- Как запустить jar в Linux
- Как запустить jar Linux
- Выводы
- How to Run Jar File in Ubuntu Linux
- How to execute Jar file in Ubuntu and other distributions
- Further troubleshooting Jar file not running on Linux
- How can I execute a .jar file from the terminal
- 8 Answers 8
- Как создать и выполнить файл .Jar в терминале Linux
- Как создать JAR-файл в Linux
- Start Java jar file during Startup in Linux
Как запустить jar в Linux
Java — это кроссплатформенный язык программирования, благодаря которому программы, написанные один раз, можно запускать в большинстве операционных систем: в Windows, Linux и даже MacOS. И всё это без каких-либо изменений.
Но программы, написанные на Java, распространяются в собственном формате .jar, и для их запуска необходимо специальное ПО — Java-машина. В этой небольшой статье мы рассмотрим, как запустить jar-файл в Linux.
Как запустить jar Linux
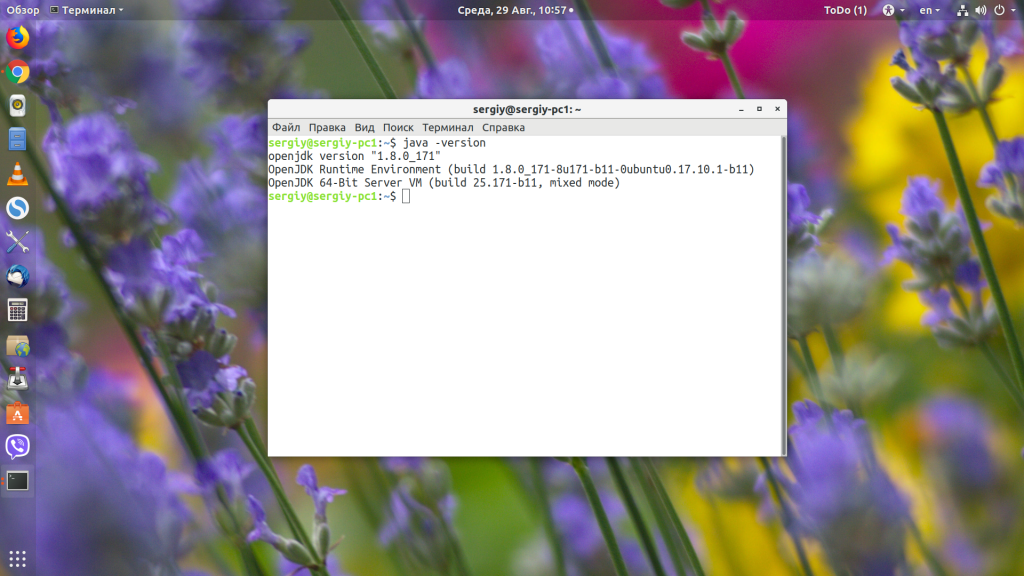
Как я уже сказал, для запуска jar-файлов нам необходимо, чтобы на компьютере была установлена Java-машина. Если вы не собираетесь ничего разрабатывать, вам будет достаточно Java Runtime Environment или JRE. Что касается версии, то, обычно, большинство программ работают с 7 или 8 версией. Если нужна только восьмая, то разработчики прямо об этом сообщают. Посмотреть версию Java и заодно убедиться, что она установлена в вашей системе, можно с помощью команды:
