- 32-Bit vs. 64-Bit OSes: What’s the Difference?
- Identify a 64-Bit OS
- Why 32-Bit at All?
- Programs in 64-Bits
- What is Better, 32-bit or 64-bit Operating System?
- 7 Answers
- What is the difference between 32-bit and 64-bit processors or OS
- Major difference between 32-bit and 64-bit Windows 10 is the way that they manage memory Where 32 bit processor or Windows limited to 4GB of RAM and 64 bit support up to 2TB! Lets take look in detail
- What is meant by a 32-bit and 64-bit processor?
- Difference between 32-bit vs 64-bit processor?
- Check You have a 64-bit processor or 32-bit processor
- Difference Between 32-Bit and 64-Bit Windows 10
- Check you are Running 64-Bit or 32-Bit Windows?
- Can I upgrade Windows 10 to 64-bit?
- What is the difference between a 32-bit and 64-bit processor?
- 10 Answers 10
- ISA and word size
- Example bit-ness of a Pentium Pro CPU with PAE
- Note on Intel x86_64
- References
32-Bit vs. 64-Bit OSes: What’s the Difference?
Chances are good you’re running an x64-based operating system, but what does that even mean?
There are a lot of ways to count, but when it comes to computers there is only binary: 0 and 1. Each one is a considered a «bit.» That means for 1-bit computing, you get two possible values; 2-bit means four values; then at 3 bits you double that to eight (2 to the third power, aka 2 cubed).
Keep going exponentially and you eventually get 32-bit (2 to the 32nd power) worth 4,294,967,296; 64-bit (or 2 to the 64th power) is worth 18,446,744,073,709,551,616 values. That’s 18.4 quintillion and change.
That’s a lot of bits, and the numbers show just how much more powerful a chip that supports higher-bit computing can be. It’s a lot more than double.
That’s because every few years, the chips inside the computers (even smartphones) and the software running on those chips make leaps forward in supporting a new number. For example:
- The Intel 8080 chip in the 1970s supported 8-bit computing.
- In 1992, Windows 3.1 was the first 16-bit desktop version of Windows.
- AMD shipped the first 64-bit desktop chip in 2003.
- Apple made Mac OS X Snow Leopard entirely 64-bit in 2009.
- The first smartphone with a 64-bit chip (Apple A7) was the iPhone 5s in 2014.
It’s pretty obvious: 64-bit, sometimes styled as x64, is capable of doing more than 32-bit. You might know 32-bit as x86, a term that originally referred to any OS with the instruction set to work on Intel chips like the 8086 through 80486.
These days, you are most likely already running 64-bit chips with 64-bit operating systems, which in turn run 64-bit apps (for mobile) or programs (on the desktop, to settle on some nomenclature). But not always. Windows 7, 8, 8.1, and 10 all came in 32-bit or 64-bit versions, for example.
How do you even tell which one you have?
Identify a 64-Bit OS
If you are running Windows on a computer less than 10 years old, your chip is almost guaranteed to be 64-bit, but you may have installed a 32-bit version of the OS. It’s easy enough to check.
In Windows 10, go to Settings > System > About or type About in the Windows 10 search box. Under the Device specifications heading, you’ll see it at System type: «64-bit operating system, x64-based processor» means you’re covered.
Mac users don’t have to worry about this, as MacOS has been 64-bit only for a long time. In fact, as of the latest version (10.14 Catalina) 32-bit applications on a Mac aren’t even technically supported, but we have a guide for running 32-Bit apps in MacOS Catalina. If you must.
Why 32-Bit at All?
Why would you install a 32-bit OS on a PC? The big reason is because you have a 32-bit processor, which requires a 32-bit OS.
Having such a CPU today is unlikely. Intel started making 32-bit processors in the 80386 range way back in 1985; it was selling 64-bit processors by 2001. If you’ve bought a PC since the Pentium D chip came out in 2005, it’s unlikely you’d have only a 32-bit instruction set inside.
