- Use dictation to talk instead of type on your PC
- Dictation commands
- Dictating letters, numbers, punctuation, and symbols
- Dictate text using Speech Recognition
- Use the Speak text-to-speech feature to read text aloud
- Add Speak to the Quick Access Toolbar
- Use Speak to read text aloud
- How to configure and use Text-to-Speech in Windows XP and in Windows Vista
- IN THIS TASK
- Summary
- References
Use dictation to talk instead of type on your PC
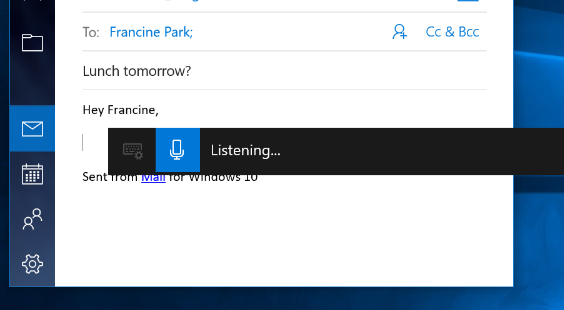
Use dictation to convert spoken words into text anywhere on your PC with Windows 10. Dictation uses speech recognition, which is built into Windows 10, so there’s nothing you need to download and install to use it.
To start dictating, select a text field and press the Windows logo key + H to open the dictation toolbar. Then say whatever’s on your mind. To stop dictating at any time while you’re dictating, say “Stop dictation.”
If you’re using a tablet or a touchscreen, tap the microphone button on the touch keyboard to start dictating. Tap it again to stop dictation, or say «Stop dictation.»
To find out more about speech recognition, read Use voice recognition in Windows 10. To learn how to set up your microphone, read How to set up and test microphones in Windows 10.
To use dictation, your PC needs to be connected to the internet.
Dictation commands
Use dictation commands to tell you PC what to do, like “delete that” or “select the previous word.”
The following table tells you what you can say. If a word or phrase is in bold, it’s an example. Replace it with similar words to get the result you want.
Clear a selection
Clear selection; unselect that
Delete the most recent dictation result or currently selected text
Delete that; strike that
Delete a unit of text, such as the current word
Move the cursor to the first character after a specified word or phrase
Go after that; move after word; go to the end of paragraph; move to the end of that
Move the cursor to the end of a unit of text
Go after word; move after word; go to the end of that; move to the end of paragraph
Move the cursor backward by a unit of text
Move back to the previous word; go up to the previous paragraph
Move the cursor to the first character before a specified word or phrase
Go to the start of the word
Move the cursor to the start of a text unit
Go before that; move to the start of that
Move the cursor forward to the next unit of text
Move forward to the next word; go down to the next paragraph
Moves the cursor to the end of a text unit
Move to the end of the word; go to the end of the paragraph
Enter one of the following keys: Tab, Enter, End, Home, Page up, Page down, Backspace, Delete
Tap Enter; press Backspace
Select a specific word or phrase
Select the most recent dictation result
Select a unit of text
Select the next three words; select the previous two paragraphs
Turn spelling mode on and off
Start spelling; stop spelling
Dictating letters, numbers, punctuation, and symbols
You can dictate most numbers and punctuation by saying the number or punctuation character. To dictate letters and symbols, say «start spelling.» Then say the symbol or letter, or use the ICAO phonetic alphabet.
To dictate an uppercase letter, say “uppercase” before the letter. For example, “uppercase A” or “uppercase alpha.” When you’re done, say “stop spelling.”
Here are the punctuation characters and symbols you can dictate.
at symbol; at sign
Pound symbol; pound sign; number symbol; number sign; hash symbol; hash sign; hashtag symbol; hashtag sign; sharp symbol; sharp sign
Dollar symbol; dollar sign; dollars symbol; dollars sign
Percent symbol; percent sign
And symbol; and sign; ampersand symbol; ampersand sign
Asterisk; times; star
Open paren; left paren; open parenthesis; left paren
Close paren; right paren; close parenthesis; right parenthesis
Dictate text using Speech Recognition
You can use your voice to dictate text to your Windows PC. For example, you can dictate text to fill out online forms; or you can dictate text to a word-processing program, such as WordPad, to type a letter.
When you speak into the microphone, Windows Speech Recognition converts your spoken words into text that appears on your screen.
To dictate text
Open Speech Recognition by clicking the Start button 
Say «start listening» or click the Microphone button to start the listening mode.
