- What is Operating System? Types of OS, Features and Examples
- What is an Operating System?
- History Of OS
- Examples of Operating System with Market Share
- Types of Operating System (OS)
- Batch Operating System
- Multi-Tasking/Time-sharing Operating systems
- Real time OS
- Distributed Operating System
- Network Operating System
- Mobile OS
- Functions of Operating System
- Features of Operating System (OS)
- Advantage of using Operating System
- Disadvantages of using Operating System
- What is a Kernel?
- Features of Kennel
- Types of Kernels
- Operating System — Overview
- Definition
- Memory Management
- Processor Management
- Device Management
- File Management
- Other Important Activities
- Types of Operating System
- Batch operating system
- Time-sharing operating systems
- Distributed operating System
- Network operating System
- Real Time operating System
- Hard real-time systems
- Soft real-time systems
What is Operating System? Types of OS, Features and Examples
What is an Operating System?
An Operating System (OS) is a software that acts as an interface between computer hardware components and the user. Every computer system must have at least one operating system to run other programs. Applications like Browsers, MS Office, Notepad Games, etc., need some environment to run and perform its tasks.
The OS helps you to communicate with the computer without knowing how to speak the computer’s language. It is not possible for the user to use any computer or mobile device without having an operating system. 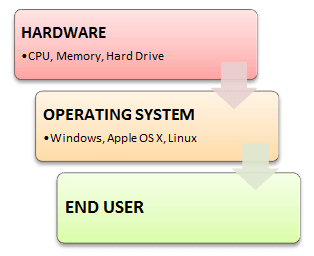
History Of OS
- Operating systems were first developed in the late 1950s to manage tape storage
- The General Motors Research Lab implemented the first OS in the early 1950s for their IBM 701
- In the mid-1960s, operating systems started to use disks
- In the late 1960s, the first version of the Unix OS was developed
- The first OS built by Microsoft was DOS. It was built in 1981 by purchasing the 86-DOS software from a Seattle company
- The present-day popular OS Windows first came to existence in 1985 when a GUI was created and paired with MS-DOS.
Examples of Operating System with Market Share
Following are the examples of Operating System with the latest Market Share
| OS Name | Share |
| Windows | 40.34 |
| Android | 37.95 |
| iOS | 15.44 |
| Mac OS | 4.34 |
| Linux | 0.95 |
| Chrome OS | 0.14 |
| Windows Phone OS | 0.06 |
Types of Operating System (OS)
Following are the popular types of Operating System:
- Batch Operating System
- Multitasking/Time Sharing OS
- Multiprocessing OS
- Real Time OS
- Distributed OS
- Network OS
- Mobile OS
Batch Operating System
Some computer processes are very lengthy and time-consuming. To speed the same process, a job with a similar type of needs are batched together and run as a group.
The user of a batch operating system never directly interacts with the computer. In this type of OS, every user prepares his or her job on an offline device like a punch card and submit it to the computer operator.
Multi-Tasking/Time-sharing Operating systems
Time-sharing operating system enables people located at a different terminal(shell) to use a single computer system at the same time. The processor time (CPU) which is shared among multiple users is termed as time sharing.
Real time OS
A real time operating system time interval to process and respond to inputs is very small. Examples: Military Software Systems, Space Software Systems are the Real time OS example.
Distributed Operating System
Distributed systems use many processors located in different machines to provide very fast computation to its users.
Network Operating System
Network Operating System runs on a server. It provides the capability to serve to manage data, user, groups, security, application, and other networking functions.
Mobile OS
Mobile operating systems are those OS which is especially that are designed to power smartphones, tablets, and wearables devices.
Some most famous mobile operating systems are Android and iOS, but others include BlackBerry, Web, and watchOS.
Functions of Operating System
Below are the main functions of Operating System: 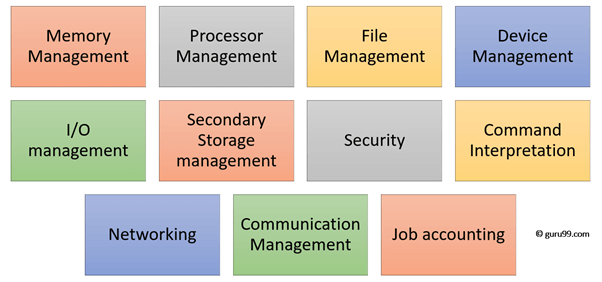
In an operating system software performs each of the function:
- Process management:- Process management helps OS to create and delete processes. It also provides mechanisms for synchronization and communication among processes.
- Memory management:- Memory management module performs the task of allocation and de-allocation of memory space to programs in need of this resources.
- File management:- It manages all the file-related activities such as organization storage, retrieval, naming, sharing, and protection of files.
- Device Management: Device management keeps tracks of all devices. This module also responsible for this task is known as the I/O controller. It also performs the task of allocation and de-allocation of the devices.
