- Тор для линукс дебиан
- 2. Install obfs4proxy
- 3. Edit your Tor config file, usually located at /etc/tor/torrc and replace its content with:
- 4. Restart Tor
- 5. Monitor your logs
- 6. Final notes
- TorBrowser
- Installing the official Debian package
- Debian 11 and later
- Debian 10 and older
- Installing from the website
- Advanced Tor Usage
- Torrc File Location
- AppArmor confinement and Xserver isolation
- Bugs and known issues
- Clarifying common misconceptions
- Tor isn’t illegal to use
- The deep web/dark web aren’t dangerous to browse, and won’t expose you to hackers and malware
- Tor isn’t only used for illegal purposes
- You won’t get arrested or get into trouble with your ISP or someone else for running Tor
- Tor and streaming/torrenting
- See also
- Tor Browser для Linux
- Руководство
- Шаг №1: Инсталляция
- Шаг №2: Первый запуск и настройка
- Репозиторий Debian
- Можно ли использовать APT через Tor?
- Можно установить Tor из репозитория Ubuntu?
- Зачем нужно включать репозиторий Tor в Debian? Как это сделать?
- Prerequisite: Verify the CPU architecture
- 1. Установите apt-transport-https
- 2. Create a new file in /etc/apt/sources.list.d/ named tor.list . Add the following entries:
- 3. Then add the gpg key used to sign the packages by running the following command at your command prompt:
- 4. Установите Tor и связку ключей Tor Debian
Тор для линукс дебиан
Get the latest version of Tor. If you’re on Debian stable, sudo apt-get install tor should give you the latest stable version of Tor.
- Note: Ubuntu users need to get it from Tor repository. Please seeDownload instructions for Ubuntu.
2. Install obfs4proxy
On Debian, the obfs4proxy package is available in unstable, testing, and stable. On Ubuntu, bionic, cosmic, disco, eoan, and focal have the package. If you’re running any of them, sudo apt-get install obfs4proxy should work.
3. Edit your Tor config file, usually located at /etc/tor/torrc and replace its content with:
Don’t forget to change the ORPort , ServerTransportListenAddr , ContactInfo , and Nickname options.
If you decide to use a fixed obfs4 port smaller than 1024 (for example 80 or 443), you will need to give obfs4 CAP_NET_BIND_SERVICE capabilities to bind the port with a non-root user:
sudo setcap cap_net_bind_service=+ep /usr/bin/obfs4proxy
To work around systemd hardening, you will also need to set NoNewPrivileges=no in /lib/systemd/system/tor@default.service and /lib/systemd/system/tor@.service and then run systemctl daemon-reload . For more details, see ticket 18356.
Note that both Tor’s OR port and its obfs4 port must be reachable. If your bridge is behind a firewall or NAT, make sure to open both ports. You can use our reachability test to see if your obfs4 port is reachable from the Internet.
4. Restart Tor
sudo systemctl restart tor
5. Monitor your logs
To confirm your bridge is running with no issues, you should see something like this (usually in /var/log/tor/log or /var/log/syslog ):
6. Final notes
If you are having trouble setting up your bridge, have a look at our help section. If your bridge is now running, check out the post-install notes.
Источник
- TorBrowser
Tor Browser protects your privacy while you are surfing the Internet: * it prevents somebody watching your Internet connection from learning what sites you visit, * it prevents the sites you visit from learning your physical location, * and it lets you access sites which are blocked.
Tor Browser is based on Firefox and will be familiar to many users.
To keep your protection strong you need to update the Tor Browser regularly. In Debian the easier way to do that is to install Tor Browser using torbrowser-launcher, which automatically installs Tor Browser, run it, and update it to keep its protection strong and protect your privacy.
The advantage of using torbrowser-launcher over the manual installation of the TorBrowser package (called Tor Browser Bundle) is threefold:
- You will benefit from automatic upgrades
If using AppArmor, you will benefit from the AppArmor profiles contained in the package
Installing the official Debian package
Debian 11 and later
With Debian 11 and later, or Debian Sid (Unstable), installing it is as simple as installing the torbrowser-launcher package with whatever tool you prefer.
