- Установка KDE в Kali Linux
- Устанавливаем KDE в Kali Linux
- Шаг 1: Загрузка компонентов
- Шаг 2: Настройка менеджера дисплеев
- Шаг 3: Вход и настройка
- Шаг 4: Удаление старой оболочки
- Решение неполадок с установкой KDE в Kali Linux
- Kali Linux 2021.1 Release (Command-Not-Found)
- Xfce & KDE Updates
- Terminals Tweaks
- Finding Commands That Didn’t Want To Be Found
- Partnerships with Tools Authors
- New Tools in Kali
- Kali’s Website
- Wallpapers
- Kali NetHunter Updates
- Kali ARM Updates
- Download Kali Linux 2021.1
Установка KDE в Kali Linux
Активные пользователи дистрибутивов операционной системы Linux иногда ставят перед собой задачу смены среды рабочего стола по разным причинам. Обладатели Kali Linux не стали исключением, ведь функциональность этой сборки позволяет поставить практически любое из доступных окружений. В рамках сегодняшней статьи мы бы хотели продемонстрировать процедуру смены графической оболочки на известную KDE.
Устанавливаем KDE в Kali Linux
KDE — одна из самых популярных графических оболочек, которая является стандартной во многих дистрибутивах. На официальном сайте Kali присутствует возможность загрузить сборку с этой средой, поэтому если вы еще не установили ОС и желаете иметь KDE, настоятельно рекомендуем сразу скачивать подходящую версию. Детальные инструкции по инсталляции платформы вы найдете в другом нашем материале по следующей ссылке, а мы же переходим непосредственно к установке оболочки.
Шаг 1: Загрузка компонентов
Вместе с изменениями внешнего вида рабочего стола пользователи получают ряд дополнительных функций — стандартные программы, расширенные настройки интерфейса и многое другое. Все это тоже нужно скачать и установить. Благо вся процедура производится через стандартную консоль с помощью одной команды.
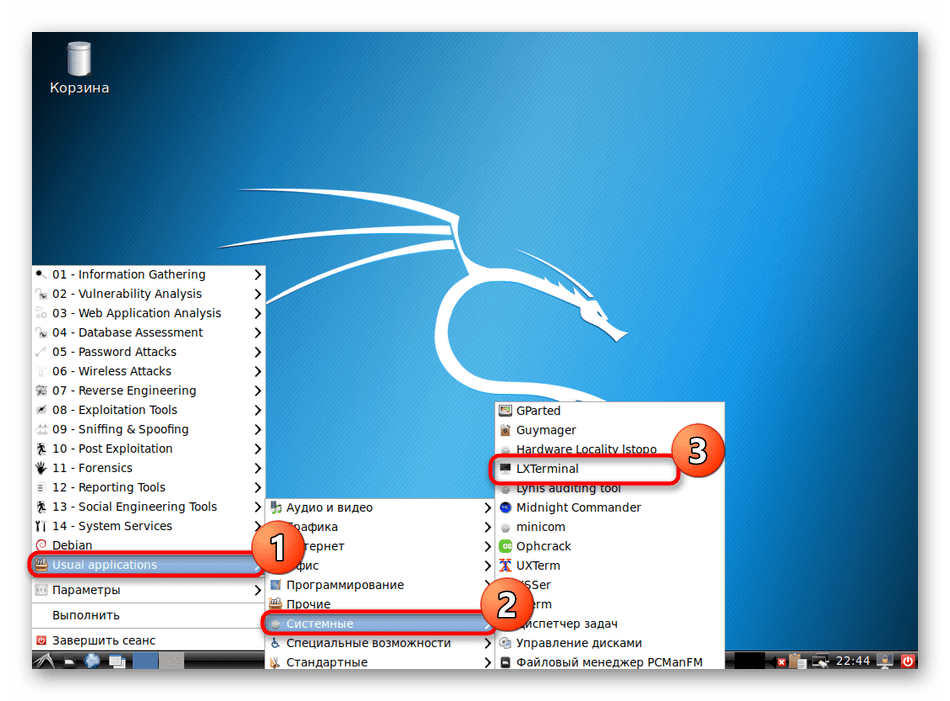
- Откройте меню, перейдите в раздел «Usual applications», выберите раздел «System» или «Системные» и отыщите там приложение «Терминал».
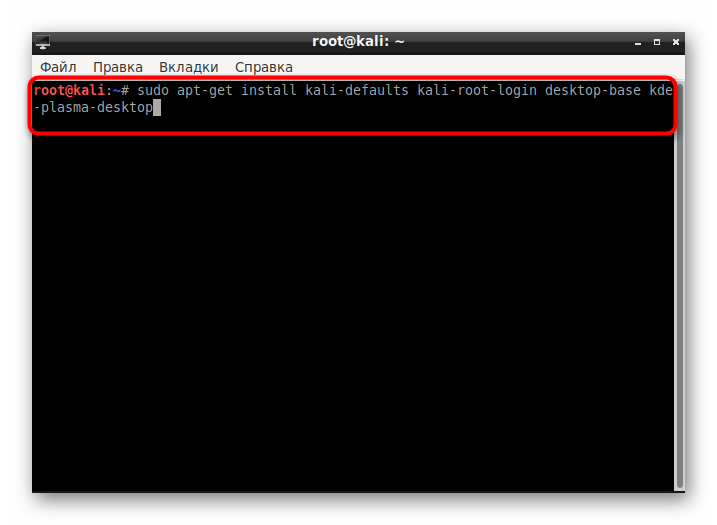
Напишите команду apt-get install kali-defaults kali-root-login desktop-base kde-plasma-desktop , если хотите установить KDE Plasma, затем нажмите на клавишу Enter.
