- Ubuntu kernels from Canonical
- Identifying a kernel
- Kernel and OS releases
- Kernel security
- General Availability (GA) and variant Ubuntu kernels
- Custom kernels
- Как установить последние версии ядра Linux в Ubuntu и Linux Mint
- Предупреждение перед обновлением ядра
- mainline — репозиторий ядер Ubuntu
- mainline (продолжение бесплатной версии ukuu) — программа с графическим и консольным интерфейсом для обновления ядра
- Утилита ubuntu-mainline-kernel.sh
- Как восстановить Linux после установки ядра
- Ubuntu Documentation
- Kernel
- Types
- Versions
- HowTo Upgrade or Recompile Kernel
- How to Remove unwanted Kernels from your system
- Experimental Kernel Options
- See also
Ubuntu kernels from Canonical
At the core of the Ubuntu operating system is the Linux kernel, which manages and controls the hardware resources like I/O (networking, storage, graphics and various user interface devices, etc.), memory and CPU for your device or computer. It is one of the first software programs a booting device loads and runs on the central processing unit (CPU). The Linux kernel manages the system’s hardware environment so other programs like the operating system’s user space programs and application software programs can run well without modification on a variety of different platforms and without needing to know very much about that underlying system.
Identifying a kernel
The easiest way to determine the kernel you’re running is to type cat /proc/version_signature on the terminal. For example:
Ubuntu 5.4.0-12.15-generic 5.4.8
This output provides important information about the kernel:
- Canonical adds » Ubuntu «
- Ubuntu kernel-release = 5.4.0-12.15-generic
- kernel version is 5.4 , which is identical to upstream stable kernel version
- .0 is an obsolete parameter left over from older upstream kernel version naming practices
- -12 application binary interface (ABI) bump for this kernel
- .15 upload number for this kernel
- -generic is kernel flavour parameter, where -generic is the default Ubuntu kernel flavour
- Mainline kernel-version = 5.4.8
Kernel and OS releases
Canonical provides long-term support (LTS) kernels for Ubuntu LTS releases. Canonical also provides interim operating system releases with updated kernels every 6 months.
For customers and business partners that don’t have specialised bleeding-edge workloads or latest hardware needs, the latest LTS release «-generic» kernel is the best option for them such as the 4.15 default kernel in Ubuntu 18.04 LTS. Customers who need the latest hardware support capability can install the latest HWE kernel such as the ones contained in interim releases, keeping in mind the shorter support lifespan associated with these kernels (9 months). HWE kernel customers are recommended to upgrade to a newer LTS release that supports their hardware and/or software needs as soon as it is available. Another option for customers is to use point releases. For example, there is an 18.04.4 point release as of February 2020, which includes an updated 5.3.x kernel but is also considered LTS, exactly like the original GA 4.15 kernel in 18.04.
Kernel security
The Canonical Kernel Team’s primary focus is the careful maintenance of kernels and their variants for regular delivery via the Ubuntu SRU process and the Canonical livepatch service. This includes rigorous management of all Linux kernel Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE) lists (with a focus on patching all high and critical CVEs) review and application of all relevant patches for all critical and serious kernel defects in the mailing lists and then rigorously testing newly updated kernels end-to-end each SRU cycle.
General Availability (GA) and variant Ubuntu kernels
The complete functionality of any given kernel is determined by the included modules and the kernel configuration for both hardware and the expected workloads that are run on it.
Kernel modules are binary programs that extend a kernel’s ability to control the computing system’s hardware or add additional system capabilities like high-performance networking or non-standard graphics, etc. The GA kernel that is shipped by default, with the Canonical Ubuntu Long Term Support (LTS) and Hardware Enablement (HWE) releases, are tuned for stable, reliable, secure, high-performance operation over a wide variety of hardware platforms and workloads.
A kernel variant is a kernel that deviates from the generic GA kernel by changes to its configuration, and/or by having modules added and/or removed.
Custom kernels
Canonical advocates for customers to use the GA kernel shipped with Ubuntu as the best and most cost-effective option in their business environment. We also offer the option for customers to customize their own Ubuntu kernels. Several of our enterprise, Telco and cloud provider customers have systems and workload needs, which justify both the time investment to optimise their kernels and the pay to develop and maintain those custom kernels over time.
© 2021 Canonical Ltd. Ubuntu and Canonical are registered trademarks of Canonical Ltd.
