- Killing a Windows Service that Hangs on Stopping or Not Responding
- How to Terminate a Hung Windows Service Process Using TaskKill?
- PowerShell: Stop Windows Service with Stopping Status
- Identify a Hang Process Using Resmon
- Process Explorer: Killing a Hung Process Running in SYSTEM Context
- Управление процессами с помощью PowerShell
- Get-Process – получение списка запущенных процессов
- Start-Process, Stop-Process: запуск и остановка процессов из PowerShell
- PowerShell: управление процессами на удаленном компьютере
- How to stop all the processes in Windows 10?
- Terminator 101: How to kill all the processes in Windows 10?
- Here are particular steps to take:
- Resolve PC Issues with Auslogics BoostSpeed
Killing a Windows Service that Hangs on Stopping or Not Responding
How to manually forcefully stop a hung Windows service process that hangs at “Stopping” or “Not responding”? Most Windows administrators have faced a problem, when they try to stop (restart) a service, but it gets stuck with the Stopping status. You won’t be able to stop this service from the Service management console (services.msc), since all control buttons for this service become inactive. The easiest way is to restart Windows, but it is not always acceptable. Let’s consider an alternative way, which allows to forcefully kill a stuck Windows service or process without system reboot.
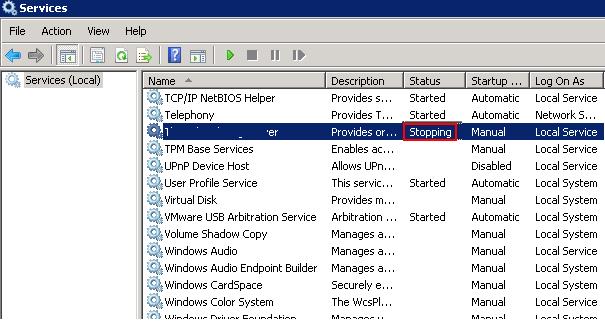
If within 30 seconds after trying to stop the service, it doesn’t stop, Windows displays this message:
If you try to stop such a service from the command prompt: net stop wuauserv , a message appears:
The service is starting or stopping. Please try again letter.

How to Terminate a Hung Windows Service Process Using TaskKill?
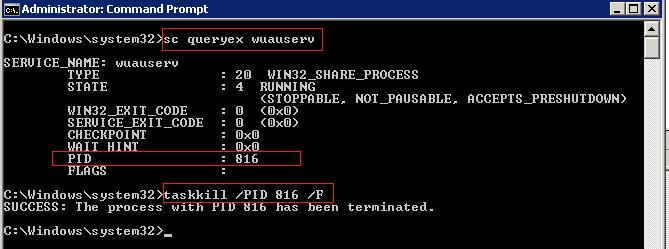
The easiest way to stop a stuck service is to use taskkill. First of all, you need to find the PID (process identifier) of the service. As an example, let’s take Windows Update service, its system name is wuauserv (you can check the name in the service properties in the services.msc console).
Run this command in the elevated command prompt (it is important, or access denied error will appear):
sc queryex wuauserv
In our case the PID of the wuauserv service is 816.
To force stop a hung process with the PID 816, run the command:
taskkill /PID 816 /F
You can stop a hung service more elegantly without checking the service PID manually. The taskkill utility has the /FI option, which allows you to use a filter to select the necessary services or processes. You can shutdown a specific service with the command:
taskkill /F /FI «SERVICES eq wuauserv»
Or you can skip the service name at all and killing all services in a hung state with the command:
taskkill /F /FI «status eq not responding»
After this, the service that hangs in the Stopping status should stop.
