- Arping Command Tutorial With Examples For Linux
- Install For Debian, Ubuntu, Mint, Kali
- Install For CentOS, Fedora, Red Hat
- Arping Help
- Ping Arp
- Set Count
- Set Source Address
- ARP сканирование локальной сети Linux
- Как выполнить ARP сканирование локальной сети?
- Утилита ARP Scan
- Установка ARP Scan
- Сканирование сети
- ARP спуфинг и ARP прокси
- Выводы
- Linux arping Command Tutorial
- Install arping on Ubuntu, Debian, Kali, Mint
- Install arping on CentOS, Fedora, RHEL
- Display arping Command Version
- Display arping Help Information
- List Current ARP Table
- Discover/Scan Hosts with ARP Protocol
- Set Ping Packet Count
- Specify Target with MAC Address
- Specify Network Interface
- Specify Source MAC Address
- arp command in Linux with examples
Arping Command Tutorial With Examples For Linux
There are a lot of tools for network troubleshooting and debugging. Arping is one of them which only pings same network hosts. So what makes arping special is it uses network layer arp packets. This works on mac protocol. It is useful especially to find hosts those do not respond layer 3 and layer 4 ping requests.
Install For Debian, Ubuntu, Mint, Kali
We can install arping command for Ubuntu, Debian, Mint, Kali with the arping package name like below.

Install For CentOS, Fedora, Red Hat
We can install arping command for CentOS, Fedora, Red Hat with the arping package name like below.
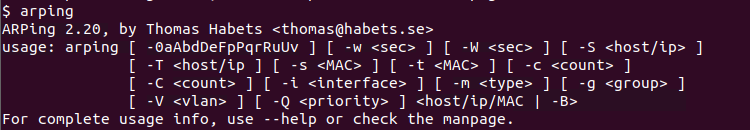
Arping Help
We can list help information and popular options with the -h option like below.

For complete usage information please use —help option.

Ping Arp
We will use arping command without providing any option. We will just provide the destination host IP address. In this example, we will ping the IP address 192.168.122.1 with the ARP packages.

From the responses to the ARP ping packets we can find the following information.
- `index` is the index number of the current ping series which starts from 0 .
- `time` is the time duration between sending ARP packet and getting a response which is generally around 10 milliseconds.
Set Count
We can set ping request count with -c option. In the example, we will set the ping packet count to 2 .
Set Source Address
Source mac address can be set with -s option. In the example, we will set aa:bb:cc:dd:ee:ff as source mac address

Источник
ARP сканирование локальной сети Linux
Иногда возникает необходимость узнать какие устройства подключены к локальной сети Linux. Это может понадобиться если вы хотите подключиться к одному из компьютеров и не помните его адрес или хотите убедиться в безопасности вашей сети и найти все скрытые устройства.
Самый надежный способ обнаружить все подключенные к сети Linux устройства, в том числе и скрытые — это ARP сканирование локальной сети. В этой статье мы рассмотрим как его выполнить и какие утилиты для этого нужны.
Как выполнить ARP сканирование локальной сети?
Как вы знаете, у всех компьютеров в сети есть IP адреса. Никогда не задавались вопросом, как сеть определяет, какому компьютеру принадлежит тот или иной адрес? Ведь сети бывают разные, проводные, беспроводные, ppp и т д. И в каждой из этих сетей аппаратный адрес компьютера имеет свой формат, зависящий от конструктивных особенностей сети, а IP адреса одни и те же.
Все очень просто. Для преобразования физических адресов, в ip адреса используется протокол ARP (Address Resolution Protocol), так и расшифровывается — протокол разрешения адресов. Когда компьютеру нужно обратиться к другому компьютеру в локальной сети, он отправляет специальный запрос в котором буквально спрашивает «У кого IP адрес 192.168.1.4», компьютер с таким ip адресом отправляет ответ «У меня, я 11:22:33:44:55», в ответе он передает свой физический адрес в этой сети. Дальше этот адрес заносится в специальную таблицу. но это уже тонкости реализации и они выходят за рамки нашей статьи. Сегодня мы поговорим как самому выполнить ARP сканирование локальной сети linux и найти все подключенные устройства.
Формат сообщений ARP — простой. Сообщение содержит либо запрос с IP адресом, либо ответ. Размер сообщения зависит от используемого сетевого протокола IPv4 или IPv6, типа оборудования сети и т д. Типы и размеры адресов определяются в заголовке сообщения. Заголовок завершается кодом сообщения. Код 1 для запроса и 2 для ответа.
Тело сообщения состоит из четырех адресов, аппаратные и сетевые адреса отправителя и получателя.
