- ИТ База знаний
- Полезно
- Навигация
- Серверные решения
- Телефония
- Корпоративные сети
- Руководство по команде SSH в Linux с примерами
- Установка клиента OpenSSH
- Как получить доступ к удаленному серверу
- Укажите имя пользователя для SSH-подключения
- Используйте другой номер порта для SSH-соединения
- Генерация ключей SSH с помощью SSH Keygen
- Копировать открытый ключ SSH
- Копирование файла удаленно через SSH с помощью SCP
- Редактировать файл конфигурации SSH
- Перезапустить службу SSH
- Выполнение команды на удаленном сервере с локального компьютера
- Параметры командной строки SSH
- leommoore / linux_ssh_basics.md
- SSH Command — Usage, Options, Configuration
- Contents
- SSH Command in Linux
- Other SSH Commands
- Using the Linux client
- Specifying a different user name
- Executing remote commands on the server
- SSH client configuration file
- Configuring public key authentication
- Configuring port forwarding
- SSH command line options
- A little history
ИТ База знаний
Курс по Asterisk
Полезно
— Узнать IP — адрес компьютера в интернете
— Онлайн генератор устойчивых паролей
— Онлайн калькулятор подсетей
— Калькулятор инсталляции IP — АТС Asterisk
— Руководство администратора FreePBX на русском языке
— Руководство администратора Cisco UCM/CME на русском языке
— Руководство администратора по Linux/Unix
Навигация
Серверные решения
Телефония
FreePBX и Asterisk
Настройка программных телефонов
Корпоративные сети
Протоколы и стандарты
Руководство по команде SSH в Linux с примерами
Про Secure Shell
SSH (Secure Shell) — это сетевой протокол, который обеспечивает безопасное удаленное соединение между двумя системами. Системные администраторы используют утилиты SSH для управления компьютерами, копирования или перемещения файлов между системами. Поскольку SSH передает данные по зашифрованным каналам, безопасность находится на высоком уровне.
Онлайн курс по Linux
Мы собрали концентрат самых востребованных знаний, которые позволят тебе начать карьеру администратора Linux, расширить текущие знания и сделать уверенный шаг к DevOps
Установка клиента OpenSSH
Есть много SSH-клиентов, бесплатных и платных, и OpenSSH является наиболее широко используемым клиентом. Он доступен на всех основных платформах, включая Linux, OpenBSD, Windows и macOS. Клиент OpenSSH предустановлен в большинстве дистрибутивов Linux по умолчанию, однако если в вашей системе не установлен клиент ssh, вы можете установить его с помощью диспетчера пакетов.
Как получить доступ к удаленному серверу
Для подключения к удаленному компьютеру вам потребуется его IP-адрес или имя. Загрузите терминал или любой SSH-клиент и введите ssh, а затем IP-адрес:
При первом подключении к хосту вы увидите следующее сообщение:
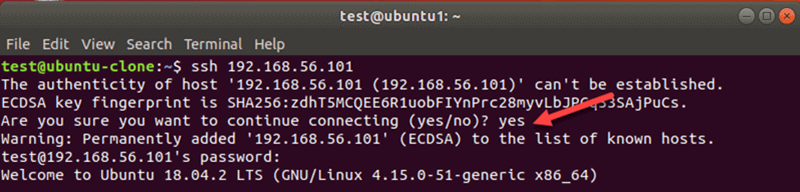
Введите yes и нажмите Enter. Возможно, вам также потребуется ввести свой пароль.
Укажите имя пользователя для SSH-подключения
SSH использует текущего пользователя при доступе к удаленному серверу. Чтобы указать пользователя для SSH-соединения, выполните команду в следующем формате:
Примечание. Если вы столкнулись с ошибкой «Connection refused», обратитесь к нашему руководству, чтобы найти решения.
Используйте другой номер порта для SSH-соединения
По умолчанию сервер SSH прослушивает соединение на порту 22. Если настройка порта в файле конфигурации SSH была изменена, вам необходимо указать порт. В противном случае вы получите такую ошибку:
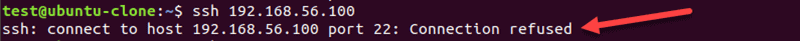
Чтобы подключиться к удаленному хосту с настраиваемым номером порта SSH, используйте флаг -p . Например:
Генерация ключей SSH с помощью SSH Keygen
Чтобы повысить безопасность соединений SSH, сгенерируйте пару ключей с помощью утилиты keygen. Пара состоит из открытого и закрытого ключей. Открытый ключ может быть общим, а закрытый ключ должен оставаться в безопасности.
