чтения. Ненулевое значение должно сильно насторожить, а большие значение и вовсе говорят о скором выходе диска из строя. Известно, что на дисках Seagate, Samsung (семейства F1 и более новые) и Fujitsu 2,5? большое значение в этом поле является нормальным. Для остальных же дисков в идеале значение должно быть равно нулю;
Spin_Up_Time — время раскрутки диска. Измеряется в миллисекундах т.е. в моём случае это 1.3 секунды. Чем меньше — тем лучше. Большие значения говорят о низкой отзывчивости;
Start_Stop_Count — количество циклом запуска/остановки шпинделя;
Reallocated_Sector_Ct — количество перераспределённых секторов. Большое значение говорит о большом количестве ошибок диска;
Seek_Error_Rate — количество ошибок позиционирования. Большое значение говорит о плохом состоянии диска;
Power_On_Hours — количество наработанных часов во включённом состоянии. По нему можно узнать сколько проработал диск во включённом состоянии. Довольно полезно, например, если покупать ноутбук с витрины и хочется узнать долго ли он там стоял;
Power_Cycle_Count — количество включений/выключений диска;
Spin_Retry_Count — количество попыток повторной раскрутки. Большое значение говорит о плохом состоянии диска;
Temperature_Celsius — температура диска в градусах Цельсия. При слишком высокой температуре диски могут быстрее выйти из строя;
Reallocated_Event_Count — количество операций перераспределения секторов;
Offline_Uncorrectable — количество неисправных секторов. Большое значение говорит о повреждённой поверхности.
Более наглядный графический способ: gnome-disk-utility
В графическом варианте и с описанием атрибутов, данные SMART представляет программа gnome-disk-utility . В русской локализации в меню она называется как «дисковая утилита». В английской локализации известна как «Disks».
Пример установки для дистрибутивов на основе Debian:
Запускаем программу. 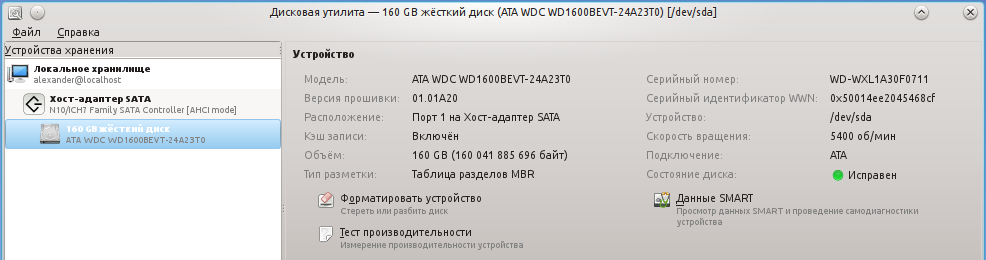
В поле «состояние диска» уже можно увидеть оценку состояния диска на основе данных S.M.A.R.T. Чтобы увидеть значение конкретных атрибутов нажимаем на кнопку «Данные SMART»:
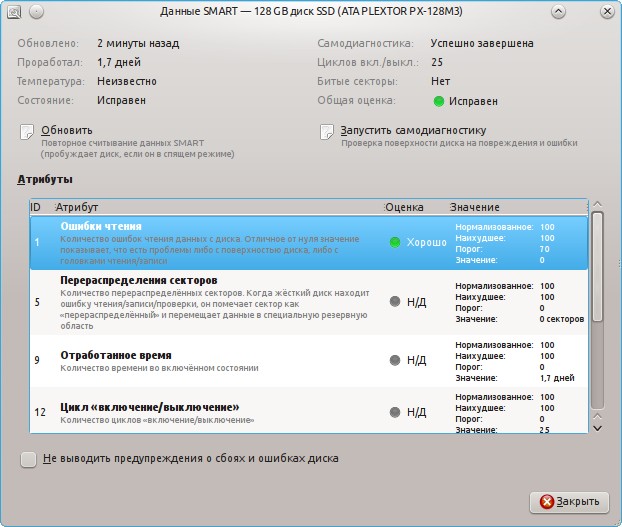
Пример данных о SSD (Твёрдотельном накопителе): 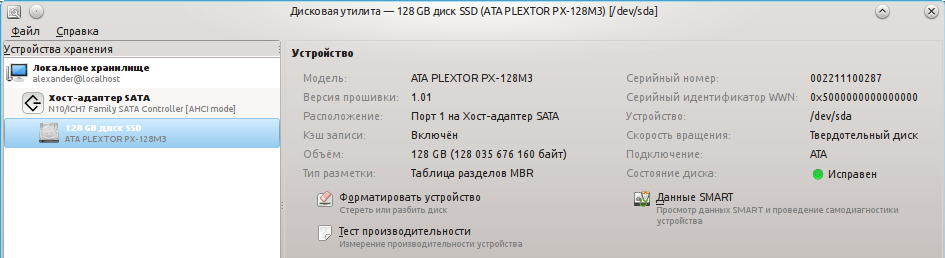
S.M.A.R.T.:
Здесь всё понятно и наглядно. Также присутствует описание атрибутов и оценка их показаний. Проблемные значения будут выделены красным цветом.
