- How do I get started with VNC Connect on Windows and Mac?
- Setting up your account
- On the computer you want to control
- Inviting people to your team
- Authentication
- Important note on Permissions
- Enterprise Deployments
- On the device you want to control from
- Vnc mac from windows
- Allowing VNC connections:
- Tweaks for Windows:
- Подключение к удаленному компьютеру по VNC
- Fast VNC from Windows to Mac?
- 4 Answers 4
- 13 Free VNC ‘Remote Desktop Connection’ For Windows, Mac And Linux
- ↓ 01 – chrome remote desktop | Free | Windows | Android | iOS
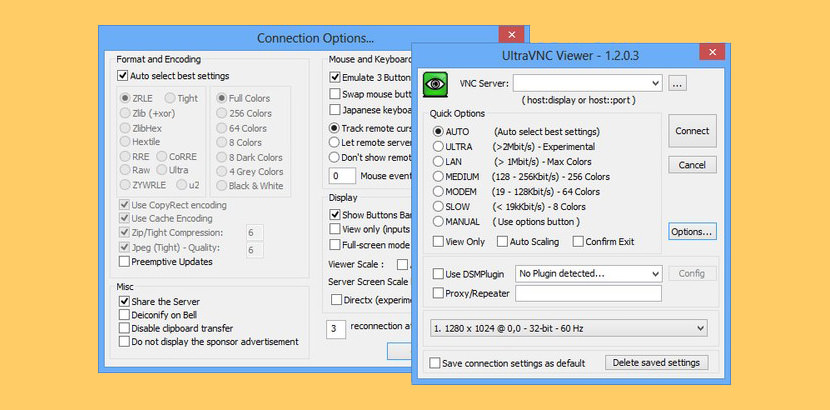
- ↓ 02 – UltraVNC | Free | Windows
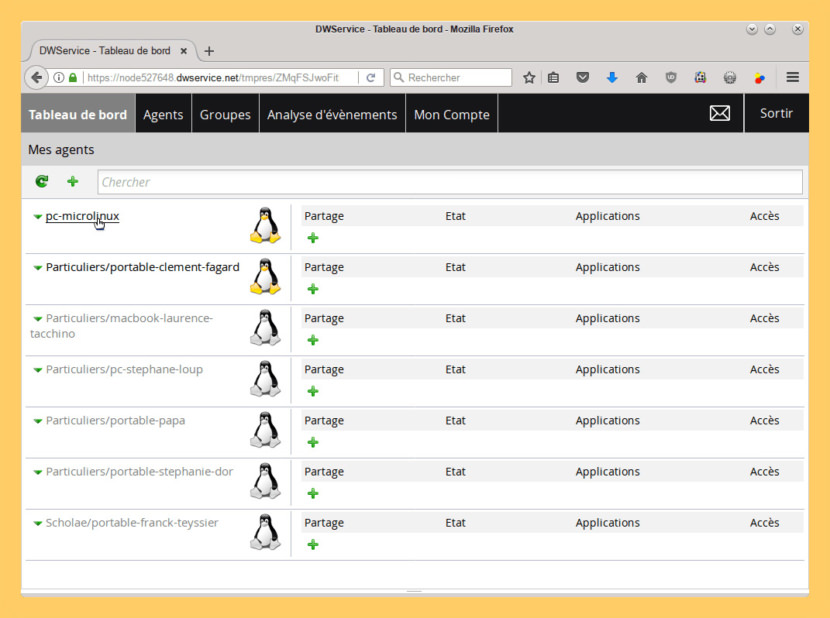
- ↓ 03 – DWService | Free | Windows | macOS | Linux
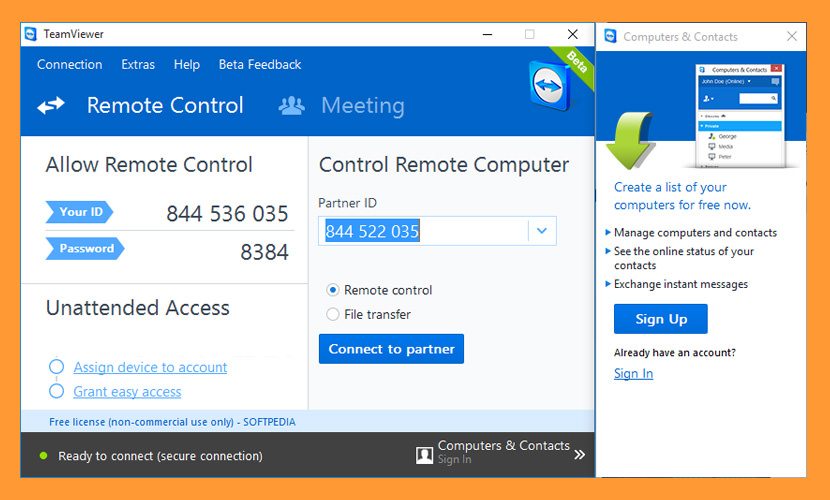
- ↓ 04 – TeamViewer | Free Personal | Windows | macOS | Linux
- ↓ 05 – Chrome Remote Desktop | Free | All Chrome Browser | Chromebook
- ↓ 06 – TightVNC | Free | Windows | Linux
- ↓ 07 – Remmina | Free | Linux
- ↓ 08 – AnyDesk | Free Personal | Windows | Linux
- ↓ 09 – TigerVNC | Free | Windows | macOS | Linux
- ↓ 10 – NoMachine | Free Personal | Windows | macOS | Linux
- ↓ 11 – X2Go | Free | Windows | macOS | Linux
- ↓ 12 – eHorus | Free | Windows | macOS | Linux
- ↓ 13 – mRemoteNG | Free
How do I get started with VNC Connect on Windows and Mac?
Setting up your account
The video below shows how to get started:
To subscribe to VNC Connect, see How do I subscribe to VNC Connect?
If you are setting up Instant Support, see How do I get started using instant support?
On the computer you want to control
- Download VNC Server
- Install VNC Server. You should be prompted to license the VNC Server program when installation finishes, but if not select Licensing from the VNC Server shortcut menu:
- Apply your subscription to VNC Server by signing in using your RealVNC account credentials.
(If you have an Enterprise subscription, you can register offline using your license key, available from the Deployment page of your RealVNC account.)