У меня установлена восьмая версия, с пакетом обновлений 171. Если вы получаете ошибку, что команда не найдена, то это значит, что вам нужно установить java. В Ubuntu OpenJDK JRE можно установить командой:
sudo apt install openjdk-8-jre
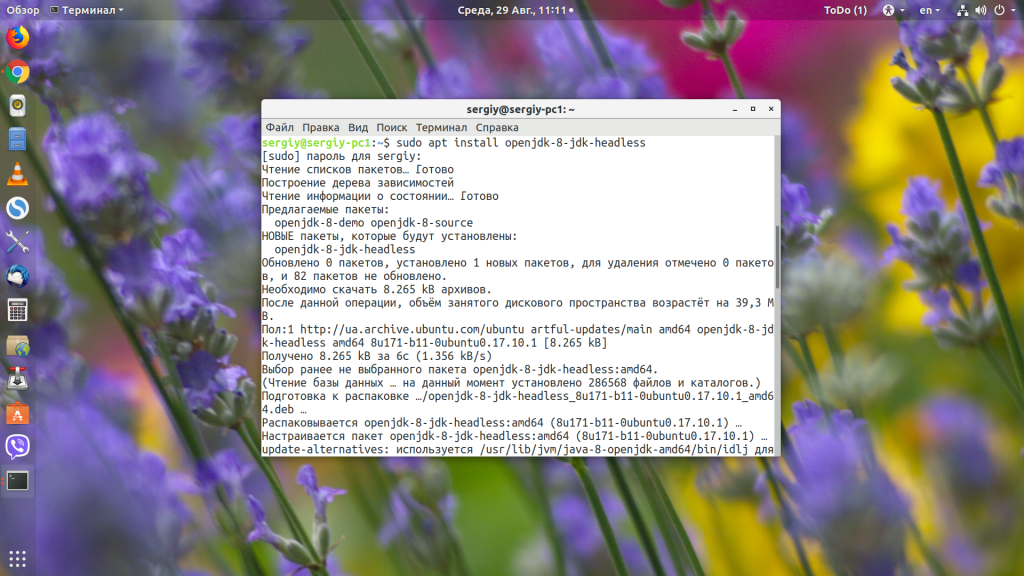
Если вы хотите скомпилировать пример из этой статьи, то вам понадобиться не JRE, а JDK, её можно установить командой:
sudo apt install openjdk-8-jdk-headless
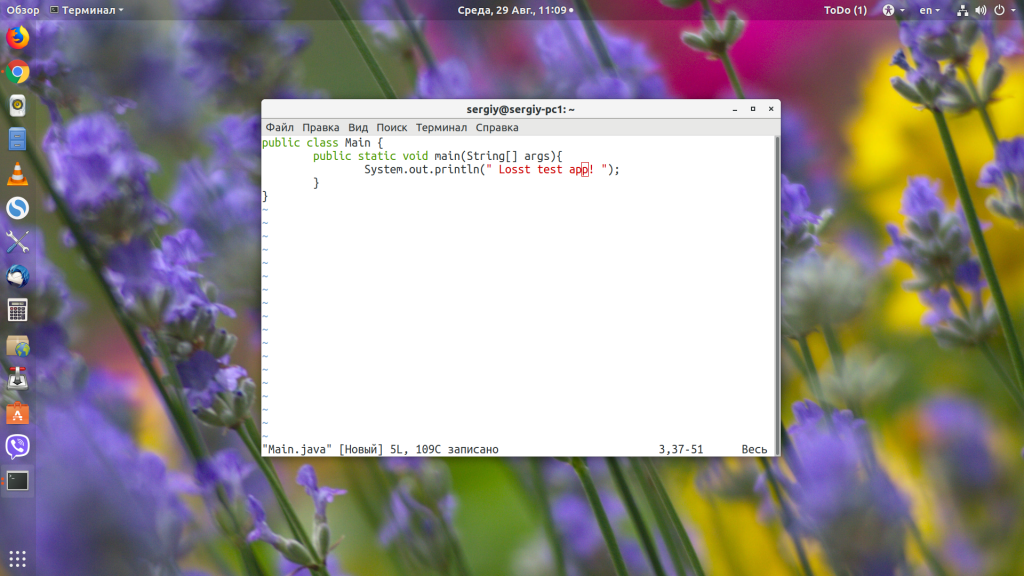
Чтобы узнать, как установить Java в других дистрибутивах, смотрите статью по ссылке выше. Когда Java будет установлена, вы можете очень просто запустить любой jar-файл в Linux, передав путь к нему в качестве параметра Java-машине. Давайте для примера создадим небольшое приложение:
public class Main <
public static void main(String[] args) <
System.out.println(» Losst test app! «);
>
>
Затем скомпилируем наше приложение в jar-файл:
javac -d . Main.java
jar cvmf MANIFEST.MF main.jar Main.class
Теперь можно запустить наш jar-файл командой java с параметром -jar:
java -jar main.jar
Таким образом вы можете запустить любой jar-файл, который собран для вашей версии Java. Но не очень удобно каждый раз открывать терминал и прописывать какую-либо команду. Хотелось бы запускать программу по щелчку мышки или как любую другую Linux-программу — по имени файла.