After installation, two new entries can be found in the launcher of your preferred desktop, «Tor Browser» and «Tor Browser Launcher Settings». The latter will allow you to configure the way that Tor Browser is downloaded (such as the mirror, whether or not you use the system Tor service to download it, etc.), while the former will simply launch the browser and download it if it isn’t currently installed.
These can both be accessed via terminal commands by running torbrowser-launcher or torbrowser-launcher --settings respectively.
Debian 10 and older
The torbrowser-launcher package isn’t available in the regular release of Debian 9 and 10, but it was made later available via the backports system and can be installed through it.
Follow the instructions to add the backports repository to your sources.list. Because the package is only available in the backports section without room for ambiguity, Apt will install it without any extra arguments necessary. Just install the torbrowser-launcher package with your preferred tool.
After installation, two new entries can be found in the launcher of your preferred desktop, «Tor Browser» and «Tor Browser Launcher Settings». The latter will allow you to configure the way that Tor Browser is downloaded (such as the mirror, whether or not you use the system Tor service to download it, etc.), while the former will simply launch the browser and download it if it isn’t currently installed.
These can both be accessed via terminal commands by running torbrowser-launcher or torbrowser-launcher --settings respectively.
Installing from the website
Tarballs containing the latest stable version of the Tor Browser Bundle can be found on the official Tor Browser website, they contain a .desktop file that’ll run the browser in-place. This can be run just by double-clicking it in most file managers. GNOME will require you to run the file from the terminal instead.
After being run, it will also auto-update in place as new versions are released.
Advanced Tor Usage
Torrc File Location
If you installed «torbrowser-launcher» on a 64-bit (amd64) system, the «torrc» advanced configuration file is located at:
If you installed «torbrowser-launcher» on a 32-bit (i386) system, the «torrc» advanced configuration file is located at:
AppArmor confinement and Xserver isolation
HolgerLevsen has written some scripts which are available in /usr/share/doc/torbrowser-launcher/examples/ if you have installed the package.
These scripts show how to run torbrowser-launcher (and thus torbrowser), confined with AppArmor, in Xephyr (a virtual Xserver running on another Xserver) as another user. This, using AppArmor and Xephyr, shall have two effects:
the browser process (and it’s subprocesses) can — thanks to AppArmor confinement — only access a tiny part of the filesystem
In order to use these scripts, please refer to /usr/share/doc/torbrowser-launcher/examples/.
Bugs and known issues
Clarifying common misconceptions
Tor isn’t illegal to use
While in some extremely authoritarian countries Tor may carry legal risk, it’s generally fine. Through United States and most of Europe, the very worst you can expect is to be potentially put on a watchlist. Your ISP is unable to see what you’re doing over Tor, but they can see that you’re using Tor.
If your government or ISP attempts to block Tor, many mirror sites offer downloads of the browser bundle, and you may consider setting up apt-transport-https to securely download it from the repositories. Tor bridges are also available in case connection to the network itself is censored.
The deep web/dark web aren’t dangerous to browse, and won’t expose you to hackers and malware
Though the terms are often used as synonyms, typically, the «deep web» refers to any website not indexed by search engines such as Google, and the «dark web» refers to websites that require a service such as Tor to view.
In both cases, neither are inherently dangerous. They carry the same risk as almost any small website, and require a vulnerability in your web browser to serve malware. As long as you update regularly, there’s generally little risk.
Tor isn’t only used for illegal purposes
While Tor is used for plenty of terrible reasons as well, journalists, free speech activists, and whistleblowers all make use of Tor in order to do important work for the common good. Citizens of oppressive countries also make use of Tor in order to access important information that otherwise is restricted.
There are numerous legal reasons to use Tor as well, such as communicating with people across authoritarian borders, or accessing legal content that you nonetheless want to keep hidden from your ISP for whatever reason.
You won’t get arrested or get into trouble with your ISP or someone else for running Tor
You will only need to worry about this if you are running a Tor exit node. There are also some excellent resources created by the Tor staff; give them a read:
Tor and streaming/torrenting
Tor’s speed comes from how many resources are provided by generous people. Torrenting or streaming over Tor not only leaks your IP address, but it also slows the network for everyone else. Tor is not for torrenting.
