- Introduction to Operating Systems
- Two Views of Operating System
- Operating System: User View
- Operating System: System View
- Operating System Management Tasks
- Types of Operating System
- What is Operating System? Types of OS, Features and Examples
- What is an Operating System?
- History Of OS
- Examples of Operating System with Market Share
- Types of Operating System (OS)
- Batch Operating System
- Multi-Tasking/Time-sharing Operating systems
- Real time OS
- Distributed Operating System
- Network Operating System
- Mobile OS
- Functions of Operating System
- Features of Operating System (OS)
- Advantage of using Operating System
- Disadvantages of using Operating System
- What is a Kernel?
- Features of Kennel
- Types of Kernels
- UNIT 4. OPERATING SYSTEMS
Introduction to Operating Systems
A computer system has many resources (hardware and software), which may be required to complete a task. The commonly required resources are input/output devices, memory, file storage space, CPU, etc. The operating system acts as a manager of the above resources and allocates them to specific programs and users, whenever necessary to perform a particular task. Therefore the operating system is the resource manager i.e. it can manage the resource of a computer system internally. The resources are processor, memory, files, and I/O devices. In simple terms, an operating system is an interface between the computer user and the machine.
It is very important for you that every computer must have an operating system in order to run other programs. The operating system mainly coordinates the use of the hardware among the various system programs and application programs for various users.
An operating system acts similarly like government means an operating system performs no useful function by itself; though it provides an environment within which other programs can do useful work.
Below we have an abstract view of the components of the computer system:
In the above picture:
The Computer Hardware contains a central processing unit(CPU), the memory, and the input/output (I/O) devices and it provides the basic computing resources for the system.
The Application programs like spreadsheets, Web browsers, word processors, etc. are used to define the ways in which these resources are used to solve the computing problems of the users. And the System program mainly consists of compilers, loaders, editors, OS, etc.
The Operating System is mainly used to control the hardware and coordinate its use among the various application programs for the different users.
Basically, Computer System mainly consists of hardware, software, and data.
OS is mainly designed in order to serve two basic purposes:
The operating system mainly controls the allocation and use of the computing System’s resources among the various user and tasks.
It mainly provides an interface between the computer hardware and the programmer that simplifies and makes feasible for coding, creation of application programs and debugging
Two Views of Operating System
Operating System: User View
The user view of the computer refers to the interface being used. Such systems are designed for one user to monopolize its resources, to maximize the work that the user is performing. In these cases, the operating system is designed mostly for ease of use, with some attention paid to performance, and none paid to resource utilization.
Operating System: System View
The operating system can be viewed as a resource allocator also. A computer system consists of many resources like — hardware and software — that must be managed efficiently. The operating system acts as the manager of the resources, decides between conflicting requests, controls the execution of programs, etc.
Operating System Management Tasks
Process management which involves putting the tasks into order and pairing them into manageable size before they go to the CPU.
Memory management which coordinates data to and from RAM (random-access memory) and determines the necessity for virtual memory.
Device management provides an interface between connected devices.
Storage management which directs permanent data storage.
An application that allows standard communication between software and your computer.
The user interface allows you to communicate with your computer.
Types of Operating System
Given below are different types of Operating System:
What is Operating System? Types of OS, Features and Examples
What is an Operating System?
An Operating System (OS) is a software that acts as an interface between computer hardware components and the user. Every computer system must have at least one operating system to run other programs. Applications like Browsers, MS Office, Notepad Games, etc., need some environment to run and perform its tasks.
The OS helps you to communicate with the computer without knowing how to speak the computer’s language. It is not possible for the user to use any computer or mobile device without having an operating system. 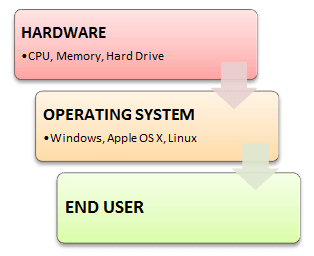
History Of OS
- Operating systems were first developed in the late 1950s to manage tape storage
- The General Motors Research Lab implemented the first OS in the early 1950s for their IBM 701
- In the mid-1960s, operating systems started to use disks
- In the late 1960s, the first version of the Unix OS was developed
- The first OS built by Microsoft was DOS. It was built in 1981 by purchasing the 86-DOS software from a Seattle company
- The present-day popular OS Windows first came to existence in 1985 when a GUI was created and paired with MS-DOS.