Note: If you want to install VNC Server remotely over RDP, see Can I install VNC Server on a Windows computer over RDP?
Note: If you want to install VNC Server on MacOS Mojave or Catalina, further setup is required. Please see Known Issues when connecting to macOS Mojave and Catalina (10.14 and 10.15).
By signing in with your RealVNC account, your computer is joined to your team. If you have multiple teams, you will be prompted to select which team to join. You can check by signing in to your RealVNC account online and checking the Computers page.
Inviting people to your team
If you are using Cloud connections, to allow others to access your computers remotely, see How do I invite people in to my team to share remote access?
Authentication
With Professional or Enterprise subscriptions, System authentication is the default.
Important note on Permissions
You need to ensure that the users you want to be able to connect remotely have been given permission (by default, only members of the Administrators group are able to connect). For more information, see What username and password do I enter when I’m trying to connect to VNC Server? and Managing users and session permissions for VNC Server Failure to do this may result in not being able to connect to your computer remotely.
Enterprise Deployments
If you have an Enterprise subscription and want to deploy, license and configure VNC Server using Group Policy, see Deploying and licensing VNC Connect using Windows MSIs and Setting up Group Policy under Windows
On the device you want to control from
- Download VNC Viewer
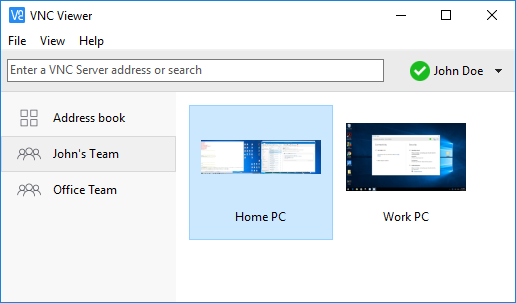
- Install or run VNC Viewer and sign in using your RealVNC account credentials. You should see the remote computer appear in your team:
If the computer you want to connect to is running Linux, please see How do I get started with VNC Connect on Linux?
