- Using SSLStrip in Kali Linux
- Kali Linux 2021.2 Release (Kaboxer, Kali-Tweaks, Bleeding-Edge & Privileged Ports)
- Introducing Kaboxer v1.0 (Again)
- Releasing Kali-Tweaks v1.0
- Refreshed Bleeding-Edge Branch
- Disabled Privileged Ports
- New Tools in Kali
- Theme Enhancement
- Command Line
- Desktop Wallpaper & Login Background
- Raspberry Pi Recharged
- Kali NetHunter Updates
- More Docker support/Parallels support/Bug fixes
- Download Kali Linux 2021.2
Using SSLStrip in Kali Linux
September 8, 2015
nmap -sP 192.168.1.0/24
The object in this step is to route traffic inbound to Kali to the port that SSLStip will be running on, which is port 1000 (this port does not have to be 1000 — you can select a different one but if you do, make sure you do not select a well-known port). With our arpspoof running in two terminal windows, we need to open a third terminal. Use the following command for iptables:
iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -p tcpВ —destination-portВ 80 -j REDIRECT —to-port 1000
Note the double dashes before destination-port and to-port. Establish a MITMNow that you know the gateway and victim IP address, you need to insert your Kali machine between the two as a man in the middle. The first step to accomplish this is to configure your Kali machine to forward ports. Run the command:
echo 1 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward
This modifies ip_forward to a 1 which enables port forwarding. If you set it to 0, then Kali will not forward ports. If you set this to 0 after the following steps, you will DOS (aka “sinkhole”) any traffic originating from your victim that would need to cross a router. This includes internet requests. In a larger network, it may also include traffic that passes between subnets.The next step is to use the arpspoof utility. Arpspoof tricks your victim into believing that you are the gateway, when you’re actually just another machine on the network. A Word of WarningThis should be relatively transparent to your victim because you are forwarding ports. However, a clever victim will be able to see the attack, if they’re monitoring for changes in their ARP table. With no man in the middle present, a Windows user could use the command arp -a [gateway IP] to see the MAC address of their router. If a man in the middle is present, the IP address the victim is using for the gateway would not change, but the MAC address returned would be the attacker’s. A clever attacker could determine the MAC address of the gateway and change their Kali interface MAC address to mimic the gateway so this would not be seen by the victim.To use arpspoof, the syntax is:
arpspoof -i eth0 -t [victim IP] [gateway IP]
The -i flag indicates what network interface to send the ARP packets on. In this case, the interface is eth0, which is the norm for a LAN (ethernet) port. -t signifies the target IP address.The terminal will begin showing ARP pings continuously until you elect to end the spoofing attack by using Ctrl + C.You’ve completed half the man in the middle. To finish, open a second terminal window and use the same command as above, except reverse the order of the IP addresses. This will trick the router into believing that you are the device requesting internet resources. Deliver the ExploitSelect Applications в†’ Kali Linux в†’ Information Gathering в†’ SSL Analysis в†’ sslstripThis spawns a 4th terminal window.Enter the command:
sslstrip -w filename.txt -l 1000
This will start SSLStrip and write the results to a file you specify. Be sure to specify the extension of the file. The -l switch identifies the port SSLStrip will be listening on, which we set as 1000 in the previous step. You’re now collecting the internet traffic for websites your target visits and decrypting the HTTPS traffic on the fly while saving the results to a file for review later. The default location for the file is under Kali’s Home folder.
- Your victim uses 192.168.1.1 as the default gateway and doesn’t notice the MAC address change because you’ve poisoned the ARP table.
- The victim sends requests to the Kali machine.
- The Kali attacker runs SSLStrip on all these packets and decrypts them; then saves the results to a file.
- Decrypted packets are forwarded to the actual gateway router.
- The router makes the internet request and returns the results to the Kali attacker.
- Kali decrypts and forwards the results to the victim IP address.