Examples of Operating System with Market Share
Following are the examples of Operating System with the latest Market Share
| OS Name | Share |
| Windows | 40.34 |
| Android | 37.95 |
| iOS | 15.44 |
| Mac OS | 4.34 |
| Linux | 0.95 |
| Chrome OS | 0.14 |
| Windows Phone OS | 0.06 |
Types of Operating System (OS)
Following are the popular types of Operating System:
- Batch Operating System
- Multitasking/Time Sharing OS
- Multiprocessing OS
- Real Time OS
- Distributed OS
- Network OS
- Mobile OS
Batch Operating System
Some computer processes are very lengthy and time-consuming. To speed the same process, a job with a similar type of needs are batched together and run as a group.
The user of a batch operating system never directly interacts with the computer. In this type of OS, every user prepares his or her job on an offline device like a punch card and submit it to the computer operator.
Multi-Tasking/Time-sharing Operating systems
Time-sharing operating system enables people located at a different terminal(shell) to use a single computer system at the same time. The processor time (CPU) which is shared among multiple users is termed as time sharing.
Real time OS
A real time operating system time interval to process and respond to inputs is very small. Examples: Military Software Systems, Space Software Systems are the Real time OS example.
Distributed Operating System
Distributed systems use many processors located in different machines to provide very fast computation to its users.
Network Operating System
Network Operating System runs on a server. It provides the capability to serve to manage data, user, groups, security, application, and other networking functions.
Mobile OS
Mobile operating systems are those OS which is especially that are designed to power smartphones, tablets, and wearables devices.
Some most famous mobile operating systems are Android and iOS, but others include BlackBerry, Web, and watchOS.
Functions of Operating System
Below are the main functions of Operating System: 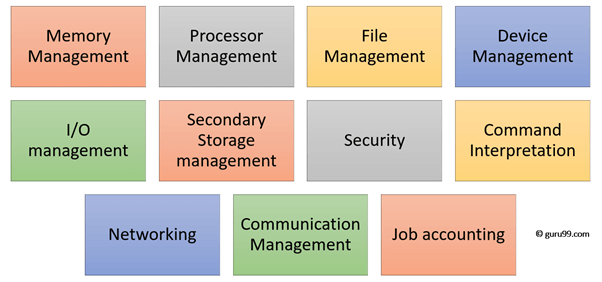
In an operating system software performs each of the function:
- Process management:- Process management helps OS to create and delete processes. It also provides mechanisms for synchronization and communication among processes.
- Memory management:- Memory management module performs the task of allocation and de-allocation of memory space to programs in need of this resources.
- File management:- It manages all the file-related activities such as organization storage, retrieval, naming, sharing, and protection of files.
- Device Management: Device management keeps tracks of all devices. This module also responsible for this task is known as the I/O controller. It also performs the task of allocation and de-allocation of the devices.
- I/O System Management: One of the main objects of any OS is to hide the peculiarities of that hardware devices from the user.
- Secondary-Storage Management: Systems have several levels of storage which includes primary storage, secondary storage, and cache storage. Instructions and data must be stored in primary storage or cache so that a running program can reference it.
- Security:- Security module protects the data and information of a computer system against malware threat and authorized access.
- Command interpretation: This module is interpreting commands given by the and acting system resources to process that commands.
- Networking: A distributed system is a group of processors which do not share memory, hardware devices, or a clock. The processors communicate with one another through the network.
- Job accounting: Keeping track of time & resource used by various job and users.
- Communication management: Coordination and assignment of compilers, interpreters, and another software resource of the various users of the computer systems.
