- SSH Tunnel Manager for Mac
- Download SSH Tunnel Manager for Mac Latest Version
- Screenshots
- Top Downloads
- Comments and User Reviews
- Join our mailing list
- Freeware
- Open Source
- Free to Play
- Trial
- Какой хороший SSH-туннельный клиент для OS X?
- Создание SSH-туннеля в OS X
- Добавить комментарий Отменить ответ
- SSH Tunnel Manager for Mac
- Review
- Free Download
- specifications
- Free and powerful front-end for the SSH command designed to help you open an encrypted tunnel between two hosts with just a couple of mouse clicks
- What’s new in SSH Tunnel Manager 2.2.7:
- Simple method of setting up SSH tunnels on your Mac
- Accessible graphical user interface for the SSH Terminal command
- Intuitive OS X app that makes it possible to set up SSH tunnels in seconds
- How to Setup SSH Tunneling in Mac OS (or Ubuntu)
- What is SSH Tunneling?
- Using MacOS/Ubuntu Terminal
- Using a .pem file
- Connect to Destination server via Remote Server:
- Conclusion:
SSH Tunnel Manager for Mac
SSH Tunnel Manager 2.2.7 LATEST
Mac OS X 10.7 or later
SSH Tunnel Manager for Mac 2021 full offline installer setup for Mac
SSH Tunnel Manager for Mac is a macOS application to manage your SSH tunnels. If you don’t know what that is, quite honestly, maybe you don’t need SSH Tunnel Manager, but if you appreciate the power of connecting together two networks using the SSH protocol, then STM is for you.
Quick Access
A single click will open a connection and establish the port redirections you need. You can also put STM in the menu bar and have it out of your way!
Secure
Use your public keys for passwordless authentication, or use passwords and store them in macOS Keychain. or not, it is up to you. «We take security very seriously and never a password will be stored unless you want it to be.»
Flexible
With all the options available to configure the connections and port redirections, you will never have to remember these esoteric arguments ever, relax now! You can even open a list of web sites automatically when a connection is established.
Sharing
You can export any connexion and share with your friends. Password information won’t be sent out of course, but you save them in the manual configuration of dozens of ports and options!
Note: Requires 64-bit processor.
Download SSH Tunnel Manager for Mac Latest Version
Screenshots
Top Downloads
Comments and User Reviews
Join our mailing list
Stay up to date with latest software releases, news, software discounts, deals and more.
Each software is released under license type that can be found on program pages as well as on search or category pages. Here are the most common license types:
Freeware
Freeware programs can be downloaded used free of charge and without any time limitations. Freeware products can be used free of charge for both personal and professional (commercial use).
Open Source
Open Source software is software with source code that anyone can inspect, modify or enhance. Programs released under this license can be used at no cost for both personal and commercial purposes. There are many different open source licenses but they all must comply with the Open Source Definition — in brief: the software can be freely used, modified and shared.
Free to Play
This license is commonly used for video games and it allows users to download and play the game for free. Basically, a product is offered Free to Play (Freemium) and the user can decide if he wants to pay the money (Premium) for additional features, services, virtual or physical goods that expand the functionality of the game. In some cases, ads may be show to the users.
Demo programs have a limited functionality for free, but charge for an advanced set of features or for the removal of advertisements from the program’s interfaces. In some cases, all the functionality is disabled until the license is purchased. Demos are usually not time-limited (like Trial software) but the functionality is limited.
Trial
Trial software allows the user to evaluate the software for a limited amount of time. After that trial period (usually 15 to 90 days) the user can decide whether to buy the software or not. Even though, most trial software products are only time-limited some also have feature limitations.
Usually commercial software or games are produced for sale or to serve a commercial purpose.
Источник
Какой хороший SSH-туннельный клиент для OS X?
Я использовал SSH Tunnel Manager для простой настройки и остановки туннелирования портов по SSH на различные серверы в моей компании. Это избавило меня от боли, связанной с открытием нового окна терминала, которое будет висеть там только ради открытого туннеля.
Это отлично работало (ну вроде), но SSH Tunnel Manager — это приложение PowerPC. С Lion это больше не поддерживается.
Что такое хорошая замена?
SSHTunnel — это бесплатный пользовательский интерфейс на основе какао для управления туннелем SSH. Работает на 10,5 и выше. Он давно не обновлялся, но код там достаточно стабилен. Это работало хорошо для меня в прошлом.
