- Sockets in windows service
- Понятие windows sockets приложения
- Список сокетов приложений в Windows
- Как посмотреть сокеты приложений у вас на компьютере
- Как изменить время жизни сокета
- Как узнать PID приложения
- сокеты Sockets
- Getting Started with Winsock
- Advanced Winsock Samples
- Windows Sockets 2
- Purpose
- Developer audience
- Run-time requirements
- socket function (winsock2.h)
- Syntax
- Parameters
- Return value
- Remarks
- Notes for IrDA Sockets
- Example Code
Sockets in windows service
Добрый день, уважаемые посетители и читатели блога, недавно я на одном из форумов наткнулся на дискуссию, на тему того, что такое сокеты windows и как их посмотреть и подумал, что это неплохая тема для статьи. Подумал и написал :)). Думаю эта заметка будет полезна начинающим системным администраторам, в понимании того, как на транспортном уровне модели OSI найти проблему или проверить доступность приложения по номеру порта, хочу отметить, что эти знания фундаментальные, и их понимание заложит в вас отличную базу, для дальнейшей работы, на любом предприятии.
Понятие windows sockets приложения
Что такое сокет — это по сути область оперативной памяти, в которой на определенном сетевом порту (TCP/UDP) работает приложение, и именно оно прослушивает нужный порт. Какая задача стояла перед программистами, задача простая переместить информацию из оперативной памяти одного компьютера, в оперативную память другого компьютера. Дальше это может быть представлено как:
Номер сокета Windows, это номер ячейки оперативной памяти к которому привязано приложение. Приложение привязавшись к некой области оперативной памяти начинает туда писать данные и сокет из этой области памяти начинает мелкими пакетами по 65 кбайт, начинает передавать в сеть на другое устройство. На другой стороне эти кусочки, так же помещаются в ОЗУ, желательно в той же последовательности, и сокет с той стороны начинает их разбирать, и представлять пользователю из какого то приложения.
Список сокетов приложений в Windows
У меня стоит операционная систем Windows 8.1, показывать я буду все на ней, в прошлый раз мы кстати в ней лечили баг, что был не найден run vbs. Для того, чтобы посмотреть какие сокеты соответствуют каким приложениям и каким TCP/UDP портам, вы должны перейти в директорию
и отыскать там файл services, он будет без расширения, но его можно открыть правой кнопкой мыши через обычный блокнот, у меня это будет notepad++.
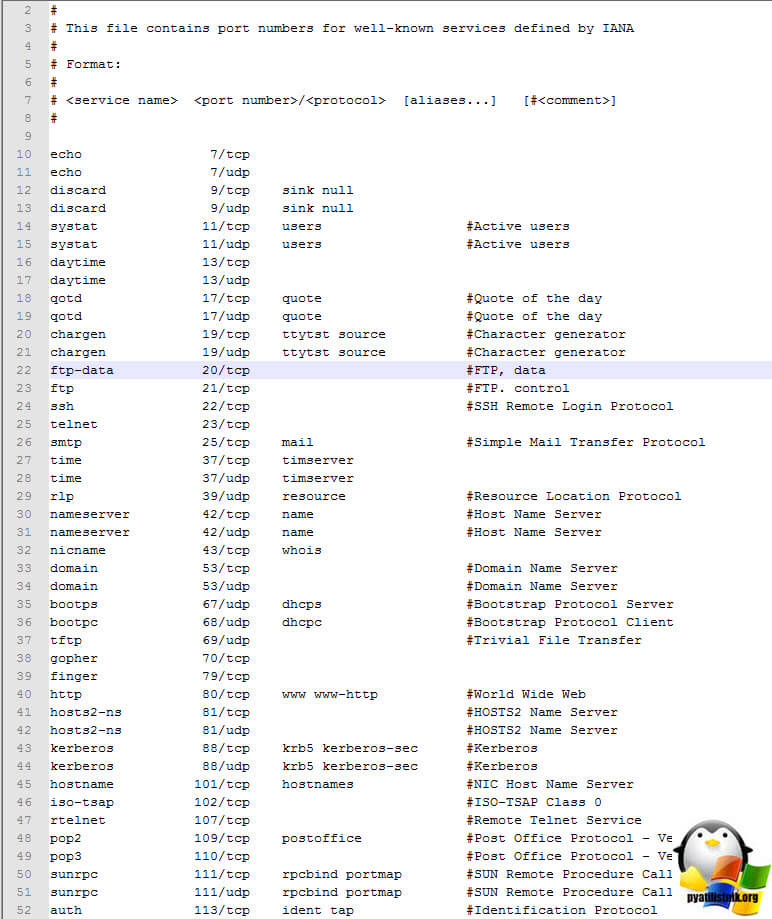
Открыв данный файл вы увидите название службы (приложения) номер сокета (TCP/UDP) и описание. Для примера видно, что сервер ftp работает по портам 20 и 21. По сути тут системе и задаются стандарты по которым должны работать службы.
