- Запуск Windows 7 в Linux через Virtualbox с реального раздела жесткого диска
- VirtualBox from an existing partition
- 5 Answers 5
- How to Access Physical Disk in VirtualBox- Windows 10
- Summary
- How to Access Entire Physical Disk from VirtualBox
- How to Access Specific Partitions of Physical Disk from VirtualBox
- You Can Read Next
- VMware Vs VirtualBox – Detailed Comparison
- Best Free Virtual Machine Software in 2021 – Start Your New Career
- VDI to VHD/VHDX – Convert VirtualBox VMs to Hyper-V
- Pre-installed Windows 98 SE VirtualBox Image – Download and Use
- Convert VirtualBox VDI to Parallels Disk Format in macOS
- Install VirtualBox Extension Pack on Windows 10/8.1 Host
- 16 thoughts on “How to Access Physical Disk in VirtualBox- Windows 10”
Запуск Windows 7 в Linux через Virtualbox с реального раздела жесткого диска
Многие, и я в том числе, держат на своих компьютерах несколько операционных систем. Почему бы и нет? Тем более, когда это необходимо. Особенно, когда некоторые программы работают только в Windows, и ни через Wine, ни за ради бога они не запускаются. Приходится скакать из системы в систему, либо пользоваться виртуальными машинами. В частности, Virtualbox позволяет создать образ VMDK c установленным разделом Windows. Об этом и пойдет речь.
В сети много подробных инструкций, как в Linux через Virtualbox запустить Windows 7, уже установленную на физический диск. Основной принцип заключается в создании образа .vmdk из реального раздела жесткого диска с помощью внутренней команды Virtualbox. Как правило, это выглядит так:
$ VBoxManage internalcommands createrawvmdk -filename /home/$USER/sdb.vmdk -rawdisk /dev/sda
Но для загрузки системы этого недостаточно. Нужна либо копия загрузчика MBR, либо iso-образ загрузчика GRUB, установленных на вашей машине.
Опишу, вкратце, основные способы установки на примере Ubuntu (Gnome).
Естественно, Windows 7 присутствует, Virtualbox уже установлен, и пользователь входит в группу «vboxusers».
Если нет, то:
$ sudo adduser $(whoami) vboxusers
Добавляем пользователя в группу «disk», для того, чтобы запускать vboxmanage без рута и не заморачиваться с правами созданных разделов, командой:
$ sudo adduser $(whoami) disk
Для применения изменений:
Реальный раздел с Windows должен быть загрузочным (активным). Для проверки:
Звездочкой будет отмечен загрузочный диск.
Если нет, то используем fdisk, gparted или кому что нравится.
Моя разметка (в дальнейшем буду приводить свои данные):
Устр-во Загр Начало Конец Блоки Id Система
/dev/sda1 1 26 208813+ 83 Linux
/dev/sda2 27 2637 20972857+ 83 Linux
/dev/sda3 * 2638 7859 41945715 7 HPFS/NTFS
/dev/sda4 7860 60801 425247745 f W95 расшир. (LBA)
/dev/sda5 7860 10470 20971520 7 HPFS/NTFS
/dev/sda6 10471 60338 400556032 83 Linux
/dev/sda7 60338 60801 3718144 82 Linux своп / Solaris
Далее первый способ с «поддельным» MBR:
Устанавливаем пакет mbr:
$ sudo apt-get install mbr
Ставим копию mbr в файл. Ваш настоящий mbr никуда не денется:
$ sudo install-mbr —force /home/$USER/.myBootRecord.mbr && sudo chmod +rwx /home/$USER/.myBootRecord.mbr
$ VBoxManage internalcommands createrawvmdk -filename /home/$USER/VirtualBox/Windows7.vmdk -rawdisk /dev/sda -partitions 3,5 -mbr /home/$USER/.myBootRecord.mbr -relative
Если все правильно, должно выдать «. created successfully»
Создаем виртуальную машину:
Задаем имя, к примеру, Windows7.
Задаем размер памяти, к примеру, 1024 МБ.
Отмечаем «Загрузочный диск», «Использовать существующий жесткий диск» и выбираем созданный файл Windows7.vmdk.