Features of Operating System (OS)
Here is a list important features of OS:
- Protected and supervisor mode
- Allows disk access and file systems Device drivers Networking Security
- Program Execution
- Memory management Virtual Memory Multitasking
- Handling I/O operations
- Manipulation of the file system
- Error Detection and handling
- Resource allocation
- Information and Resource Protection

Advantage of using Operating System
- Allows you to hide details of hardware by creating an abstraction
- Easy to use with a GUI
- Offers an environment in which a user may execute programs/applications
- The operating system must make sure that the computer system convenient to use
- Operating System acts as an intermediary among applications and the hardware components
- It provides the computer system resources with easy to use format
- Acts as an intermediator between all hardware’s and software’s of the system
Disadvantages of using Operating System
- If any issue occurs in OS, you may lose all the contents which have been stored in your system
- Operating system’s software is quite expensive for small size organization which adds burden on them. Example Windows
- It is never entirely secure as a threat can occur at any time
What is a Kernel?
The kernel is the central component of a computer operating systems. The only job performed by the kernel is to the manage the communication between the software and the hardware. A Kernel is at the nucleus of a computer. It makes the communication between the hardware and software possible. While the Kernel is the innermost part of an operating system, a shell is the outermost one.
Features of Kennel
- Low-level scheduling of processes
- Inter-process communication
- Process synchronization
- Context switching
Types of Kernels
There are many types of kernels that exists, but among them, the two most popular kernels are:
1.Monolithic
A monolithic kernel is a single code or block of the program. It provides all the required services offered by the operating system. It is a simplistic design which creates a distinct communication layer between the hardware and software.
2. Microkernels
Microkernel manages all system resources. In this type of kernel, services are implemented in different address space. The user services are stored in user address space, and kernel services are stored under kernel address space. So, it helps to reduce the size of both the kernel and operating system.
UNIT 4. OPERATING SYSTEMS
1. Make sure you are familiar with these words and phrases:
Hardware; software; computer’s language; application; entire operating system; kernel; account; advantages; different versions; execute and provide services; gooey.
2. Before you read the text below, discuss these questions.
1. What is an operating system?
2. What is its function?
3. Where is an operating system (OS) stored?
4. What are the most common operating systems?
Now read the text and check some of your answers.
When a brand new computer comes off the factory assembly line, it can do nothing. The hardware needs software to make it work. We are not talking only about application software such as word processing or spreadsheet software as an application software package doesn’t communicate directly with the hardware. Between the applications software and hardware is a software interface – an operating system. An operating system or OS is a software on the hard drive that enables the computer hardware to communicate and operate with the computer software. Without a computer operating system, a computer and software programs would be useless. An operating system manages the computer’s memory, processes, and all of its software and hardware. It also allows you to communicate with the computer without knowing how to speak the computer’s language.
The most important program in the operating system, the program that manages the operating system, is the supervisor program. It is referred to as resident as most of it remains in memory. The supervisor controls the entire operating system and loads into memory other operating programs (called nonresident) from disk storage only as needed.
An operating system has three main functions: 1) manage the computer’s resources, such as the CPU, memory, disk drives, and printers; 2) establish a user interface; 3) execute and provide services for application software.
Furthermore, all input and output operations, although invoked by an applications program, are actually carried out by the operating system.
Modern operating systems use a graphical user interface, or GUI (pronounced gooey). A GUI lets you use your mouse to click icons, buttons, and menus, and everything is clearly displayed on the screen using a combination of graphics and text.
All computers do not use the same operating systems. It is therefore important to assess the operating system used on a particular model before initial commitment because some software is only designed to run under the control of specific operating systems.
Operating systems usually come preloaded on any computer you buy. Most people use the operating system that comes with their computer, but it’s possible to upgrade or even change operating systems.
The three most common operating systems for personal computers are Microsoft Windows, Apple Mac OS X, and Linux.
Microsoft created the Windows operating system in the mid-1980s. Over the years, there have been many different versions of Windows, but the most recent ones are Windows 8 (released in 2012), Windows 7 (2009), and Windows Vista (2007). Windows comes preloaded on most new PCs, which helps to make it the most popular operating system in the world.
