- Linux commands for Windows
- 4 Ways to Run Linux Commands in Windows
- Using Linux commands inside Windows
- 1. Use Linux Bash Shell on Windows 10
- 2. Use Git Bash to run Bash commands on Windows
- 3. Using Linux commands in Windows with Cygwin
- 4. Use Linux in virtual machine
- Как выполнять Linux-команды внутри Windows: официальный и сторонние способы
- Содержание
- WSL — официальная подсистема Linux внутри Windows
- CoreUtils — лёгкий инструмент для запуска базовых команд
- Cygwin — запуск команд и Bash-скриптов
- AF_UNIX comes to Windows
- Introduction:
- Overview :
- Addressing scheme – sockaddr_un :
- Security:
- Implementation:
- Unsupported \unavailable :
- How can I write a Windows AF_UNIX app ?
- What’s next?
Linux commands for Windows
It’s very common scenario in IT field that people who are familiar with one OS have to learn/work with another OS. I do see many people, who are familiar with Linux commands, looking for their equivalent commands in Windows OS. Below I have attempted to list down the Windows commands for most widely used Linux commands. If I have missed any, please write in the comments section and let me know.
Ls : The Windows equivalent one is dir. ‘Dir‘ has many switches to list files based on different attributes, sort the list on size or date modified etc.
Grep : Findstr is the closet matching one for grep. find is also for searching strings in files, but it does not have many options.
Adduser: We can use net user to manage user accounts.
Useradd: net localgroup can be used to manage user groups. Net group can be used to manage active directory (domain) groups.
Uname : ver command shows Windows OS version. Systeminfo shows lot of hardware and software information.
Ps : The closest matching command is tasklist, though it’s not as feature rich as ps.
Echo : echo. Very much similar to Linux’s echo.
Md : mkdir
rm: Del deletes files whereas rmdir can be used to delete directories.
Du : du can be used to monitor the disk usage. However, this tool is not part of Windows OS. We need to install it separately. See the link for more information.
Df : Net use. We can list the network shares mapped on the computer.
Mount : Net use . Map network share to local drive
Cat : Type print the contents of a text file in the console/command prompt.
Head : there’s no equivalent command I am aware of.
Tail : Tail resource kit tool.
touch: Fsutil can be used to create files of require size.
I will add few more commands to the list soon…If you are searching for some specific command and do not find it here, please let me know.
4 Ways to Run Linux Commands in Windows
Last updated October 29, 2020 By Abhishek Prakash 16 Comments
Brief: Want to use Linux commands but don’t want to leave Windows? Here are several ways to run Linux bash commands in Windows.
If you are learning Shell scripting probably as a part of your course curriculum, you need to use Linux commands to practice the commands and scripting.
Your school lab might have Linux installed but personally you don’t have a Linux laptop but the regular Windows computer like everyone else. Your homework needs to run Linux commands and you wonder how to run Bash commands and scripts on Windows.
You can install Linux alongside Windows in dual boot mode. This method allows you to choose either Linux or Windows when you start your computer. But taking all the trouble to mess with partitions for the sole purpose of running Linux command may not be for everyone.
You can also use Linux terminals online but your work won’t be saved here.
The good news is that there are several ways you can run Linux commands inside Windows, like any regular application. Isn’t it cool?
Using Linux commands inside Windows
As an ardent Linux user and promoter, I would like to see more and more people using ‘real’ Linux but I understand that at times, that’s not the priority. If you are just looking to practice Linux to pass your exams, you can use one of these methods for running Bash commands on Windows.
1. Use Linux Bash Shell on Windows 10
Did you know that you can run a Linux distribution inside Windows 10? The Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) allows you to run Linux inside Windows. The upcoming version of WSL will be using the real Linux kernel inside Windows.
This WSL, also called Bash on Windows, gives you a Linux distribution in command line mode running as a regular Windows application. Don’t be scared with the command line mode because your purpose is to run Linux commands. That’s all you need.