Open the program you want to use or select the text box you want to dictate text into.
Say the text that you want dictate.
There are several ways to correct mistakes made during dictation. You can say «correct that» to correct the last thing you said. To correct a single word, say «correct» followed by the word that you want to correct. If the word appears more than once, all instances will be highlighted and you can choose the one that you want to correct. You can also add words that are frequently misheard or not recognized by using the Speech Dictionary.
To use the Alternates panel dialog box
Open Speech Recognition by clicking the Start button 
Say «start listening» or click the Microphone button to start the listening mode.
Do one of the following:
To correct the last thing you said, say «correct that.»
To correct a single word, say «correct» followed by the word that you want to correct.
In the Alternates panel dialog box, say the number next to the item you want, and then «OK.»
Note: To change a selection, in the Alternates panel dialog box, say «spell» followed by the number of the item you want to change, and then «OK.»
To use the Speech Dictionary
Open Speech Recognition by clicking the Start button 
Say «start listening» or click the Microphone button to start the listening mode.
Say «open Speech Dictionary.»
Do any of the following:
To add a word to the dictionary, click or say Add a new word, and then follow the instructions in the wizard.
To prevent a specific word from being dictated, click or say Prevent a word from being dictated, and then follow the instructions in the wizard.
To correct or delete a word that is already in the dictionary, click or say Change existing words, and then follow the instructions in the wizard.
Note: Speech Recognition is available only in English, French, Spanish, German, Japanese, Simplified Chinese, and Traditional Chinese.
Use the Speak text-to-speech feature to read text aloud
Speak is a built-in feature of Word, Outlook, PowerPoint, and OneNote. You can use Speak to have text read aloud in the language of your version of Office.
Text-to-speech (TTS) is the ability of your computer to play back written text as spoken words. Depending upon your configuration and installed TTS engines, you can hear most text that appears on your screen in Word, Outlook, PowerPoint, and OneNote. For example, if you’re using the English version of Office, the English TTS engine is automatically installed. To use text-to-speech in different languages, see Using the Speak feature with Multilingual TTS.
To learn how to configure Excel for text-to-speech, see Converting text to speech in Excel.
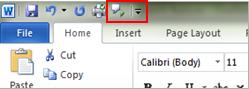
Add Speak to the Quick Access Toolbar
You can add the Speak command to your Quick Access Toolbar by doing the following in Word, Outlook, PowerPoint, and OneNote:
Next to the Quick Access Toolbar, click Customize Quick Access Toolbar .
Click More Commands.
In the Choose commands from list, select All Commands.
Scroll down to the Speak command, select it, and then click Add.
Use Speak to read text aloud
After you have added the Speak command to your Quick Access Toolbar, you can hear single words or blocks of text read aloud by selecting the text you want to hear and then clicking the Speak icon on the Quick Access Toolbar.
How to configure and use Text-to-Speech in Windows XP and in Windows Vista
IN THIS TASK
Summary
Text-to-Speech (TTS) capabilities for a computer refers to the ability to play back text in a spoken voice. This article describes how to configure and use text-to-speech in Windows XP and in Windows Vista.
TTS is the ability of the operating system to play back printed text as spoken words. An internal driver, called a TTS engine, recognizes the text and using a synthesized voice chosen from several pre-generated voices, speaks the written text. A TTS engine is installed with the operating system. Additional engines are also available through third-party manufacturers. These engines often use a certain jargon or vocabulary; for example, a vocabulary specializing in medical or legal terminology. They can also use different voices allowing for regional accents such as British English, or speak a different language altogether such as German, French, or Russian.
The Text-to-Speech tab in the Speech tool in Control Panel presents the options for each TTS engine. See the individual Help topics for specific help. In addition to the general options, each engine can have a different set of specific features. For that reason, not all the resulting dialog boxes will look the same. It is possible that no special features have been included and some of the properties buttons will not have an associated dialog box.
NOTE: This article assumes that you use Classic View in Control Panel. To change views, follow these steps:
Click Start, and then click Control Panel.
In Control Panel, click Switch to Classic View or Switch to Category View.
Speakers vary greatly in design and purpose. Consult the speaker manual for hardware and software specifics. However, most models can be installed in a similar fashion.
To set up speakers, follow these steps:
Locate the sound connections and connect the speaker jack to the computer. Most computers use an internal sound card and often the connections are in the back of the computer. These are a series of connections the same size and diameter as the speaker jack. In many cases there are two sound out connections:
One will be labeled as a line-out connection. Most speakers that require a separate power supply (such as an electrical (AC) adapter or batteries) should use this connection. It is also used to export amplified sound to recording devices including recordable CDs and tape cassette systems.