Another Word of Warning The moment you launch SSLStrip in the previous command, your victim’s internet browsing will become extremely slow for two reasons:
- There’s now an extra step in the route between your victim and the actual gateway as your attack machine is forwarding traffic back and forth between the gateway and the victim
- SSLStrip is a decrypt process and, therefore,В resource-intensive on your attacker machine. Your attacker will delay the forwarded traffic in addition to it being an extra step in the route. This will be noticeable by your victim and may prompt a restart (which may change the IP address of the victim and kill the attack). Depending on the environment, this may also trigger a call to tech support or an investigation into the cause of the slowdown.
I’ve also seen this attack trigger 403 errors on the victim’s machine, which will alert the target that something’s wrong (this seems to occur when a remote server forces a higher-grade TLS connection). You may be able to capture a username and password, nonetheless. Usually the pertinent information is located at the bottom of the entry in the file you save the date to. It can be seen with a parameter, such as user= and passwd=. Thanks!
Источник
Kali Linux 2021.2 Release (Kaboxer, Kali-Tweaks, Bleeding-Edge & Privileged Ports)
Say hello to Kali Linux 2021.2! This release welcomes a mixture of new items as well as enhancements of existing features, and is ready to be downloaded (from our updated page) or upgraded if you have an existing Kali Linux installation.
A quick summary of the changelog since the 2021.1 release from February 2021 is:
- Releasing Kaboxer v1.0 — Introducing Kali Applications Boxer v1.0! Applications in containers
- Releasing Kali-Tweaks v1.0 — Our way to make it easier to configure Kali Linux to your taste
- Refreshed Bleeding-Edge branch — We did a complete make over for our backend that produces packages for the latest updates
- Disabled privileged ports — Opening a listener on ports 1024/TCP-UDP and below no longer requires super-user access
- New tools added — Ghidra & Visual Studio Code. Along with CloudBrute, Dirsearch, Feroxbuster, pacu, peirates, & Quark-Engine
- Theme enhancements — We added a way to quickly swap between double & one-line terminal prompt and made Xfce4 Quick launch + file manager tweaks
- Desktop wallpaper & login background updates — Default images have changed with more to choose from
- Raspberry Pi images recharged — RPi 400 fully supported, built-in bluetooth working, & first-run wait time dramatically reduced
- Kali NetHunter support for Android 11 — Android 11 support and various other improvements for our NetHunter platform
- More Docker support — Now supporting ARM64 & ARM v7 (along with previous AMD64)
- Parallels support — Kali is fully supported for Apple M1 users who have Parallels
- Various bug fixes — Pkexec patched, Wireshark permissions, command-not-found issues, & more accessibility features are all resolved
Introducing Kaboxer v1.0 (Again)
In case you missed it, we have previously covered Kaboxer in it’s own dedicated blog post, which goes into a lot more detail of why we love it so! For developers, this is a great new tool in the arsenal. Users will, hopefully, not realise that they are using it, only noticing that previously problematic tools now work correctly!
Without repeating what has already been posted, this technology allows us to correctly package up programs that were previously difficult, with items such as complex dependencies or legacy programs & libraries (such as Python 2 or dated SSL/TLS).
With Kaboxer’s launch, we have released 3 packages using it:
- Covenant — Daemon using server/client network model
- Firefox (Developer Edition) — Big GUI desktop application
- Zenmap — Legacy libraries (Python 2) application
If you want to read more, please see either our blog post covering it, or our documentation around it.
Kaboxer is still in its infancy, so please be nice & patient with it.
Releasing Kali-Tweaks v1.0
Announcing Kali-Tweaks! This is our little helping hand for Kali users, with the idea to help customize Kali to your own personal taste quickly, simply, and the correct way. This should help you to stop doing repetitive tasks.