If you are setting up a Home subscription, see Activating a VNC Connect Home subscription
Vnc mac from windows
A little-known fact about Mac versions 10.4 (Tiger) and over, is that they come with a built-in VNC server. This feature is included in a couple of the “Sharing” options and can be accessed with a regular VNC viewer/client.
However, when connecting from a Windows machine (particularly when running TightVNC as the viewer), I found I had to configure a few extra settings to make it work without constant freezes on my Mac, forcing me to hard reset. Here are some of the tweaks I had to make to ensure I could connect without issues. I am running 10.7.5 (Lion), so your steps may vary slightly.
Firstly, you need to allow VNC connections. The two options are either Screen Sharing or Remote Management. Screen Sharing is what the “average” VNC user may need, while the latter is helpful if you need more permissions and control over the host machine.
Allowing VNC connections:
- Step 1 – Go to your System Preferences and under the Internet and Wireless heading, click on Sharing.
Step 2 – Enable either the Screen Sharing or the Remote Management checkboxes.
Step 3 – Click on Computer Settings and enable “VNC viewers may control screen with password.”
Step 4 – Provide a password and click “OK”.
(Only for Remote Management)
Step 5 – Click on Options and enable any other permissions you may need.
You should now have a VNC server running on the standard port 5900 of your machine. You should (in theory) be able to connect to your Mac with any viewer using your machine’s IP address and the port. As I mentioned before, I had some issues connecting from Windows, and had to take a few precautions. I’m using TightVNC, so these changes may or may not be necessary on other viewers.
Tweaks for Windows:
- To prevent receiving a patterned, gray screen after the login, be sure to logout of your current user on your Mac first. The viewer will prompt for a password, but once connected, will not display the actual desktop unless no users are logged in on the host.
- In the Options menu:
- Enable “Disable clipboard transfer.” This was a major issue that would cause freezing immediately upon on connect unless enabled. Of course, you will not be able to share the clipboard across the host and client machines, but at least the host machine will continue running properly.
- Set the “Preferred Encoding” to either “Raw” or “ZRLE”. The other options appeared to work, but seemed to cause some minor freeze-ups on the Mac.
- Oftentimes after closing the viewer, the Mac would freeze yet again, requiring a reset. One workaround is to click the “Pause” button (double red bar) in the active Viewer before closing the connection. Have not yet gotten a chance to look into why this works, but it seems to solve the problem for the time being.
Following these steps should help ensure you can connect to your Mac from a Windows machine. Just enter :5900 as the Remote Host and enter the password from before to connect.
Of course, another option is to simply user a third-party VNC server, but if you don’t feel like installing more software, hopefully this should help in preventing a few headaches.
Подключение к удаленному компьютеру по VNC
Работа с VNC-клиентом. Материал ориентирован на неопытного пользователя.
1. Установка VNC-клиента
2. Подключение VNC-клиента к удаленному компьютеру
3. Отключение VNC-клиента от удаленного компьютера
4. Тюнинг VNC-клиента
5. Частые проблемы
Для работы с удаленным компьютером по VNC на компьютере пользователя нужно запустить программу-клиент (VNC viewer, VNC client). Эта программа передает на удаленный компьютер данные о нажатиях на клавиши и о движениях мыши, сделанных пользователем, и показывает информацию, предназначенную к выводу на экран.
1. Установка VNC-клиента
Для ОС Windows можно бесплатно скачать и инсталлировать VNC-клиент UltraVNC и TightVNC.
Mac OS X начиная с версии 10.5 имеет поддержку VNC-клиента в RemoteDesktop. Для предыдущих версий можно использовать VNC-клиенты JollysFastVNC и Chicken.