The other connection is for the non-powered speakers. Because the signal is boosted by the computer, powered speakers may be damaged if connected.
Plug the speaker into the proper connection.
To test the connection, follow these steps:
Click Start, click Control Panel, and then double-click Speech.
On the Text-to-Speech tab, click Preview Voice to hear the currently selected voice. The text is spoken and the words are highlighted as they are spoken. If the speakers are working properly, you will hear the spoken words.
If you do not hear sound after you connect the speakers, see the «Possible Text-to-Speech Problems» section of this article for troubleshooting procedures.
To select an audio output device, follow these steps:
Click Start, click Control Panel, and then double-click Speech.
On the Text-to-Speech tab, click Audio Output.
Select either Use preferred audio output device or Use this audio output device.
Use preferred audio device sets the output device as the default for the system. Select this option if you want to use the same output device for speech as all other sound for the system. It is also the default option for Speech properties. Often, computers will have only one output device, such as a pair of speakers. The default device is designated in the appropriate sounds or multimedia properties in Control Panel for each operating system. Additional information for the specific panel is available through the associated Help files.
Use this audio output device allows you to select another device for speech programs only. The drop-down list is active if other devices are available. In this drop-down list, select the device that you want. This does not change the default device for other audio programs. For example, you may want all speech output to go through your headset rather than the speakers.
By default, this option is disabled. However, other speech engines may include advanced properties for audio line out options. If so, Audio Output will be available. Follow instructions on the screen or those documented separately for the specific engine.
To set up audio output device options, follow these steps:
Click Start, click Control Panel, and then double-click Speech.
On the Text-to-Speech tab, click Audio Output.
Follow the instructions presented on the screen.
To determine the selected Text-to-Speech voice, follow these steps:
Click Start, click Control Panel, and then double-click Speech.
On the Text-to-Speech tab, the displayed name in the Voice selectiondrop-down list is the currently active voice.
Click Preview Voice to hear the active voice. The text is spoken and the words are highlighted as they are spoken.
To preview the Text-to-Speech voice, follow these steps:
Click Start, click Control Panel, and then double-click Speech.
On the Text-to-Speech tab, the displayed name in the Voice selectiondrop-down list is the active voice.
Click Preview Voice to hear the currently selected voice. The text is spoken and the words are highlighted as they are spoken.
During playback, Preview Voice will change to Stop. Click Stop to interrupt the voice playback.
NOTE:You can change the text to be read by the Preview Voice by highlighting the text and typing in new text. These changes are not permanent and when you reopen Speech properties or select a different voice, the text will reset to the default.
To change the Text-to-Speech voice or engine, follow these steps:
Click Start, click Control Panel, and then double-click Speech.
On the Text-to-Speech tab, the name displayed in the Voice selection drop-down list is the active voice.
Click the active voice inside the drop-down list, or use the arrow to display a list of available voices.
Click a new voice to select it.
The newly selected voice speaks the text in Preview Voice box.
Click OK or Apply to accept the new voice.
A Text-to-Speech voice is closely associated with a particular speech engine. It may not be clear from the displayed name which language a voice is using. After selecting a speech engine or voice, test the voice and language by clicking Preview Voice.
The language or voices supported by a speech engine may not be obvious from the engine’s displayed name. Refer to the specific user’s guide for detailed information about the engine. This includes not only the language supported, but also the lexicon purpose. The lexicon purpose indicates whether it is a general grammar or jargon specific to a profession such as legal or medical.
Microsoft does not provide additional speech engines (voices), but a number of third-party products are available that support the new Microsoft Speech API. For information on these products, visit the following Microsoft Web site:
To change the Text-to-Speech voice rate, follow these steps:
Click Start, click Control Panel, and then double-click Speech.
Select the Text-to-Speech tab.
Move the Voice speed slider to change the rate of the Text-to-Speech voice. By default, it is set to Normal.
Click Preview Voice to hear the currently selected voice at the new rate. The text is spoken and the words are highlighted as they are spoken.
To adjust the volume output levels, follow the procedure below. Note that not all devices support this option in the same way. Some devices will not support volume control and the Volume button will be unavailable. Other devices may use their own display. In those cases, follow the instructions presented on the screen or documented separately with the engine.
Click Start, click Control Panel, and then double-click Speech.