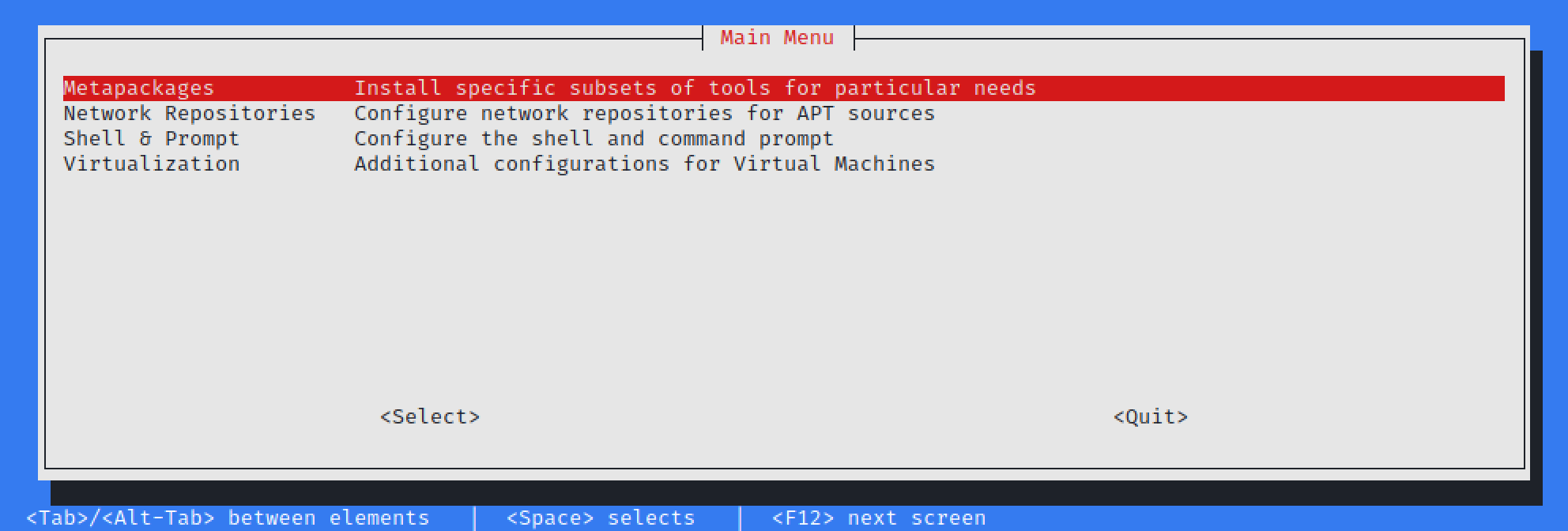
Currently Kali-Tweaks will help out with:
- Metapackages — Installing/removing groups of tools, which may not have been available while installing Kali if you did not use the installer image
- Network Repositories — Enabling/disabling “bleeding-edge” & “experimental” branches
- Shell & Prompt — Switch between two or one line prompt, enable/disable the extra line before the prompt, or configure Bash or ZSH as the default shell
- Virtualization — Using Kali as a guest VM? Do a few actions to make the experience easier!
Our philosophy is to always understand what you are running, before you run it. That way, it reduces the chances of any undesirable nasty surprises. Which is why we will always encourage anyone to do actions manually before automating it, so you get to understand what is happening under the hood. On the flip side, we also understand there is so much to remember. Then when you sprinkle in people’s bad habits, which often have long term implications and end up breaking Kali, there is room for improvement. So, we started developing Kali-Tweaks. Where possible, Kali-Tweaks will also display what commands are being executed to help educate users.
We do want to mention a few things:
- kali-tweaks has been marked as “recommended” rather than “required”. As a result, if you are upgrading Kali, it may not be included. On the other hand, you can remove kali-tweaks without removing anything else
- On the subject of upgrading; depending on how old your Kali installation is, you may need to reset your shell resource(e.g. .bashrc & .zshrc ) before you can use the “configure prompt” section. This is because it will not have the necessary variables. Should you want to, make sure to backup, reset, and restore
- The last thing to point out, when changing the default login shell; please log out and in again(either graphically or remote console) for it to have an effect
It is still early days with Kali-Tweaks, and we already have ideas of what to expand into, but we welcome any suggestions from you!