More likely, you have an old system with an operating system you installed that only came as 32-bit. Subsequent upgrades, if any, may not have jumped your install up to 64-bit. That may be fine—not all of the earliest 64-bit processors had all the features in place. You can determine if your PC is really ready for full 64-bit by using software like 64bit Checker. It works on all versions of Windows going back to Windows 95.
Installing a 32-bit OS on a 64-bit-architecture system can work, but it’s not optimal. A 32-bit OS, for example, has more limitations—the standout being it can only really utilize 4GB of RAM. Installing more RAM on a system with a 32-bit OS doesn’t have much impact on performance. However, upgrade that system with excess RAM to the 64-bit version of Windows, and you’ll notice a difference.
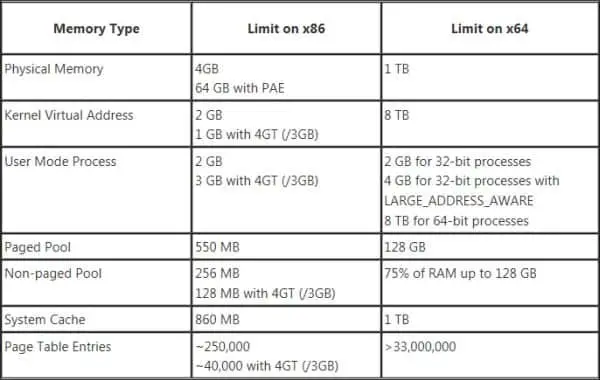
This should spell it out in the starkest way: the officially supported maximum RAM on Windows 10 is 2 terabytes (or 128GB on Windows 10 Home).
The theoretical limit of RAM at 64-bit: 16 exabytes. That’s equal to 1 million terabytes or 1 billion gigabytes. But we’re a long way from having hardware that could ever support that. (Either way, it makes buying a new laptop with 16GB of RAM seem unimpressive, doesn’t it?)
64-bit computing features many other improvements, though in ways that may not be noticeable to the naked eye. Wider data paths, larger integer sizes, eight-octet memory addresses. It’s all stuff for the computer scientists to take advantage of, to make your computing all the more powerful.
Programs in 64-Bits
You may also notice that some programs you download for your desktop operating system come in 32- and 64-bit versions. Firefox is a good example, where the options are «Windows 32-bit» and «Windows 64-bit» (as well as «Linux» or «Linux 64-bit»—the macOS version is 64-bit only).
Why do that? Because 32-bit OSes are still out there for some. Those systems need 32-bit software—they typically can’t even install a 64-bit program, and certainly won’t run them. However, a 64-bit OS can support a 32-bit program—Windows in particular has built in an emulation subsystem for that, called Windows32 on Windows64, or WoW64.
What is Better, 32-bit or 64-bit Operating System?
i was gonna re-install my operating system, so i just wanted to know if i should get 32-bit or 64-bit.
plz include info such as softwares and applications (if they will work on 64-bit)
AMD Athlon(tm) 64 X2 Dual Core Processor 5400+ 2.80 GHz
7 Answers
i use 64 exclusivley now, from xp pro 64 on including testing linux distros.
windows 7 ultimate comes w/ an ie32 as well as 64 and also has an xp mode for older programs/hardware, built in/free
To install a 64-bit version of Windows Vista, you need a processor that’s capable of running a 64-bit version of Windows. The benefits of using a 64-bit operating system are most apparent when you have a large amount of random access memory (RAM) installed on your computer (typically 4 GB of RAM or more). In such cases, because a 64-bit operating system can handle large amounts of memory more efficiently than a 32-bit operating system, a 64-bit operating system can be more responsive when running several programs at the same time and switching between them frequently.
Most programs designed for the 32-bit version of Windows will work on the 64-bit version of Windows. Notable exceptions are many antivirus programs.
Device drivers designed for 32-bit versions of Windows won’t work on computers running a 64-bit version of Windows. If you’re trying to install a printer or other device that only has 32-bit drivers available, it won’t work correctly on a 64-bit version of Windows. If you are unsure whether there is a 64-bit driver available for your device, go online to the Windows Vista Compatibility Center.