Юзерам, которые желают установить только набор стандартных компонентов, версию для нетбуков или полный пакет KDE, советуем обратить на три отдельные команды, представленные далее.
apt-get install kali-defaults kali-root-login desktop-base kde-plasma-netbook
apt-get install kali-defaults kali-root-login desktop-base kde-standard
apt-get install kali-defaults kali-root-login desktop-base kde-full
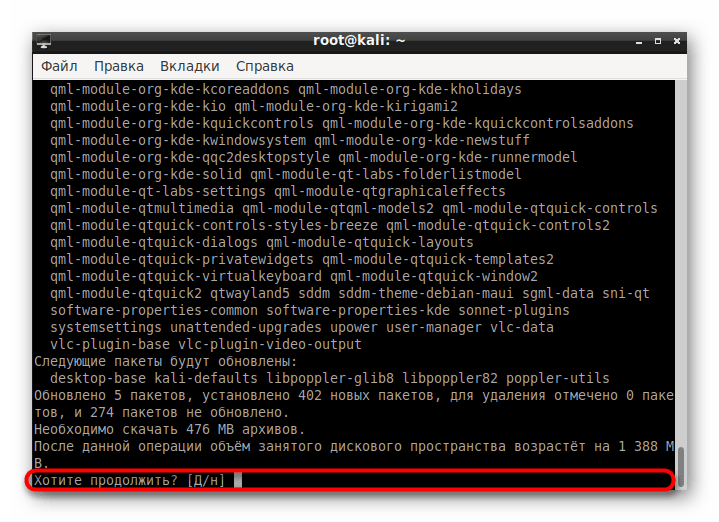
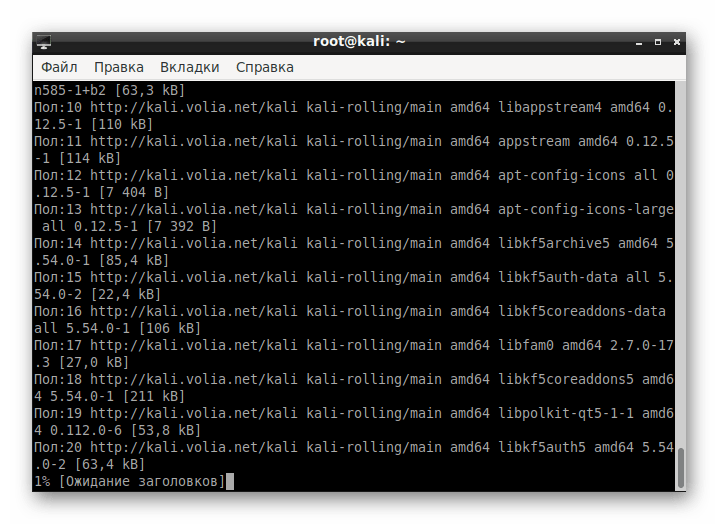
Ожидайте скачивания и установки пакетов. Скорость выполнения этого этапа зависит от стабильности интернет-соединения и мощности компьютера.
Шаг 2: Настройка менеджера дисплеев
За работоспособность графической оболочки отвечает Менеджер дисплеев. Для Линукс их было разработано несколько, чтобы обеспечить корректное функционирование самых разных сред рабочего стола. Во время установки KDE также будет добавлен новый Менеджер, его потребуется настроить:
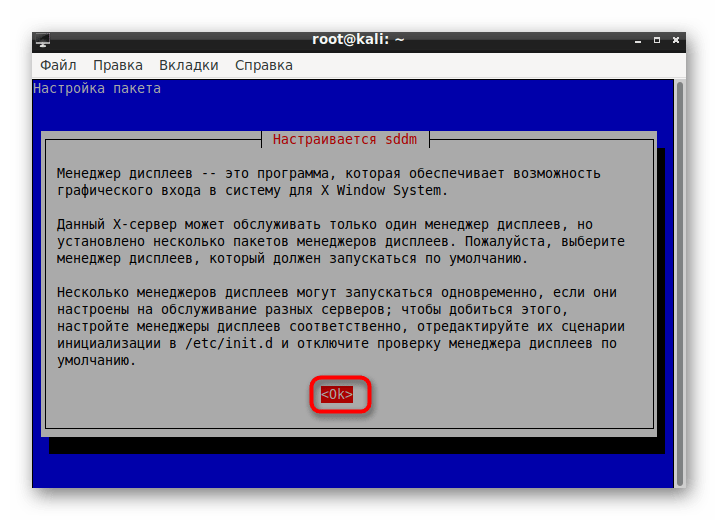
- После определенного момента во время загрузки пакетов в консоли всплывет отдельное окно с уведомлением о настройке Менеджера дисплеев. Подтвердите переход к конфигурации, выбрав «ОК».
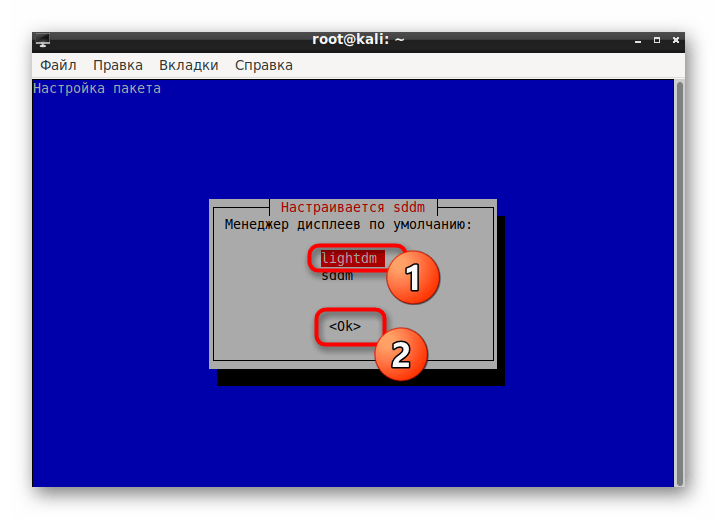
С помощью стрелочек на клавиатуре переключите стандартный Менеджер на lightdm, затем щелкните на «ОК».