Источник
Как установить последние версии ядра Linux в Ubuntu и Linux Mint
Последние версии ядра Linux имеют драйверы для новых устройств и другие нововведения. К сожалению, многие популярные дистрибутивы Linux не спешат обновить ядро. Данная инструкция покажет, как легко, без компиляции, установить любую версию ядра Linux в Ubuntu и Linux Mint. Вы можете выбрать для установки как более новое ядро, так и более старое, чем предлагает репозиторий вашего дистрибутива.
При желании, вы без проблем можете удалить установленные ядра Linux и вернуться к ядру из репозитория.
Поскольку Linux Mint основана на Ubuntu, то данная инструкция в полной мере применима и к дистрибутивам Linux Mint, кроме LMDE. Для LMDE (Linux Mint Debian Edition) смотрите статью «Как установить последние версии ядра Linux в Debian и основанные на Debian дистрибутивы».
Предупреждение перед обновлением ядра
Необходимо помнить, что из-за несовместимости ядра с программами (в первую очередь, с проприетарными видео драйверами), вы можете столкнуться с проблемами, в том числе с чёрным экраном во время загрузки.
В большинстве случаев, возникшие проблемы можно решить без переустановки дистрибутива. Начните с того, что в меню загрузки перейдите в дополнительные параметры и загрузитесь с предыдущей версией ядра. Выполнив загрузку, удалите проблемное ядро.
Проблемы могут вызвать проприетарные драйверы для видеокарт, поскольку старые версии могут быть не совместимы с последними версиями ядра без патча. Если у вас установлены проприетарные видео драйверы, то серьёзной подумайте, прежде чем следовать инструкциям ниже. Также подготовьтесь, поищите инструкции, как решить проблему при загрузки дистрибутива в чёрный экран.
Следует быть особенно осторожным владельцам старых дистрибутивов — настоятельно рекомендуется обновлять ядро только на последних версиях ОС.
Ещё одна вполне вероятная проблема, с которой вы можете столкнуться если установите ядро самой последней версии — проблема с неразрешёнными зависимостями и как следствие невозможность использования менеджера пакетов apt для обновления и установки программ. Если вы столкнулись с ситуацией, когда после успешной установки нового ядра не получается обновить пакеты с помощью apt, то попробуйте устанавливать более ранние версии ядра, которые вам подходят, а версии, вызывающие проблемы с зависимостями, удаляйте. Помните, что невозможно удалить ядро с которым вы загрузились — перед удалением загрузите компьютер с любой другой версией ядра.
mainline — репозиторий ядер Ubuntu
Для Ubuntu имеется репозиторий скомпилированных ядер mainline всех версий, в том числе самых последних, поэтому установка не вызывает особых сложностей — компилировать ядро Linux не нужно. Более того, имеются инструменты, в том числе с графическим интерфейсом для установки любых ядер.
На самом деле, если ядра уже скомпилированы, то достаточно скачать из одной папки с сервера файлы следующего вида:
- linux-headers-*-generic_*_amd64.deb
- linux-headers-*_all.deb
- linux-image-unsigned-*-generic_*_amd64.deb
- linux-modules-*-generic_*_amd64.deb
И установить их командой:
Но процесс можно упростить ещё больше, используя утилиты для работы с ядрами.
mainline (продолжение бесплатной версии ukuu) — программа с графическим и консольным интерфейсом для обновления ядра
Если вы предпочитаете графический интерфейс, то используйте Mainline.
Чтобы установить программу выполните следующие команды:
Для запуска графического интерфейса выполните:
Для запуска консольной версии выполните:
Использование графической версии не должно вызвать затруднений. При запуске будет получена информация о доступных ядрах, вы можете выбрать любое ядро и установить его, просто нажав на кнопку «Установка». Дополнительно доступны такие действия как удаление ядер и просмотр списков изменений для каждой версии ядра.

Использование консольной версии следующее:
Справка по опциям и командам:
(1) Строка версии должна браться из вывода —list
(2) Одна или более строк версий (разделённые запятыми) берутся из вывода —list
Перезагрузите компьютер, чтобы использовать новое ядро.