Kali-Tweaks is still in its infancy, so please be nice & patient with it.
Refreshed Bleeding-Edge Branch
Kali’s Bleeding-Edge branch has been around since March 2013, but we have recently completely restructured the backend.
For those not too familiar with Bleeding-Edge branch, here is a breakdown:
- Kali by default opts to be stable where possible when packaging. This means some tools may appear to be “out-dated”
- We do this by looking to see when the tool author(s) signals “everything up to to this point is good”, by doing a “point release” (e.g. 1.0 or 2.1 )
- Developers often use source-code version control, allowing them to track any changes
- How programmers use source-code version control depends on their work flow, experience, and team size
- Developers can use a “tag” feature found in most source-code version control to signal when there is a new version (this is what Kali prefers)
- However, some people may say if it makes it to “master” or “main” branch, then it is “production ready”
- There are times where it has been “a while”(months or even years)since doing a tag for a stable release (aka point release), and people get frustrated that there are no updates (e.g. hashcat or impacket).
- In other cases, you want the latest code which may include an exploit 0day (e.g. Metasploit-framework, Empire, or Exploit-DB) so waiting for a tag release may not be an option
You may then end up skipping the Kali package and compiling your favorite tool’s source-code. This might then conflict with Kali’s packaging, and it is your responsibility to maintain the program. This is where bleeding-edge branch comes in.
Since moving over to GitLab, we have been able to create Kali-Bot to help with heavy lifting and automation
- Automatically package tag’d releases to kali-experimental branch
- Automatically package the last commit to kali-bleeding-edge branch
This is a fully automated procedure, as a result, the testing that goes into our packaging is automated as well (unlike anything that is in kali-rolling branch which has manual testing involved). If there has not been a unit test created, its not going to be tested for. This means there is a chance packages will be broken, and more trust goes into the tool author having correctly developed the tool.
If you want to give it a try, have a look at our kali-bleeding-edge documentation to learn how to enable the repository and how to tell apt to select a package from this repository. Once the repository has been enabled, it looks like this:
Not every tool has made it to the new system yet as there are still many limitations to overcome, but to see what is supported and also how many:
The numbers will only grow bigger and better as time goes on, with less bugs in the code and more unit tests in place!
If you are a tool author and want to get your software on the list, please chat to us, and we can show how to enable webhooks!
Disabled Privileged Ports
We have patched our kernel to remove the restriction of requiring privilege permission in order to use TCP & UDP ports under 1024 (meaning 0/TCP-UDP $ sudo
,
- Let’s reduce any possible attack surface!
Now, this change won’t appear in all instances as some flavors of Kali operate without our kernel. This depends on which platform you use (such as Cloud instances, Docker or WSL). If you are on a platform that does not use our customized Kernel, this change will not be applied. For example, the top one uses Kali’s kernel on a bare metal install, and below uses Kali in a docker container, so its using the host’s kernel:
New Tools in Kali
It would not be a Kali release if there were not any new tools added! A quick run down of what’s been added (to Kali’s archive and network repositories):
- CloudBrute — Find a company infrastructure, files, and apps on the top cloud providers
- Dirsearch — Brute force directories and files in web servers
- Feroxbuster — Simple, fast, recursive content discovery
- Ghidra — Reverse engineering framework
- Pacu — AWS exploitation framework
- Peirates — Kubernetes penetration
- Quark-Engine — Android malware scoring system
- VSCodea.k.a. Visual Studio Code Open Source (“Code-OSS”) — Code editor
Ghidra and VSCode have been included into the kali-linux-large metapackage, so they are included on the installer image for people doing a fresh install. Otherwise you will need to upgrade Kali (if you already have the kali-linux-large install) or manually install them (if you want them!):
A few notes about code-oss (aka VSCode):
- We are compiling this from source, rather than using the pre-built binaries
- The upside to this is that telemetry data is disabled by default
- The downside is that some aspects of the marketplace may not work. If you find these limitations a problem, you may wish to uninstall the Kali package and switch to the VSCode pre-built binaries
- You also may question why it was named code-oss , rather than code
- Code-OSS is what the source-codecalls itself, which is used as the base before the configurations are applied for the pre-compiled binaries that gets distributed as “code”
- As we are using the source-code, we used the variables defined by it
- The two different names help to distinguish the differences between them (also prevents any clashes and conflicts!)