Если в вашей сети есть устройства, которые не отвечают на любые запросы, такие как Ping, HTTP, HTTPS и т д, то их можно найти послав ARP запрос. Это могут быть различные фаерволы и маршрутизаторы, в том числе маршрутизаторы компании Cisco, такое поведение заложено их протоколом. В таком случае ARP сканирование сети Linux будет единственным способом найти такое устройство.
Утилита ARP Scan
ARP Scan или еще называемый MAC Scanner — это очень быстрый инструмент для сканирования локальной сети Linux с помощью ARP. Утилита показывает все IPv4 адреса устройств в вашей сети. Поскольку ARP не использует маршрутизацию, то такой вид сканирования работает только в локальной сети.
ARP Scan находит все активные устройства, даже если у них включен брандмауэр. Компьютеры не могут скрыться от ARP также как они скрываются от ping. Но ARP сканирование не подходит для поиска компьютеров за пределами локальной сети, в таких ситуациях используйте ping сканирование.
Установка ARP Scan
Этот arp сканер сети доступен для следующих операционных систем:
- Debian, поставляется по умолчанию;
- Ubuntu, можно установить с репозитория Universe;
- Fedora, официальные репозитории начиная с версии 6;
- RedHat — доступна начиная с версии 5;
- Gentoo, официальные репозитории;
- ArchLinux — официальные репозитории Pacman.
Для установки в Ubuntu выполните:
sudo apt install arp-scan
Сканирование сети
ARP Scan позволяет находить активные компьютеры как в проводных сетях ethernet, так и в беспроводных Wifi сетях. Также есть возможность работать с Token Ring и FDDI. Не поддерживаются последовательные соединения PPP и SLIP, поскольку в них не используется ARP. Программу нужно запускать с правами суперпользователя.
Но сначала надо узнать сетевой интерфейс, который используется для подключения к сети. Для этого можно воспользоваться программой ip:
В данном случае, это enp24s0. Самый простой способ выполнить ARP сканирование и обнаружить все подключенные к локальной сети компьютеры — запустить программу со следующими параметрами:
sudo arp-scan —interface=enp24s0 —localnet
Здесь параметр —interface, задает интерфейс для сканирования, а —localnet, говорит, что нужно использовать все возможные IP адреса для текущей сети.
Первый параметр можно опустить, тогда программа будет искать все узлы для интерфейса с меньшим номером в системе. В нашем примере имя интерфейса — enp24s0.
Вместо параметра —localnet, можно указать маску сети:
sudo arp-scan —interface=enp24s0 10.0.1.0/24
ARP сканирование можно использовать, даже если у вашего интерфейса нет IP адреса. Тогда в качестве исходящего адреса будет использован 0.0.0.0. Правда, на такие запросы могут ответить не все системы. Тогда ARP сканер сети не так эффективен.
ARP спуфинг и ARP прокси
Поскольку в ARP нет поддержки аутентификации, ARP ответ на запрос может отправить любая машина, даже не та которой он был адресован. Иногда такое поведение используется в архитектуре сети — ARP прокси или маршрутизатор предает свой IP адрес вместо адреса запрашиваемой машины. Но также может использоваться для перехвата данных, отправляемых компьютером. Хакер может использовать ARP чтобы выполнить атаку «Человек посередине» или «Отказ в обслуживании» на других пользователей сети. Для защиты от таких атак существует специальное программное обеспечение.
Выводы
ARP Scan это простой, но очень мощный инструмент, с помощью которого можно выполнять сканирование ip адресов в локальной сети linux. Те, кто знаком с Cisco маршрутизаторами и коммутаторами, знают что найти такие устройства можно только с помощью ARP. Это полезный инструмент, возможно, когда-то вам он пригодится.
Источник
Linux arping Command Tutorial
The arping command is a command-line tool used in the Linux operating system to discover and detect hosts on the network. The arping uses the ARP protocol in order to ping hosts with the Layer 2 ARP requests. The ARP protocol is used to resolve IP addresses to the MAC addresses in order to communicate inside a LAN. The arping will try to resolve all network addresses into the MAC addresses and the hosts will provide the ARP reply for the ARP request with their MAC addresses. The arping name consists of arp+ing where the arp refers to the ARP protocol and ing or ping refers to the ping command.
Install arping on Ubuntu, Debian, Kali, Mint
The arping command can be installed on deb based distributions like Ubuntu, Debian, Kali and Mint. The package name is the same with the command arping.
Install arping on CentOS, Fedora, RHEL
The arping command also provided by the rpm based distributions like CentOS, Fedora, RHEL etc. The following command will install the arping for CentOS, Fedora, RHEL.
Display arping Command Version
After installing the arping command we can check the installation and its version without providing any option. This will list the version of the arping command and supported options in short form.