Если мы дадим программе право на выполнение:
chmod u+x ./main.jar
И попытаемся её запустить, то получим ошибку:
Чтобы её исправить, нам понадобиться пакет jarwrapper:
sudo apt install jarwrapper
Теперь можно запускать java в Linux по щелчку мыши или просто командой.
Выводы
В этой небольшой статье мы рассмотрели, как запустить jar Linux с помощью java-машины, а также как упростить команду запуска. Если у вас остались вопросы, спрашивайте в комментариях!
Источник
How to Run Jar File in Ubuntu Linux
Last updated October 29, 2019 By Abhishek Prakash 19 Comments
Got a Jar file but struggling to execute it? Learn how to run a Jar file in Ubuntu and other Linux distributions.
How to execute Jar file in Ubuntu and other distributions
A Jar file is basically a Java executable file. So you must have Java installed on your system. If you have Java installed in your Ubuntu, you should be able to run it either by double clicking or by selecting from right click options.
The problem here is that most Linux distributions don’t come with Java pre-installed. So please make sure to install Java on Ubuntu. or whichever distribution you are using.
You only need the Java Runtime Environment and you can install it using the command below in Ubuntu-based distributions:
Even with Java installed, sometimes running a Java application is not as straightforward as double-clicking the icon. You might have to go through a few steps.
When I tried to open the .jar file by double clicking, I was presented with the following error:
Fixing this error is very trivial. Right click the .jar file, and open properties.
Now in the properties menu, open the ‘Permissions’ tab. Enable the ‘Allow executing this file as program’ checkbox.
Now, you can simply double click the .jar file to launch the application, AndroMouse in my case. You can see that it works without any problems.
You have to keep in mind that you have to enable the ‘Allow executing as program’ permission for every .jar application you download. It is disabled by default as a security measure. You should enable it only for the applications that you trust and know are safe.
Further troubleshooting Jar file not running on Linux
Even if you have Java Runtime Environment installed and execution permission set, in some older versions of Ubuntu, the Jar file won’t run. Here’s a fix for that.
Right click on the .jar file and choose the option “Open With Other Application“:
Now on the next screen, select the option Show other applications:
In other applications, if you do not find option for Java, install the Java Runtime Environment first. Normally, you should be able to see the option Open With OpenJDK Java x Runtime. Select it and successfully run it.
Enjoy running Jar file on Ubuntu!
I hope this short guide was useful to all of you. Which Java based applications do you use? Do you have any other problems with them? Let me know in the comments below!
Like what you read? Please share it with others.
Источник
How can I execute a .jar file from the terminal
I know that to execute a file, I use the . command, then the file name with a space between them. But I’m trying to execute a .jar file using the . and it does not work. I went into the properties and marked it as executable and made it run with Java.
Is there a way to execute a file with Java in the Bash Terminal?
I am trying to execute the Minecraft.jar file.
8 Answers 8
The . syntax can only be used to run (by «sourcing») shell scripts.
You’ll need to use the java command to run a .jar file:
If you don’t have java installed, you can fix that by installing the default-jre ¹ package. You can see if you already have java installed by running in a terminal:
[1]: This will install the default openjdk Java runtime. You can use openjdk-8-jre , or openjdk-7-jre , or openjdk-6-jre instead, if you prefer — whichever is available on your version of Ubuntu.
Linux is perfectly capable of running a foreign binary, like a JAR file. This is how Wine works, for example. To run JAR files as executable do the following in a console
Cd to your JAR file and change it to executable (you can also do this through file properties in Nautilus)
Run your jar file just as if it was any other binary executable or shell script
Note: Be sure you have binfmt_misc linux kernel module loaded. If you use your custom compiled kernel without this module, binfmt-support won’t work.
If it is an executable jar, then
Not all jar-Archives contain an executable class, declared to be started in the Manifest file, but if there is, this will work.
Btw.: You don’t start most programs from the shell with the dot. The dot is a shortcut for source , and it only works in the bash and some other shells, to include a script in the scope of the current session.