- We also included various aliases in our package to help bridge between the two different versions. Meaning, calling vscode and code will use our package, code-oss , with a friendly notice (when installed)
- If you already have the pre-compiled version installed, upgrading Kali will not replace it
- However, when manually installing code-oss , it will then replace it!
Theme Enhancement
Command Line
If you are using ZSH, with the latest Kali profile applied, you can toggle between the two-line prompt and one-line prompt by pressing: CTRL + p (at the same time). This will only have an effect for the current session. If you would like to set it permanently, see kali-tweaks .
Your browser does not support the video tag.
We have switched up the quick launch tray in the top left, by:
- Dropping the screen recorder button (as a result package can also be removed, kazam )
- Adding a text editor shortcut (this uses mousepad as it is a quick and light)_
- If you are looking for something that is more substantial, try code-oss
- Adding in a web browser icon, which starts the default browser (often FireFox )
- Adding a drop-down menu to select the user for default terminal( terminal or root terminal & Kali’s default is QTerminal )
To give you an idea of how the toggling between the terminal user works:
Your browser does not support the video tag.
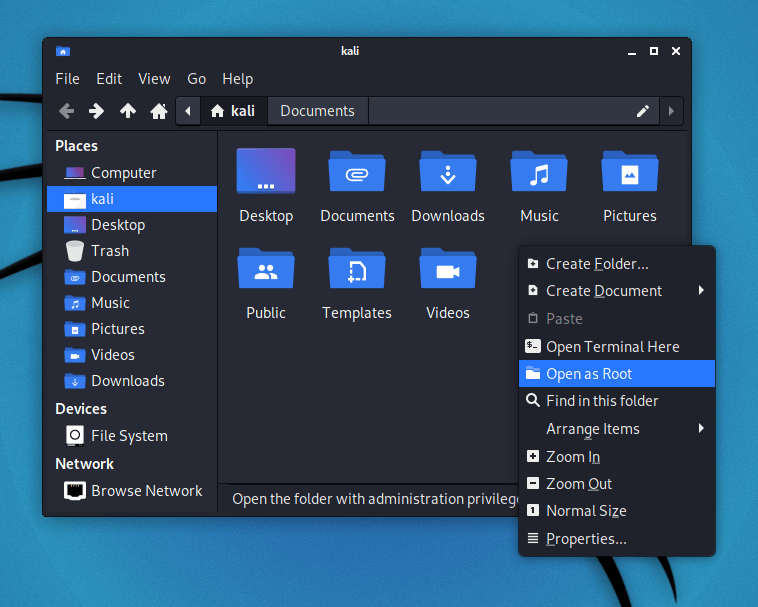
Inside of Thunar (Xfce’s default file manager), if you right-click in the main window, you should have a new option, Open as Root:
With these theme changes, you may not get them if you upgrade Kali. This is because the theme settings are copied to your home folder when your user is first created. When you upgrade Kali, it is upgrading the operating system, so upgrading does not alter personal files (just system files). As a result, in order to get these theme tweaks, you need to either:
- Do a fresh Kali install
- Create a new user and switch to that
- Delete your Xfce profile for the current user and force reboot
Desktop Wallpaper & Login Background
People who have upgraded, you may have spotted that there is a new default login wallpaper and desktop background, but there are extras as well in this release:
Whilst on the subject of wallpapers, if you have not noticed, previously we had been operating on an refresh cycle about every 6 months, where we would change the default login and desktop as well as included other art work if they were not to your taste. Going forwards, we are aiming to change the defaults at every 20xx.1 release (meaning it happens right at the start of every year). So it will still change again in 6 months, but this will be the last time! We will still aim to add extra wallpapers every 6 months, however, only change the defaults yearly.