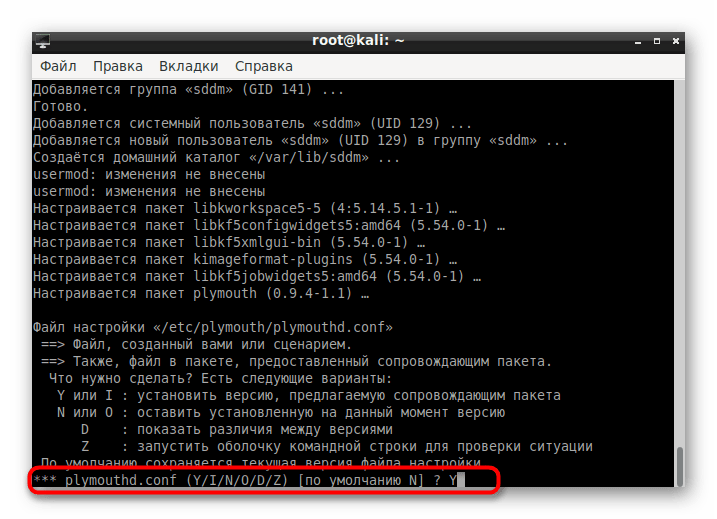
В «Терминале» подтвердите внесение изменений в системные файлы вариантом Y.
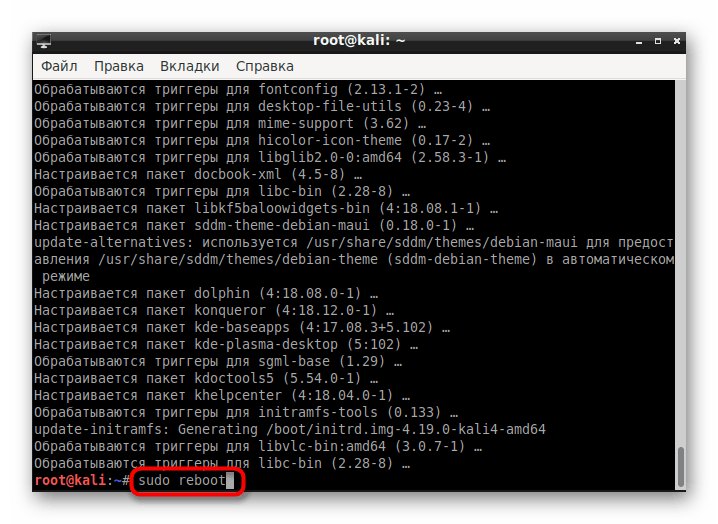
По завершении инсталляции перезагрузите операционную систему через sudo reboot .
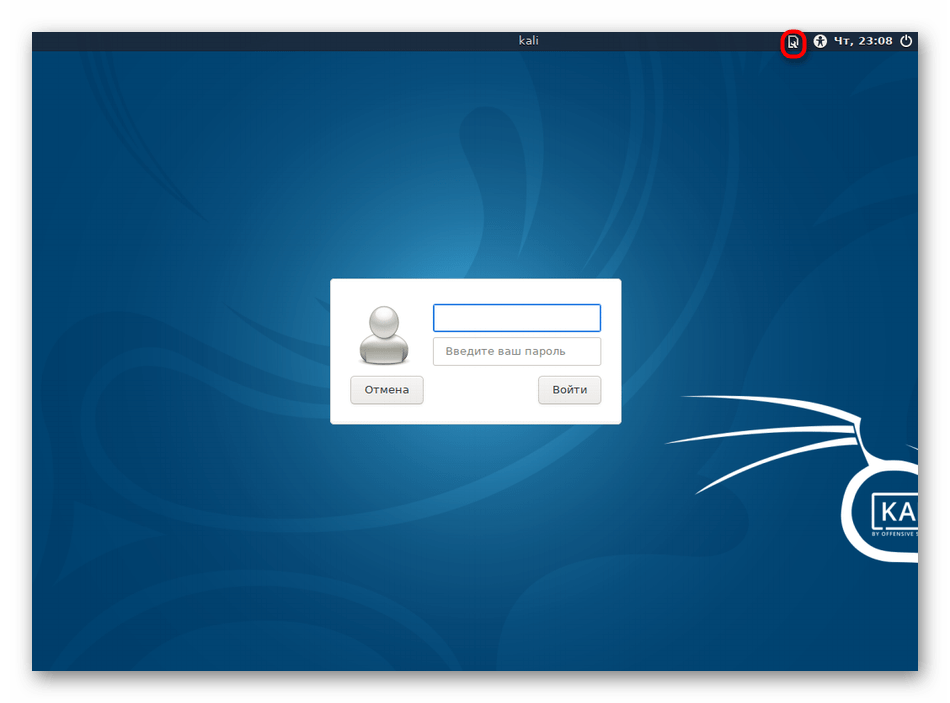
Шаг 3: Вход и настройка
Если до этого у вас не стояло никаких сред рабочего стола, после перезагрузки можно сразу приступить к настройке. В противном случае придется в стартовом окне производить выбор оболочки, что осуществляется так:
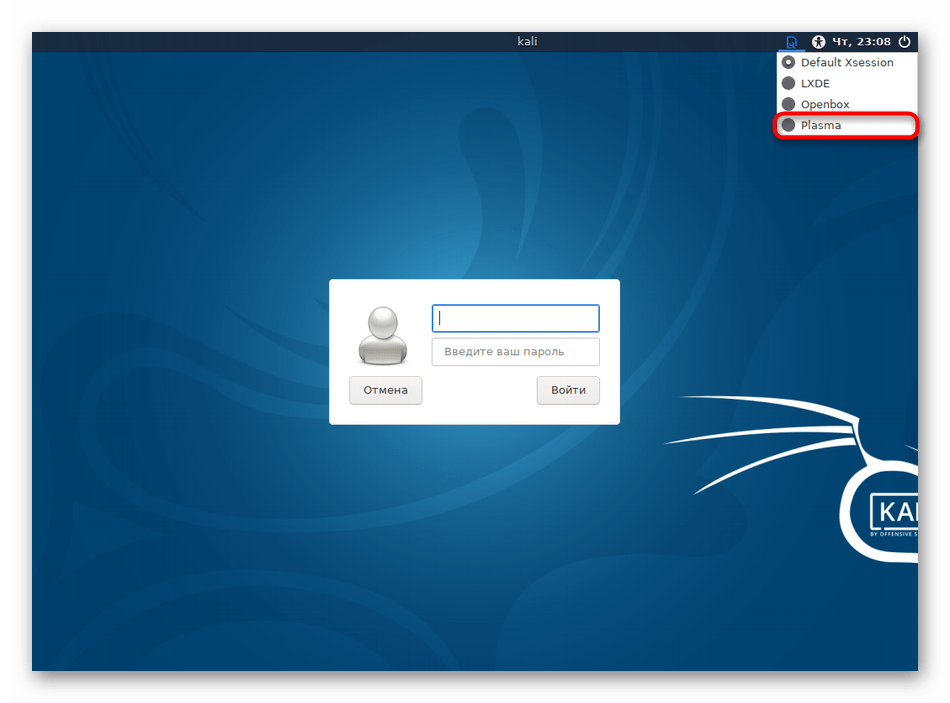
- В правом верхнем углу выберите значок настроек.