Почему бы просто не использовать SSH Tunnel через встроенный в OSX терминал? .
Запустите SSH туннель
Чтобы запустить SSH-туннель, просто откройте Mac OSX Terminal.app и подключитесь к удаленному серверу через SSH со следующими флагами:
Это запустит наш SSH-туннель через порт 8080 и направит весь трафик (безопасно) через сервер на example.com.
Сидеть в сети
Теперь давайте начнем просматривать веб-страницы, используя новый SSH-туннель (Chrome):
- Откройте Google Chrome
- Выберите «Chrome» вверху слева
- Выберите «Настройки»
- Выберите «Показать дополнительные настройки…»
- Выберите «Изменить настройки прокси…»
- Выберите «SOCKS Proxy»
- Введите «127.0.0.1»
- Введите порт ‘8080 ′
- Сохраните изменения, выбрав «ОК»
Источник
Создание SSH-туннеля в OS X
Хорошо, когда для совершения платежей или передачи какой-то очень важной информации используется защищённое соединение по протоколу HTTPS. Но что делать, если защиты соединения нет, и при этом есть необходимость быть уверенным на 100% в том, что данные, передаваемые через публичные Wi-Fi сети останутся конфидециальными? В этом случае вам поможет организация SSH-туннеля. Всё, что вам потребуется, — SSH-доступ к какому-либо серверу и 5 минут времени.
Выполняем в терминале следующую комманду:
user_name — ваше имя для соединения на удалённом сервере
server_address — собственно, адрес сервера, через который будет происходить туннелирование
После того, как вы выполните эту команду, вас попросят ввести пароль, соответствующий указанному в соединении пользователю. Как только вы это сделаете (при условии, что введёте правильный пароль), у вас готов SSH-туннель, и теперь можно указывать системе, чтобы трафик шёл не напрямую, через Wi-Fi-соединение, а через созданное вами безопасное соединение.
Запустите приложение «Системные настройки» и выберите в нём пункт «Сеть», в открывшемся окне выберите пункт с вашим беспроводным соединением и нажмите кнопку «Дополнительно», в окне дополнительных настроек выберите вкладку «Прокси», включите пункт «SOCKS-прокси», в поле адреса и порта впишите настройки: 127.0.0.1 (адрес вашего внутреннего сетевого интерфейса) и 9999 (порт, указанный при создании SSH-туннеля).
Теперь нажмите кнопку «ОК», затем «Применить» и теперь ваш беспроводной трафик будет идти через SSH-туннель, что не позволит злоумышленникам его перехватить и прочитать.
Чтобы выключить проксирование, вернитесь к настройкам прокси и отключите пункт «SOCKS-прокси», после чего подтвердите внесённые изменения, а в терминале с включённым туннелем нажмите комбинацию клавиш Ctrl+C, которая остановит выполнение приложения ssh.
Добавить комментарий Отменить ответ
Для отправки комментария вам необходимо авторизоваться.
Источник
SSH Tunnel Manager for Mac
Review
Free Download
specifications
Free and powerful front-end for the SSH command designed to help you open an encrypted tunnel between two hosts with just a couple of mouse clicks
What’s new in SSH Tunnel Manager 2.2.7:
- Fix a bug causing application to crash when editing tunnels
- Fix the menu bar icon appearance on Mac OS X Dark theme
Read the full changelog
The SSH command allows you to create an encrypted tunnel between two hosts and is included in OS X, but it can only be operated from the command console by default, which novices may find a bit too difficult.
SSH Tunnel Manager can make this task a whole lot easier, as it enables you to set up any number of connections from a simple, intuitive GUI, ensuring that even users with no prior experience can get things running in no time.
Simple method of setting up SSH tunnels on your Mac
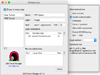
When first launching the application, you are presented with the Preferences panel, where you can add your first connection and configure it. You can define its name, the remote host and the port to be used, as well as the username.
Additionally, you can specify if the application should connect to a particular tunnel on launch, use system authentication, enable compression, force use of the SSH v1 protocol, allow LAN connections or enable SOCKS4 proxy on a specified port.
Furthermore, it is possible to set up any number of local or remote redirections for each configured connection.
Accessible graphical user interface for the SSH Terminal command
Once everything has been set up, you can monitor the status of each tunnel from the Connections window, which lets you know whether they are active or not.