On the Text-to-Speech tab, click Audio Output, and then click Volume.
A volume control mixer will be displayed. Adjust the appropriate device to the required level.
Narrator is a Text-to-Speech utility for users who are blind or have impaired vision. Narrator reads what is displayed on your screen: the contents of the active window, menu options, or the text that you type.
Narrator is designed to work with the Notepad, WordPad, Control Panel programs, Microsoft Internet Explorer, the Windows desktop, and Windows Setup. Narrator may not read words aloud correctly in other programs.
Narrator has a number of options that allow you to customize the way screen elements are read.
You can have new windows, menus, or shortcut menus read aloud when they are displayed.
You can have typed characters read aloud.
You can have the mouse pointer follow the active item on the screen.
You can adjust the speed, volume, or pitch of the voice.
The accessibility tools included with Windows are intended to provide a minimum level of functionality for users with special needs. Most users with disabilities will need utility programs with more advanced functionality for daily use.
Narrator is not available for all languages and is only supported on the English version of Windows XP and Windows Vista.
Start Narrator by using one of the following methods:
Click Start, point to Programs, point to Accessories, point to Accessibility, and then click Narrator.
Press CTRL+ESC, press R, type
narrator, and then press ENTER.
In the Narrator dialog box, select the Announce events on screencheck box.
Press CTRL+ESC, press R, type
narrator, and then press ENTER.
Select the Read typed characters check box.
Press CTRL+ESC, press R, type
narrator, and then press ENTER.
Select the Move mouse pointer to the active item check box.
To read an entire window, click the window and then press CTRL+SHIFT+SPACEBAR.
To get information about the current item, press CTRL+SHIFT+ENTER.
To get a more detailed description of an item, press CTRL+SHIFT+INSERT.
To read the title bar of a window, press ALT+HOME.
To read the status bar of a window, press ALT+END.
To read the contents of an edit field, press CTRL+SHIFT+ENTER, or use the arrow keys.
To silence the speech, press CTRL.
To switch to another program, press ALT+TAB.
To switch to the next button or tool, press TAB. To go back, press SHIFT+TAB.
To select an item from a drop-down list, use the arrow keys.
To select a check box or option button, press SPACEBAR.
To open Utility Manager, press the Windows logo key+U.
Press CTRL+ESC, press R, type
narrator, and then press ENTER. Click Voice.
In the Voice Settings dialog box, select the voice options that you want to change:
To change the speed of the voice, click a number in the
Speed box.
To change the volume of the voice, click a number in the Volume box.
To change the pitch of the voice, click a number in the
Pitch box.
Note: When you change voice settings, it may take from a few seconds to a minute before the new settings take effect.
You may find it useful to run Narrator minimized (after you have set the options in Narrator), because you do not need to see the Narrator dialog box when Narrator is running.
Press CTRL+ESC, press R, type
narrator, and then press ENTER.
Select the Start Narrator minimized check box.
To determine if Text-to-Speech is working properly, use the following tests.
Click Start, click Control Panel, and then double-click Speech.
On the Text-to-Speech tab, click Preview Voice. The text in Preview Voice should be spoken audibly with each word highlighted in turn. If so, TTS and the speakers are working. If you cannot hear the Preview Voice and see words highlighted as they are spoken, see «Possible Text-to-Speech Problems» section of this article for troubleshooting solutions.
If you do not hear speech after testing the system, consider the following:
The speaker volume is not turned up or is muted. Some speakers have external controls for volume and muting. Make sure the volume is turned up sufficiently or that muting is off.
The speakers may not be selected as the current output device. On the Text-to-Speech tab, click Audio Output to make sure that the speakers are selected.
The speakers might not be connected properly. Consult the speaker hardware documentation for additional information. Make certain that the sound card for the computer is also properly seated and installed, and that the correct drivers are available. See «Set Up Speakers» for additional connection information.
The Text-to-Speech engine may be corrupted. To test for corruption, switch to another engine. See the «Changing the TTS voice or engine» section of this article. If another engine is working properly, reinstall the specific engine from the original source. If no engine is working properly, reinstall the speech engine from the original source or CD.
References
For additional information about using speech in Windows XP, click the article numbers below to view the articles in the Microsoft Knowledge Base:
306537 How to Install and Configure Speech Recognition in Windows
306901 How to Use Speech Recognition in Windows XP
278927 WD2002: Part 1: Speech and Handwriting Recognition Frequently Asked Questions