Для Linux ветви Debian (Ubuntu) VNC-клиент устанавливается из репозитория командой:
apt-get install vncviewer
Для ветви RedHat (CentOS, Fedora) — командой:
yum install vnc
Для FreeBSD VNC-клиент (TightVNC) устанавливается из пакетов командой:
pkg_add -r tightvnc
2. Подключение VNC-клиента к удаленному компьютеру
Для подключения VNC-клиента к удаленному компьютеру требуется указать его IP-адрес или DNS-имя, и номер дисплея (по умолчанию, :0) или номер TCP-порта (по умолчанию, 5900). Если VNC-сервер требует авторизации, то при подключении к нему VNC-клиент запросит пароль. Обратите внимание, что пароль доступа к VNC-серверу не связан с каким-либо аккаунтом (учетной записью пользователя) на удаленном компьютере, а служит только для ограничения доступа к дисплею VNC-сервера.
После установки соединения и открытия экрана, в зависимости от настроек VNC-сервера может потребоваться авторизация пользователя на виртуальном сервере или может быть открыта уже запущенная рабочая сессия какого-либо пользователя.
Так как на компьютере одновременно могут работать несколько VNC-серверов, для их разделения используют параметр номер дисплея. Например, один VNC-сервер может быть запущен на дисплее :0, другой — на дисплее :1. Каждому номеру дисплея соответствует номер TCP-порта, на котором VNC-сервер принимает соединения. Номер порта для дисплея получается прибавлением номера дисплея к базовому номеру порта — 5900. Дисплею :0 соответствует TCP-порт 5900, дисплею :1 — порт 5901.
3. Отключение VNC-клиента от удаленного компьютера
При закрытии окна VNC-клиента или после выхода из окружения средствами рабочего стола, в зависимости от настроек VNC-сервера, рабочая сессия пользователя может закрыться с остановкой всех используемых программ, или продолжать работу и быть доступной снова при повторном подключении к VNC-серверу.
4. Тюнинг VNC-клиента
Большое количество передаваемой на экран информации влечет за собой повышенные требования к скорости канала — к его пропускной способности и времени передачи пакетов. Нахватка пропускной способности приводит к некомфортным задержкам при больших изменениях показывамой на экране информации — открытии новых окон, скроллинге и т.д. Особенно большие задержки будут возникать при показывании фотографий и других изображений или элементов интерфейса, имеющих большое количество цветов и сложные формы.
Главный параметр, который влияет на объем передаваемых данных — алгоритм кодирования передаваемой графики. Для уменьшения объема и, соответственно, ускорения работы, рекомендуется использовать алгоритмы Tight, ZLib, ZRLE — по сравнению с несжатыми данными (Raw), они обеспечивают сжатие в десятки раз, заметно нагружая процессор. Эти алгоритмы кодирования обеспечивают комфортную работу даже на каналах со скоростью 256-512 Кбит/сек.
Для сокращения объема передаваемой по сети информации также можно устанавливать высокий уровень сжатия (Compression Level, Compression Value), низкий уровень качества JPEG (JPEG Quality) и включать режим уменьшения количества цветов (-bgr233, Restricted colors). Самый большой эффект из них при заметном снижении качества изображения дает режим уменьшения количества цветов — объем передаваемой информации уменьшается в 1.5-3 раза, соответственно, в 1.5-3 раза ускоряется отображение на экране.
JPEG применяется алгоритмом кодирования Tight для сжатия участков экрана, содержащих фотографии и другие сложные изображения с большим числом цветов. Использование Tight+JPEG сокращает в 2-5 раз объем передаваемых при этом данных. Другие алгоритмы кодирования JPEG не поддерживают.