Как посмотреть сокеты приложений у вас на компьютере
Тут два метода которыми я пользуюсь. Представим себе ситуацию, что вы установили некое приложение, все работает пытаетесь на него попасть с другого компьютера по сети, но не можете. Отключаете брандмауэр на том компьютере, и все начинает работать, вывод блокируется какой то порт этого приложения. Его вычислить поможет нам две утилиты, первая из командной строки, а вторая имеет удобный графический интерфейс.
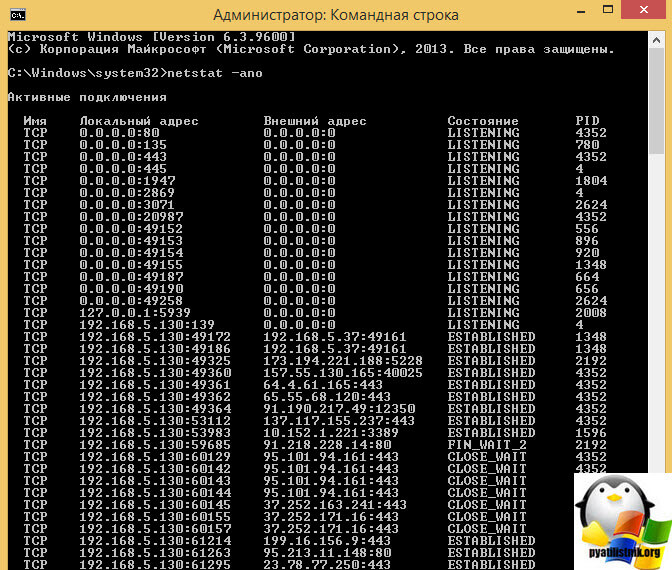
Более подробно про утилиту netstat и ее использование читайте по ссылке. В итоге вы получите сводную таблицу, в которой будет вот, что интересно:
- Тип протокола — TCP или UDP
- Адрес отправителя с указанием портов
- Адрес получателя с указанием портов
- Состояние — либо слушает либо установил соединение и закрыто
- PID это номер идентифицирующий приложение
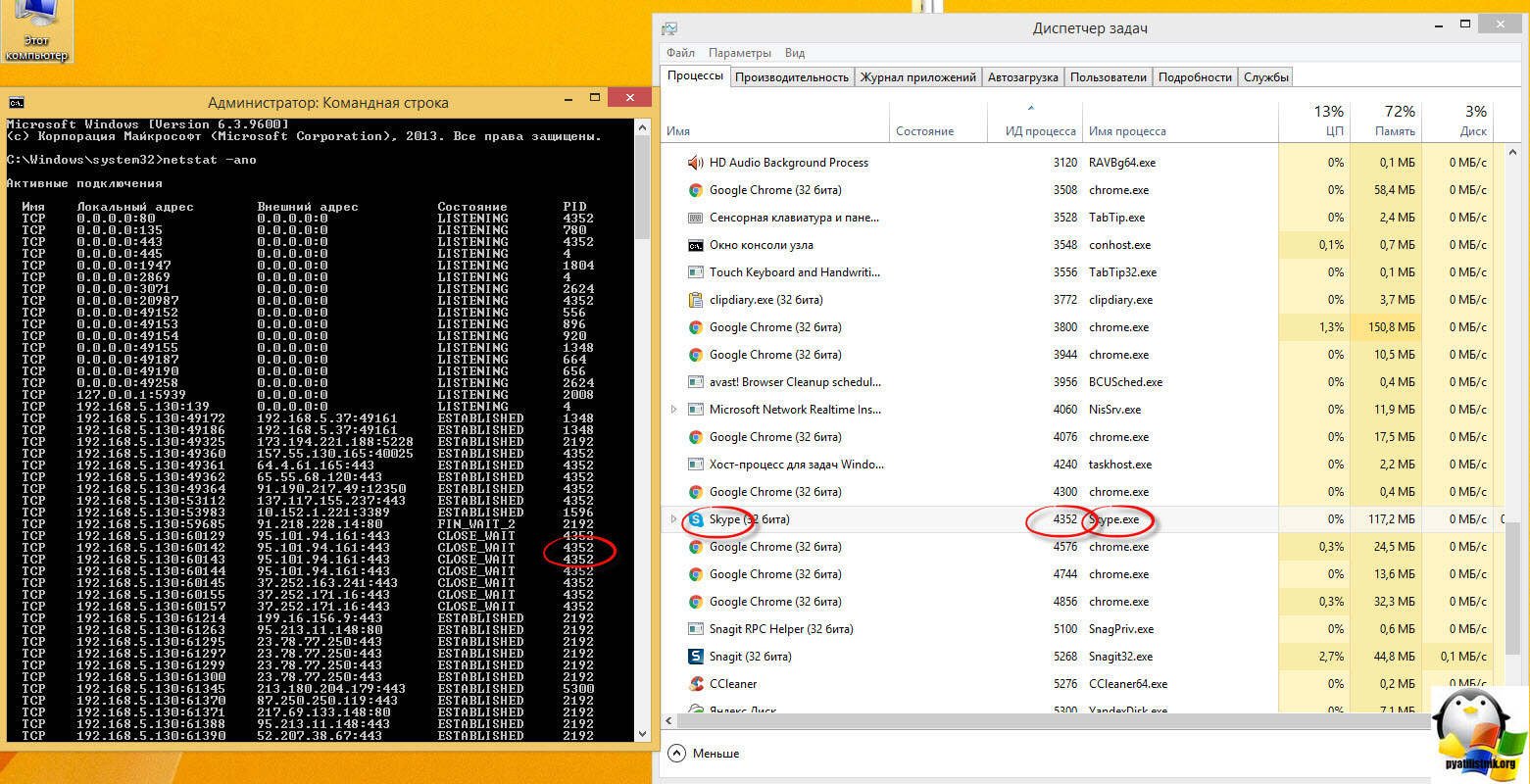
Как видите в примере у меня много сессий по 443 и 80 порту по сути это браузер Google Chrome.
Приложение заняв сокет, уже не позволит на нем же открыться другому приложению, Сокет живет минут 10.
Как изменить время жизни сокета
Для того, чтобы в операционной системе Windows изменить TTL или как его еще называют время жизни сокета, вам необходимо воспользоваться реестром. Открываете редактор реестра Windows 8.1. Переходите в раздел
Там есть ключ TcpTimedWaitDelay, если его нет то нужно его создать. Укажите нужное вам десятичное значение. TcpTimedWaitDelay — Этот параметр определяет интервал времени, в течение которого подключение находится в состоянии TIME_WAIT, прежде чем будет закрыто. Пока подключение находится в состоянии TIME_WAIT, пара сокетов не может быть использована повторно (это т. н. «состояние 2MSL»). Согласно документу RFC793, данное значение должно в два раза превышать максимальное время жизни пакета в сети.