A compiled binary xybin is simply started with its name if it is in the path:
or, with its absolute path:
or with its relative path:
or if you happen to be in the directory of the file, with this relative path:
The file has to be marked executable for you (see: chmod). All of the above is true for shellscripts too, but they often have an extension .sh, and you can start a shellscript by invoking the interpreter, and then it needn’t be marked executable:
If you don’t want to start a new bash, you can use source, and you do so, to consume function definitions, aliases and variable settings.
Источник
Как создать и выполнить файл .Jar в терминале Linux
JAR (Java ARchive) – это независимый от платформы формат файла, используемый для объединения многих файлов классов Java и связанных с ними метаданных и ресурсов, таких как текст, изображения и т. д., в один файл для распространения.
Он позволяет Java-средам эффективно разворачивать целое приложение в одном архиве и предоставляет множество преимуществ, таких как безопасность, его элементы могут быть сжаты, сокращено время загрузки, позволяетcz уплотнение пакетов и управление версиями, поддерживает переносимость.
Он также поддерживает упаковку для расширений.
В этой статье мы покажем, как создать простое приложение Java и связать его с JAR-файлом и продемонстрируем, как выполнить файл .jar из терминала Linux.
Для этого у вас должен быть установлен инструмент командной строки java для запуска приложения Java и флаг -jar для выполнения программы, инкапсулированной в файл JAR.
Когда этот флаг используется, указанный JAR-файл является источником всех пользовательских классов, а другие параметры пути класса игнорируются.
Как создать JAR-файл в Linux
1. Сначала начните с написания простого Java-класса с основным методом для приложения TecmintApp для демонстрационных целей.
Скопируйте и вставьте следующий код в файл TecmintApp.java.
Сохраните файл и закройте.
2. Затем нам нужно скомпилировать и упаковать класс в JAR-файл, используя утилиты javac и jar, как показано ниже:
3. Создана Ounce tecmint app.jar, теперь вы можете выполнить файл с помощью команды java, как показано ниже:
Из вывода приведенной выше команды видно, что мы столкнулись с ошибкой. JVM (Java Virtual Machine) не смог найти наш основной атрибут, поэтому он не смог найти основной класс, содержащий основной метод (public static void main (String [] args)).
Файл JAR должен иметь манифест, содержащий строку в форме Main-Class: classname, которая определяет класс с основным методом, который служит отправной точкой нашего приложения.
4. Чтобы исправить вышеуказанную ошибку, нам нужно будет обновить JAR-файл, чтобы включить атрибут манифеста вместе с нашим кодом.
Давайте создадим файл MANIFEST.MF.
Скопируйте и вставьте следующую строку в файл MANIFEST.MF.
Сохраните файл и добавьте файл MANIFEST.MF в наш tecmintapp.jar, используя следующую команду:
5. Наконец, когда мы снова выполним файл JAR, он должен предоставить нам ожидаемый результат, как показано на выводе:
Для получения дополнительной информации см. Man-страницы java, javac и jar.
Источник
Start Java jar file during Startup in Linux
Situation :
I have jar file on server PC (PC act as server), a.jar, which will be running infinite loop to listen for TCPIP connection from client PC. When connection has been made, client PC can send a zip file to server PC, a.jar will unzip it and execute a script with that zip, which will start another full screen display java file, b.jar.
a.jar will also trying to run b.jar during bootup, if b.jar already exist.
Approach 1:
I wrote a script in /etc/init.d/ to start a.jar, as it’s infinite loop, the system hang forever during bootup (in terminal screen, can’t even get into GUI). I have to boot into single user mode to remove that script in order to boot up normally.
Approach 2:
When I changed the script to run a.jar as a daemon, it runs normally, listen for connection, I can connect to the server pc and send zip file.
Problem:
- b.jar is not executed even when execution permission and files are all correctly set.
- After I sent a zip file, b.jar is executed (because it is connected to a device and that device is activated). But the full screen display is not shown like it did when executed via terminal.
Reasons of doing so
It may seems a bit complicated, but because b.jar will be constantly updated and it has to be auto start when after update, thus I use a.jar to unzip and execute new version fo b.jar.
And b.jar is required to run as root as it needs to access serial port.
(Server pc is required to be automated, thus it is required to start b.jar during startup and remotely controlled)
Question
May I know is there any better way of doing this? Or what did I do wrong? Can someone show me a better script to start it during startup?
Источник