PowerShell: Stop Windows Service with Stopping Status
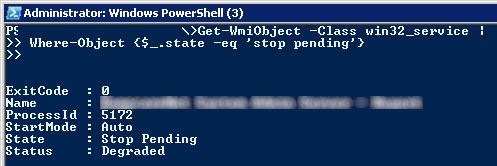
You can also use PowerShell to force the service to stop. Using the following command you can get a list of services in the Stopping state:
Get-WmiObject -Class win32_service | Where-Object
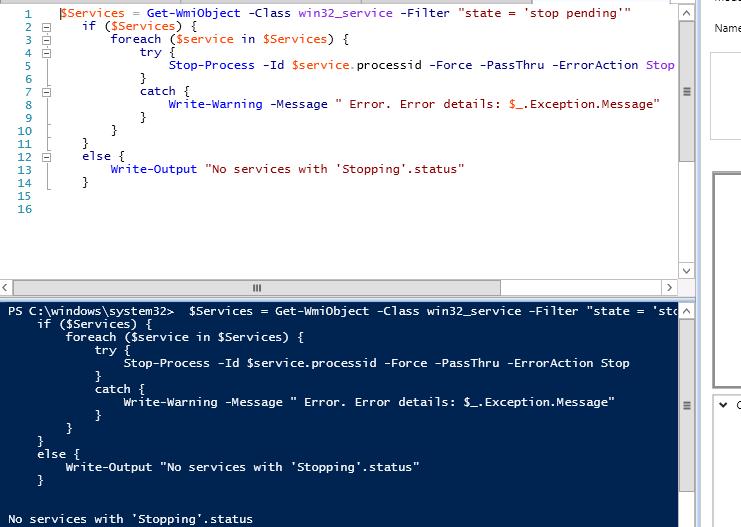
The Stop-Process cmdlet allows to terminate the processes of all found services. Let’s combine both operations into a loop and get a script that automatically terminates all the processes of the stuck services:
$Services = Get-WmiObject -Class win32_service -Filter «state = ‘stop pending'»
if ($Services) <
foreach ($service in $Services) <
try <
Stop-Process -Id $service.processid -Force -PassThru -ErrorAction Stop
>
catch <
Write-Warning -Message » Error. Error details: $_.Exception.Message»
>
>
>
else <
Write-Output «No services with ‘Stopping’.status»
>
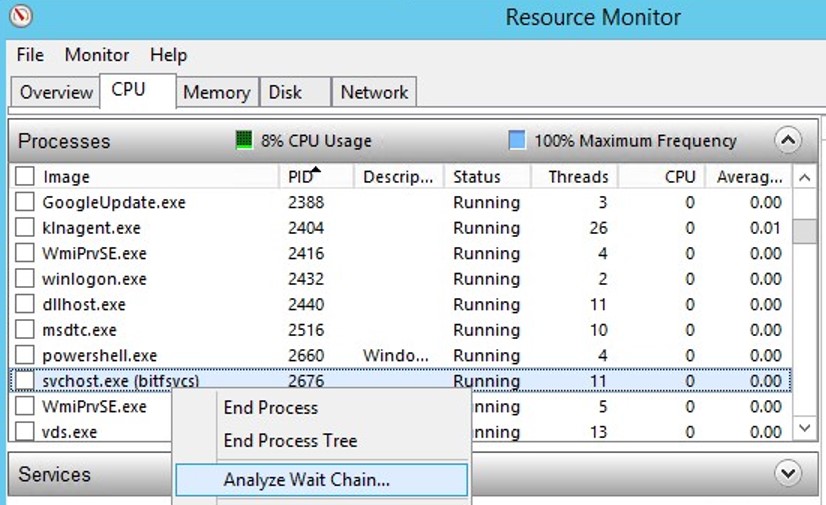
Identify a Hang Process Using Resmon
You can detect the process that caused the service freeze using the resmon (Resource Monitor).
- In the Resource Monitor window, go to the CPU tab and locate the hung service process;
- Select the item Analyze Wait Chain from the context menu;
- In the new window, you will most likely see that your process is waiting for another process. End the process. If you are waiting for the svchost.exe or another system process, you don’t need to terminate it. Try to analyze the wait chain for this process. Find the PID of the process that your svchost.exe is waiting for and kill it.
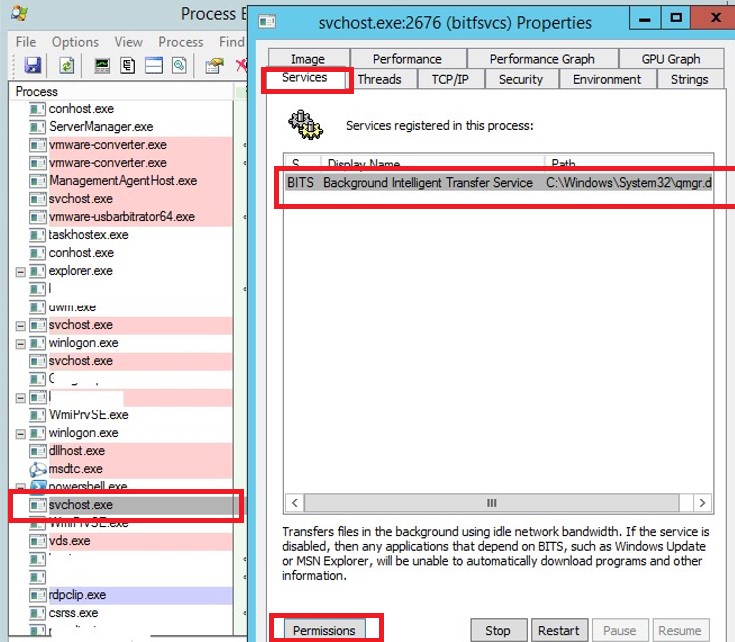
Process Explorer: Killing a Hung Process Running in SYSTEM Context
Even the local administrator cannot terminate some processes that run in the SYSTEM context. The fact is that the admin account simply haven’t permissions on some processes or services. To stop such a process (services), you need to grant permissions to the service (process) to the local Administrators group, and then terminate them. To do this, we will need two small tools: psexec.exe and ProcessExplorer (available on the Microsoft website).
