- Изучаем команды linux: split
- 1. Введение
- 2. Часто используемые опции
- 3. Разрезание файла на части заданного размера
- 4. Разрезание файла на заданное количество частей
- 5. Использование числовых суффиксов
- 6. Восстановление исходного файла
- 7. Разрезание архивов tar на лету
- 8. Заключение
- How to Split Large Text File into Smaller Files in Linux
- Split
- Split Examples
- Split a file into multiple pieces by default usage
- Split the file, based upon the number of lines
- Split a large file into 500MB files
- Split a large file into 200MB files with the given prefix
- Split the file and name it with numbers
- Csplit
- Csplit Examples
- Split files based on the number of lines
- Split files using regular expressions
- Split files with the given prefix
- Split a file by suppressing a line that matches the input pattern
- Customize the number of digits in the output files names
- Forcing csplit to save the output file in case of error
- Wrapping up
- 11 Useful Split Command Examples for Linux Systems
- Example: 1) Split File into Pieces
- Example: 2) Split Command with verbose option
- Example: 3) Split files with customize line numbers (-l)
- Example: 4) Split files with file size using option -b
- Example: 5) Create Split files with numeric suffix instead of alphabetic (-d)
- Example: 6) Split file with Customize Suffix
- Example: 7) Generate n chunks output files with split command (-n)
- Example: 8) Prevent Zero Size Split output files with option (-e)
- Example:9) Create Split output files of customize suffix length (-a option)
- Example: 10) Split ISO file and merge it into a single file.
- Example: 11) Verify the Integrity of Merge file using md5sum utility
Изучаем команды linux: split
1. Введение
Если вы не слышали о команде split, вы многое потеряли. Как можно понять из ее названия, эта команда может помочь вам разделить файл на несколько меньших файлов. split работает с любыми файлами, как текстовыми, так и бинарными. Это очень полезно, если ваш файл не помещается на флешку, или вам нужно отправить большой файл по электронной почте. Вы также можете разделять большие текстовые файлы, такие как логи, на несколько частей заданного размера. В данной статье описан синтакис и применение команды split.
2. Часто используемые опции
-b, —bytes=SIZE
Эта опция задает размер выводимых файлов.
-d, —numeric-suffixes
использовать цифровые суффиксы вместо алфавитных
-n, —number=CHUNKS
задает количество выводимых файлов
3. Разрезание файла на части заданного размера
Если не используется опция suffix, по умолчанию команда split будет разделять файлы на части, название которых будет начинаться с x, за которым будут следовать еще два символа в алфавитном порядке. Например, первый файл будет называться xaa, за которым будет идти xab, xac, а последний файл будет называться xzz. Это значит, что в данном случае вы можете разбить свой файл не более чем на 676 частей (26×26). Возьмем для примера файл размером 10 Мб:
Теперь мы можем разбить этот файл на части размером 1 Мб с помощью опции -b:
4. Разрезание файла на заданное количество частей
Также может возникнуть ситуация, когда нам нужно разбить файл на определенное количество частей. В приведенном ниже примере мы разрезаем наш файл размером 10 Мб на максимум три части с помощью опции -n:
5. Использование числовых суффиксов
Команда split позволяет создавать файлы с числовыми суффиксами вместо символьных. Приведенная ниже команда создает файл для каждого символа в строке «linuxcareer.com». Секрет заключается в том, что мы разрезаем файл, задавая размер части в байтах, а 1 байт эквивалентен 1 символу. Также вместо символьных мы используем числовые суффиксы:
6. Восстановление исходного файла
Разрезать файл легко, но как собрать его обратно? Допустим, у нас есть какой-либо ISO-образ, и мы хотим разделить его пополам.
Теперь мы разрезаем образ пополам с помощью опции -n:
Мы можем восстановить исходный файл ubuntu-12.04.1-server-amd64.iso, используя команду cat и оператор перенаправления STDOUT:
Чтобы убедиться, что файл restored-ubuntu-12.04.1-server-amd64.iso восстановлен корректно и представляет собой точную копию оригинального файла ubuntu-12.04.1-server-amd64.iso, мы используем команду md5sum для создания контрольной суммы обоих файлов:
Как вы можете видеть, восстановленный файл является точной копией исходного, так как их контрольные суммы совпадают.
7. Разрезание архивов tar на лету
Теперь, когда мы ознакомились с основами, рассмотрим более сложный пример.
В приведенном ниже примере мы архивируем директорию /tmp/Software. Однако вместо создания архива мы разрежем его на лету с помощью команды split.
Как вы можете видеть, наш архив диретории /tmp/Software разрезан на части с максимальным размером 2 Мб. Далее мы восстановим исходную директорию:
8. Заключение
Как вы можете видеть, при использовании операционной системы GNU/Linux вы ограничены только своим воображением и навыками, а не размером вашего кошелька. В данной статье описаны только основы работы с командой split. Узнать больше вы можете с помощью команды:
Источник
How to Split Large Text File into Smaller Files in Linux
Linux has several utilities for breaking down large files into small files. Split and csplit are two of the popular commands which are used for this purpose. These utilities will help to break down big log files and even archive files to make it into a smaller size. This will make convenient to split large files into smaller sizes so that it fits on smaller media storage devices like USB to meet our purpose. By this technique, we can even speed up network file transfers, because parallel transfers of small files are usually faster.