Откроется всплывающее меню, где следует отметить маркером пункт «Plasma».
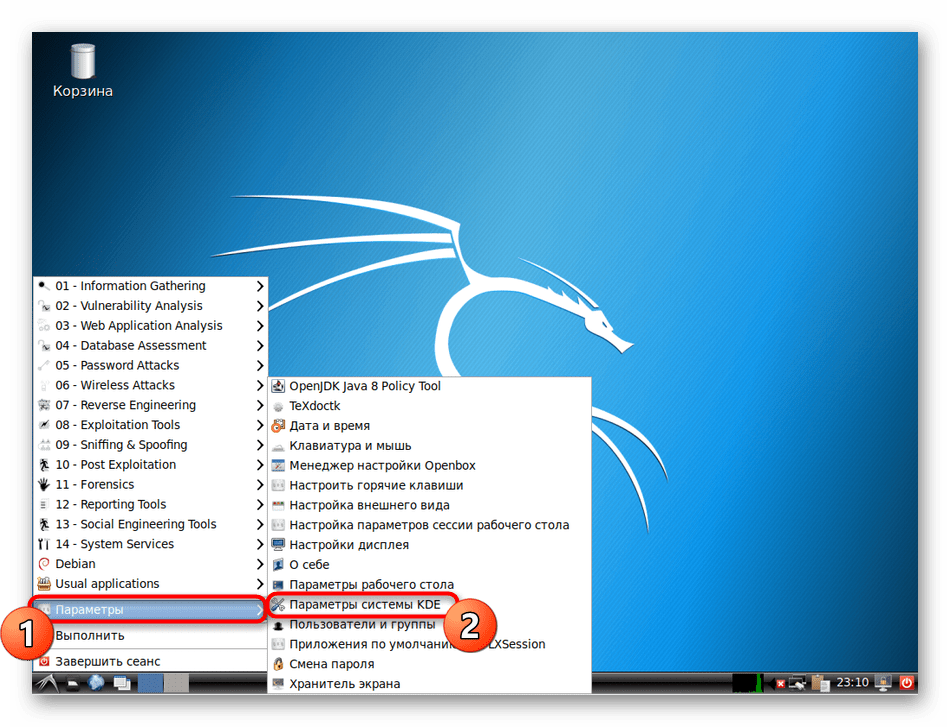
После входа через меню перейдите в «Параметры» > «Параметры системы KDE».
Настройте компоненты KDE на свое усмотрение. Пунктов здесь достаточно много, что позволит создать гибкую конфигурацию.
Отдельно бы хотелось отметить и консольную команду update-alternatives —config x-session-manager . Она позволяет изменить текущую оболочку через консоль.
Шаг 4: Удаление старой оболочки
Некоторым пользователям не хочется иметь на компьютере две оболочки. В таком случае старую можно удалить всего за пару минут, оставив только KDE. Давайте рассмотрим удаление на примере известной LXDE:
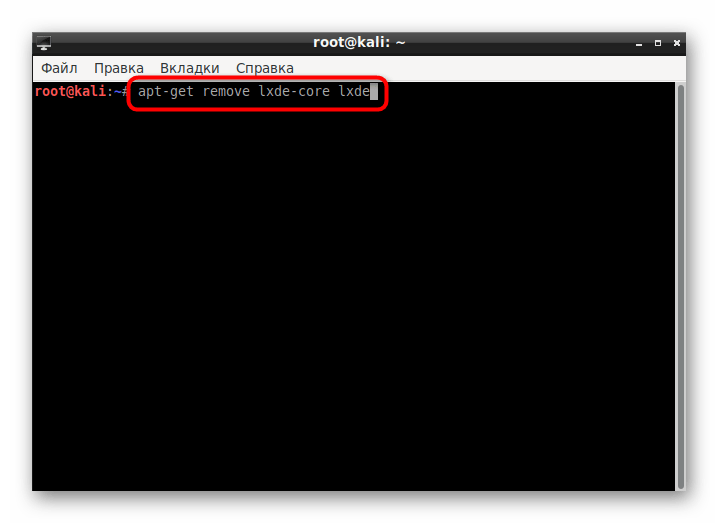
- Откройте консоль и пропишите команду apt-get remove lxde-core lxde .