You may also be interested in the Tor Metrics pages which will show you how common the use of Tor is in your country:
See also
Good additions to the Tor Browser are the uBlock Origin and Privacy Badger Firefox-add-ons.
Notes
It is suggested to consider using uBlock Origin instead of AdBlock Plus. Mostly because uBlock Origin has a better track record at fully protecting your privacy, than AdBlock Plus. Also there is a controversy around AdBlock Plus and a for-profit corporation trying to monetize it via ad whitelisting. Also uBlock Originuses fewer resources and has better performance than AdBlock Plus.
uBlock Origin is not to be confused with uBlock. As of May 2017 uBlock Origin is actively maintain and updated, compare to uBlock who has not been maintained or updated for more than 2 years, since 2015.
Alternative WebBrowsers under Debian
Источник
Tor Browser для Linux
Тор чрезвычайно ценится среди пользователей, заинтересованных в сохранении анонимности и личных данных в ходе веб-серфинга. Связано это с тем, что разработчики интернет-обозревателя сделали основной акцент на защищенности. И вполне логично, что он был в кратчайшее время портирован для операционной системы Линукс. Ведь она тоже славится своей безопасностью, при правильной эксплуатации, разумеется. Tor Browser для Linux предельно прост в инсталляции, настройке и использовании, если знать порядок действий. Специально для вашего удобства мы подготовили понятную инструкцию.
Руководство
Мы решили разбить статью на две основных части. В первой пойдет речь непосредственно о процедуре инсталляции, применимой к большинству сборок Линукс (Ubuntu, Debian и многие другие). А во второй будет рассмотрен первый запуск приложения и его настройка для правильного подключения.
Шаг №1: Инсталляция
И начнем мы именно с процедуры установки Tor Browser на Linux. Распишем ее в пошаговом варианте:
- Перейдите на официальный сайт проекта, открыв ссылку из конца статьи.
- Здесь нажмите на внушительных размеров кнопку DownloadTor.
- На новой странице загрузите подходящую версию приложения, в зависимости от разрядности операционной системы (64bit – 64-разрядная, 32bit – 32-разрядная).
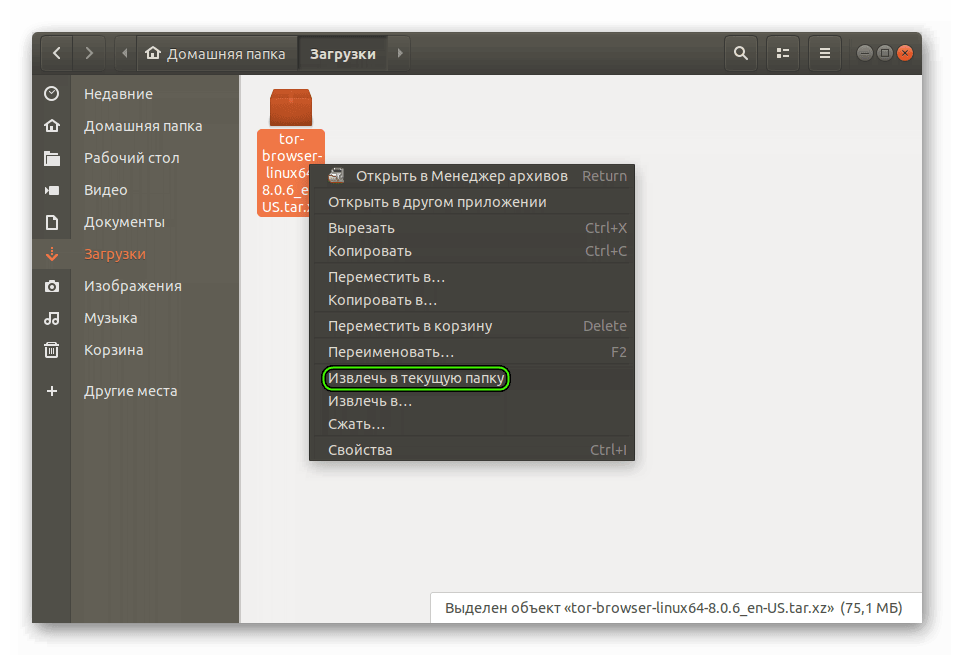
- Перейдите в каталог, куда был сохранен архив с расширением .tar.xz.