In this tutorial, I’ll explain more on how to use these split and csplit utilities to break-down large files in Linux.
Split
To split large files into smaller files, we can use this command utility in Linux.
You can replace filename with the name of the large file you wish to split. And «prefix» with the name you wish to give the small output files. You can exclude [options], or replace it with either of the following:
The split command will give each output file it creates the name prefix with an extension tacked to the end that indicates its order. By default, the split command adds aa to the first output file, proceeding through the alphabet to zz for subsequent files. By default, most systems use x as the prefix.
Split Examples
Split command splits the file into n lines per file and names the files as PREFIXaa, PREFIXab, PREFIXac, and so on. By default the PREFIX is x , and the number of lines is 1000 lines per file.
Split a file into multiple pieces by default usage
I’ve my log file namely system log with 1099 lines, let’s see the status of my log file after splitting it using this command.
The command splits the log file into two files xaa and xab, with the first one having 1000 lines and dumps the leftover in the second file.
Split the file, based upon the number of lines
We can split the file into multiple pieces based on the number of lines using -l option. Here, I’m splitting my system log file with 1099 lines into smaller files with 200 lines each. Let’s see the commands for the same:
You can see that the command has split my log file into five smaller files with 200 lines each and the last one with the leftover.
Split a large file into 500MB files
You can use the option -b to specify the required size limit to split the files. Please see this command which I used for splitting my 1GB Apache log file into two 500MB files each.
Split a large file into 200MB files with the given prefix
You can use the option -b to specify the 200M file size and the required prefix as the second argument. Please see the command which I used to split my 1GB Apache log to 200MB files with a prefix named split.log below:
In this example, you can see that my log files are broken down into 200MB files with my required prefix.
Split the file and name it with numbers
You can use the option -d to name the files with number suffixes as 00, 01, 02 .. and so on, instead of aa, ab, ac. Please see the command which I used to split my 1GB Apache log to 200MB files with a prefix named log and add numbers to the suffix using the option -d instead of alphabets below:
You can see the manual page of split command using the command man split to see more information.
Csplit
Csplit is another command utility which divides single files into multiple files determined by context lines.
The files created by csplit normally have names of the form
xxnumber
where number is a two digit decimal number which begins at zero and it increments by one for each new file that csplit creates.
csplit also displays the size, in bytes, of each file that it creates as output.
Csplit Examples
By default, the files that csplit produces in output have ‘xx’ as the prefix and the numbers produced in the output are the byte count for the files the command produced.
Split files based on the number of lines
I have a file which contains 8 lines with the domain names, and my requirement is to split that file at the fourth line, then this can be done by passing ‘4’ as a command line argument after the command and file name.
By passing 4 as a command-line argument, this command splits our domainslist file at the 4th line. The numbers produced in the output are the byte count for the files the command produced. Apparently, two files were produced in the output, namely xx00 and xx01.
Split files using regular expressions
We can use regular expressions with the csplit command. For example, in the previous case, if you want the command to repeat the pattern one more time, then you can do this using the following command:
In this case, we can get three output files.
You can use the asterisk wildcard <*>to tell csplit to repeat your split as many times as possible.
Split files with the given prefix
By default, csplit spilts files and produces the output files to have xx as the prefix. However, if you want, you can change that default prefix using the option -f in the command line with a required prefix.
For example, the following command will produce files having ‘domain’ as prefix.
Split a file by suppressing a line that matches the input pattern
This csplit command provides an option to suppress lines that match the input pattern. The option in question is —suppress-matched .
For example, the following command splits our file at line 4 (xx00 will contain upto line 3, while xx11 will contain rest of the lines excluding line 4).
Customize the number of digits in the output files names
By default, the number of digits that follow the prefix in the output filename is 2. We can use this option -n to customize the number of digits following the prefix in the output file names. For example, if you want to have names like xx001, you can use the command line option which requires the input number signifying the number of digits like -n 3 as below:
Forcing csplit to save the output file in case of error
By default, csplit removes the output files created in case of any error situation. However, if you want to forcefully save this output file by using the -k option in the command. Please check this example to see the difference in the execution of this command with and without -k option.
By default, csplit removes the output files created in case of any error situation. However, we can forcefully save this output file by using the ‘-k’ option in the command. Please check this example to see the difference in the execution of this command with and without -k option. On this first example, the command is meant to split our file ‘domainslist’ on line 3 and repeat the command twice like that which means it should split the second file too at line 3 and should repeat it once again. But since our source file has only eight lines, after the first split it repeats once but unable to iterate twice due to the insufficient range. Hence, no output files are produced due to this error.
But when we executed the same command with this option -k, the output files were not deleted. Please see the result below:
You can check the man page for this tool using man csplit to get more information about this.