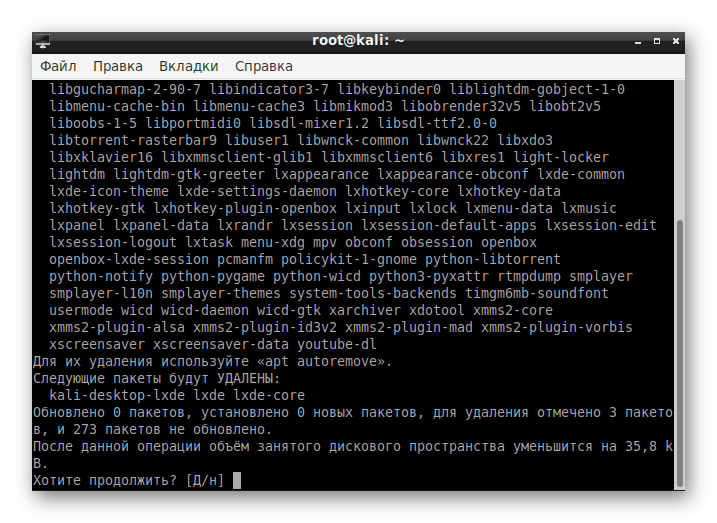
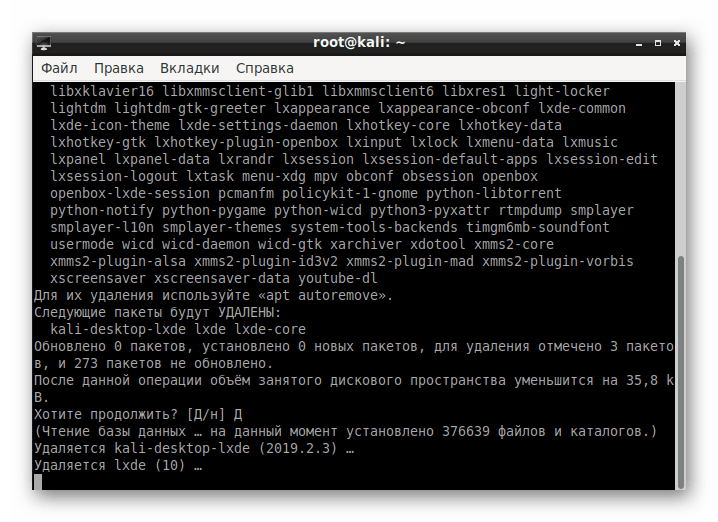
Подтвердите выполняемое действие.
Ожидайте окончания процедуры.
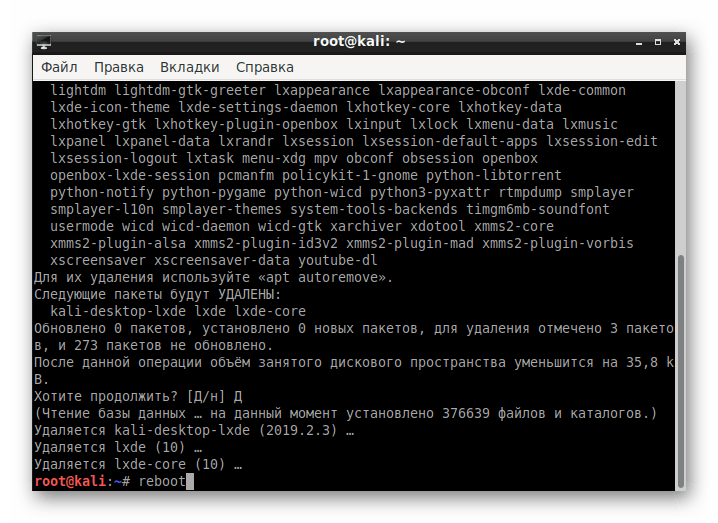
После деинсталляции перезагрузите ПК через команду reboot .
После на экране появится значок KDE и начнется загрузка.
Теперь можно переходить к работе с новой оболочкой.
Обладателям других окружений придется вводить команды немного иного содержания:
- Cinnamon — apt-get remove cinnamon
- Xfce — apt-get remove xfce4 xfce4-places-plugin xfce4-goodies
- Gnome — apt-get remove gnome-core
- MATE — apt-get remove mate-core
Если в этом списке вы не нашли своего окружения, обратитесь к официальной документации, чтобы отыскать там необходимую информацию.
Решение неполадок с установкой KDE в Kali Linux
В некоторых случаях юзеры сталкиваются с различного рода проблемами при попытке загрузки KDE. В большинстве ситуаций после запуска команды появляется уведомление «Unable to locate package kde-plasma-desktop», что свидетельствует о невозможности нахождения пакета. Если вы столкнулись с такой проблемой, советуем выполнить следующую инструкцию.
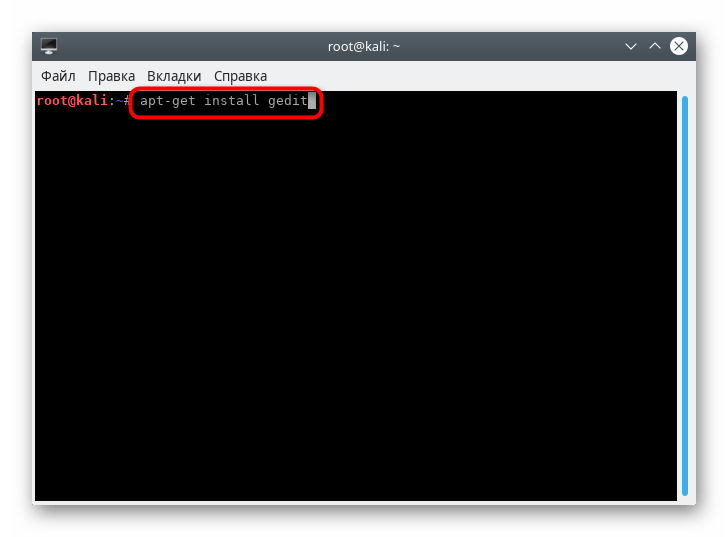
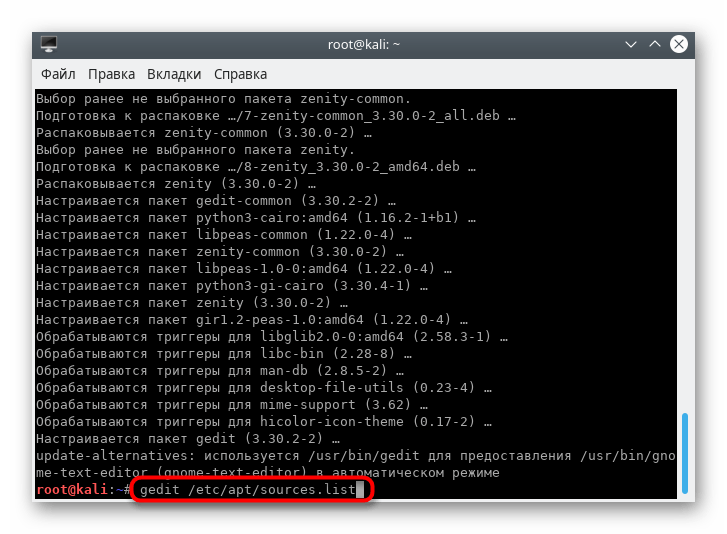
- Для начала установите текстовый редактор gedit, чтобы упростить дальнейшую работу с конфигурационным файлом. Для этого введите команду apt-get install gedit .