- To run ProcessExplorer with the system privileges (runas SYSTEM), run the utility in this way: PSExec -s -i ProcExp.exe
- In the Process Explorer process list, find the stuck service process and open its properties;
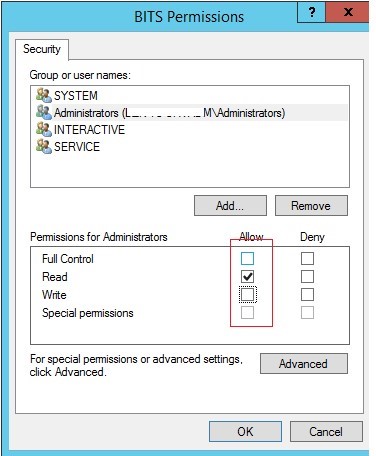
- Go to the Services tab, find your service and click the Permissions button;
- Grant the Full Control right in the service permissions for the Administrators group. Save the changes;
- Now try to stop the service process.
Управление процессами с помощью PowerShell
PowerShell предоставляет широкие возможности управления процессами на локальном или удаленном компьютере. С помощью PowerShell можно получить список запущенных процессов, приостановить зависший процесс, найти процесс по заголовку окна, запустить новый процесс в скрытом или интерактивном режиме.
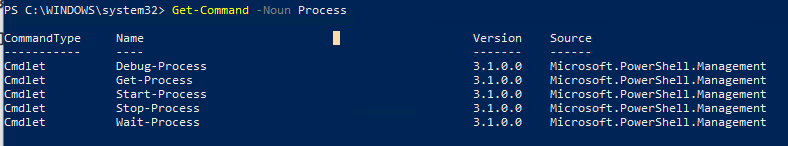
Список доступных командлетов управления процессами в Windows 10 можно вывести так:
Get-Command –Noun Process
- Get-Process – получить список запущенных процессов;
- Start-Process – запустить процесс/программу;
- Stop-Process – принудительно остановить процесс;
- Debug-Process – используется для отладки процессов;
- Wait-Process – используется для ожидания окончания процесса.
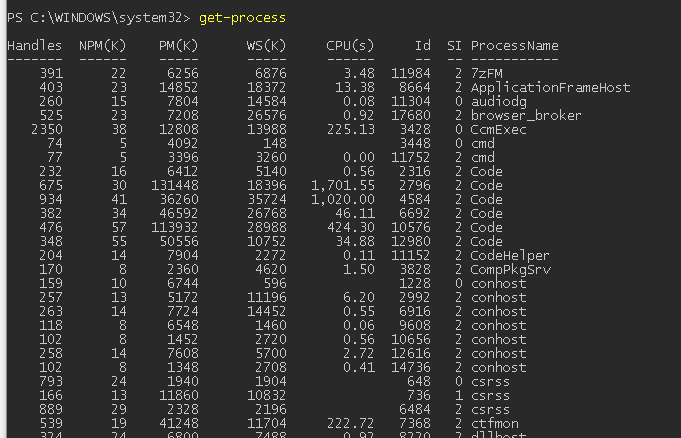
Get-Process – получение списка запущенных процессов
Командлет Get-Process позволяет вывести список запущенных процессов на локальном компьютере.
По-умолчанию выводятся следующие свойства запущенных процессов:
- Handles – количество дескрипторов ввода — вывода, которые отрыл данный процесс;
- NPM(K) — Non-paged memory (невыгружаемый пул). Размер данных процесса (в Кб.), которые никогда не попадают в файл подкачки на диск;
- PM(K) – размер памяти процесса, которая может быть выгружена на диск;
- WS(K) – размер физической памяти в Кб, используемой процессом (working set).
- CPU(s) – процессорное время, использованное процессом (учитывается время на всех CPU);
- ID — идентификатор процесса;
- SI (Session ID) – идентификатор сеанса процесса (0 — запущен для всех сессий, 1 – для первого залогиненого пользователя, 2 — для второго и т.д.);
- ProcessName – имя процесса.