- Щелкните по нему ЛКМ и выберите опцию извлечения в текущее место.
- Дождитесь окончания распаковки.
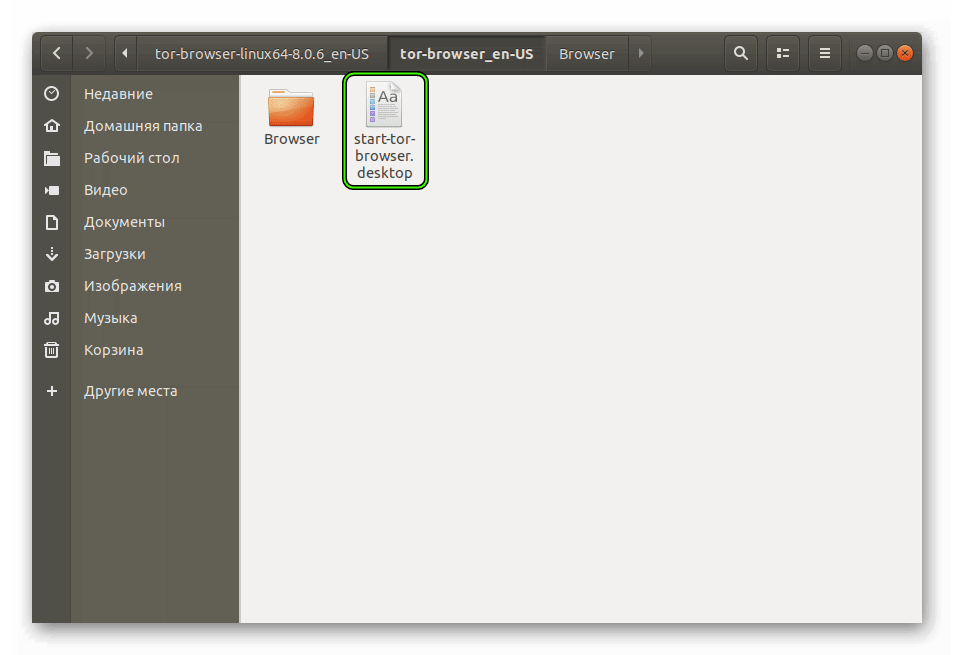
- Теперь откройте папку с названием исходного архива.
- Из нее перейдите в tor—browser—xx, где xx – исходный язык приложения (если там стоит en-US, то русский язык все равно присутствует).
- Откройте файл start-tor-browser.desktop.
- Если появится предупреждение о безопасности, то согласитесь на запуск приложения.
- Название файла сменится на TorBrowser, а его иконкой станет зелено-фиолетово-серый глобус. Вместе с тем и откроется сам интернет-обозреватель.