Виртуальная машина создана.
Теперь правим свойства машины:
В разделе «Система» на вкладке «Материнская плата» отмечаем IO APIC. Обязательно ставим галочку на CD/DVD-ROM. Он должен стоять первым в порядке загрузки. Все остальное по желанию.
В разделе «Носители» SATA контроллер должен быть Windows7.vmdk.
Теперь ищем DVD диск, с которого устанавливалась Windows, либо iso-образ установочного DVD. Добавляем в IDE контроллер привод оптических дисков (реальный или образ).
Все остальное — кто на что горазд.
Запускаем машину.
При первом запуске должно выдать: «Press any key to boot from cd or dvd». Восстанавливаем загрузчик Windows. Думаю, все знают, как это делать. После восстановления извлекаем установочный диск. Все. Windows должна запускаться как обычно.
Так вот, в этом способе присутствует очень огромный минус: при обычном запуске Windows, не через виртуальную машину, придется так же восстанавливать загрузчик. И так каждый раз.
Теперь второй способ с GRUB (v. 0.97), записанный в iso-образ (инструкции в сети разнятся, в зависимости от системы):
Создаем директорию:
$ mkdir -p .iso/boot/grub
Копируем файл в созданную директорию:
$ cp /usr/lib/grub/i386-pc/* .iso/boot/grub
Создаем iso-образ с GRUB:
$ genisoimage -R -b boot/grub/stage2_eltorito -no-emul-boot -boot-load-size 4 -boot-info-table -iso-level 2 -input-charset utf-8 -o grub.iso /home/$USER/.iso/
Создаем VMDK-образ:
$ VBoxManage internalcommands createrawvmdk -filename /home/$USER/VirtualBox/Windows7.vmdk -rawdisk /dev/sda -partitions 3,5 -relative
Далее создаем и настраиваем виртуальную машину так же как и в первом способе, за исключением пункта «Носители». Для IDE контроллера выбираем созданный grub.iso.
А теперь третий способ, который, почему то, я нигде в сети не встретил, по крайней мере, относящийся к Virualbox.
Может быть кому-то это покажется элементарным, но все же:
загрузка с помощью GRUB2 (v. 1.97) записанный в iso-образ.
В этой директории любым способом создал файл grub.cfg следующего содержания:
(Раздел menuentry «Windows 7» скопировать со своего grub.cfg, расположенного по адресу /boot/grub/)
insmod part_msdos
set default=0
set timeout=0
menuentry «Windows 7 (loader) (on /dev/sda3)» —class windows —class os <
insmod part_msdos
insmod ntfs
set root='(/dev/sda,msdos3)’
search —no-floppy —fs-uuid —set=root C070671099FC2625
chainloader +1
>
Здесь убрано все лишнее, GRUB проскакивает быстро и незаметно.
Создаем iso-образ с GRUB2:
$ grub-mkrescue —output=/home/$USER/.iso/grub.iso /home/$USER/.iso/
$ VBoxManage internalcommands createrawvmdk -filename /home/$USER/VirtualBox/Windows7.vmdk -rawdisk /dev/sda -partitions 3,5 -relative
Далее создаем и настраиваем виртуальную машину так же как и во втором способе.
Так же выбираем grub.iso.
Едиственный нюанс: при автоматической установке дополнений гостевой оси, образ этого iso заменится на VBoxGuestAdditions.iso. Поменяйте его обратно.
Еще раз повторюсь, в примерах используются мои настройки. Вносите изменения.
Для справки:
Ноутбук Asus M50VM (Core2Duo T9400 2.53GHz, RAM 4058MB, GeForce 9600M)
OS: основная Linux Mint 11 Katya 2.6.38-12-generic (x86_64), вторая Windows 7 64 bit
Virtualbox 4.1.6
Данная статья не подлежит комментированию, поскольку её автор ещё не является полноправным участником сообщества. Вы сможете связаться с автором только после того, как он получит приглашение от кого-либо из участников сообщества. До этого момента его username будет скрыт псевдонимом.
VirtualBox from an existing partition
I installed VirtualBox on my Ubuntu Hardy Heron installation, and I would like to use it to virtualize Windows for those rare occasions that I actually need to do something there.