You can find some popular Linux distributions like Ubuntu, Kali Linux, openSUSE etc in Windows Store. You just have to download and install it like any other Windows application. Once installed, you can run all the Linux commands you want.

2. Use Git Bash to run Bash commands on Windows
You probably know what Git is. It’s a version control system developed by Linux creator Linus Torvalds.
Git for Windows is a set of tools that allows you to use Git in both command line and graphical interfaces. One of the tools included in Git for Windows is Git Bash.
Git Bash application provides and emulation layer for Git command line. Apart from Git commands, Git Bash also supports many Bash utilities such as ssh, scp, cat, find etc.
In other words, you can run many common Linux/Bash commands using the Git Bash application.
You can install Git Bash in Windows by downloading and installing the Git for Windows tool for free from its website.
3. Using Linux commands in Windows with Cygwin
If you want to run Linux commands in Windows, Cygwin is a recommended tool. Cygwin was created in 1995 to provide a POSIX-compatible environment that runs natively on Windows. Cygwin is a free and open source software maintained by Red Hat employees and many other volunteers.
For two decades, Windows users use Cygwin for running and practicing Linux/Bash commands. Even I used Cygwin to learn Linux commands more than a decade ago.
You can download Cygwin from its official website below. I also advise you to refer to this Cygwin cheat sheet to get started with it.
4. Use Linux in virtual machine
Another way is to use a virtualization software and install Linux in it. This way, you install a Linux distribution (with graphical interface) inside Windows and run it like a regular Windows application.
This method requires that your system has a good amount of RAM, at least 4 GB but better if you have over 8 GB of RAM. The good thing here is that you get the real feel of using a desktop Linux. If you like the interface, you may later decide to switch to Linux completely.
There are two popular tools for creating virtual machines on Windows, Oracle VirtualBox and VMware Workstation Player. You can use either of the two. Personally, I prefer VirtualBox.
Conclusion
The best way to run Linux commands is to use Linux. When installing Linux is not an option, these tools allow you to run Linux commands on Windows. Give them a try and see which method is best suited for you.
Like what you read? Please share it with others.
Как выполнять Linux-команды внутри Windows: официальный и сторонние способы
Под GNU/Linux-дистрибутивы создано огромное количество полезных и удобных инструментов и приложений для обычных пользователей и разработчиков. Далеко не всё из этого доступно на Windows, но, к счастью, для ОС от Microsoft есть решения, исправляющие эту проблему.
Содержание
WSL — официальная подсистема Linux внутри Windows
В Windows 10 существует крайне полезная вещь под названием Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL). Она позволяет использовать GNU/Linux-среду прямо в Windows и запускать не только команды, но и, например, Bash-скрипты. Для использования WSL необходимо следовать инструкции ниже.
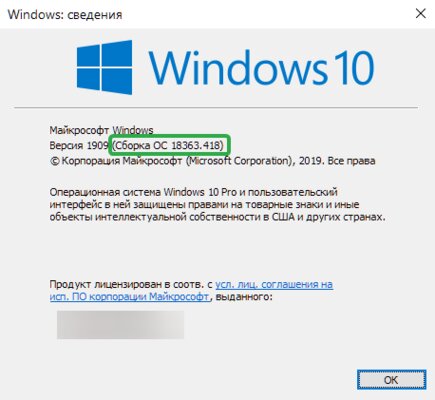
Шаг 1. Проверьте, подходит ли текущая версия Windows требованиям. Для этого нажмите сочетание клавиш Win+R, затем введите winver. Найдите строку «Сборка ОС» — она должна быть свежее версии 14316.
Шаг 2. Запустите стандартную утилиту PowerShell от имени администратора и введите в ней команду для включения WSL:
dism.exe /online /enable-feature /featurename:Microsoft-Windows-Subsystem-Linux /all /norestart
Шаг 3. Если версия Windows, определённая в первом пункте, свежее 18362, вы можете установить WSL 2, который в разы быстрее первой версии и обладает доработанным ядром. Введите команду ниже, если нужно установить WSL 2:
dism.exe /online /enable-feature /featurename:VirtualMachinePlatform /all /norestart
После этого скачайте и установите пакет обновления с официального сайта.