To get the most out of your motherboard, you want to use a 64-bit OS. But, be aware that some software is designed only to be used with 32-bit Operating Systems.
Most computer are now 64-bit, but some software can operate on 32 and 64, but may be two different software by the same name, you will just need to read on it.
What is the difference between 32-bit and 64-bit processors or OS
Major difference between 32-bit and 64-bit Windows 10 is the way that they manage memory Where 32 bit processor or Windows limited to 4GB of RAM and 64 bit support up to 2TB! Lets take look in detail
When you download Windows 10, MS Office or any other software You might notice there is a 32-bit and a 64-bit version available. You might have a question in mind Which one do you need? Here in this article, we figure out What is the Difference Between Windows 10 32-Bit and 64-Bit and which one is suitable for you.
Before go ahead lets first understand the difference between 32 bit and 64-bit architecture (Processor)
What is meant by a 32-bit and 64-bit processor?
In terms of Computer processors, the number of bits refers to the size of the data types that it handles and the size of its registry. And the 32-bit and 64-bit refer to the way a computer’s processor (also called a CPU), handles information. Where 64-bit processors are exponentially more powerful than their 32-bit counterparts because they can hold and process so much more information.
To understand the actual differences between 32-bit and 64-bit, you have to understand a bit about counting in binary. Unlike our decimal system, which has ten digits per place, binary only has two: 0 or 1.
Thus, a 32-bit number has 2^32 possible addresses, or 4,294,967,296. On other side, a 64-bit number’s capacity is 2^64, or 18,446,744,073,709,551,616. Comparing
4 billion bytes (about 4 gigabytes) to
18 quintillion bytes (about 18 billion gigabytes or 16 exabytes) showcases the vast difference.
Difference between 32-bit vs 64-bit processor?
In computer architecture, 64-bit is the use of processors that have datapath widths, integer size, and memory address widths of 64 bits.
- 64-bit hardware and software is often referred to as x64 or x86-64 and 32-bit hardware and software are often referred to as x86 or x86-32.
- 64-bit computer architecture provides higher performance than 32-bit architecture by handling twice as many bits of information in the same clock cycle.
- A computer with a 32-bit processor can only run a 32-bit operating system and 32-bit software. But a computer with 64-bit processor can run both 64-bit and 32-bit operating systems and software.
Note: if you have installed 32-bit operating system on a 64-bit computer, then it can run 32-bit software only.
- One more big difference between 32 bit processors and 64 bit processors is the maximum amount of memory (RAM) that is supported.
32bit operating systems can allocate only 4GB of memory (2^32 = 4294967296), whereas 64bit ones can allocate a lot more (2^64 = 18446744073709551616). So if you have under 4 GB of RAM in your computer, you don’t need a 64-bit CPU, but if you have 4 GB or more, Then you must have 64 Bit CPU and operating system.
Check You have a 64-bit processor or 32-bit processor
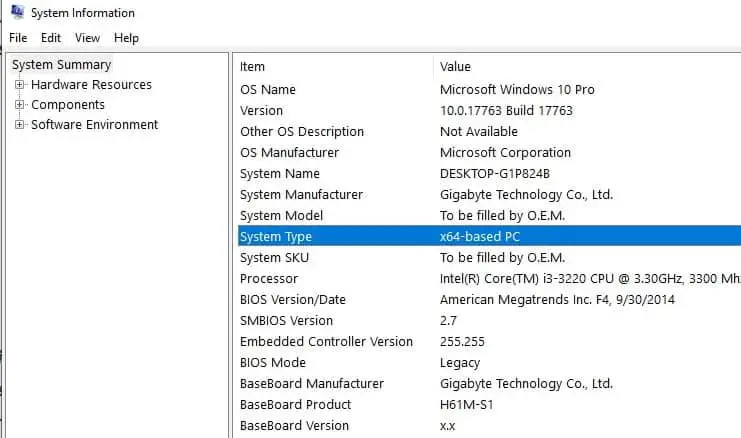
After understanding the difference between 32 bit and 64-bit processor, now you might be thinking my computer has a 64-bit processor or 32-bit processor. Yes, you can check which type of processor (not the Operating system) your computer has from the System Information utility.