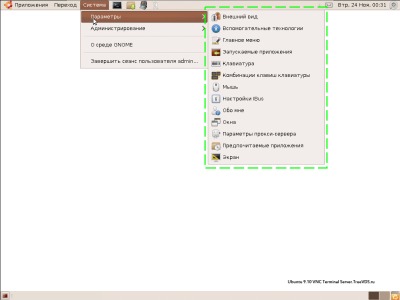
1. Выпадающего меню «Система -> Параметры»
Объем передаваемых данных и скорость отображения на канале 1 Мбит/сек при открытии выпадающего меню «Система -> Параметры» (на рисунке меню выделено зеленым пунктиром):
| Полноцветный режим | 256 цветов (BGR233) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Объем | Время | Объем | Время | |
| ZLib | 11 Кб | 0.09 сек | 7 Кб | 0.06 сек |
| HexTile | 208 Кб | 1.6 сек | 118 Кб | 0.95 сек |
| Raw | 248 Кб | 2 сек | 128 Кб | 1 сек |
5. Частые проблемы
Не удается подключиться к VNC-серверу
Медленная работа через достаточно быстрый канал
Если VNC-клиент не может согласовать с VNC-сервером использование алгоритм кодирования графики с компрессией данных, выбирается алгоритм по умолчанию — Raw, который передает данные без сжатия. Также кодирование без сжатия или с низким уровнем сжатия может автоматически выбираться VNC-клиентом при работе через быструю локальную сеть. Данную проблему можно исправить, принудительно указав в настройках VNC-клиента алгоритм кодирования с высоким уровнем сжатия — ZLib, ZRLE, Tight.
Однако, для некоторых сочетаний клиента и сервера такое решение может быть бесполезным из-за ошибок в согласовании алгоритма кодирования. Например, клиент TightVNC с сервером RealVNC часто могут работать только с кодировкой Raw. Решением в этом случае будет смена VNC-клиента или VNC-сервера.
Fast VNC from Windows to Mac?
I regularly need to connect from a Windows box to an OSX box over VNC.
OSX has VNC built-in as part of its «Screen Sharing» tool, but for some reason, it’s much faster to connect from OSX to OSX or from OSX to Windows than it is to connect from Windows to OSX. (I use UltraVNC on Windows.) Windows to OSX connectivity is almost unusably slow, even when the two boxes are sitting right next to each other, plugged into the same router.
How can I improve performance in this case? Should I explore alternate Windows clients? Alternate OSX VNC servers? Should I use some other screen-sharing tool instead of VNC? (If so, what?)
(Note that this question is more specific than other more general questions.)
4 Answers 4
OS X Leopard with its own ScreenSharing client, connecting to another OS X native screen sharing server, does some negotiation on colour depth, etc., so it’s transferring less data.
(You can see this effect exaggerated if you connect to an OS X system from Windows using the RealVNC client over a higher latency connection. It will take a long time to build up the screen output.)
I couldn’t find a way to make RealVNC request a lower colour depth so what I did, to work around this, was run a copy of VineServer on OS X with the ‘-maxdepth 8’ option (and ‘-rfbport 5901’ to run it as an alternate server), and connect to that when I connect long distance (which I always do through an SSH tunnel, before anyone states the obvious.)
13 Free VNC ‘Remote Desktop Connection’ For Windows, Mac And Linux
Undeniably, TeamViewer is the best VNC in the market. Virtual Network Connection software, also known as remote desktop software allows you to control a client’s device, be it an Android Tablet, or iPhone via another computer.
In computing, Virtual Network Computing (VNC) is a graphical desktop sharing system that uses the Remote Frame Buffer protocol (RFB) to remotely control another computer. It transmits the keyboard and mouse events from one computer to another, relaying the graphical screen updates back in the other direction, over a network. Without further ado, here are 8 free and some are open source VNC client/server.
↓ 01 – chrome remote desktop | Free | Windows | Android | iOS
Securely access your computer from your phone, tablet, or another computer. Alternatively, you can also get remote support for your computer, or give remote support to someone else. On each of your computers, set up remote access using the Chrome Remote Desktop app from Chrome Web Store. It’s fast, simple, and free.
↓ 02 – UltraVNC | Free | Windows
Ultra VNC is a powerful, easy to use and free – remote pc access softwares – that can display the screen of another computer (via internet or network) on your own screen. The program allows you to use your mouse and keyboard to control the other PC remotely. It means that you can work on a remote computer, as if you were sitting in front of it, right from your current location.