Подтвердите добавление новых файлов в систему.
По окончании инсталляции запустите конфигурационный файл, введя gedit /etc/apt/sources.list .
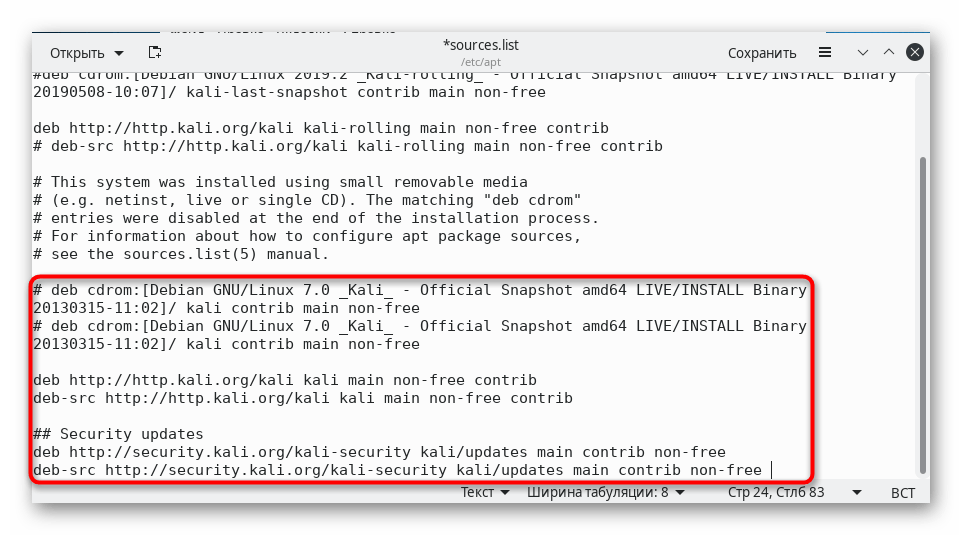
Вставьте в конец файла следующее содержимое:
# deb cdrom:[Debian GNU/Linux 7.0 _Kali_ — Official Snapshot amd64 LIVE/INSTALL Binary 20130315-11:02]/ kali contrib main non-free
# deb cdrom:[Debian GNU/Linux 7.0 _Kali_ — Official Snapshot amd64 LIVE/INSTALL Binary 20130315-11:02]/ kali contrib main non-free
deb http://http.kali.org/kali kali main non-free contrib
deb-src http://http.kali.org/kali kali main non-free contrib
## Security updates
deb http://security.kali.org/kali-security kali/updates main contrib non-free
deb-src http://security.kali.org/kali-security kali/updates main contrib non-free
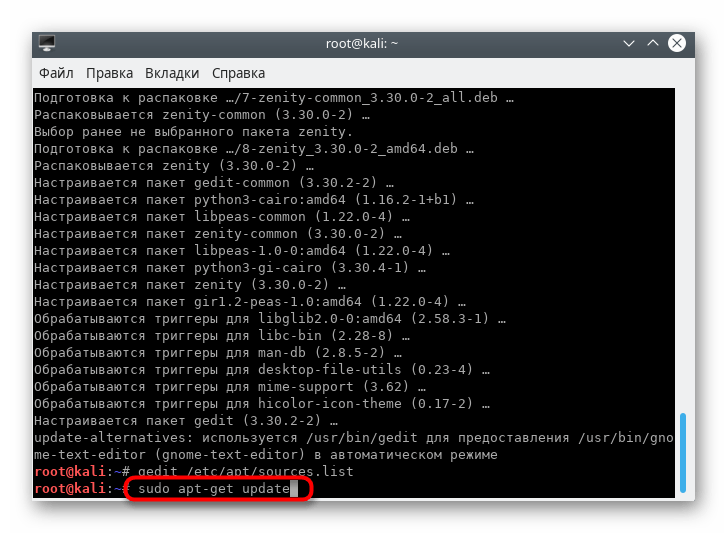
Сохраните изменения, нажав на соответствующую кнопку.
Введите sudo apt-get update , активируйте ее, а после появления новой строки ввода повторите попытку инсталляции.
Другие проблемы возникают достаточно редко, а связаны они в основном с невнимательностью самих пользователей. Например, где-то была пропущена буква или после слова нет пробела. При появлении уведомлений всегда сначала читайте их, возможно, они решаются просто. В других ситуациях рекомендуем обращаться к официальной документации дистрибутива и окружения рабочего стола.
Теперь вы знакомы с процедурой инсталляции KDE в Kali Linux. Примерно по такому же принципу устанавливаются и другие среды. Узнать информацию о самых популярных из них мы предлагаем в другом нашем руководстве по ссылке ниже.
Помимо этой статьи, на сайте еще 12315 инструкций.
Добавьте сайт Lumpics.ru в закладки (CTRL+D) и мы точно еще пригодимся вам.
Отблагодарите автора, поделитесь статьей в социальных сетях.
Источник
Kali Linux 2021.1 Release (Command-Not-Found)
Today we’re pushing out the first Kali Linux release of the year with Kali Linux 2021.1. This edition brings enhancements of existing features, and is ready to be downloaded or upgraded if you have an existing Kali Linux installation.