Как узнать PID приложения
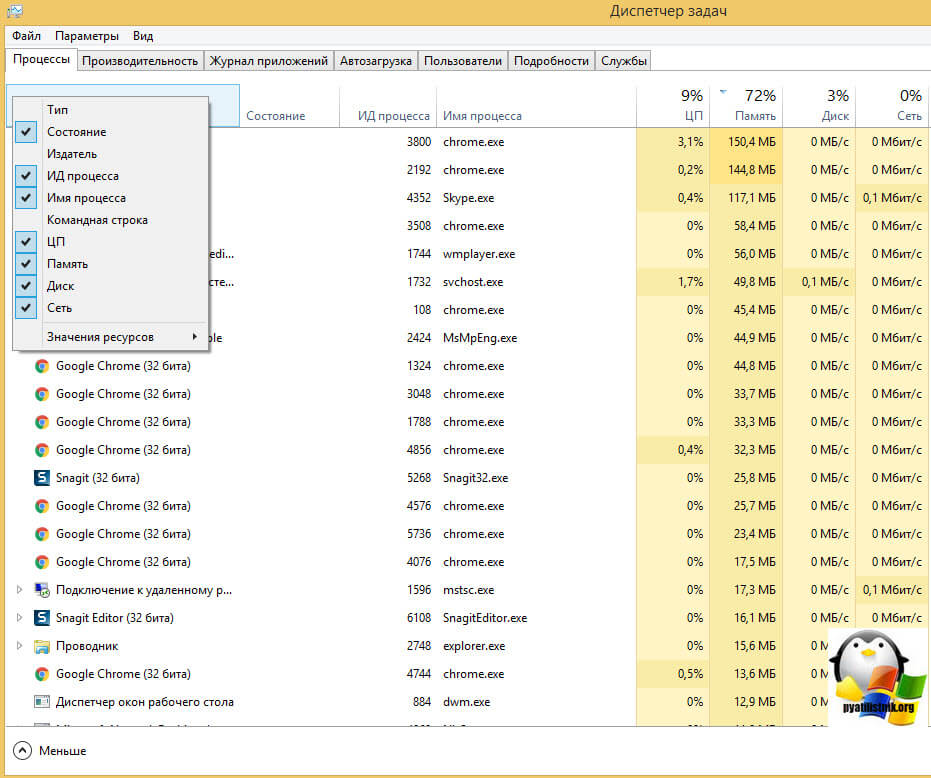
Для того, чтобы узнать PID приложения в Windows, вам нужно в области пуск кликнуть правой кнопкой мыши и из контекстного меню выбрать Диспетчер задач
В диспетчере задач, найдите поле ИД процесса .если его не будет то добавьте.
Теперь давайте смотреть, в правой части я вижу приложение skype и оно имеет PID 4352, смотрим в левой части экрана и видим порты и Ip адрес, которые слушает данной приложение.