- I/O System Management: One of the main objects of any OS is to hide the peculiarities of that hardware devices from the user.
- Secondary-Storage Management: Systems have several levels of storage which includes primary storage, secondary storage, and cache storage. Instructions and data must be stored in primary storage or cache so that a running program can reference it.
- Security:- Security module protects the data and information of a computer system against malware threat and authorized access.
- Command interpretation: This module is interpreting commands given by the and acting system resources to process that commands.
- Networking: A distributed system is a group of processors which do not share memory, hardware devices, or a clock. The processors communicate with one another through the network.
- Job accounting: Keeping track of time & resource used by various job and users.
- Communication management: Coordination and assignment of compilers, interpreters, and another software resource of the various users of the computer systems.
Features of Operating System (OS)
Here is a list important features of OS:
- Protected and supervisor mode
- Allows disk access and file systems Device drivers Networking Security
- Program Execution
- Memory management Virtual Memory Multitasking
- Handling I/O operations
- Manipulation of the file system
- Error Detection and handling
- Resource allocation
- Information and Resource Protection

Advantage of using Operating System
- Allows you to hide details of hardware by creating an abstraction
- Easy to use with a GUI
- Offers an environment in which a user may execute programs/applications
- The operating system must make sure that the computer system convenient to use
- Operating System acts as an intermediary among applications and the hardware components
- It provides the computer system resources with easy to use format
- Acts as an intermediator between all hardware’s and software’s of the system
Disadvantages of using Operating System
- If any issue occurs in OS, you may lose all the contents which have been stored in your system
- Operating system’s software is quite expensive for small size organization which adds burden on them. Example Windows
- It is never entirely secure as a threat can occur at any time
What is a Kernel?
The kernel is the central component of a computer operating systems. The only job performed by the kernel is to the manage the communication between the software and the hardware. A Kernel is at the nucleus of a computer. It makes the communication between the hardware and software possible. While the Kernel is the innermost part of an operating system, a shell is the outermost one.
Features of Kennel
- Low-level scheduling of processes
- Inter-process communication
- Process synchronization
- Context switching
Types of Kernels
There are many types of kernels that exists, but among them, the two most popular kernels are:
1.Monolithic
A monolithic kernel is a single code or block of the program. It provides all the required services offered by the operating system. It is a simplistic design which creates a distinct communication layer between the hardware and software.
2. Microkernels
Microkernel manages all system resources. In this type of kernel, services are implemented in different address space. The user services are stored in user address space, and kernel services are stored under kernel address space. So, it helps to reduce the size of both the kernel and operating system.
Operating System — Overview
An Operating System (OS) is an interface between a computer user and computer hardware. An operating system is a software which performs all the basic tasks like file management, memory management, process management, handling input and output, and controlling peripheral devices such as disk drives and printers.
Some popular Operating Systems include Linux Operating System, Windows Operating System, VMS, OS/400, AIX, z/OS, etc.
Definition
An operating system is a program that acts as an interface between the user and the computer hardware and controls the execution of all kinds of programs.
Following are some of important functions of an operating System.
- Memory Management
- Processor Management
- Device Management
- File Management
- Security
- Control over system performance
- Job accounting
- Error detecting aids
- Coordination between other software and users
Memory Management
Memory management refers to management of Primary Memory or Main Memory. Main memory is a large array of words or bytes where each word or byte has its own address.
Main memory provides a fast storage that can be accessed directly by the CPU. For a program to be executed, it must in the main memory. An Operating System does the following activities for memory management −
Keeps tracks of primary memory, i.e., what part of it are in use by whom, what part are not in use.
In multiprogramming, the OS decides which process will get memory when and how much.
Allocates the memory when a process requests it to do so.
De-allocates the memory when a process no longer needs it or has been terminated.
Processor Management
In multiprogramming environment, the OS decides which process gets the processor when and for how much time. This function is called process scheduling. An Operating System does the following activities for processor management −
Keeps tracks of processor and status of process. The program responsible for this task is known as traffic controller.
Allocates the processor (CPU) to a process.
De-allocates processor when a process is no longer required.
Device Management
An Operating System manages device communication via their respective drivers. It does the following activities for device management −
Keeps tracks of all devices. Program responsible for this task is known as the I/O controller.
Decides which process gets the device when and for how much time.
Allocates the device in the efficient way.
File Management
A file system is normally organized into directories for easy navigation and usage. These directories may contain files and other directions.
An Operating System does the following activities for file management −
Keeps track of information, location, uses, status etc. The collective facilities are often known as file system.
Decides who gets the resources.
Allocates the resources.
De-allocates the resources.
Other Important Activities
Following are some of the important activities that an Operating System performs −
Security − By means of password and similar other techniques, it prevents unauthorized access to programs and data.
Control over system performance − Recording delays between request for a service and response from the system.