Источник
S.M.A.R.T.
S.M.A.R.T. (Self-Monitoring, Analysis, and Reporting Technology) is a supplementary component built into many modern storage devices through which devices monitor, store, and analyze the health of their operation. Statistics are collected (temperature, number of reallocated sectors, seek errors. ) which software can use to measure the health of a device, predict possible device failure, and provide notifications on unsafe values.
Contents
Smartmontools
The smartmontools package contains two utility programs for analyzing and monitoring storage devices: smartctl and smartd . Install the smartmontools package to use these tools.
SMART support must be available and enabled on each storage device to effectively use these tools. You can use #smartctl to check for and enable SMART support. That done, you can manually #Run a test and #View test results, or you can use #smartd to automatically run tests and email notifications.
smartctl
smartctl is a command-line tool that «controls the Self-Monitoring, Analysis and Reporting Technology (SMART) system built into most ATA/SATA and SCSI/SAS hard drives and solid-state drives.»
The -i / —info option prints a variety of information about a device, including whether SMART is available and enabled:
If SMART is available but not enabled, you can enable it:
You may need to specify a device type. For example, specifying —device=ata tells smartctl that the device type is ATA, and this prevents smartctl from issuing SCSI commands to that device.
Run a test
There are three types of self-tests that a device can execute (all are safe to user data):
- Short: runs tests that have a high probability of detecting device problems,
- Extended or Long: the test is the same as the short check but with no time limit and with complete disk surface examination,
- Conveyance: identifies if damage incurred during transportation of the device.
The -c / —capabilities flag prints which tests a device supports and the approximate execution time of each test. For example:
Use -t / —test= flag to run a test:
View test results
You can view a device’s overall health with the -H flag. «If the device reports failing health status, this means either that the device has already failed, or that it is predicting its own failure within the next 24 hours. If this happens […] get your data off the disk and to someplace safe as soon as you can.»
You can also view a list of recent test results and detailed information about a device:
Generate table with attributes of all disks

smartd
The smartd daemon monitors SMART statuses and emits notifications when something goes wrong. It can be managed with systemd and configured using the /etc/smartd.conf configuration file. The configuration file syntax is esoteric, and this wiki page provides only a quick reference. For more complete information, read the examples and comments within the configuration file, or read smartd.conf(5) .
daemon management
To start the daemon, check its status, make it auto-start on system boot and read recent log file entries, simply start/enable the smartd.service systemd unit.
smartd respects all the usual systemctl and journalctl commands.
Define the devices to monitor
To monitor for all possible SMART errors on all disks, the following setting must be added in the configuration file.
Note this is the default smartd configuration and the -a parameter, which is the default parameter, may be omitted.
To monitor for all possible SMART errors on /dev/sda and /dev/sdb , and ignore all other devices:
To monitor for all possible SMART errors on externally connected disks (USB-backup disks spring to mind) it is prudent to tell smartd the UUID of the device since the /dev/sdX of the drive might change during a reboot.