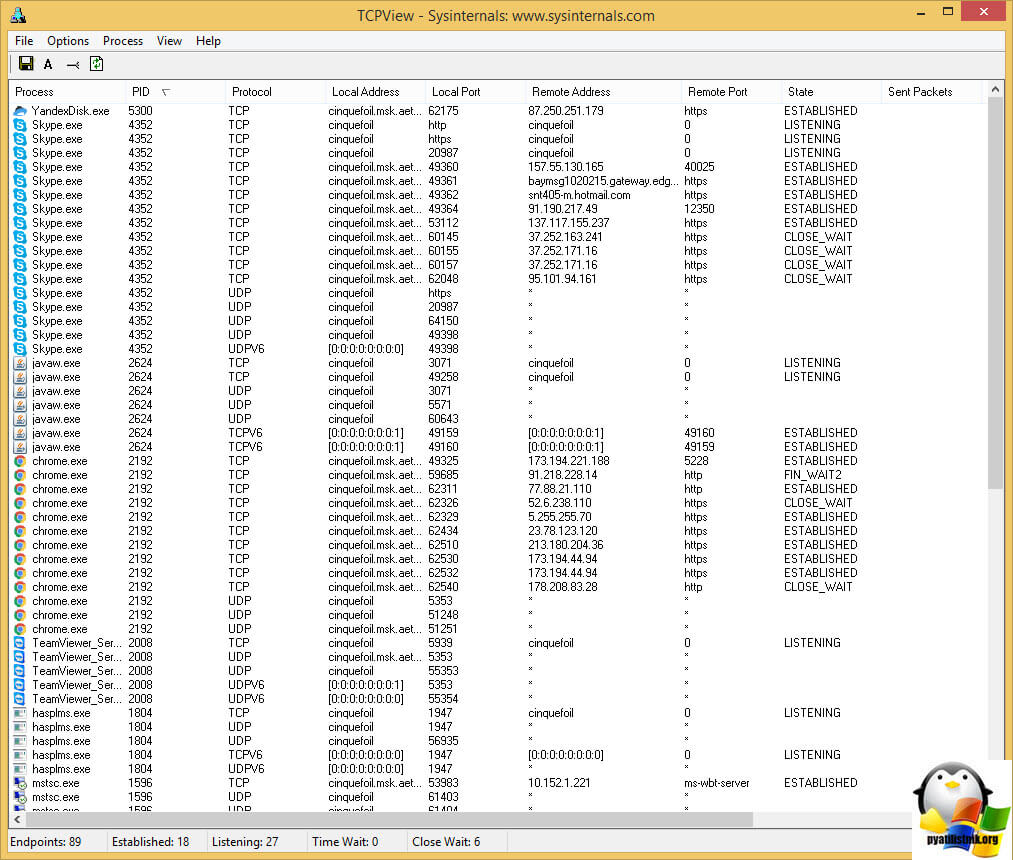
Ну и еще есть утилита TCPView, про нее я уже отдельно писал. Утилита бесплатная и имеет графический интерфейс, запустив ее вы сразу видите кому какой PID принадлежит. Так же видно все сокеты и их состояния.
Думаю, у вас теперь не должно быть вопроса, что такое сокеты windows и как их посмотреть, всем спасибо за прочтение.
сокеты Sockets
Пространство имен System.Net.Sockets содержит управляемую реализацию интерфейса Windows Sockets. The System.Net.Sockets namespace contains a managed implementation of the Windows Sockets interface. Все остальные классы для доступа к сети в пространстве имен System.Net основываются на этой реализации сокетов. All other network-access classes in the System.Net namespace are built on top of this implementation of sockets.
Класс Socket платформы .NET Framework — это версия служб сокетов на основе управляемого кода, предоставляемая API Winsock32. The .NET Framework Socket class is a managed-code version of the socket services provided by the Winsock32 API. В большинстве случаев методы класса Socket просто маршалируют данные в аналогичные собственные методы Win32 и осуществляют все необходимые проверки безопасности. In most cases, the Socket class methods simply marshal data into their native Win32 counterparts and handle any necessary security checks.
Класс Socket поддерживает два основных режима: синхронный и асинхронный. The Socket class supports two basic modes, synchronous and asynchronous. В синхронном режиме при вызове функций, выполняющих сетевые операции (например, Send и Receive), ожидается завершение операций, прежде чем управление возвращается вызывающей программе. In synchronous mode, calls to functions that perform network operations (such as Send and Receive) wait until the operation completes before returning control to the calling program. В асинхронном режиме вызовы возвращаются немедленно. In asynchronous mode, these calls return immediately.
Getting Started with Winsock
The following is a step-by-step guide to getting started with Windows Sockets programming. It is designed to provide an understanding of basic Winsock functions and data structures, and how they work together.