VNC, the Remote Frame Buffer protocol (RFB) allows a desktop to be viewed and controlled remotely over the Internet. A VNC server must be run on the computer sharing the desktop, a VNC client must be run on the computer that will access the shared desktop.
↓ 03 – DWService | Free | Windows | macOS | Linux
DWService offers a service that allows access to remote systems using a standard web browser. Suppose you are anywhere in the world having the need to use your home computer, you can start the web browser from any device connect to DWService website and immediately gain control of the computer. How is it possible? Very easy, register on DWService and install DWAgent on your home computer.
DWService actually allows you to do much more by giving you the ability to securely share, through Applications, everything your system has to offer. Also you can share with other people not registered on DWService without using the existing cloud systems. For example you can directly share the folder on your PC containing your holiday photos with family and friends without having to publish the photos on other servers.
↓ 04 – TeamViewer | Free Personal | Windows | macOS | Linux
TeamViewer lets you establish a connection to any PC or server within just a few seconds. You can remote control the PC of your partner as if you were sitting right in front of it. New features such as VoIP, webcam and application selection will give you an even better, easier and faster desktop sharing experience. Remote support, remote access, and online meeting software that the world relies on – 1 billion installations and 20+ million devices online at any time. Why TeamViewer?
- Save time and money – Support, assist, interact, and collaborate with people. Exchange information. Access and use technology. One tool makes it possible to work as if you were all in the same room without travel time and expenses. With TeamViewer, you have everything you need right in front of you.
- Focus on your work, not getting it to work – Solve issues remotely or bring customers and colleagues together without complex steps or onerous prep time. TeamViewer is designed to get you working in seconds on any device.
- Secure and powerful – TeamViewer enables you to do what you want without any hassle and without any worries. Private data, private conversations, and private meetings stay that way.
↓ 05 – Chrome Remote Desktop | Free | All Chrome Browser | Chromebook
Access other computers or allow another user to access your computer securely over the Internet. Chrome Remote Desktop allows users to remotely access another computer through Chrome browser or a Chromebook. Computers can be made available on an short-term basis for scenarios such as ad hoc remote support, or on a more long-term basis for remote access to your applications and files. All connections are fully secured.
Chrome Remote Desktop is fully cross-platform. Provide remote assistance to Windows, Mac and Linux users, or access your Windows (XP and above) and Mac (OS X 10.6 and above) desktops at any time, all from the Chrome browser on virtually any device, including Chromebooks.
↓ 06 – TightVNC | Free | Windows | Linux
TightVNC is a free remote control software package. With TightVNC, you can see the desktop of a remote machine and control it with your local mouse and keyboard, just like you would do it sitting in the front of that computer.
- Free for both personal and commercial usage, with full source code available,
- Useful in administration, tech support, education, and for many other purposes,
- Cross-platform, available for Windows and Unix, with Java client included,
- Compatible with standard VNC software, conforming to RFB protocol specifications.
↓ 07 – Remmina | Free | Linux
Remmina is a remote desktop client written in GTK+, aiming to be useful for system administrators and travellers, who need to work with lots of remote computers in front of either large monitors or tiny netbooks. Remmina supports multiple network protocols in an integrated and consistent user interface.
- Protocols supported: RDP, VNC, NX, XDMCP, SSH, Telepathy
- Maintain a list of remote desktop files, organized by groups
- Make quick connections by directly putting in the server name
- Remote desktops with higher resolutions are scrollable/scalable in both window and fullscreen mode
- Viewport fullscreen mode: remote desktop automatically scrolls when the mouse moves over the screen edge.
- Floating toolbar in fullscreen mode, allows you to switch between modes, toggle keyboard grabbing, minimize, etc.
- Tabbed interface, optionally managed by groups
↓ 08 – AnyDesk | Free Personal | Windows | Linux
AnyDesk is the world’s most comfortable remote desktop application. Access all your programs, documents and files from anywhere, without having to entrust your data to a cloud service. An excellent alternative and great competitor in the Remote Desktop market. They have a pretty solid architecture that easily competes with strong competitors.