By default, SSH Tunnel Manager is displayed in your Dock, but you can remove this icon to reduce clutter.
Moreover, the application can be sent to your menu bar, allowing you to start, stop or just keep track of connections with one or two mouse clicks.
Intuitive OS X app that makes it possible to set up SSH tunnels in seconds
In short, SSH Tunnel Manager is a great tool for novices and experts alike, as it can save you a lot of time regardless of whether or not you are familiar with the standard Terminal commands. It provides an intuitive GUI and allows you to manage connections from your Mac’s menu bar.
Источник
How to Setup SSH Tunneling in Mac OS (or Ubuntu)
LAST UPDATED: AUGUST 10, 2021
If you want to setup SSH tunnel with your remote server using your Macbook, you can easily do so using the default Terminal application available in the Mac OS. Yes, we do not have to install any other application for doing so, like we do in Windows.
If you are a Windows user, I would recommend using Mobaxterm application for doing this.
What is SSH Tunneling?
An SSH tunnel or SSH port forwarding is a mechanism to establish a secure connection between a client machine and a server.
Let’s take a simple example to understand this. If we have a database server, let’s say MySQL running on a remote server with some IP address XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX and for which the port number 3306 which is the default port for MySQL is only available on the local network of the remote server. In this case, if you want to access the DB server from your local machine(connected to the internet), you won’t be able to do it. In such a scenario, we set up an SSH tunnel with the remote server, to securely connect to the local network of the remote server to access the 3306 port on the remote server.
Let’s take another example If we are using AWS service and we have two servers one is a DB server and another is the SSH server on which the Web Server is running. On the SSH server, because we are running the Web server, port 80 would be open to all, because then only the website or the web application hosted on that server will be available to its users. But, for security, the DB server is never exposed to the internet and is kept on the local network, which will be accessible via the SSH server, as the SSH server is on the same local network.
Now, if you want to check something or do something on the DB server. or want to connect your local SQL client with the remote database, you won’t be able to do it directly. But because the DB server is accessible via the SSH server, we can setup an SSH tunnel with the SSH server to reach the DB server.
I hope the two examples are clear, and now you know, why SSH tunneling is needed. So let’s see how we can do this.
Using MacOS/Ubuntu Terminal
We can use the ssh command to set up an SSH tunnel with a remote server, considering the SSH port which is port number 22 is open for the remote server.
If our remote server name is my-remote-server.host and the SSH user is st-user, and on the same server a DB service let’s say MySQL is installed which is accessible via localhost:3306 on the remote server.
Then to connect to the DB server, we can run the following command to setup an SSH tunnel:
8888: This is the local port that we will open for the SSH tunnel on the local machine. Here you can give any port number after 1024, because until 1024 port number, all ports are privilege ports.
127.0.0.1: This is the IP for the localhost running on the remote server, this is also the destination we aim to reach via the SSH server.
3306: This is the destination port, assigned to the MySQL sever on the remote SSH server.
and then st-user@my-remote-server.host is the username and the IP address/URI for the SSH server.
Once you do this, you will be prompted to enter the password for the user st-user, so enter the password an hit Enter, and the SSH tunnel will be created. Now, you will be able to access the MySQL server using 127.0.0.1:8888 address from your local machine.
Using a .pem file
If your remote server is an EC2 instance on AWS and you have a .pem file as the SSH key, run the following command for the above scenario:
In this case you will not be asked for the password, as authentication will be done using your SSH key.
This was the scenario where the DB server was running on the localhost of the remote server. Next, let’s see how to connect to a separate DB server via a remote server.
Connect to Destination server via Remote Server:
If our DB server is my-db-server.host on which port 3306 is available for connection on the private network access to the remote SSH server my-remote-server.host, as shown in the picture below.
Then we can run the following command:
Note: If SSH connection is enabled on a different port other than the port number 22, then we can specify the port number in the above command using -p [PORT_NUMBER] argument. So, for example we have 2200 port for SSH enabled on our remote server, then the command would be:
Conclusion:
I hope this article helped you in understanding what SSH tunneling is and how we can setup an SSH tunnel using the Terminal in MacOS and in Ubuntu or other Linux based operating systems. If you were not able to do this or faced any issue running the above command do share in the comments below and we will help you out.
Источник