Чтобы получить все свойства нескольких процессов:
Get-Process winword, notep* | Format-List *
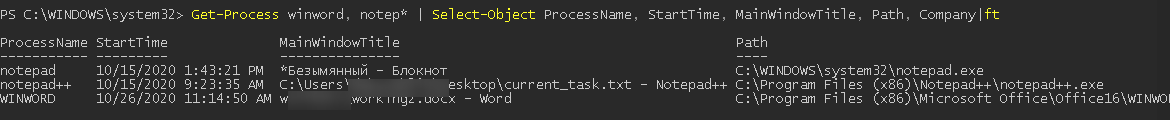
Можно вывести только определенный свойства процессов. Например, имя (ProcessName) время запуска (StartTime), заголовок окна процесса (MainWindowTitle), имя исполняемого файла (Path) и наименование разработчика (Company):
Get-Process winword, notep* | Select-Object ProcessName, StartTime, MainWindowTitle, Path, Company|ft
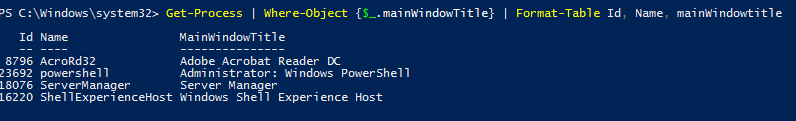
Вывести список запущенных процессов пользователя с графическими окнами (в список не попадут фоновые и системные процессы):
Get-Process | Where-Object <$_.mainWindowTitle>| Format-Table Id, Name, mainWindowtitle
С помощью параметра IncludeUserName можно вывести имя пользователя (владельца), который запустил процесс:
Get-Process -Name winword -IncludeUserName
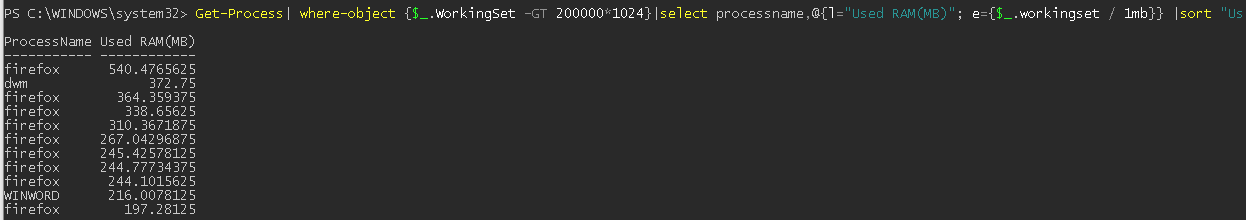
С помощью Where-Object можно выбрать процессы в соответствии с заданными критериями. Например, выведем все процессы, которые используются более 200 Мб оперативной памяти, отсортируем процессы в порядке убывания используемого объема RAM, размер памяти из Кб преобразуем в Мб:
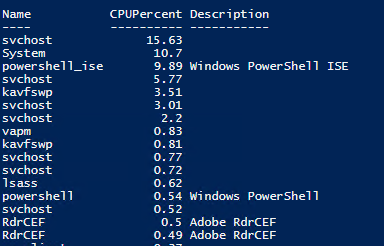
Как мы уже говорили ранее командлет Get-Process в параметре CPU содержит время использования процессора конкретным процессом в секундах. Чтобы отобразить процент использования CPU процессами (по аналогии с Task Manager), используйте такую функцию:
function Get-CPUPercent
<
$CPUPercent = @<
Name = ‘CPUPercent’
Expression = <
$TotalSec = (New-TimeSpan -Start $_.StartTime).TotalSeconds
[Math]::Round( ($_.CPU * 100 / $TotalSec), 2)
>
>
Get-Process | Select-Object -Property Name, $CPUPercent, Description | Sort-Object -Property CPUPercent -Descending | Select-Object -First 20
>
Чтобы найти зависшие процессы (которые не отвечают), выполните команду:
Start-Process, Stop-Process: запуск и остановка процессов из PowerShell
Чтобы запустить новый процесс с помощью PowerShell используется команда:
Start-Process -FilePath notepad
Если каталог с исполняемым файлом отсутствует в переменной окружения $env:path, нужно указать полный путь к файлу:
Start-Process -FilePath ‘C:\distr\app.exe’
Можно запустить программу и передать ей аргументы:
Start-Process -FilePath ping -ArgumentList «-n 10 192.168.1.11»
С помощью параметра WindowStyle вы можете задать режим запуска окна процесса (normal, minimized, maximized, hidden). Например, чтобы запустить программу в максимально развернуом окне и дождаться завершения процесса, выполните команду:
Start-Process -FilePath tracert -ArgumentList «192.168.1.11» –wait -windowstyle Maximized
С помощью командлета Stop-Process можно завершить любой процесс. Например, чтобы закрыть все запущенные процессы notepad:
Stop-Process -Name notepad
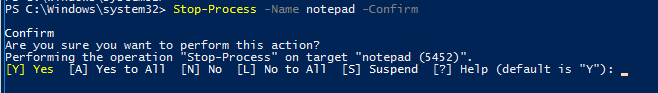
По-умолчанию не запрашивается подтверждение завершения процесса. Закрываются все процессы, которые соответствуют указанным критериям. Чтобы запросить подтверждение завершения для каждого процесса, добавьте –Confirm.