The client and server application that is used for illustration is a very basic client and server. More advanced code examples are included in the samples included with the Microsoft Windows Software Development Kit (SDK).
The first few steps are the same for both client and server applications.
The following sections describe the remaining steps for creating a Winsock client application.
The following sections describe the remaining steps for creating a Winsock server application.
The complete source code for these basic examples.
Advanced Winsock Samples
Several more advanced Winsock client and server samples are included with the Windows SDK. By default, the Winsock sample source code is installed in the following directory by the Windows SDK for WindowsВ 7:
C:\Program Files\Microsoft SDKs\Windows\v7.0\Samples\NetDs\winsock
On earlier versions of the Windows SDK, the version number in the above path would change. For example, the Winsock sample source code is installed in the following default directory by the Windows SDK for WindowsВ Vista
C:\Program Files\Microsoft SDKs\Windows\v6.0\Samples\NetDs\winsock
The more advanced samples listed below in order from higher to lower performance are found in the following directories:
This directory contains three sample programs that use I/O completion ports. The programs include a Winsock server (iocpserver) that uses the WSAAccept function, a Winsock server (iocpserverex) that uses the AcceptEx function, and a simple multithreaded Winsock client (iocpclient) used to test either of these servers. The server programs support multiple clients connecting via TCP/IP and sending arbitrary sized data buffers which the server then echoes back to the client. For convenience, a simple client program, iocpclient, was developed to connect and continually send data to the server to stress it using multiple threads. Winsock servers that use I/O completion ports provide the most performance capability.
This directory contains a sample server program that uses overlapped I/O. The sample program uses the AcceptEx function and overlapped I/O to handle multiple asynchronous connection requests from clients effectively. The server uses the AcceptEx function to multiplex different client connections in a single-threaded Win32 application. Using overlapped I/O allows for greater scalability.
This directory contains a basic sample program that demonstrates the use of the WSAPoll function. The combined client and server program are non-blocking and use the WSAPoll function to determine when it is possible to send or receive without blocking. This sample is more for illustration and is not a high-performance server.
This directory contains three basic sample programs that demonstrate the use of multiple threads by a server. The programs include a simple TCP/UDP server (simples), a TCP-only server (simples_ioctl) that uses the select function in a Win32 console application to support multiple client requests, and a client TCP/UDP program (simplec) for testing the servers. The servers demonstrates the use of multiple threads to handle multiple client requests. This method has scalability issues since a separate thread is created for each client request.
This directory contains a basic sample server and client program. The server demonstrates the use of either non-blocking accept using the select function or asynchronous accept using the WSAAsyncSelect function. This sample is more for illustration and is not a high-performance server.
Windows Sockets 2
Purpose
Windows Sockets 2 (Winsock) enables programmers to create advanced Internet, intranet, and other network-capable applications to transmit application data across the wire, independent of the network protocol being used. With Winsock, programmers are provided access to advanced MicrosoftВ® WindowsВ® networking capabilities such as multicast and Quality of Service (QoS).
Winsock follows the Windows Open System Architecture (WOSA) model; it defines a standard service provider interface (SPI) between the application programming interface (API), with its exported functions and the protocol stacks. It uses the sockets paradigm that was first popularized by Berkeley Software Distribution (BSD) UNIX. It was later adapted for Windows in Windows Sockets 1.1, with which Windows Sockets 2 applications are backward compatible. Winsock programming previously centered around TCP/IP. Some programming practices that worked with TCP/IP do not work with every protocol. As a result, the Windows Sockets 2 API adds functions where necessary to handle several protocols.
Developer audience
Windows Sockets 2 is designed for use by C/C++ programmers. Familiarity with Windows networking is required.
Run-time requirements
Windows Sockets 2 can be used on all Windows platforms. Where certain implementations or capabilities of Windows Sockets 2 platform restrictions do exist, they are clearly noted in the documentation.
socket function (winsock2.h)
The socket function creates a socket that is bound to a specific transport service provider.