- Open System Information (msinfo32)Window from start menu search
- Under System Summary, you’ll see your type of system listed next to System Type.
- If you see “x64-based PC,” you have a 64-bit processor.
- If you see “x86-based PC,” you have a 32-bit processor
Difference Between 32-Bit and 64-Bit Windows 10
Windows 10 also comes in two architectures: 32-bit and 64-bit. If you have brought the new system with 4GB or more RAM, Windows 10 64-bit is recommended that supports up to 2TB or RAM while Windows 10 32-bit can utilize up to 3.2 GB only.
Note:
- There is a workaround called Physical Address Extension (PAE) that allows 32-bit systems to address up to 64GB of RAM, but only server editions of Windows offer it.
- 64 Bit Windows 10 Home Edition support 128 GB while the Windows 10 Pro Edition supports up to 2048 GB.
The 64-bit version of Windows handles large amounts of random access memory (RAM) more effectively than a 32-bit system.
Windows 10 64-bit includes a few additional security features that aren’t available in Windows 10 32-bit.
For example, 64-bit versions of Windows require that all device drivers be signed. Driver signature enforcement means that you can only use drivers that Microsoft recognizes. This prevents malicious or buggy drivers from being used on your system and Enhanced security features. Here some other different
Check you are Running 64-Bit or 32-Bit Windows?
I hope you have better knowledge of the difference between 64 bit and 32 bit windows OS, So how to check you have Installed 64 bit Windows or 32-bit windows on your system.
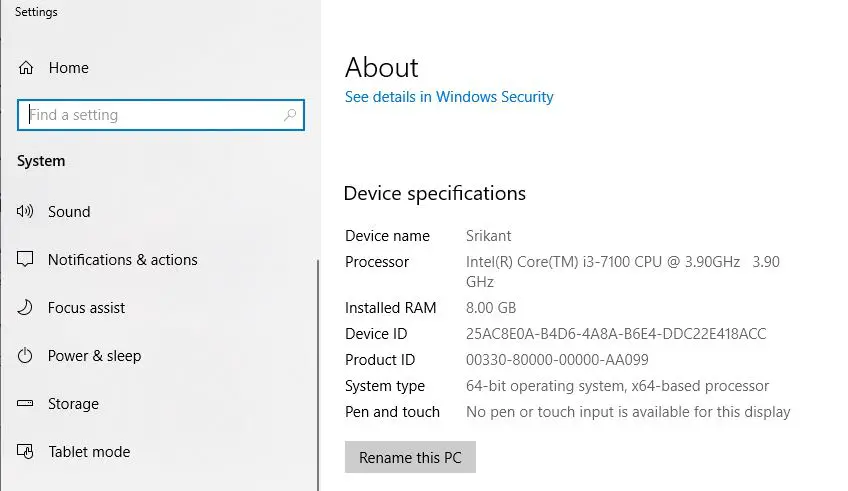
- Right-click on the Windows 10 Start menu and select the system.
- Or you can open Settings > System > About to get the System properties window.
- Under Device specifications header Look system type
- Here you notice Windows lists whether your installation is 32 or 64-bit, include your processor architecture.
Can I upgrade Windows 10 to 64-bit?
Yes, If you’re running a 32-bit version of Windows 10 on a 64-bit processor, You can Upgrade Windows 10 64 Bit using the windows media creation tool. But Users running 32-bit version of Windows on a 32-bit processor can’t upgrade. You’ll need to purchase a new machine to take advantage of 64-bit.
Did this post help to understand the difference between 64 bit and 32 bit Procesor, Windows 10 or software? Let us know on comments below, Also read
What is the difference between a 32-bit and 64-bit processor?
I have been trying to read up on 32-bit and 64-bit processors (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/32-bit_processing). My understanding is that a 32-bit processor (like x86) has registers 32-bits wide. I’m not sure what that means. So it has special «memory spaces» that can store integer values up to 2^32?