Stop-Process -Name notepad.exe -Confirm
(Get-Process -Name notepad).Kill()
Из PowerShell можно принудительно завершить все приложения, которые не отвечают диспетчеру процессов Windows:
Get-Process | where-object <$_.Responding -eq $false>| Stop-Process
PowerShell: управление процессами на удаленном компьютере
С помощью аргумента ComputerName командлет Get-Process позволяет управлять процессами на удаленных компьютерах (должен быть включен и настроен WinRM).
Get-Process -ComputerName dc01, dc02| Format-Table -Property ProcessName, ID, MachineName
Если вы хотите завершить процесс на удаленном компьютере, имейте в виду, что у командлета Stop-Process отсутствует параметр –ComputerName. Для завершения процесса на удаленном компьютере можно использовать такой PowerShell код:
$RProc = Get-Process -Name notepad -ComputerName dc01
Stop-Process -InputObject $RProc
How to stop all the processes in Windows 10?
Terminator 101: How to kill all the processes in Windows 10?
Multiple open and running windows on your desktop or laptop can lead the system to become slow and even face some errors. So you might wonder: can I stop all the processes running or kill all open applications in Windows 10?
Perhaps in seeking to terminate all running processes, the first thing you’re considering is forceful restarting. Forget about doing it – forceful restarting could lead to computer and system files damage. Instead, follow these methods on how to kill all the processes in Windows 10 properly:
- Through the Command Prompt – Learn how to terminate Windows 10 processes in the Command Prompt, particularly unresponding ones. Do this through the following steps:
- Go to Search. Type cmd and open Command Prompt.
- Once there, enter this line taskkill /f /fi “status eq not responding” and then press Enter.
- This command should end all processes deemed unresponding
- Via Task Manager – More recent Windows 10 versions have related processed bundled under a common cluster. End all the processes under a single cluster through right-clicking on that cluster and choosing End Task.
- Use CloseAll and other powerful tools – Freeware tool CloseAll is third-party software that automatically closes all running processes, leaving the user on Desktop. Simply open it and then press OK. KillThemAll, a creation of a Neowin user, also does the same task but gives users a chance to save their data. Take note, though, that it leaves Explorer.exe open.
- Use PowerShell – Kill a process that runs elevated by opening PowerShell as Administrator. Type the command Get-Process for you to see the list of running processes. Kill a process by its name by executing this cmdlet: Stop-Process -Name “ProcessName” -Force. Kill a process by its PID by running this command: Stop-Process -ID PID -Force.
- Clean boot your computer – This technique allows you to start Windows through only a minimal number of drivers and programs. However, you would need to restart your PC in order to get the desired effect. Here are some steps:
- Go to Start. Type msconfig and then hit Enter.
- Go to System Configuration. Once there, click on Services, check the Hide All Microsoft services check box, and then click Disable all.
- Go to Startup. Open Task Manager.
- Select every startup item and click Disable.
- Close Task Manager and then restart the computer.
How about if you want to end specific processes, programs, or apps in Windows 10?
Here are particular steps to take:
- To end all background processes, go to Settings, Privacy, and then Background Apps. Turn off the Let apps run in the background
- To end all Google Chrome processes, go to Settings and then Show advanced settings. Kill all related processes by unchecking Continue running background apps when Google Chrome is closed.
- To end all Internet Explorer processes, use the Command Prompt as an administrator. Enter the command taskkill /F /IM iexplore.exe and then press Enter.
Resolve PC Issues with Auslogics BoostSpeed
Besides cleaning and optimizing your PC, BoostSpeed protects privacy, diagnoses hardware issues, offers tips for boosting speed and provides 20+ tools to cover most PC maintenance and service needs.
Good luck and we hope you’ll have a smooth PC experience from here!