↓ 09 – TigerVNC | Free | Windows | macOS | Linux
TigerVNC is a high-performance, platform-neutral implementation of VNC (Virtual Network Computing), a client/server application that allows users to launch and interact with graphical applications on remote machines. TigerVNC provides the levels of performance necessary to run 3D and video applications, and it attempts to maintain a common look and feel and re-use components, where possible, across the various platforms that it supports. TigerVNC also provides extensions for advanced authentication methods and TLS encryption.
↓ 10 – NoMachine | Free Personal | Windows | macOS | Linux
NoMachine NX is an enterprise-class solution for secure remote access, desktop virtualization, and hosted desktop deployment built around the self-designed and self-developed NX suite of components. Thanks to its outstanding compression, session resilience and resource management and its integration with the powerful audio, printing and resource sharing capabilities of the Unix world, NX makes it possible to run any graphical application on any operating system across any network connection. NX is SSH encrypted, has random cookie generation, and is compressed for speed. Free version is available to everyone, and enterprise and server editions are available at cost.
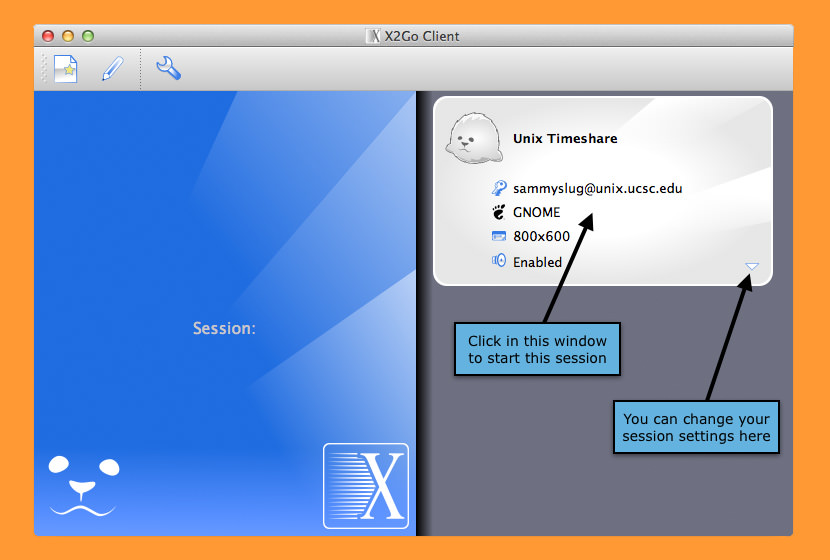
↓ 11 – X2Go | Free | Windows | macOS | Linux
X2Go is an open source remote desktop software for Linux that uses the NX technology protocol. X2Go can be used to access PC desktops, but its main use case is providing secure standalone remote sessions via ssh. The server package must be installed on a Linux host; client packages can be run on Linux, OS X, or Windows. Basic features of X2Go
- Graphical Remote Desktop that works well over both low bandwidth and high bandwidth connections
- The ability to disconnect and reconnect to a session, even from another client
- Support for sound
- Support for as many simultaneous users as the computer’s resources will support (NX3 free edition limited you to 2.)