Шаг №2: Первый запуск и настройка
При первом запуске пользователю нужно выполнить настройку Tor для Linux. Кнопка Connect применит стандартные параметры подключения, а спустя некоторое время откроется сам интернет-обозреватель.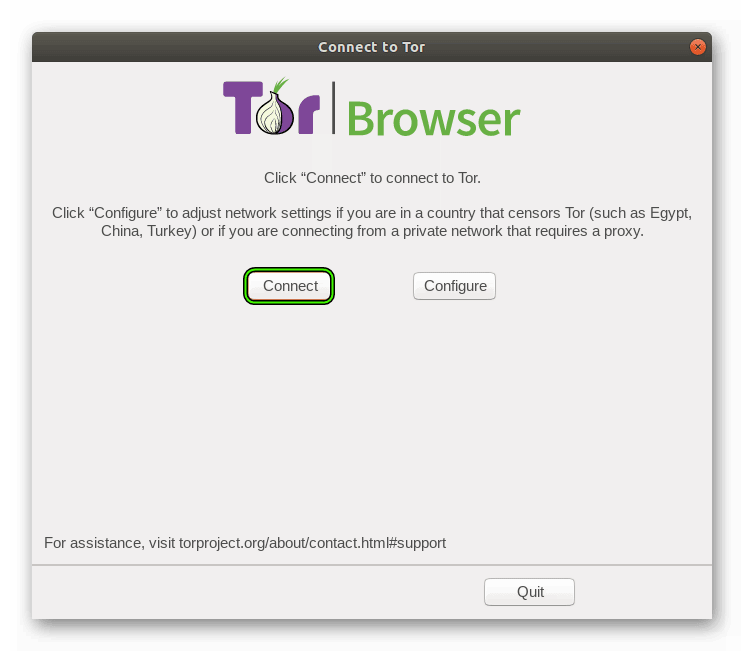
Скачать браузер Тор для Линукс на официальном сайте проекта 32-bit (sig) / 64-bit (sig)
Источник
Репозиторий Debian
Репозиторий Debian
Можно ли использовать APT через Tor?
Примечание. Символ # означает, что команда отдается от лица суперпользователя. Это значит, что вы должны иметь доступ к аккаунту пользователя с правами администратора, например, ваш пользователь может быть в группе sudo.
Чтобы использовать Apt через Tor, нужно установить пакет apt transport:
Потом вам нужно добавить следующие строки в /etc/apt/sources.list или новый файл в папке /etc/apt/sources.list.d/ :
Замените кодом вашей операционной системы. Выполните lsb_release -c или cat /etc/debian_version , чтобы узнать код операционной системы.
Теперь обновите свои источники и попробуйте снова установить Tor:
Можно установить Tor из репозитория Ubuntu?
Нет. Не используйте пакеты из окружения Ubuntu. Известно, что в прошлом они не обновлялись как следует. Вы можете потерять в стабильности, а некоторые ошибки останутся без исправлений. Лучше используйте репозиторий Tor Debian.
Зачем нужно включать репозиторий Tor в Debian? Как это сделать?
У Tor Project есть собственный репозиторий Debian. В самой Debian включена LTS-версия Tor. С ней вы не всегда сможете иметь самую свежую и стабильную версию Tor. Поэтому мы рекомендуем устанавливать Tor из нашего репозитория.
Вот как подключить репозиторий пакетов Tor в сборках Linux на основе Debian:
Примечание. Символ # означает, что команда отдается от лица суперпользователя. Это значит, что вы должны иметь доступ к аккаунту пользователя с правами администратора, например, ваш пользователь может быть в группе sudo.
Prerequisite: Verify the CPU architecture
The package repository offers amd64 , arm64 , and i386 binaries. Verify your operating system is capable of running the binary by inspecting the output of the following commend:
It should output either amd64 , arm64 , or i386 . The repository does not support other CPU architectures.
Note on Raspbian: The package repository does not offer 32-bit ARM architecture ( armhf ) images. You should either build Tor from source, or install the version Debian offers.
1. Установите apt-transport-https
Чтобы включить все менеджеры пакетов с использованием библиотеки libapt-pkg для доступа к метаданным и пакетам в ресурсах, доступных по https:
2. Create a new file in /etc/apt/sources.list.d/ named tor.list . Add the following entries:
If you want to try experimental packages, add these in addition to the lines from above (Note, use whatever is the current experimental version instead of 0.4.6.x from the example below):
Или «ночные сборки»:
Замените кодом вашей операционной системы. Выполните lsb_release -c или cat /etc/debian_version , чтобы узнать код операционной системы.
Примечание. В Ubuntu Focal уже не поддерживаются 32-битные приложения, поэтому делайте так:
Тревожный симптом при выполнении sudo apt update:
3. Then add the gpg key used to sign the packages by running the following command at your command prompt:
4. Установите Tor и связку ключей Tor Debian
Мы предлагаем пакет Debian, чтобы помочь вам сохранять самую свежую версию вашего ключа для подписи. Для установки используйте следующие команды:
Источник