- Xfce 4.16 — Our preferred and current default desktop environment has been updated and tweaked
- KDE 5.20 — Plasma also received a version bump
- Terminals — mate-terminal , terminator and tilix all had various work carried out on them
- Command Not Found — A helping hand to say if a program needs to be installed
- Partnership with more tool authors — BC Security & Joohoi have been producing great tools and we want to support them
- New tools & updates — Multiple new tools have been added to Kali and are ready for you
- Kali NetHunter — New BusyBox & Rucky version, and boot-animation
- Kali ARM — Preliminary support for Parallels on Apple Silicon (Apple M1) & Raspberry Pi 400 (WiFi Support)
The Kali project itself also has a couple different changes:
- New Kali website — You may have noticed a few things looking different
- Kali newsletter — Rather than you coming to us for updates, we can push them to your inbox
Xfce & KDE Updates
How you choose to interact with Kali is completely up to you. You may want to access Kali locally or remotely, either graphically or on the command line. Even when you pick a method, there are still options you can choose from, such as a desktop environment.
By default, Kali uses Xfce, but during the setup process, allows for GNOME, KDE, or no GUI to be selected. After the setup is complete, you can install even more. We have pre-configurations for Enlightenment, i3, LXDE, and MATE as well.
So when a desktop environment gets an update, they often enhance day-to-day activities for their users. It’s best to hear it straight from the authors, for a tour of what’s changed:
Below is our tweaked GTK3 theme, on Xfce:
Terminals Tweaks
When we use Kali, we spend a significant amount of time using the command line. A lot of the time, we do it using a local terminal (rather than in a console or remote SSH). With the options of desktop environments, there are also choices when it comes to the terminals (same with what shell to use). We have been working away on various terminals ( xfce4-terminal , tmux , tilix , konsole , qterminal , and mate-terminal ) to “Kali-fy” them:
Finding Commands That Didn’t Want To Be Found
A while ago, we changed the default set of tools installed in Kali. Most users know they can either install a one-off package, or revert back to the old set of defaults ( apt install kali-linux-large ). But to help communicate our changes (as well as any new tools), we have now included command-not-found by default. This is an “optional” package, which can be removed without removing all of kali-linux-default .
Without command-not-found installed:
If you are wondering “How does this help me?”, or has the above ever happened to you, we like to think people’s next stage would be to do apt-cache search gitleaks and see it in the network repositories. But we can do better. Now with command-not-found :
As you can see from the above example:
- gitleaks — If the command you entered is the name of an executable available in Kali, it will say the package that you need to install (if its not already!)
- gitleakss — If you are “fat fingered” and make a typo, it may make a suggestion
- badcmd — If you typed in an invalid command that doesn’t exist in Kali, it will give the original message of “command not found”.
So, how can I get this magic? Good question! If you’re:
- Doing a fresh install of Kali Linux 2021.1 or later, it will “just happen” during the setup.
- Updating Kali and you are using a Bash shell, then it will “just happen” too.
- Updating Kali and you are using a Zsh shell, you will need to add the following lines to your
But it doesn’t have to end here. By adding COMMAND_NOT_FOUND_INSTALL_PROMPT=1 to your shell’s environment (e.g.
/.zshrc ), command-not-found will take it one step further, and also prompt you if you want to install the missing package. This change is something we will be putting in in a future release.
Partnerships with Tools Authors
Carrying on from our previous partnership with byt3bl33d3r, we have expanded to supporting:
- BC Security — Giving Kali exclusive early access to “Empire” ( powershell-empire ) & “StarKiller”
- Joohoi — The creator of “Fuzz Faster U Fool (ffuf)”
The announcement with Joohoi is new for Kali 2021.1. Like the previous sponsorships, you can either sponsor him directly to get the latest access to ffuf, use Kali Linux, or wait 30 days until the source code becomes public. However, he has also announced anyone who makes a significant contribution, which gets accepted into the project, also gets access!
New Tools in Kali
It wouldn’t be a Kali release if there weren’t any new tools added! A quick run down of what’s been added (to the network repositories):
- Airgeddon — Audit wireless networks
- AltDNS — Generates permutations, alterations and mutations of subdomains and then resolves them
- Arjun — HTTP parameter discovery suite
- Chisel — A fast TCP/UDP tunnel over HTTP
- DNSGen — Generates combination of domain names from the provided input
- DumpsterDiver — Search secrets in various filetypes
- GetAllUrls — Fetch known URLs from AlienVault’s Open Threat Exchange, the Wayback Machine, and Common Crawl
- GitLeaks — Searches Git repo’s history for secrets and keys
- HTTProbe — Take a list of domains and probe for working HTTP and HTTPS servers
- MassDNS — A high-performance DNS stub resolver for bulk lookups and reconnaissance
- PSKracker — WPA/WPS toolkit for generating default keys/pins
- WordlistRaider — Preparing existing wordlists
Kali’s Website
Until recently, the only way you could be reading this would have been from our RSS feed or directly from our blog (as we only recently made the announcement of the Kali Newletter). You may of noticed already, and we said that it was coming, and it finally has — kali.org has had a face-lift!
We have (finally) moved away from WordPress to Hugo. Similarly to Kali, the website will also be a rolling distribution. The recent change is mostly cosmetic and content (both were long overdue), and we have made plans for new features to be added.
Another upside of the switch is that we can take more advantage of what GitLab has to offer. We recently had an interview with GitLab about the switch.
On the subject of interviews, we also had a word with Mr Robot’s ARG Society if you missed that.
Wallpapers
Just a quick little thing, we have tweaked our wallpaper packages:
- kali-wallpapers-2020.4 — Kali’s wallpapers from 2020.4 and onwards (for the time being)
- kali-wallpapers-2019.4 — Kali’s wallpapers between 2019.4 and 2020.3.
- kali-wallpapers-legacy — BackTrack & Kali nostalgic backgrounds
- kali-wallpapers-all — Every wallpaper
- kali-community-wallpapers — created and submitted by the community (submit yours today!)
With the alterations to the packages, we have taken the time to improve support for Xfce when using them.