Wrapping up
These command-line utilities may not be required for a Linux user on daily basis, but this is one of the important utility which will be helpful for you in your server administration. I hope this article explained all the basic options and uses for these tools. Please post your valuable comments and suggestions on this.
Источник
11 Useful Split Command Examples for Linux Systems
As the name suggests ‘split‘ command is used to split or break a file into the pieces in Linux and UNIX systems. Whenever we split a large file with split command then split output file’s default size is 1000 lines and its default prefix would be ‘x’.
In this article we will discuss 11 useful split command examples for Linux Users. Apart from this we will also discuss how split files can be merge or reassembled into a single file. Syntax for split command:
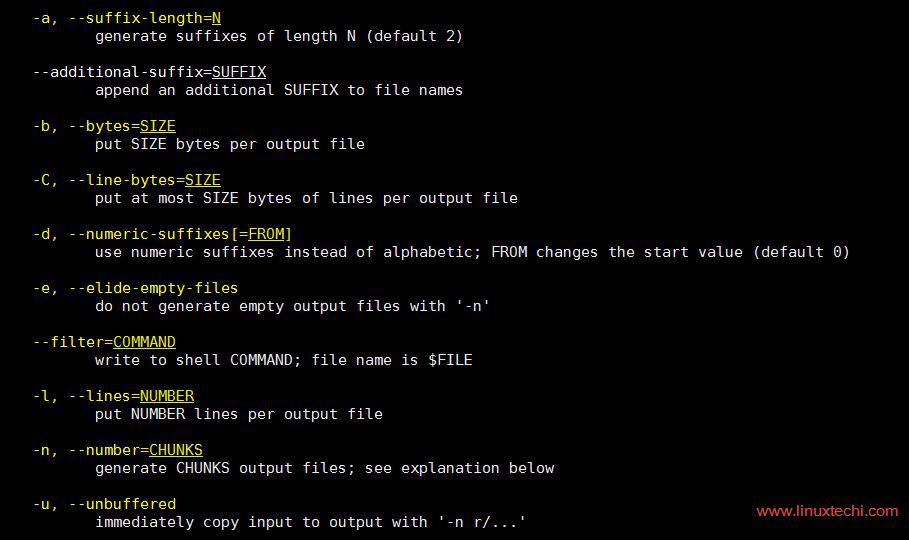
Some of the important options of split command is shown below:
Example: 1) Split File into Pieces
Let’s assume we have file name with tuxlap.txt, Use below split command to break into the pieces
As we can see the above output ‘tuxlab.txt‘ is split into two pieces with the name ‘xaa’ and ‘xab’.
Example: 2) Split Command with verbose option
We can run split command in verbose mode with option ‘–verbose‘, example is shown below:
Example: 3) Split files with customize line numbers (-l)
Let’s suppose we want to split a file with customize line numbers, let say I want max 200 lines per file.
To achieve this, use ‘-l’ option in split command.
Verify the lines of each file using below command
Example: 4) Split files with file size using option -b
Using Split command we can split a file with file size. Use the following syntax to split files with size in bytes, KB , MB and GB
# split -b nK
# split -b nM
# split -b nG
Split file based on bytes:
Split file based on KB:
Split file based on MB:
Split file based on GB:
Example: 5) Create Split files with numeric suffix instead of alphabetic (-d)
In the above examples we have seen that split command output files are created with alphabetic suffix like xaa, xab….. xan , Use ‘-d’ option with split command to create split output files with numeric suffix like x00, x01, … x0n
Example: 6) Split file with Customize Suffix
With split command we can create split output files with customize suffix. Let’s assume we want to create split output files with customize suffix
Syntax:
Example: 7) Generate n chunks output files with split command (-n)
Let’s suppose we want to split an iso file into 4 chunk output files. Use ‘-n’ option with split command limit the number of split output files.
Verify the Split out files using ll command.
Example: 8) Prevent Zero Size Split output files with option (-e)
There can be some scenarios where we split a small file into a large number of chunk files and zero size split output files can be created in such cases, so to avoid zero size split output file, use the option ‘-e’
Example:9) Create Split output files of customize suffix length (-a option)
Let’s suppose we want to split an iso file and where size of each split output file is 500MB and suffix length is to be 3. Use the following split command:
Example: 10) Split ISO file and merge it into a single file.
Let’s suppose we have a Windows Server ISO file of size 4.2 GB and we are unable to scp this file to remote server because of its size.
To resolve such type of issues we can split the ISO into n number of pieces and will copy these pieces to remote sever and on the remote server we can merge these pieces into a single file using cat command,
View the split output files using ll command,
Now scp these files to remote server and merge these files into a single using cat command
Example: 11) Verify the Integrity of Merge file using md5sum utility
As per Example 10, once the split output files are merged into a single file, then we can check the integrity of actual & merge file with md5sum utility. Example is shown below:
As per the above output, it is confirm that integrity is maintained and we can also say split file are successfully restored to a single file.
That’s all from this article, If you like these examples then please do share your valuable feedback and comments in the comments section below.
Read Also : 16 Echo Command Examples in Linux
Источник