First, you will have to get the UUID of the disk to monitor: ls -lah /dev/disk/by-uuid/ now look for the disk you want to Monitor
I know that my USB disk attached to /dev/sde during boot. Now to tell smartd to monitor that disk simply use the /dev/disk/by-uuid/ path.
Note that you may additionally need -d removable for smartd to work.
Now your USB disk will be monitored even if the /dev/sdX path changes during reboot.
Notifying potential problems
To have an email sent when a failure or new error occurs, use the -m option:
To be able to send the email externally (i.e. not to the root mail account) a MTA (Mail Transport Agent) or a MUA (Mail User Agent) will need to be installed and configured. Common MUAs are msmtp and Postfix, but perhaps the easiest dma will suffice. Common MTAs are sendmail and Postfix. It is enough to simply configure S-nail if you do not want anything else, but you will need to follow these instructions.
The -M test option causes a test email to be sent each time the smartd daemon starts:
Emails can take quite a while to be delivered. To make sure you are warned immediately if your hard drive fails, you may also define a script to be executed in addition to the email sending:
To send an email and a system notification, put something like this into /usr/local/bin/smartdnotify :
If you are running a desktop environment, you might also prefer having a popup to appear on your desktop. In this case, you can use this script (replace X_user and X_userid with the user and userid running X respectively) :
This requires libnotify and a compatible desktop environment. See Desktop notifications for more details.
You can also put your custom scripts into /usr/share/smartmontools/smartd_warning.d/ :
This scripts notifies every logged in users on the system via libnotify.
This script requires libnotify and procps-ng and a compatible desktop environment.
You can execute your custom scripts with
Power management
If you use a computer under control of power management, you should instruct smartd how to handle disks in low power mode. Usually, in response to SMART commands issued by smartd, the disk platters are spun up. So if this option is not used, then a disk which is in a low-power mode may be spun up and put into a higher-power mode when it is periodically polled by smartd.
On some devices the -n does not work. You get the following error message in syslog:
As an alternative, you can use the -i option of smartd. It controls how often smartd spins the disks up to check their status. Default is 30 minutes. To change it create and edit /etc/default/smartmontools .
For more info see smartd(8) .
Schedule self-tests
smartd can tell disks to perform self-tests on a schedule. The following /etc/smartd.conf configuration will start a short self-test every day between 2-3am, and an extended self test weekly on Saturdays between 3-4am:
Alert on temperature changes
smartd can track disk temperatures and alert if they rise too quickly or hit a high limit. The following will log changes of 4 degrees or more, log when temp reaches 35 degrees, and log/email a warning when temp reaches 40:
Complete smartd.conf example
Putting together all of the above gives the following example configuration:
- DEVICESCAN smartd scans for disks and monitors all it finds
- -a monitor all attributes
- -o on enable automatic offline data collection
- -S on enable automatic attribute autosave
- -n standby,q do not check if disk is in standby, and suppress log message to that effect so as not to cause a write to disk
- -s . schedule short and long self-tests
- -W . monitor temperature
- -m . mail alerts
Console applications
- skdump — utility to monitor and manage SMART devices to monitor and report hard disk drive health.
http://0pointer.de/blog/projects/being-smart.html || libatasmart
iostat -x (from sysstat ) also provides some disk health metrics: in particular, high values in the f_await column mean that the disk does not respond quickly to requests, and might be failing.
Источник
LINUX — Жизнь в консоли ЕСТЬ.
Главное меню
Последние статьи
Счетчики
SMART. Смотрим состояние жесткого диска.
S.M.A.R.T. (англ. Self-Monitoring, Analysis and Reporting Technology) —
технология оценки состояния жёсткого диска встроенной аппаратурой самодиагностики, а также механизм предсказания времени выхода его из строя.
Ставим утилиту для просмотра SMART:
sudo su
apt-get install smartmontools
Смотрим названия жестких дисков в системе:
fdisk -l
Информация о диске, в том числе, поддерживает ли SMART:
smartctl -i /dev/sda
где /dev/sda «имя» диска
smartctl —smart=on /dev/sda
smartctl —all /dev/sda
А теперь немного о параметрах, выводимых программой.