По умолчанию ваша система будет загружена с последним ядром, если вы хотите это изменить, то перейдите в дополнительные параметры загрузки
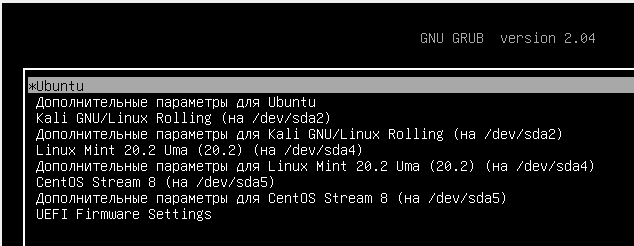
и выберите желаемую версию из установленных ядер.

Утилита ubuntu-mainline-kernel.sh
Последнюю версию ядра на Ubuntu и Linux Mint также можно установить с помощью утилиты командной строки ubuntu-mainline-kernel.sh.
Загружаем и устанавливаем скрипт ubuntu-mainline-kernel.sh:
Справка по ubuntu-mainline-kernel.sh
Пример установки последней версии ядра
Проверяем текущую версию ядра:

Ядро имеет версию 5.11.
Проверяем, какая версия ядра является последней:
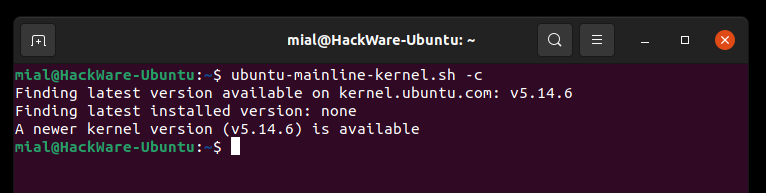
Чтобы вывести список доступных для установки версий ядер выполните команду:
Например, мы хотим установить ядро версии v5.12.11, тогда команда следующая (префикс «v» указывать не надо):
Если вы хотите установить последнюю на данный момент версию, то запустите следующую команду:
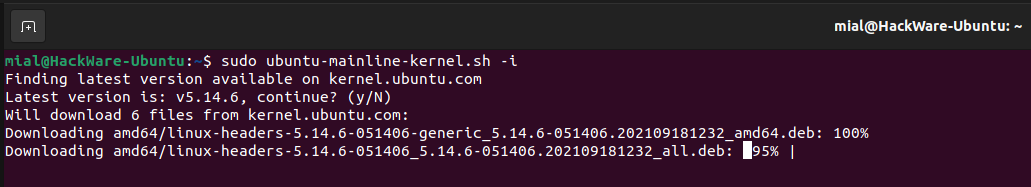
Вам будет задан вопрос, хотите ли вы продолжить, введите «y»:
Программа завершила работу — чтобы изменения вступили в силу, требуется перезагрузка.
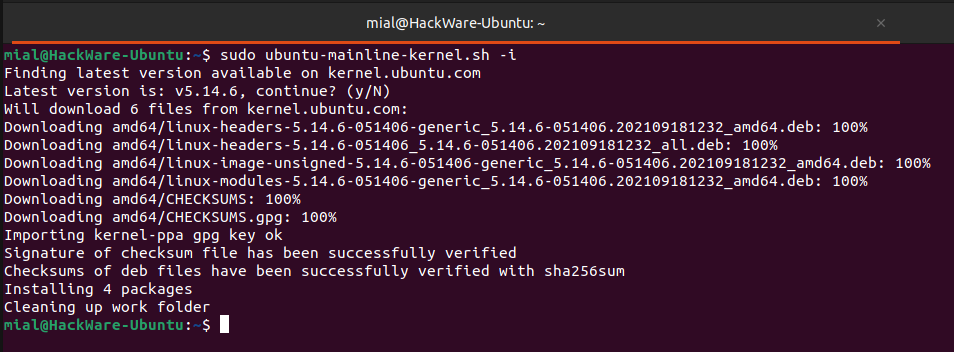
Опять проверяем версию ядра:
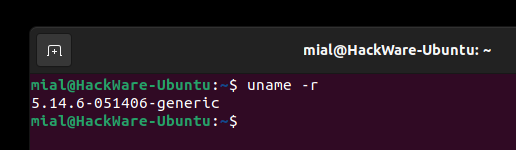
Как восстановить Linux после установки ядра
Если ваш компьютер загружается с чёрным экраном, зависает или что-то не работает после обновления ядра, перезагрузитесь и выберите Дополнительные параметры для вашего дистрибутива в меню GRUB:

Затем выберите предыдущую версию ядра и нажмите Enter:

Независимо от причины, вам необходимо загрузиться с предыдущей версией ядра, если вы хотите удалить последнее ядро. Это потому, что вы не можете удалить ядро, которое в настоящее время используется.