Шаг 4. Перезагрузите компьютер. Если была произведена установка WSL 2, введите в PowerShell от имени администратора следующую команду:
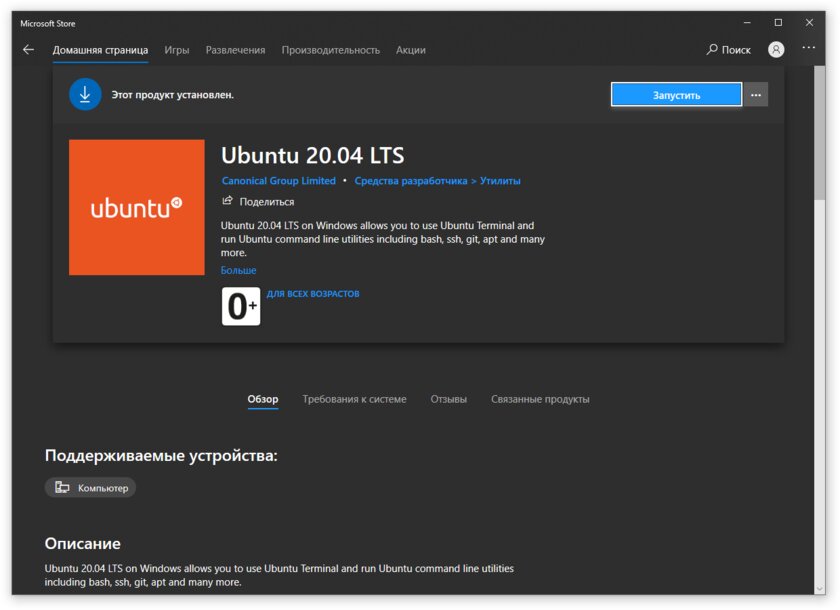
Шаг 5. После перезагрузки откройте фирменный магазин приложений Microsoft Store и найдите подходящий GNU/Linux-дистрибутив. Самым популярным является Ubuntu — вы можете установить любую версию из представленных в Microsoft Store.
Шаг 6. Как только установка завершится, найдите дистрибутив в меню «Пуск» и запустите его.
Шаг 7. Пройдите этап первоначальной настройки, введя имя нового пользователя и придумав пароль.
Шаг 8. Теперь различные GNU/Linux-команды можно выполнять, запустив дистрибутив, либо введя в командной строке wsl . Например, для просмотра всех файлов в текущей директории достаточно в командной строке выполнить wsl ls -a.
Обращу внимание на то, что путь к дискам в WSL отличается от такового в Windows. Вместо привычного C:/ используйте /mnt/c/. Также не забывайте про экранирование пробелов с помощью символа \ — это также пригодится при вводе путей к файлам.
Помимо выполнения базовых команд, с помощью WSL можно даже запускать приложения с графическим интерфейсом. Правда, рассчитывать на большое количество поддерживаемых подобных программ не стоит.
Шаг 1. Загрузите X-сервер и установите его.
Шаг 2. Запустите его с помощью ярлыка на рабочем столе. В открывшемся окне выберите вариант Multiple windows, затем Start no client. Завершите настройку кнопкой Finish.
Шаг 3. Откройте дистрибутив через меню Пуск и выполните команду export DISPLAY=:0
Шаг 4. Запустив приложение с графическим интерфейсом в WSL, вы увидите новое окно прямо в Windows.
CoreUtils — лёгкий инструмент для запуска базовых команд
Плюс данной утилиты — возможность запуска не только на Windows 10, но и на более старых версиях ОС. Кроме того, она легка и не занимает много места. Не обошлось без недостатков — программа скудна на функционал и не обновлялась очень давно. Она не только не умеет запускать скрипты и приложения с GUI, но и поддерживает лишь самые базовые GNU/Linux-команды. Установка CoreUtils весьма проста.