Mac OS is a line of operating systems created by Apple. It comes preloaded on all new Macintosh computers, or Macs. All of the recent versions are known as OS X (pronounced O-S Ten), and the specific versions include Yosemite (released in 2014), Mavericks (2013), Mountain Lion (2012), Lion (2011), and Snow Leopard (2009).
According to StatCounter Global Stats, Mac OS X users account for 9.5% of the operating systems market as of September 2014—much lower than the percentage of Windows users (almost 90%). One reason for this is that Apple computers tend to be more expensive.
Linux (pronounced LINN-ux) is a family of open-source operating systems, which means they can be modified and distributed by anyone around the world. This is different from proprietary software like Windows, which can only be modified by the company that owns it (Microsoft). The advantages of Linux are that it is free, and there are many different distributions—or versions—you can choose from.
Linux is named after Linus Torvalds, who created the Linux kernel in 1991.
According to StatCounter Global Stats, Linux users account for less than 2% of the operating systems market as of September 2014. However, most servers run Linux because it’s relatively easy to customize.
Study the v ocabulary list:
assembly n — 1) компоновка, ассемблирование 2) сборка, монтаж 3) компоновочный узел (устройства); скомпонованный блок
spreadsheet n – электронная таблица
OS n (operating system) – операционная система
useless adj — бесполезный
supervisor n — супервизор; управляющая программа; диспетчер
remain v — оставаться
load v — загружать
preload v — предварительно загружать
manage v — управлять
establish v — устанавливать
execute v – выполнять, осуществлять
provide v — обеспечивать
invoke v — вызывать, запускать активировать программу, процедуру или процесс
GUI (gooey) n — графический пользовательский интерфейс GUI
release v – выпускать, пускать
include v — включать
reason n — причина
tend v – иметь склонность (к), тяготеть
proprietary adj — частный, собственный, патентованный 1) разработанный внутри фирмы для собственных целей (о программных или аппаратных средствах)
distribution n — распределение
customize v – настраивать
1. Practise reading the following words and collocations.
a) Interface; useless; process; allow; CPU; establish; furthermore; although; invoked; actually; gooey; mouse; icon; button; menu; preloaded; upgrade; change; common; create; percentage; own; advantages; distributions; versions; choose; kernel; account.
b) Word processing; spreadsheet software; hard drive; computer’s language; supervisor program; disk storage; computer’s resources; disk drives; different versions; specific version; proprietary software.
c) Factory assembly line; application software package; communicate and operate; refer to a resident; entire operating system; load into memory; establish a user interface; execute and provide services; all input and output; graphical user interface; clearly displayed on the screen; combination of graphics and text; operating system market; open-resource operating system; can be modified and distributed; relatively easy to customize.
2. Find in the text English equivalents for the following.
Обработка текстов; программное обеспечение электронных таблиц; пакет прикладных программ; взаимодействовать непосредственно; программный интерфейс; программное обеспечение на жестком диске; управлять памятью компьютера; программа супервизора; загружать в память; основные функции; установить пользовательский интерфейс; программа ввода и вывода; четко отражается на экране; предварительно загружены (установлены); семейство операционных систем с открытым исходным кодом; могут быть изменены и распределены; относительно легко настроить.
3. Give the most suitable Russian equivalents for the following expressions.
Come off; factory assembly line; application software; spreadsheet software; application software package; communicate directly; interface; hard drive; manage the computer’s memory; supervisor program; it’s referred to as resident; entire OS; load into memory; disk storage; furthermore; invoked by; are actually carried out; modern; GUI; use your mouse to click icons; clearly displayed; come preloaded on any computer; upgrade; common OSs; tend to be more expensive; different from proprietary software; can be modified; relatively easy to customize.