Syntax
Parameters
The address family specification. Possible values for the address family are defined in the Winsock2.h header file.
On the Windows SDK released for WindowsВ Vista and later, the organization of header files has changed and the possible values for the address family are defined in the Ws2def.h header file. Note that the Ws2def.h header file is automatically included in Winsock2.h, and should never be used directly.
The values currently supported are AF_INET or AF_INET6, which are the Internet address family formats for IPv4 and IPv6. Other options for address family (AF_NETBIOS for use with NetBIOS, for example) are supported if a Windows Sockets service provider for the address family is installed. Note that the values for the AF_ address family and PF_ protocol family constants are identical (for example, AF_INET and PF_INET), so either constant can be used.
The table below lists common values for address family although many other values are possible.
| Af | Meaning | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF_UNSPEC 0 | The address family is unspecified. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| AF_INET 2 | The Internet Protocol version 4 (IPv4) address family. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| AF_IPX 6 | The IPX/SPX address family. This address family is only supported if the NWLink IPX/SPX NetBIOS Compatible Transport protocol is installed. This address family is not supported on WindowsВ Vista and later. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| AF_APPLETALK 16 | The AppleTalk address family. This address family is only supported if the AppleTalk protocol is installed. This address family is not supported on WindowsВ Vista and later. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| AF_NETBIOS 17 | The NetBIOS address family. This address family is only supported if the Windows Sockets provider for NetBIOS is installed. The Windows Sockets provider for NetBIOS is supported on 32-bit versions of Windows. This provider is installed by default on 32-bit versions of Windows. The Windows Sockets provider for NetBIOS is not supported on 64-bit versions of windows including WindowsВ 7, Windows ServerВ 2008, WindowsВ Vista, Windows ServerВ 2003, or WindowsВ XP. The Windows Sockets provider for NetBIOS only supports sockets where the type parameter is set to SOCK_DGRAM. The Windows Sockets provider for NetBIOS is not directly related to the NetBIOS programming interface. The NetBIOS programming interface is not supported on WindowsВ Vista, Windows ServerВ 2008, and later. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| AF_INET6 23 | The Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6) address family. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| AF_IRDA 26 | The Infrared Data Association (IrDA) address family. This address family is only supported if the computer has an infrared port and driver installed. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| AF_BTH 32 | The Bluetooth address family. This address family is supported on WindowsВ XP with SP2 or later if the computer has a Bluetooth adapter and driver installed. The type specification for the new socket. Possible values for the socket type are defined in the Winsock2.h header file. The following table lists the possible values for the type parameter supported for Windows Sockets 2:
В In Windows Sockets 2, new socket types were introduced. An application can dynamically discover the attributes of each available transport protocol through the WSAEnumProtocols function. So an application can determine the possible socket type and protocol options for an address family and use this information when specifying this parameter. Socket type definitions in the Winsock2.h and Ws2def.h header files will be periodically updated as new socket types, address families, and protocols are defined. In Windows Sockets 1.1, the only possible socket types are SOCK_DGRAM and SOCK_STREAM. The protocol to be used. The possible options for the protocol parameter are specific to the address family and socket type specified. Possible values for the protocol are defined in the Winsock2.h and Wsrm.h header files. On the Windows SDK released for WindowsВ Vista and later, the organization of header files has changed and this parameter can be one of the values from the IPPROTO enumeration type defined in the Ws2def.h header file. Note that the Ws2def.h header file is automatically included in Winsock2.h, and should never be used directly. If a value of 0 is specified, the caller does not wish to specify a protocol and the service provider will choose the protocol to use. When the af parameter is AF_INET or AF_INET6 and the type is SOCK_RAW, the value specified for the protocol is set in the protocol field of the IPv6 or IPv4 packet header. The table below lists common values for the protocol although many other values are possible.
|