Пары ключей SSH используются для автоматической аутентификации клиентов на серверах. Когда вы создаете пару ключей SSH, больше не нужно вводить пароль для доступа к серверу.
На терминале хост-машины используйте эту команду для создания пары ключей:
Чтобы использовать настройки по умолчанию, нажмите Enter в ответ на запрос местоположения файла и парольной фразы.
Копировать открытый ключ SSH
Чтобы использовать пару ключей для аутентификации SSH, вам необходимо скопировать открытый ключ на сервер. Ключ — это файл id_rsa.pub , ранее созданный с помощью утилиты генерации ключей SSH.
Чтобы скопировать ключ на сервер, запустите эту команду на клиенте:
Вы также можете указать имя пользователя, если не хотите использовать текущего пользователя.
Введите пароль для аутентификации, когда его спросят. После этого вам больше не нужно будет использовать пароль для подключения к тому же серверу.
Копирование файла удаленно через SSH с помощью SCP
Вы можете безопасно копировать файлы по протоколу SSH с помощью инструмента SCP. Базовый синтаксис:
Например, чтобы скопировать файл sample3 на рабочий стол на удаленном сервере с проверкой имени пользователя, введите:
Выходные данные показывают сводку операции.
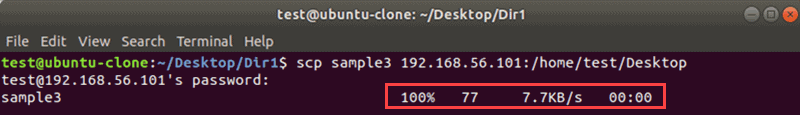
Обязательно используйте флаг -P в верхнем регистре, если вам нужно указать порт.
Редактировать файл конфигурации SSH
Вы можете контролировать, как удаленные пользователи могут получить доступ к серверу через SSH. Измените настройки в файле sshd_config , чтобы настроить параметры сервера SSH. Обязательно редактируйте только те параметры, которые вам знакомы. Сервер может стать недоступным из-за неправильной конфигурации.
Используйте любой редактор по вашему выбору, чтобы отредактировать файл. Для внесения изменений вам потребуются права суперпользователя. В Linux мы используем vim.
В командной строке на удаленном хосте введите:
Введите пароль sudo, и оболочка откроет файл в редакторе, который вы использовали.
Перезапустить службу SSH
Когда вы вносите изменения в конфигурацию SSH, вам нужно будет перезапустить службу в Linux.
В зависимости от дистрибутива Linux выполните одну из следующих команд на машине, на которой вы изменили настройки:
Наконец, введите пароль, чтобы завершить процесс. В результате в следующем сеансе SSH будут использоваться новые настройки.
Выполнение команды на удаленном сервере с локального компьютера
Этот метод не создает новую оболочку. Вместо этого он запускает команду и возвращает пользователя в локальную подсказку. Вы можете создать файл, скопировать файлы или запустить любую другую команду SSH в этом формате.
Чтобы удаленно выполнить команду с локального компьютера, добавьте инструкцию к команде SSH. Например, чтобы удалить файл, введите:
Введите пароль, и файл на удаленном сервере будет удален без создания новой оболочки.
Параметры командной строки SSH
Инструмент SSH имеет множество дополнительных параметров. Ниже перечислены общие параметры SSH и соответствующие описания.
- -1 — указывает ssh использовать версию протокола 1
- -2 — указывает ssh использовать протокол версии 2.
- -4 — разрешает только адреса IPv4.
- -6 — разрешает только адреса IPv6.
- -A — включает переадресацию соединения агента аутентификации. Используйте эту опцию с осторожностью.
- -a — Отключает переадресацию соединения агента аутентификации.
- -b bind_address — используйте эту опцию на локальном хосте с более чем одним адресом, чтобы установить исходный адрес соединения.
- -C — включает сжатие данных для всех файлов. Только для использования с медленными соединениями.
- -c cipher_spec — используется для выбора спецификации шифра. Перечислите значения через запятую.
- -E log_fileName — прикрепляет журналы отладки к log_file вместо стандартной ошибки.
- -f — отправляет ssh в фоновый режим даже до ввода пароля или ключевой фразы.
- -g — Разрешает удаленным хостам подключаться к портам, перенаправленным на локальном компьютере.
- -q — запускает ssh в тихом режиме. Он подавляет большинство сообщений об ошибках и предупреждениях.
- -V — отображает версию инструмента ssh и завершает работу.
- -v — печатает отладочные сообщения для ssh-соединения. Подробный режим полезен при устранении неполадок конфигурации.
- -X — Используйте этот параметр, чтобы включить пересылку X11.