4. Match the following words and phrases to make complete expressions from the text:
with the computer
5. Match the following words with their synonyms in the brackets: divide, function, distribute, stop, initiate, make, load(ing), substitute for, apply for, modify, activate (open, demand, separate, allot, process, disrupt, stand in for, utilization, start, vary, produce)
6. Consult the dictionary and give the Russian equivalents for the following:
System: s ystem accounting; system activity; system administration; system aging; system ambiguity; system analysis; system application; system approach; system architecture; system area; system behaviour; system BIOS; system bus; system capability; system catalogue; system characteristic; system check; system check-out; system code; system console; system construction; system cover; system costs; system crash; system database; system cutover; system cursor; system designer; system engineer; system failure.
Main: main office; main body of a program; main program; main storage; main click; mainframe (computer); mainly
Network: network adapter; network administrator; network architecture; network controller; network database; network diagram; network drive; network hardware; network management; network operating system; network printer; network processor; neutral network; radio network; television network; networked TV programme; networking specialist.
Access: to have access to something; access authority; access category; access control; access line; access level; access period; access privilege; access rights; direct memory access; to access the file; accessible.
7. Match the following common DOS (disk operating systems) commands from the box below with the appropriate explanation.
BACKUP, CHDIR or CD, CHKDSK, CLS, DEL, DIR:SORT, REN, TYPE, FIND, DISKCOPY.
1. Searches for a specific string of a text in a file.
2. Allows a text file from the current directory to be displayed on screen.
3. Allows the user to change name of a file.
4. Saves the contents of the hard disk to a floppy disk for security purposes.
5. Is used when it is necessary to change the current directory.
6. Clears data from the screen.
7. Alphabetically sorts and lists a disk directory.
8. Makes back-up copies of the contents of one disk to another.
9. Deletes a specified file from the current directory, specified drive, or specified path.
10. Produce a status report of the currently logged-on disk, indicating the amount of disk space used, the available capacity (in bytes), and the number of files on disk.
8. Here is a list of typical tasks performed by an operating system. In each case the main verb has been omitted. Complete the sentences using the words from the box. Sometimes more than one may apply.
Execute, monitor, format, diagnose
1.……………. input and output devices.
2……………. the status of hardware devices.
3…………….. hardware interrupts.
5…………….. disk directories.
6…………….. disk reading and writing operations.
8…………….. disk commands relating to the detection, copying, renaming, and dumping of files.
9. Translate into Russian:
1. Almost all computers, including hand-held computers, desktop computers, supercomputers, and even modern video game consoles, use an operating system of some type. Some of the oldest models may however use an embedded OS, that may be contained on a compact disk or other storage device. 2. Common contemporary operating systems include Microsoft Windows, Mac OS x, Linux and Solaris. Microsoft Windows has a significant majority of market share in the desktop and notebook computer markets, while servers generally run in Linux or other Unix-like systems. Embedded device markets are split amongst several operating systems. 3. Interrupts are central to operating systems as they allow the operating system to deal with the unexpected activities of running programs and the world outside the computer. Interrupt-based programming is one of the most basic forms of time-sharing, being directly supported by most CPUs. 4. Modern CPUs support something called dual mode operation. CPUs with this capacity use two modes: protected mode and supervisor mode, which allow certain CPU functions to be controlled and affected only by the operating system kernel. 5. Among other things, a multiprogramming operating system kernel must be responsible for managing all system memory which is currently in use by programs. 6. Currently most operating systems support a variety of networking protocols, hardware, and applications for using them. This means that computers running dissimilar operating systems can participate in a common network for sharing resources such as computing, files, printers, and scanners using either wired or wireless connection.
10. Answer the questions.
1. What is an operating system (OS)?
2. Why is an operating system so important?
3. What are the main functions of an OS?
4. Why is a supervisor program the most important operating program?
5. What do modern OSs use? Why?
6. Is it possible to change an OS?
7. What are the most common operating systems? Which one is the most and least popular and why?
11. Say if the statements are true or false.
1. Application software package communicates directly with the hardware.
2. An operating system is a master control program which controls the functions of the computer system as a whole and the running of application programs.