Finally, we have updated kali-community-wallpapers & kali-wallpapers-legacy packages as well!
Raspberry Pi Recharged
Two new packages:
- kalipi-config — raspi-config on steroids to assist in the initial setup of Kali Linux on a Raspberry Pi
- kalipi-tft-config- assist in the initial setup of TFT displays on a Raspberry Pi
And other improvements:
- Got built-in Bluetooth working on Raspberry Pi 4 & Raspberry Pi 400 (meaning all Raspberry Pi’s built-in bluetooth work!)
- This is due to bluez , bluez-firmware , and pi-bluetooth packages forked and patched
- Raspberry Pi kernel updated to 5.4.83
- mt76 devices now work on Raspberry Pi 2 and 3 if you pass the option disable_usb_sg=1 when loading the mt76_usb module
- 1500% performance improvement
- First boot from 20 minutes to 15 seconds
- Console scrolling working
Kali NetHunter Updates
Plenty of improvements under the hood, including:
- Improved compatibility with dynamic partitions
- Improvements to persistence of Magisk root
- Improvements to Bluetooth and settings menus
- Inclusion of rtl88xxau patches for older kernels in the kernel builder
And the highlight:
Android 11 support for:
- Nokia 6.1
- OnePlus Nord
- OnePlus One
- Samsung Galaxy S20 FE 5G
- Xiaomi Mi A3
- Xiaomi Poco F1
The Kali NetHunter repository now contains 179 kernels for 72 devices and 32 pre-built images are available on our download page
Huge thanks to @kim0coder, @yesimxev, @Svirusx, @Martinvlba, @CaliBerrr, @maade69 and the entire Kali NetHunter community for making this release happen. You absolutely rock!
More Docker support/Parallels support/Bug fixes
There are even more improvements to Kali, that are outside of the above text. Below are other note-worthy items:
- Our Kali-Docker images are now available for arm64 and armhf as well as amd64
- We have patched pkexec , so now Qt applications which have been ran as root will maintain the dark theme and the HiDPI setting
- On a fresh Kali install, wireshark can now be run by unprivileged users
- A couple of bugs were fixed in command-not-found, which is the terminal helper that helps you installing missing programs
- Accessibility features were not installed by default(this was a mistake on our side that is now fixed)
- Fixed a terminal font issue with special characters
- Apple M1 users, Parallels is no longer in “Technical Preview” and as part of the release, they’ve fixed Kali image detection.
- Win-KeX v2.10 has been released which now supports multiscreen
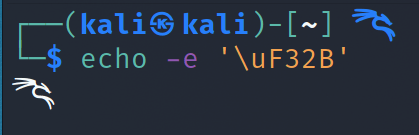
- Kali’s logo is now included in the nerd-fonts project, so, with their next release you’ll be able to customize your terminal with the dragon. If you want to try it now, we’ve created a patched Fira-Code font with these new changes (the code for the logo is \uF32B )
Download Kali Linux 2021.2
Fresh Images: So what are you waiting for? Start grabbing Kali already!
Seasoned Kali Linux users are already aware of this, but for the ones who are not, we do also produce weekly builds that you can use as well. If you cannot wait for our next release and you want the latest packages (or bug fixes) when you download the image, you can just use the weekly image instead.
This way you’ll have fewer updates to do.
Just know that these are automated builds that we do not QA like we do our standard release images. But we gladly take bug reports about those images because we want any issues to be fixed before our next release!
Existing Installs: If you already have an existing Kali Linux installation, remember you can always do a quick update:
You should now be on Kali Linux 2021.2. We can do a quick check by doing:
NOTE: The output of uname -r may be different depending on the system architecture.
As always, should you come across any bugs in Kali, please submit a report on our bug tracker. We’ll never be able to fix what we do not know is broken! And Twitter is not a Bug Tracker!
Источник