Kali NetHunter Updates
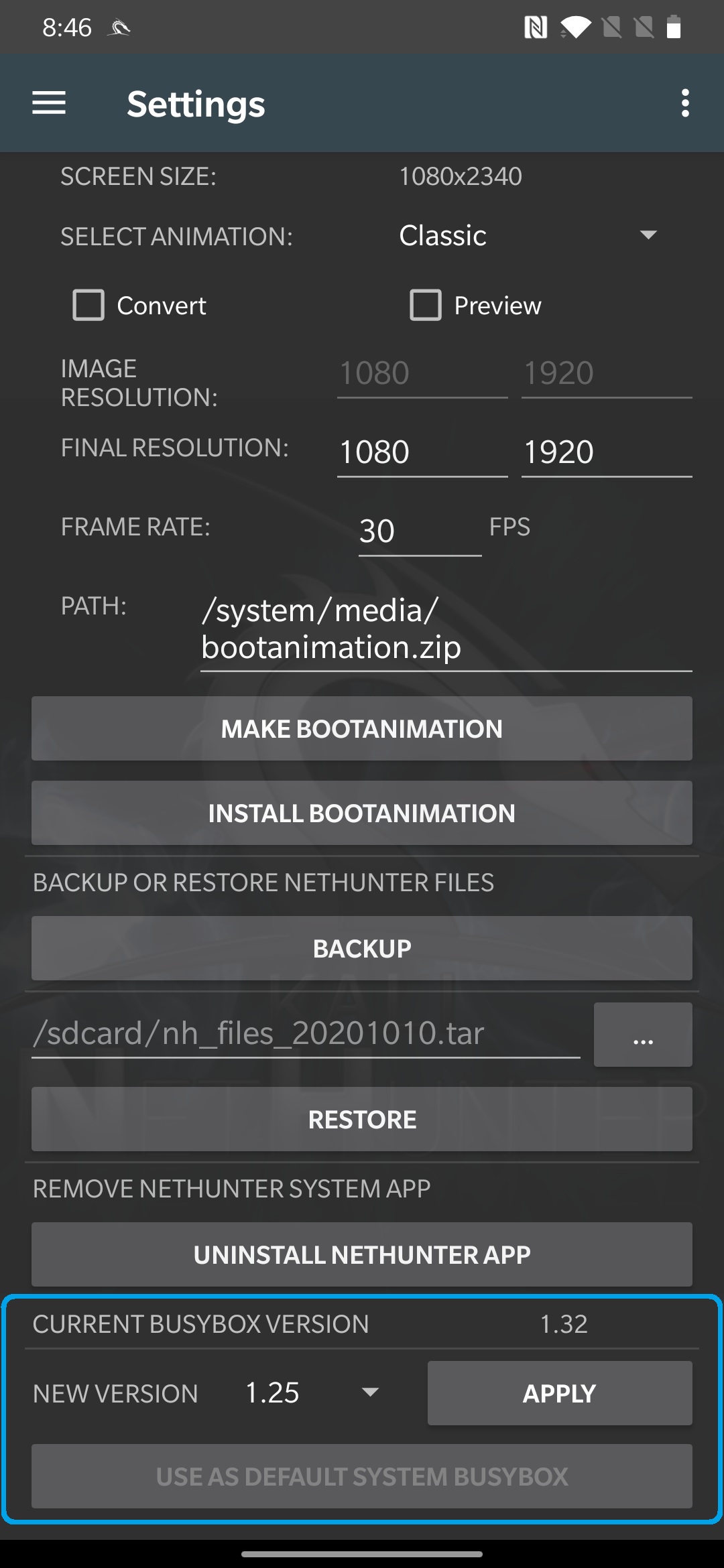
BusyBox, one of the core engines of Kali NetHunter, has received a well deserved upgrade to version “1.32.0-nethunter”. BusyBox is used internally to ensure that NetHunter tools and commands are executed consistently across the vast number of different Android versions and vendor modifications. This change, whilst big, should go unnoticed by users and will help developers to port their code to NetHunter with no hassles at all. @yesimxev has added a handy section to the settings menu, which allows developers to select different BusyBox versions for testing:
Speaking of developers: If you have any cool ideas you’d like to see included in Kali NetHunter or if you would like to contribute to this amazing project, please reach out to us in our forums or on GitLab. We would love to hear from you!
Tools have been updated to the latest versions, notably Rucky — the “modern looking USB Rubber Ducky Editor and Attack Launcher”, which has been completely re-written by its author @mayankmetha and released in the Kali NetHunter App Store as version 2.1.
We’ve also been busy working on the visual aspects of Kali NetHunter, with @s133py adding a stunning new boot-animation to the growing selection:
If you have a cool boot-animation you’d like to share, please submit a merge request to our Kali NetHunter boot-animation repository.
Kali ARM Updates
As you may have heard, Apple have released new Macs with their own processors, known as Apple Silicon (Apple M1). So far, only Parallels have released something publicly that people can use for virtualization. To that end, we have generated both an installer & live ISOs ( kali-linux-2021.1-installer-arm64.iso and kali-linux-2021.1-live-arm64.iso ) that can be used with VMs on Apple Silicon Macs. Many thanks to the people who reached out and offered to test and helped us to iron out the bugs. If you’d like to see it in action, David Bombal has put out a video of it.
We have also added support for the Raspberry Pi 400’s wireless card, however it is very important to note that this is not a nexmon firmware, as nexmon does not currently support it.
The Kali ARM build scripts have seen a few more improvements from Francisco Jose Rodriguez Martos and we appreciate the assistance greatly. If you’d like to get involved with ARM, check out the GitLab issue list.
Download Kali Linux 2021.1
Fresh Images: So what are you waiting for? Start downloading already!
Seasoned Kali Linux users are already aware of this, but for the ones who are not, we do also produce weekly builds that you can use as well. If you cannot wait for our next release and you want the latest packages (or bug fixes) when you download the image, you can just use the weekly image instead. This way you’ll have fewer updates to do. Just know that these are automated builds that we do not QA like we do our standard release images. But we gladly take bug reports about those images because we want any issues to be fixed before our next release!
Existing Installs: If you already have an existing Kali Linux installation, remember you can always do a quick update:
You should now be on Kali Linux 2021.1. We can do a quick check by doing:
NOTE: The output of uname -r may be different depending on the system architecture.
As always, should you come across any bugs in Kali, please submit a report on our bug tracker. We’ll never be able to fix what we do not know is broken! And Twitter is not a Bug Tracker!
Источник