Каждый атрибут имеет величину — Value. Value Изменяется в диапазоне от 0 до 255 (задается производителем). Низкое значение говорит о быстрой деградации диска или о возможном скором сбое. т.е. чем выше значение Value атрибута, тем лучше.
Raw Value — это значение атрибута во внутреннем формате производителя значение малоинформативно для всех кроме сервисманов.
Threshold — минимальное возможное значение атрибута, при котором гарантируется безотказная работа накопителя.
Если VALUE стало меньше THRESH — Атрибут считается failed и отображается в столбце WHEN_FAILED. При значении атрибута меньше Threshold очень вероятен сбой в работе или полный отказ.
WORST — минимальное нормализованное значение. Это минимальное значение которое достигалось с момента включения SMART на диске.
Атрибуты бывают критически важными (Pre-fail) и некритически важными (Old_age). Выход критически важного параметра за пределы Threshold фактический означает выход диска из строя, выход за переделы допустимых значений некритически важного параметра свидетельствует о наличии проблемы, но диск может сохранять свою работоспособность.
Критичные атрибуты:
Raw Read Error Rate — частота ошибок при чтении данных с диска, происхождение которых обусловлено аппаратной частью диска.
Spin Up Time — время раскрутки пакета дисков из состояния покоя до рабочей скорости. При расчете нормализованного значения (Value) практическое время сравнивается с некоторой эталонной величиной, установленной на заводе. Не ухудшающееся немаксимальное значение при Spin Up Retry Count Value = max (Raw равном 0) не говорит ни о чем плохом. Отличие времени от эталонного может быть вызвано рядом причин, например просадка по вольтажу блока питания.
Spin Up Retry Count — число повторных попыток раскрутки дисков до рабочей скорости, в случае если первая попытка была неудачной. Ненулевое значение Raw (соответственно немаксимальное Value) свидетельствует о проблемах в механической части накопителя.
Seek Error Rate — частота ошибок при позиционировании блока головок. Высокое значение Raw свидетельствует о наличии проблем, которыми могут являться повреждение сервометок, чрезмерное термическое расширение дисков, механические проблемы в блоке позиционирования и др. Постоянное высокое значение Value говорит о том, что все хорошо.
Reallocated Sector Count — число операций переназначения секторов. SMART в современных дисках способен произвести анализ сектора на стабильность работы «на лету» и в случае признания его сбойным, произвести его переназначение.
Некритичные атрибуты:
Start/Stop Count — полное число запусков/остановов шпинделя. Гарантировано мотор диска способен перенести лишь определенное число включений/выключений. Это значение выбирается в качестве Treshold. Первые модели дисков со скоростью вращения 7200 оборотов/мин имели ненадежный двигатель, могли перенести лишь небольшое их число и быстро выходили из строя.
Power On Hours — число часов проведенных во включенном состоянии. В качестве порогового значения для него выбирается паспортное время наработки на отказ (MTBF). Обычно величина MTBF огромна, и маловероятно, что этот параметр достигнет критического порога. Но даже в этом случае выход из строя диска совершенно не обязателен.
Drive Power Cycle Count — количество полных циклов включения-выключения диска. По этому и предыдущему атрибуту можно оценить, например, сколько использовался диск до покупки.
Temperatue — Здесь хранятся показания встроенного термодатчика. Температура имеет огромное влияние на срок службы диска (даже если она находится в допустимых пределах). Вернее имеет влияние не на срок службы диска а на частоту возникновения некоторых типов ошибок, которые влияют на срок службы.
Current Pending Sector Count — Число секторов, являющихся кандидатами на замену. Они не были еще определенны как плохие, но считывание их отличается от чтения стабильного сектора, так называемые подозрительные или нестабильные сектора.
Uncorrectable Sector Count — число ошибок при обращении к сектору, которые не были скорректированы. Возможными причинами возникновения могут быть сбои механики или порча поверхности.
UDMA CRC Error Rate — число ошибок, возникающих при передаче данных по внешнему интерфейсу. Могут быть вызваны некачественными кабелями, нештатными режимами работы.
Write Error Rate — показывает частоту ошибок происходящих при записи на диск. Может служить показателем качества поверхности и механики накопителя.
Источник