Шаг 1. Скачайте утилиту с официального сайта.
Шаг 2. Следуйте инструкциям установщика.
Шаг 3. Откройте «Панель управления», в разделе «Система и безопасность» выберите пункт «Система». На панели слева откройте «Дополнительные параметры системы». Нажмите кнопку «Переменные среды» и в открывшемся окне найдите область с заголовком «Системные переменные». В случае, когда там есть переменная Path, выберите её, нажмите «Изменить» и далее создайте новую строку. Содержимым этой строки должен быть путь к папке, который был указан при установке. Если вы ничего не меняли, то введите следующее:
Переменной Path нет? Тогда для начала создайте её кнопкой «Создать», затем в поле имени введите Path, а в поле значения — строку выше.
Шаг 4. Запустите командную строку и выполняйте команды прямо там.
Cygwin — запуск команд и Bash-скриптов
Ещё одна утилита, схожая с CoreUtils, но обладающая более широким функционалом — в том числе и возможностью запуска скриптов. Из минусов — немалый вес и более сложная установка. Разумеется, не идёт ни в какое сравнение с максимально удобным WSL, но для базовых команд вполне подойдёт.
Шаг 1. Загрузите Cygwin и запустите установку.
Шаг 2. Выберите Install from Internet, укажите директории для установки и загрузки пакетов, а также любой подходящий сайт из списка для скачивания файлов.
Шаг 3. В процессе установки можете выбрать необходимые пакеты, либо сразу нажать «Далее», оставив базовый набор.
Шаг 4. Откройте «Панель управления», в разделе «Система и безопасность» выберите пункт «Система». На панели слева откройте «Дополнительные параметры системы». Нажмите кнопку «Переменные среды» и в открывшемся окне найдите область с заголовком «Системные переменные». В случае, когда там есть переменная Path, выберите её, нажмите «Изменить» и далее создайте новую строку. Содержимым этой строки должен быть путь к папке, который был указан при установке. Если вы ничего не меняли, то введите следующее:
Переменной Path нет? Тогда для начала создайте её кнопкой «Создать», затем в поле имени введите Path, а в поле значения — строку выше.
Шаг 5. Команды можно выполнять как через командную строку, так и через специальный терминал.
Шаг 6. Для удаления Cygwin достаточно удалить папку, в которую программа была установлена, а также (по желанию) значение из переменной Path по методу, обратному тому, что был описан в 4 шаге (не удаляйте саму переменную).
AF_UNIX comes to Windows
December 19th, 2017
Introduction:
Beginning in Insider Build 17063 , you’ll be able to use the unix socket ( AF_UNIX ) address family on Windows to communicate between W in32 processes . Unix sockets allow inter-process communication (IPC) between process es on the same machine.
Overview :
Support for the unix socket has existed both in BSD and Linux for the longest time, but, not on Windows. On Windows, there were some alternatives for local IPC, such as named pipes . But, calling conventions are different between the named pipes and sockets , making writing low-maintenance cross-platform applications difficult. For example, one such place where these two constructs differ (other than the API) is terminating the connection. BSD Socket API provides a bidirectional close semantics using shutdown . There is no direct equivalent of that in named pipes. Such differences make it difficult to port unix socket applications from Linux to Windows and vice versa; up until now!
Build 17063 brings native support for the unix socket to Windows. Starting this build, two Win 32 process es can use the AF_UNIX address family over Winsock API (which is very similar to the BSD socket API) to communicate with each other. Currently, the support only exists for the stream ( SOCK_STREAM ) socket type , which is a connection-oriented protocol for one-to-one communication. Support for the datagram (SOCK_DGRAM) can be considered in future depending on the adoption, feedback and scenario s .