We can see from the output that the current arping command version is 2.20 . As a basic and MAC related tool the arping command do not updated regularly.
Display arping Help Information
Detailed help information and supported options can be listed with the –help option. This will list all provided options and their descriptions like below.
List Current ARP Table
Linux stores the IP address and MAC address records in a table named ARP table. ARP table is created with the ARP request responses and these table records are stored temporarily to get recent updates and prevent errors. The current ARP table and its records can be listed with the arp command like below. We will also provide the -a option to list all records.
The output will be like below.
Discover/Scan Hosts with ARP Protocol
The arping command can ping an IP address via the ARP protocol with the MAC address. But the IP address scan is provided like below. This will ping the target IP address continuously. As the arping command uses the low-level network protocol stack like creating ARP packets etc. it requires root or administrative privileges. These root privileges can be provided with the sudo command or running the arping command in the root user session.
The output will be like below. From the output we can see that the ARP packet number is provided with the index=0. Also the RTT or round trip time for the current ping is provided with the time= information. Every arp ping provides the remote IP address MAC address.
The ping will run continuously and can be stopped with the CTRL+c keys. After the ping stopped some basic statistics about the arping will be displayed.
- 6 packets transmitted describes total transmitted ARP packets to the target.
- 6 packets received describes total received packets against transmitted packets.
- 0% unanswered describes unanswered packets.
- min is the minimum transmission time.
- avg is the average transmission time.
- max is the maximum transmission time.
Set Ping Packet Count
By default the arping command ping the remote target continuously which will run forever unless we stop it or specify a ping packet count. The packet-count can be specified with the -c option by providing the number. In the following example, we will set the ARP ping packet count as 5.
The command will stop after 5 ping and provide the following output.
Specify Target with MAC Address
The arping command can be also used with the MAC address as a target. By default the IP address is used to specify target but as standard operation the IP address is resolved into MAC address and all ping packets sent to MAC address. So the target can be a MAC address.
The output will be as below. Different from the IP address as target the source interface should be devices according to the MAC address and ARP table.
Specify Network Interface
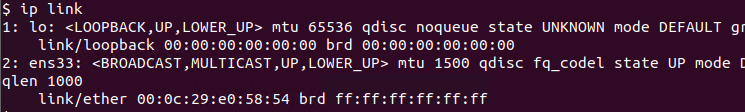
A system may have multiple network interfaces connected to different networks. These interfaces can be an Ethernet Card or Wireless NIC etc. By default, the arping command decides the source interfaces according to the target IP address, MAC address, and ARP table. After this investigation, if there is no reliable information the interface may be guessed. But we can also specify the source interface with the -I option by providing the interface name. So before specifying the source interface listing the current interfaces and their names is a great idea. We can list interfaces with the ip link command like below.
We can see that there are two interfaces named lo and ens33. the lo interface is the localhost interface and ens33 is an ethernet interface to the LAN. So we will provide the ens33 as the source interface.
Specify Source MAC Address
By default the arping command uses the default network interface MAC address. The -s option is used to specify the source MAC address.
Источник
arp command in Linux with examples
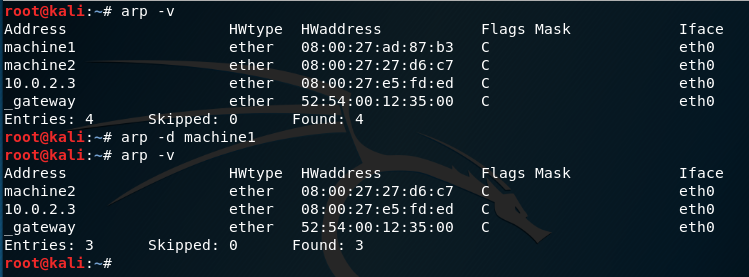
arp command manipulates the System’s ARP cache. It also allows a complete dump of the ARP cache. ARP stands for Address Resolution Protocol. The primary function of this protocol is to resolve the IP address of a system to its mac address, and hence it works between level 2(Data link layer) and level 3(Network layer).