- Traffic is securely tunneled over SSH
- File Sharing from client to server
- Printer Sharing from client to server
- Easily select from multiple desktop environments (e.g., MATE, GNOME, KDE)
- Remote support possible via Desktop Sharing
- The ability to access single applications by specifying the name of the desired executable in the client configuration or selecting one of the pre-defined common applications
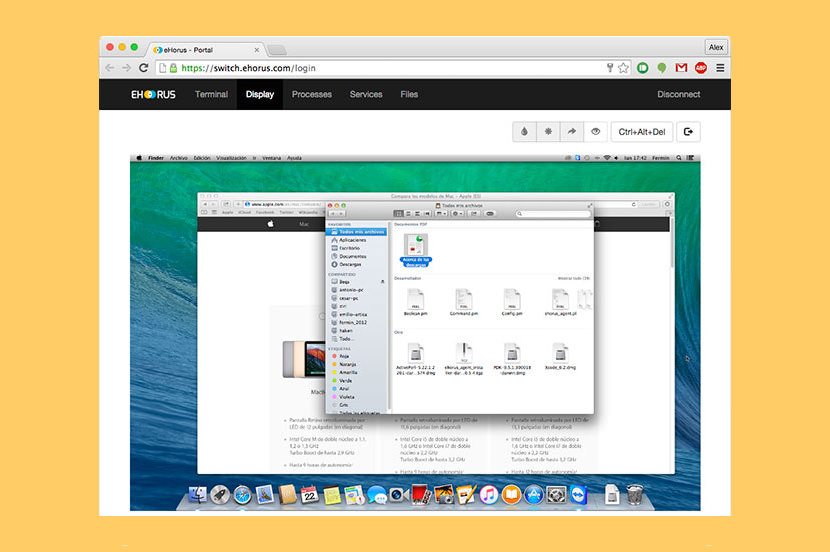
↓ 12 – eHorus | Free | Windows | macOS | Linux
eHorus is a Cloud-based remote management system (SaaS). It installs an agent on your device which is run as a service. These agents connect to our servers so that you can connect to them from any Internet-enabled device. Imagine being able to connect to your home PC and access your desktop and files from the comfort of your office. Safely and without having to install anything on the computer from which you connect with the others.
- Bidirectional file downloading – Upload or download files to your remote devices. Do it in the background with the browser, while you continue to work with your device.
- Service and process control – Start processes up, for services. Comfortable and fast. No need to even access your desktop. You’ll be able to see your CPU and memory usage for each process, as well as view the general system status.
- Remote Shell – Solve problems even quicker from the remote Shell. Whether it’s Windows, Mac OS or Linux, you’ll have direct access to a Shell from the browser.
- Remote desktop – Managed comfortably from your browser. No need to install anything additionally. Even when accessing from a Tablet or cell phone.
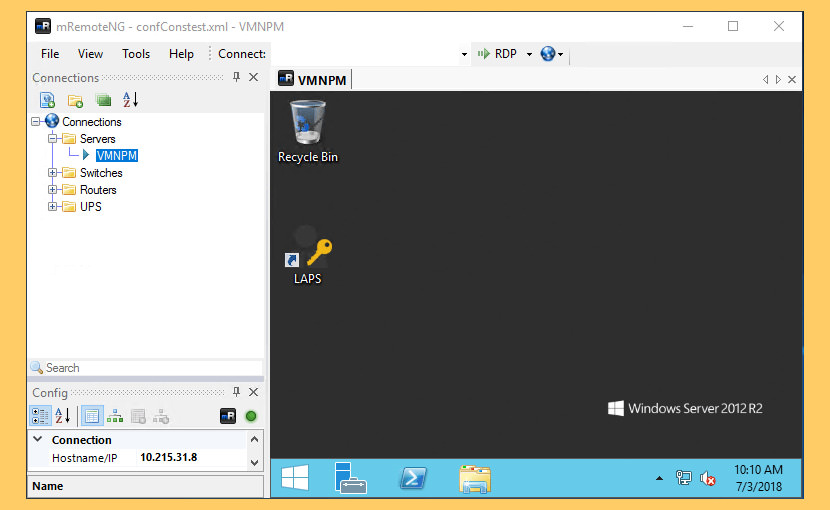
↓ 13 – mRemoteNG | Free
mRemoteNG is a fork of mRemote: an open source, tabbed, multi-protocol, remote connections manager. mRemoteNG adds bug fixes and new features to mRemote. It allows you to view all of your remote connections in a simple yet powerful tabbed interface. mRemoteNG supports the following protocols:
- RDP (Remote Desktop/Terminal Server)
- VNC (Virtual Network Computing)
- ICA (Citrix Independent Computing Architecture)
- SSH (Secure Shell)
- Telnet (TELecommunication NETwork)
- HTTP/HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol)
- rlogin
- Raw Socket Connections