Если вы не видите меню GRUB2, нажмите и удерживайте клавишу Shift или несколько раз нажмите клавишу Esc (это может варьироваться в зависимости от загрузки BIOS или UEFI и от используемой вами версии Ubuntu/Linux Mint) при загрузке GRUB. Должно появиться меню Grub, позволяющее выбрать предыдущую версию ядра.
После загрузки предыдущего ядра вы можете удалить неисправное ядро. ubuntu-mainline-kernel.sh позволяет удалять ядра, установленные из PPA ядра Ubuntu.
С помощью ubuntu-mainline-kernel.sh вы можете удалить версию ядра, запустив:
Где ВЕРСИЯ — это версия ядра, например 5.14. Вы также можете эту утилиту с -u без указания версии, и в этом случае инструмент выведет список до 10 версий ядра и спросит вас, какую из них вы хотите удалить. Стоит отметить, что ubuntu-mainline-kernel.sh не будет показывать в этом списке официальные ядра Ubuntu.
Обновите настроки GRUB если это не было сделано автоматически:
Источник
Ubuntu Documentation
Kernel
What is the kernel ?
The kernel is the software that directly manages your hardware, allowing application libraries and software like GNOME and Firefox to run on many types of hardware without much difficulty. Because the Linux kernel is the core component of a GNU/Linux system, a full restart is required to complete the kernel update.
Types
Ubuntu packages the Linux kernel for a variety of architectures, including several variants of the x86 architecture. These include a 386 version, a 686 version, and versions for the AMD k6 and k7 processors. While most software for x86 processors in Ubuntu is compiled for 386 or better instruction sets, the kernel and a few other packages are specifically compiled for certain processors for speed reasons. Check the package documentation to determine what type of kernel will perform best for your processor.
Versions
Ubuntu currently packages the 3.8 kernel for optimal desktop speed and features.
Some motherboards have more than one processor on them, and some processors have multiple cores. If your computer is like this, then the SMP kernel is for you. Non-SMP kernels will not be able to take advantage of your multiple processors. However, if you do not have multiple processors, the additional code in an SMP kernel will only slow you down. Naturally, Ubuntu provides both SMP and non-SMP kernels for all supported architectures.
PAE (Physical Address Extension) allows the 32 bit version of Ubuntu to access up to 64 Gb of memory and is the standard for all members of the Ubuntu family from release 12.10 and beyond, as the non-PAE version has been dropped. For more on this please see here.
If your hardware does not support PAE, refer to the PAE pages with topics like installing, upgrading and enabling (with) PAE.
HowTo Upgrade or Recompile Kernel
The precompiled kernels that are supplied with your distro should be fine however if you wish to update or optimise (or standardise) for your platform :
From easier (1) to the more difficult (3):
1) You can Kernel/Upgrade easily using Ubuntu.
3) Run the following Terminal commands to install a new Ubuntu kernel from http://kernel.ubuntu.com/
Just press instead of a number if you get stuck on a certain question in the python script.
The script by default filters out (i.e. does not show) the release candidates. If you want the latest release candidates, please use: python kmpd.py -d
How to Remove unwanted Kernels from your system
Open the Synaptic package manager from the System->Administration menu. Click the “Search” button on the tool bar and search for «linux-image-2». The results should show every available and installed kernel. A green box on the left indicates that the package is installed. The only linux-image you want installed is the latest one. Find the package corresponding to the kernel to you running currently (this is the kernel you found in the terminal window). Make sure you keep that one. Now you can uninstall the old kernels from the list by clicking their boxes and selecting “Mark for Removal”.
Or you can uninstall kernels using the ubuntu-tweak Ubuntu PPA package.
Instructions are here:
Experimental Kernel Options
As per the Ubuntu Kernel Team, their typical Kernel configuration policy is that options marked EXPERIMENTAL are disabled by default, until a request has been made to justify enabling it. For example, one may find out if an option is marked this way via:
See also
Kernel (последним исправлял пользователь ckimes 2017-09-26 21:10:21)
The material on this wiki is available under a free license, see Copyright / License for details
You can contribute to this wiki, see Wiki Guide for details
Источник