- -x — Отключить пересылку X11.
Онлайн курс по Linux
Мы собрали концентрат самых востребованных знаний, которые позволят тебе начать карьеру администратора Linux, расширить текущие знания и сделать уверенный шаг к DevOps
Источник
leommoore / linux_ssh_basics.md
#Linux — SSH (Secure SHell) Basics ssh is a secure mechanism to interact with a computer remotely.
##Logging on ssh allows a user to log in remotely to a server with a ssh server running (ie openSSHServer). For example:
or, using a domain name like:
will log in the user pi to the specified computer.
##SSH Session Timeout If you are experiencing problems with your session timing out. This can be resolved by editing the ssh config file using:
##Compression If you want to add compression add this to the config:
##Transferring files scp (Secure CoPy) allows a user to copy a file onto a computer running a scp server.
This will copy the file into the /home/pi directory on the remote computer. You can also copy a file from the remote machine to the user’s machine using:
This will copy the file in the directory in /home/pi/ to the current directory.
If you need to use a different port then use:
You can also copy all the subdirectories to the destination using the -r switch:
However if you are only making updates, not re-creating the whole thing, you will probably find things move along faster if you use rsync over ssh instead of scp. Probably something like
##Running Commands Remotely You can also run commands in the remote computer using ssh user@server command . For example:
will return the current directory. You can also run multiple command by enclosing them in quotes and separating them with a semi-colon such as:
This will give your the current directory, followed by the file in the directory. You can also feed the results into a local command.
In this case the process list (ps) is being returned from the remote computer and fed into grep on the local computer which is checking to see if node is running.
##Running Applications Remotely You can also run GUI applications remotely on your local Linux instance if you have X11Forwarding yes in your /etc/ssh/sshd_config file. To run gedit remotely for example:
##SSH Aliases It is also possible to shorten the ssh commands by adding the host details to the
You can then access the machine using:
You can also use and identity file to remove the need to use a user and password to authenticate. This can be particularly useful when you want to have a process to copy files from one server to another (ie backup process).
##Creating a key pair Running ssh-keygen will generate a pair of key files in the
/.ssh directory. By default the names are id_rsa and id_rsa.pub . The id_rsa file is readable only by your account and its contents are further protected by encrypting them with supplied during generation.
Copy the .pub file to the server and add its contents to
/.ssh/authorized_keys . You don’t need a password. You can copy and add the key with this command.
Security Note: Key based authentication can be a security risk, especially if you cannot ensure the security of your local client.
##Adding the key pair to your agent You may encounter an error:
If this happens, you may need to add the key pair to your ssh agent so that it is presented when you connect. This can be done by:
This will add the default id_rsa to your ssh agent.
##Changing the SSH Port It is a good idea to change the default port from Port 22 to some other port to reduce the number of malicious login attempts. There are many people scanning the default ports and attempting to log in using default or weak user logins. Note: ports below 1024 are normally reserved for system processes so it is better to choose one above 1024.
##Removing Password Authentication If you are using Key Based Authentication you can disable authentication via passwords to increase security by editing the remote server’s config file which is usually in /etc/ssh/sshd_config and changing the PasswordAuthentication parameter from ‘yes’ to ‘no’.
##Restricting Users It is also a good idea to not permit root login’s. You can still login and switch to the root user later.
You can also go further and specify which users can login remotely over ssh by adding AllowUsers to the end of the config file and specifying the users that can login.
##Restricting Remote IP Addresses It is always a good idea to restrict the access to users and hosts that you trust. To do this you need to:
Edit the /etc/hosts.deny and create a rule
This will deny access to all hosts. Next, edit the /etc/hosts.allow file and add:
This will give access to the 192.168.1.0/24 network and the 201.130.177.31 host.
More information on the syntax for hosts.allow and hosts.deny can be found on man hosts_access . Information on additional options can be found on man hosts_options .
##Agent Forwarding It is also possible to copy from one server to another server from a remote location (ie your laptop). In this case you may want to do the following:
In this case you may get an error:
This is because when you run scp on your local machine, it first contacts server2.remote.com . But since we are copying the file to a third host, scp also invokes a second scp command to server3.remote.com . It is this second command that has the error. This is because while you have an active session to server2 and you can instruct it to copy to server3 but since you are not connected to server3 then you cannot authenticate using a password or key. You can edit your users config file in
/.ssh/config , or the system-wide configuration file (usually in /etc/ssh/ssh_config ) and add the following:
This will cause the request for authentication to be forwarded to all remote hosts. When agent forwarding is turned on, the SSH authentication requests aren’t passed directly to the local SSH agent.