3. All computers do not use the same OSs.
4. You can’t change or upgrade operating systems.
5. Most people use the operating systems that comes with their computer.
6. Windows OS was created by Apple.
7. Linux OS cannot be modified by anyone in the world.
8. Windows OS can only be modified by Microsoft.
9. Most servers run Windows because it’s relatively easy to customize.
12. Say what you have learnt from the text
1. The term “operating system”.
2. Supervisor program
3. The main functions of an OS.
4. The most common OSs.
13. Read the interview with Bill Thomson, a program developer, and answer the following questions:
1. Why is Windows so popular? Give two reasons.
2. Which Windows Vista edition is aimed at high-end PC users, gamers and multimedia professionals?
Interviewer: There is no doubt that Windows has revolutionized the way we use computers today. Bill, can you explain just why it’s so popular?
Bill: Well, very simply, people find Windows very easy to use because everything is presented in graphic images. It’s also compatible with thousands of programs.
Interviewer: The big news at the moment is, of course, the launch of Windows Vista – the successor to Windows XP. I understand that there are several versions of Vista available. Could you give us some advice on which one to get?
Bill: Yes, you are right. There are four main editions: Home Basic, Home Premium, Business and Ultimate. Home Basic is designed for users with basic needs, such as email and internet access. Home Premium is for more advanced home computing and entertainment. It includes a DVD maker, a movie maker and a Media Centre, which lets you listen to music, watch video and record TV programmes on your PC. The business edition is ideal for business organizations of all sizes. It offers new backup technologies and advanced networking capabilities. Finally, the Ultimate edition combines all the features of the other editions, making it the most complete. It has everything you need to enjoy the latest in music, games, digital photography and high-definition TV. It’s aimed at high-end PC users, gamers and multimedia professionals.
Interviewer: And what other factors make Windows Vista so attractive?
Bill: The user interface has been redesigned with new icons and a new visual style. The system gives you more flexibility when you search and organize your files, and it offers support for the latest technologies, from DVD creation to speech recognition.
Interviewer: What about internet connections? Have you been improved?
Bill: Yes, Internet Explorer is more reliable and secure. The Security Centre includes an anti-spyware program called Windows Defender and a firewall that protects your computer from internet attacks.
Interviewer: And what sort of application software can you use with Windows?
Bill: The most popular is still Microsoft Office, a suite that includes the word processor, Word, an email program, the Excel spreadsheet program, and the presentation graphics program, Power Point.
Exercise 14. Translate into English.
1. Операционная система (ОС) – базовый комплекс компьютерных программ, обеспечивающий управление аппаратными средствами компьютера, работу с файлами, ввод и вывод данных, а также выполнение прикладных программ и утилит. 2. Операционная система или ОС представляет собой программное обеспечение на жестком диске, позволяющее аппаратным средствам компьютера взаимодействовать и работать с программным обеспечением. 3. Операционная система необходима для работы компьютера. Она управляет памятью, компьютерными процессами и всем его программным и аппаратным обеспечением. 4. Наиболее важная программа в операционной системе — это программа, которая управляет операционной системой — программа супервизора. 5. Современные операционные системы используют графический интерфейс пользователя. 6. Большинство людей используют операционную систему, которая была предварительно установлена на их компьютере. Тем не менее операционная система может быть обновлена или изменена. 8. Наиболее распространенные операционные системы для персональных компьютеров — это Microsoft Windows, AppleMac OS X и Linux. Самой распространенной является операционная система Microsoft Windows , так как она легка в эксплуатации и совместима со многими программами. Операционная система Linux относится к семейству операционных систем с открытым исходным кодом. Она имеет наименьшую долю на рынке операционных систем. 9. Графические станции видеостудии работают под управлением операционной системы Linux . 10. Язык пакета установки не поддерживается операционной системой. 11. Когда придет время установки операционной системы, базовой системы или дополнительных пакетов, укажите программе установки на привод CD — ROM .
Exercise 15. Divide into several groups. Each group chooses one operating system and gives the arguments why it is the best one.