Unfortunately, I don’t have an installation disk at the moment, but I do have Vista already installed on a partition (it came with the machine).
Is there a way I can easily copy this partition into a .vdi virtual image?
5 Answers 5
You can download the free version of vmware converter which can do a physical to virtual machine conversion. I believe VirtualBox can run vmware VMs.
I’m in the process of doing this myself.
As Ferruccio says, vmware converter is one option. This will not work if your windows boot.ini is also loading another operating system, even if vista is the default.
There’s a VirtualBox guide just for this but it was written for XP. Still but may be worth trying.
This «create new partition, xcopy stuff in» approach» guide (specifically post 5) is what I was planning on trying next.
Good luck, keep us updated!
You can do this if you’re using Microsoft’s virtualization program, but I don’t know that you can pack Windows into a .vdi file, but there is a way to run Windows as-is off of your physical partition:
There’s an old version of Dot Net Rocks that was all about running Virtual Machines. A lot of it is not relevant to your specific situation, but it’s a good listen, and they talk about this type of migration (ie, the tools you’ll need to run on the physical machine to migrate it, etc).
I don’t think I’ve actually seen exactly that from any of the virtual machine vendors. The reason, I think, is simple (assuming that the majority of virtual machines run are going to be Windows): you can’t simply take an existing Windows installation and move it whole-hog onto a new machine (even onto a new virtual machine). Swapping out important components (motherboard, for example) will make the installation extremely unstable; Windows, when installed, is installed to work with the components that were there when it was installed, and moving it without a significant amount of driver prep among other things (which the MS migration tools are designed to address) will leave you with a mess.
This is amplified when you move a physical machine to a virtual machine (where you are, in effect, swapping out every hardware component).
Another option is to access the raw partition using vbox.
How to Access Physical Disk in VirtualBox- Windows 10
VirtualBox has a shared folder feature that allows accessing the host computer physical hard drive partition and folders from the virtual machine. Once the VirtualBox guest additions installed properly, by doing additional steps, this can be enabled easily. But in some cases, if you want to attach a physical drive partition to a virtual machine from its settings, then you need to follow the steps to accomplish.
This step by steps method explains how you can access the physical disk in VirtualBox. Unfortunately, this cannot be done easily as how we do VMware workstation. Few commands and hard drive mapping involved in this process to access the physical disk partition in VirtualBox. This access method is called ‘Raw Disk’ access. Read more about what is Raw Disk
Summary
Before starting the procedure, let me explain how it’s going to work.
As I said earlier, it’s not easy as giving access to physical disk in VMware workstation. We have to create a configuration VMDK file for the host’s entire physical disk or partition. Then add this VMDK in Virtual Media Manager. Then allocate the disk to any Virtual Machine in VirtualBox.
Ok, now let’s start the steps.
How to Access Entire Physical Disk from VirtualBox
1) Open Command prompt in Host computer then go to the installation folder of the VirtualBox program, in most cases, it will be under this location.
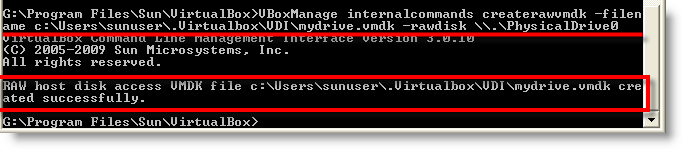
2) Type: (This command is to access entire physical disk as Raw Disk)
VBoxManage internalcommands createrawvmdk -filename c: \Users \sunuser \.Virtualbox \VDI \mydrive.vmdk -rawdisk \ \ . \PhysicalDrive0
c: \Users \sunuser \.Virtualbox \VDI \mydrive.vmdk : Location and ‘ mydrive.vmdk’ is the configuration VMDK file of your entire physical drive.
Do not think that the new VMDK file will take huge size as your physical disk size. It’s just a 1KB size file. After you added this file to Virtual Media Manager, then you will get the full size of the physical disk.