Job accounting − Keeping track of time and resources used by various jobs and users.
Error detecting aids − Production of dumps, traces, error messages, and other debugging and error detecting aids.
Coordination between other softwares and users − Coordination and assignment of compilers, interpreters, assemblers and other software to the various users of the computer systems.
Types of Operating System
Operating systems are there from the very first computer generation and they keep evolving with time. In this chapter, we will discuss some of the important types of operating systems which are most commonly used.
Batch operating system
The users of a batch operating system do not interact with the computer directly. Each user prepares his job on an off-line device like punch cards and submits it to the computer operator. To speed up processing, jobs with similar needs are batched together and run as a group. The programmers leave their programs with the operator and the operator then sorts the programs with similar requirements into batches.
The problems with Batch Systems are as follows −
- Lack of interaction between the user and the job.
- CPU is often idle, because the speed of the mechanical I/O devices is slower than the CPU.
- Difficult to provide the desired priority.
Time-sharing operating systems
Time-sharing is a technique which enables many people, located at various terminals, to use a particular computer system at the same time. Time-sharing or multitasking is a logical extension of multiprogramming. Processor’s time which is shared among multiple users simultaneously is termed as time-sharing.
The main difference between Multiprogrammed Batch Systems and Time-Sharing Systems is that in case of Multiprogrammed batch systems, the objective is to maximize processor use, whereas in Time-Sharing Systems, the objective is to minimize response time.
Multiple jobs are executed by the CPU by switching between them, but the switches occur so frequently. Thus, the user can receive an immediate response. For example, in a transaction processing, the processor executes each user program in a short burst or quantum of computation. That is, if n users are present, then each user can get a time quantum. When the user submits the command, the response time is in few seconds at most.
The operating system uses CPU scheduling and multiprogramming to provide each user with a small portion of a time. Computer systems that were designed primarily as batch systems have been modified to time-sharing systems.
Advantages of Timesharing operating systems are as follows −
- Provides the advantage of quick response.
- Avoids duplication of software.
- Reduces CPU idle time.
Disadvantages of Time-sharing operating systems are as follows −
- Problem of reliability.
- Question of security and integrity of user programs and data.
- Problem of data communication.
Distributed operating System
Distributed systems use multiple central processors to serve multiple real-time applications and multiple users. Data processing jobs are distributed among the processors accordingly.
The processors communicate with one another through various communication lines (such as high-speed buses or telephone lines). These are referred as loosely coupled systems or distributed systems. Processors in a distributed system may vary in size and function. These processors are referred as sites, nodes, computers, and so on.
The advantages of distributed systems are as follows −
- With resource sharing facility, a user at one site may be able to use the resources available at another.
- Speedup the exchange of data with one another via electronic mail.
- If one site fails in a distributed system, the remaining sites can potentially continue operating.
- Better service to the customers.
- Reduction of the load on the host computer.
- Reduction of delays in data processing.
Network operating System
A Network Operating System runs on a server and provides the server the capability to manage data, users, groups, security, applications, and other networking functions. The primary purpose of the network operating system is to allow shared file and printer access among multiple computers in a network, typically a local area network (LAN), a private network or to other networks.
Examples of network operating systems include Microsoft Windows Server 2003, Microsoft Windows Server 2008, UNIX, Linux, Mac OS X, Novell NetWare, and BSD.
The advantages of network operating systems are as follows −
- Centralized servers are highly stable.
- Security is server managed.
- Upgrades to new technologies and hardware can be easily integrated into the system.
- Remote access to servers is possible from different locations and types of systems.
The disadvantages of network operating systems are as follows −
- High cost of buying and running a server.
- Dependency on a central location for most operations.
- Regular maintenance and updates are required.
Real Time operating System
A real-time system is defined as a data processing system in which the time interval required to process and respond to inputs is so small that it controls the environment. The time taken by the system to respond to an input and display of required updated information is termed as the response time. So in this method, the response time is very less as compared to online processing.
Real-time systems are used when there are rigid time requirements on the operation of a processor or the flow of data and real-time systems can be used as a control device in a dedicated application. A real-time operating system must have well-defined, fixed time constraints, otherwise the system will fail. For example, Scientific experiments, medical imaging systems, industrial control systems, weapon systems, robots, air traffic control systems, etc.
There are two types of real-time operating systems.
Hard real-time systems
Hard real-time systems guarantee that critical tasks complete on time. In hard real-time systems, secondary storage is limited or missing and the data is stored in ROM. In these systems, virtual memory is almost never found.
Soft real-time systems
Soft real-time systems are less restrictive. A critical real-time task gets priority over other tasks and retains the priority until it completes. Soft real-time systems have limited utility than hard real-time systems. For example, multimedia, virtual reality, Advanced Scientific Projects like undersea exploration and planetary rovers, etc.