Источник
SSH Command — Usage, Options, Configuration
Practically every Unix and Linux system includes the ssh command. This command is used to start the SSH client program that enables secure connection to the SSH server on a remote machine. The ssh command is used from logging into the remote machine, transferring files between the two machines, and for executing commands on the remote machine.
Contents
SSH Command in Linux
The ssh command provides a secure encrypted connection between two hosts over an insecure network. This connection can also be used for terminal access, file transfers, and for tunneling other applications. Graphical X11 applications can also be run securely over SSH from a remote location.
Other SSH Commands
There are other SSH commands besides the client ssh . Each has its own page.
ssh-keygen — creates a key pair for public key authentication
ssh-copy-id — configures a public key as authorized on a server
ssh-agent — agent to hold private key for single sign-on
ssh-add — tool to add a key to the agent
scp — file transfer client with RCP-like command interface
sftp — file transfer client with FTP-like command interface
Using the Linux client
Linux typically uses the OpenSSH client. The ssh command to log into a remote machine is very simple. To log in to a remote computer called sample.ssh.com, type the following command at a shell prompt:
If this is the first time you use ssh to connect to this remote machine, you will see a message like:
Type yes to continue. This will add the server to your list of known hosts (
/.ssh/known_hosts ) as seen in the following message:
Each server has a host key , and the above question related to verifying and saving the host key, so that next time you connect to the server, it can verify that it actually is the same server.
Once the server connection has been established, the user is authenticated. Typically, it asks for a password. For some servers, you may be required to type in a one-time password generated by a special hardware token.
Once authentication has been accepted, you will be at the shell prompt for the remote machine.
Specifying a different user name
It is also possible to use a different username at the remote machine by entering the command as:
The above can also be expressed with the syntax:
Executing remote commands on the server
The ssh command is often also used to remotely execute commands on the remote machine without logging in to a shell prompt. The syntax for this is:
For example, to execute the command:
on host sample.ssh.com, type the following command at a shell prompt:
After authenticating to the remote server, the contents of the remote directory will be displayed, and you will return to your local shell prompt. -x Disables X11 forwarding.
SSH client configuration file
The ssh command reads its configuration from the SSH client configuration file
/.ssh/config . For more information, see the page on SSH client configuration file .
Configuring public key authentication
To configure passwordless public key authentication , you may want to create an SSH key and set up an authorized_keys file. See the pages on ssh-keygen and ssh-copy-id for more information.
Configuring port forwarding
Command-line options can be used to set up port forwarding. Local fowarding means that a local port (at the client computer) is tunneled to an IP address and port from the server. Remote forwarding means that a remote port (at the server computer) is forwarded to a given IP address and port from the client machine. See the page on configuring port forwarding on how to configure them.
OpenSSH also supports forwarding Unix domain sockets and IP packets from a tunnel device to establish a VPN (Virtual Private Network).
SSH command line options
Some of the most important command-line options for the OpenSSH client are:
-1 Use protocol version 1 only.
-2 Use protocol version 2 only.
-4 Use IPv4 addresses only.
-6 Use IPv6 addresses only.
-A Enable forwarding of the authentication agent connection.
-a Disable forwarding of the authentication agent connection.
-C Use data compression
-c cipher_spec Selects the cipher specification for encrypting the session.
-D [bind_address:] port Dynamic application-level port forwarding. This allocates a socket to listen to port on the local side. When a connection is made to this port, the connection is forwarded over the secure channel, and the application protocol is then used to determine where to connect to from the remote machine.
-E log_file Append debug logs to log_file instead of standard error.
-F configfile Specifies a per-user configuration file. The default for the per-user configuration file is
-g Allows remote hosts to connect to local forwarded ports.
-i identity_file A file from which the identity key (private key) for public key authentication is read.
-J [user@] host [:port] Connect to the target host by first making a ssh connection to the pjump host[(/iam/jump-host) and then establishing a TCP forwarding to the ultimate destination from there.
-l login_name Specifies the user to log in as on the remote machine.
-p port Port to connect to on the remote host.
-V Display the version number.
-X Enables X11 forwarding.
A little history
SSH replaced several older commands and protocols in Unix and Linux the 1990s. The include telnet , rlogin , and rsh .
SSH runs at TCP/IP port 22. This is right between ftp and telnet, which are 20 years older. Read the story of how SSH got port 22 .
The following video summarizes how and why SSH was originally developed.
Together with our customers, our mission is to secure their digital business on on-premises, cloud, and hybrid ecosystems cost-efficiently, at scale, and without disruptions to their operations or business continuity.
Источник