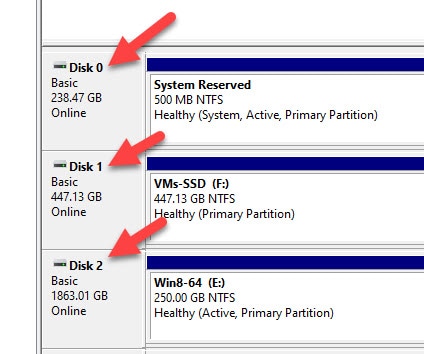
\ \. \PhysicalDrive0 : is the physical drive of the host computer. 0,1, 2 numbers can be seen from Disk management in Windows OS under Computer Management. You insert the number as required physical disk number normally starts with 0.
3) You can confirm that the command worked correctly by visiting the location of the VMDK file created.
4) Now, Open VirtualBox, and go to Virtual Media Manager.
5) Add the newly created ‘mydrive.vmdk’ under the hard disk. Click here to read more about how to add VMDK file in VirtualBox
6) Add the newly added hard disk to the virtual machines in VirtualBox and start accessing them from the Virtual Machine Guest Operating system. Since this access has the write permission, ensure that any overwriting access from guest VM will not create any issues on the host OS.
How to Access Specific Partitions of Physical Disk from VirtualBox
To access specific partitions of host physical disk from VirtualBox, run the same command with additional switches,
VBoxManage internalcommands createrawvmdk -filename c: \Users \sunuser \.Virtualbox \VDI \ mydrive.vmdk -rawdisk \ \. \ PhysicalDrive0 -partitions 1,3
-partitions 1,3 : The partition numbers of PhysicalDrive 0. It will allow you to access the first and third partitions of the physical drive in this example.
This command also will create a VMDK file and you can access the drives as explained in the first method.
Remeber, by using these methods you can attach a physical disk partition and boot the OS if it has a bootable OS.
Dinesh
Dinesh is the founder of Sysprobs and written more than 400 articles. Enthusiast in Microsoft and cloud technologies with more than 15 years of IT experience.
You Can Read Next
VMware Vs VirtualBox – Detailed Comparison
Best Free Virtual Machine Software in 2021 – Start Your New Career
VDI to VHD/VHDX – Convert VirtualBox VMs to Hyper-V
Pre-installed Windows 98 SE VirtualBox Image – Download and Use
Convert VirtualBox VDI to Parallels Disk Format in macOS
Install VirtualBox Extension Pack on Windows 10/8.1 Host
16 thoughts on “How to Access Physical Disk in VirtualBox- Windows 10”
help with this one. im using windows 7, running Ubuntu 9.10 inside virtualbox 3.1. when i type the command it shows invalid parameter -users.
please help. desperately want to use my Ubuntu OS and access all my files from the host.
Hi, it’s not – users (parameter). It’s the location of vmdk configuration file. I used Vista as my host, so I created in that location. Windows 7 also must be the same. Try and let me know.
This works great, but the only problem is Windows 7 rearranges the order of the physical disks in disk manager every time I reboot. Annoying.
Hi – Are you positive that you use Vista (or 7) as a host and XP as a guest, XP being on a physical partition ?
I can’t have this to run with my Win7 and XP (BSOD with UNMOUNTABLE_BOOT_VOLUME). The VB logs says that the physical XP partition cannot be written
The vdmk was created w/o problem, my VB runs “elevated”, the XP partition is not “mounted” etc … I’ve even tried installing a Kubuntu host instead of the Win7, and using the _exact_ same XP partition in the Kubuntu host, and this run fine. I’m used to use XP and Kubuntu on physical partition w/o problems for years …
Hi Philippe,
I have Windows 7 and XP as Host and having same Operating systems as guest too. The above steps I tested on Windows vista host but not Windows XP physical partition. To be honest, I’m scared to mount system physical partition inside VirtualBox. But I did later. I mounted Windows XP physical partition in Sun VirtualBox and started same physical computer in VirtualBox. Guess what? Once I restart Host Windows XP later, it says some boot sector or loader corrupted. I struggled to get my host OS back.
So from that point, I don’t boot or mount physical Host OS in VB. It’s little risky. (I’m not sure; I understand your point correctly).
Anyway, Thanks for your comment.
One should install some kernel-mode hack to workaround this.