Syntax:
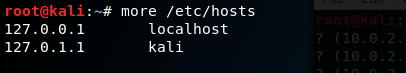
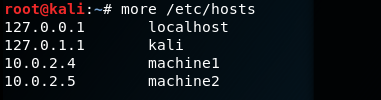
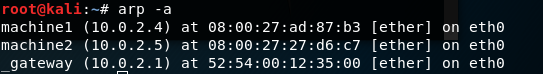
Example: Here we created two machines with name machine1 and machine2 with IP address 10.0.2.4 and 10.0.2.5
- Screenshot of hosts before adding
Addition of host
Hosts file after adding machines
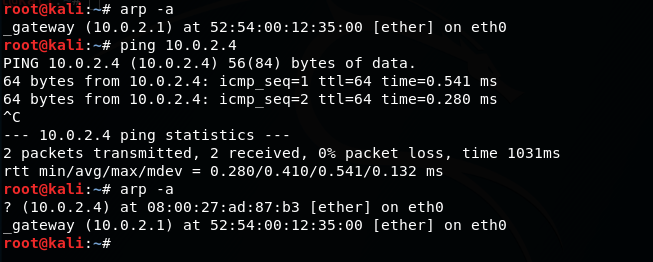
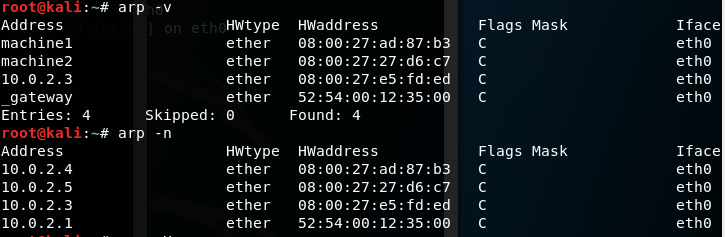
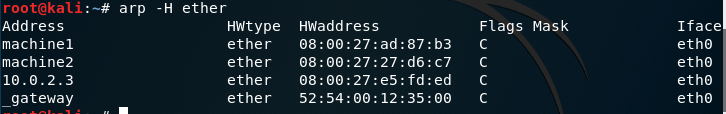
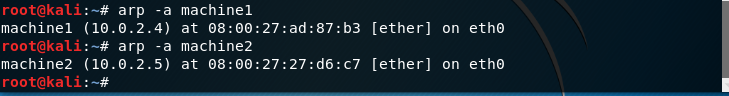
Now checking arp for all
Options:
- -v, –verbose: This option shows the verbose information.
- -n, –numeric: This option shows numerical addresses instead of symbolic host, port or usernames.
-H type, –hw-type type, -t type: This tells arp which class of entries it should check for. Default value is ether. List of possible hardware types(which support ARP) are ash(Ash), ether(Ethernet), ax25(AMPR AX.25), netrom (AMPR NET/ROM), rose (AMPR ROSE), arcnet (ARCnet), dlci (Frame Relay DLCI), fddi (Fiber Distributed Data Interface), hippi (HIPPI), irda (IrLAP), x25 (generic X.25), eui64 (Generic EUI-64).
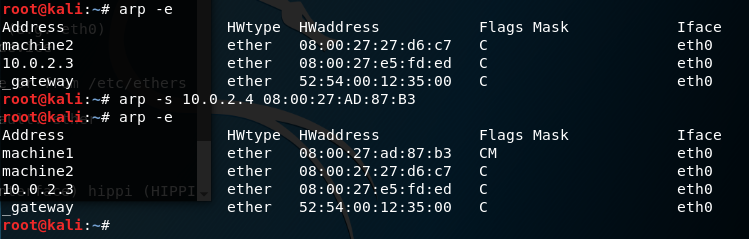
-a [hostname] –all: This option is used for showing entries of the specified host. If nothing is passed all entries will be displayed.
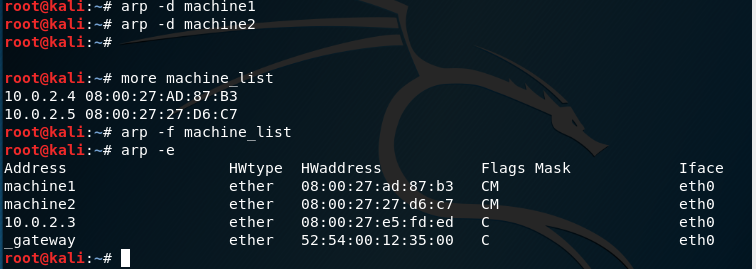
-d hostname, –delete hostname: Removes any entry for the specified host. If any host is down, there is no need of keeeping its entry in arp cache so this command is used to delete those entries explicitly by the user.
-D, –use-device: Use the given interface’s hardware address.

Note: This has to be different from the interface to which the IP datagrams will be routed.
-s hostename hw_address: Manually create an ARP address mapping entry for the host hostname with its mac address as hw_address.
-f filename: Works same as -s but instead of giving the entries manually, it takes entry from the file given as parameter.
Some useful flags are:
- -C: Complete entry.
- -M: Permanent entry.
- -P: Published entry.
Some useful file related to these data are:
- /proc/net/arp
- /etc/networks
- /etc/hosts/
- /etc/ethers
Источник