Addressing scheme – sockaddr_un :
The ‘ sockaddr_un ’ structure is used for defining the address of a unix socket. In the Windows implementation of the unix socket, we have kept the name, definition and semantics of the unix socket address the same as that in Linux , to make cross-platform development easier .
There are three different addressing formats for unix sockets. ‘pathname’, ‘abstract’ and ‘unnamed’ sockets. ‘pathname’ sockets are bound to the filesystem , where in the ‘ sun_path ’ member of the struct is used to specify a null-terminated UTF-8 file system path. You can expect the same from the Windows implementation , where ‘ sun_path ’ specifies a Win32 UTF-8 file system path.
The second category is the ‘abstract’ socket address where the first character in ‘ sun_path ’ is a null byte. Windows implementation of AF_UNIX socket can also accept abstract addresses. The one difference noteworthy here is that the Windows unix socket implementation currently does not support the auto bind feature whereby an abstract address is auto-generated by the implementation on behalf of the user.
Lastly, ‘unnamed’ sockets, where the socket is bound to a pathname with no name. This is also supported on Windows unix socket implementation . Although, one of the socket API’s socketpair that generates unnamed sockets, itself is not supported in Winsock 2.0 .
Security:
Unix sockets provide a mechanism for secure communication. C ommunication over unix sockets can be secured by controlling the file (or directory) permissions on the pathname sockets ( or the parent directory ) . For example, the bind socket API creates a ‘socket’ file with the given pathname . The creation of the new socket file will fail if the calling process does not has write permission on the directory where the file is being created. Similarly, for connecting to a stream socket, the connecting process should have write permission on the socket. The same level of security is available and enforced on the Windows unix socket implementation . See the man page on AF_UNIX for more details on the security .
Implementation:
Majority of the functionality for the Windows AF_UNIX is implemented in the Windows kernel in a driver : afunix.sys . The Windows kernel networking stack provides a very pluggable and extensible model, that makes it easy to support new network providers. The socket file itself that is created as part of the bind call is a custom NTFS reparse point .
Unsupported \unavailable :
Summarizing from the above, the following Linux unix socket features are either currently unavailable or unsupported in the Windows unix socket implementation.
- AF_UNIX datagram (SOCK_DGRAM) or sequence packet (SOCK_SEQPACKET) socket type.
- Ancillary data: Linux ‘s unix socket implementation supports passing ancillary data such as passing file descriptors ( `SCM_RIGHTS` ) or credentials (‘ SCM_CREDENTIALS` ) over the socket . There is no support for ancillary data in the Windows unix socket implementation .
- Autobind feature (see the section on ‘ sockaddr_un ’ for details).
- socketpair : socketpair socket API is not supported in Winsock 2.0.
How can I write a Windows AF_UNIX app ?
- Download the Windows Insiders SDK f or the Windows build 17061 — available here .
- Check whether your Windows build has support for unix socket by running “ scqueryafunix ” from a Windows admin command prompt.
- #include afunix.h > in your Windows application and w rite a Windows unix socket winsock application as you would write any other unix socket application, but, using Winsock API ’s .
Note: As mentioned above in the ‘ security’ section , when a socket binds a socket to a valid pathname address, a socket file is created within the filesystem. On Linux, the application is expected to unlink (see the notes section in the man page for AF_UNIX ) before any other socket can be bound to the same address. The same applies to Windows unix sockets , except that, DeleteFile (or any other file delete API) should be used to delete the socket file prior to calling bind with the same path.
What’s next?
We are listening. Please try out the Windows unix socket provider and let us know what works, what doesn’t work, what you like, what you don’t like or what improvements would you like . For now, the best way to provide feedback is either via Feedback Hub under apps -> Hyper-V, the WSL GitHub issue tracker, or as a comment on this blog.
And, if you are wondering, there is already support for unix socket within Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL), how does that work with the Windows un ix s ocket implementation? Well, currently, it doesn’t, but stay tuned!