I don’t want to sound stupid, but I have no idea about processors. I’m assuming 64-bits is, in general, better than 32-bits. Although my computer now (one year old, Win 7, Intel Atom) has a 32-bit processor.
10 Answers 10
All calculations take place in the registers. When you’re adding (or subtracting, or whatever) variables together in your code, they get loaded from memory into the registers (if they’re not already there, but while you can declare an infinite number of variables, the number of registers is limited). So, having larger registers allows you to perform «larger» calculations in the same time. Not that this size-difference matters so much in practice when it comes to regular programs (since at least I rarely manipulate values larger than 2^32), but that is how it works.
Also, certain registers are used as pointers into your memory space and hence limits the maximum amount of memory that you can reference. A 32-bit processor can only reference 2^32 bytes (which is about 4 GB of data). A 64-bit processor can manage a whole lot more obviously.
There are other consequences as well, but these are the two that comes to mind.
First 32-bit and 64-bit are called architectures.
These architectures means that how much data a microprocessor will process within one instruction cycle i.e. fetch-decode-execute
In one second there might be thousands to billions of instruction cycles depending upon a processor design.
32-bit means that a microprocessor can execute 4 bytes of data in one instruction cycle while 64-bit means that a microprocessor can execute 8 bytes of data in one instruction cycle.
Since microprocessor needs to talk to other parts of computer to get and send data i.e. memory, data bus and video controller etc. so they must also support 64-bit data transfer theoretically. However, for practical reasons such as compatibility and cost, the other parts might still talk to microprocessor in 32 bits. This happened in original IBM PC where its microprocessor 8088 was capable of 16-bit execution while it talked to other parts of computer in 8 bits for the reason of cost and compatibility with existing parts.
Imagine that on a 32 bit computer you need to write ‘a’ as ‘A’ i.e. in CAPSLOCK, so the operation only requires 2 bytes while computer will read 4 bytes of data resulting in overhead. This overhead increases in 64 bit computer to 6 bytes. So, 64 bit computers not necessarily be fast all the times.
Remember 64 bit windows could be run on a microprocessor only if it supports 64-bit execution.
Processor calls data from Memory i.e. RAM by giving its address to MAR (Memory Address Register). Selector electronics then finds that address in the memory bank and retrieves the data and puts it in MDR (Memory Data Register) This data is recorded in one of the Registers in the Processor for further processing. Thats why size of Data Bus determines the size of Registers in Processor. Now, if my processor has 32 bit register, it can call data of 4 bytes size only, at a time. And if the data size exceeds 32 bits, then it would required two cycles of fetching to have the data in it. This slows down the speed of 32 bit Machine compared to 64 bit, which would complete the operation in ONE fetch cycle only. So, obviosly for the smaller data, it makes no difference if my processors are clocked at the same speed. Again, with 64 bit processor and 64 bit OS, my instructions will be of 64 bit size always. which unnecessarily uses up more memory space.
32bit processors can address a memory bank with 32 bit address with. So you can have 2^32 memory cells and therefore a limited amount of addressable memory (
4GB). Even when you add another memory bank to your machine it can not be addressed. 64bit machines therefore can address up to 2^64 memory cells.
This answer is probably 9 years too late, but I feel that the above answers don’t adequately answer the question.
The definition of 32-bit and 64-bit are not well defined or regulated by any standards body. They are merely intuitive concepts. The 32-bit or 64-bit CPU generally refers to the native word size of the CPU’s instruction set architecture (ISA). So what is an ISA and what is a word size?
ISA and word size
ISA is the machine instructions / assembly mnemonics used by the CPU. They are the lowest level of a software which directly tell what the hardware to do. Example:
The old definition of word size would be the number of bits the CPU can compute in one instruction cycle. In modern context the word size is the default size of the registers or size of the registers the basic instruction acts upon (I know I kept a lot of ambiguity in this definition, but it’s an intuitive concept across multiple architectures which don’t completely match with each other). Example:
Example bit-ness of a Pentium Pro CPU with PAE
First, various word sizes in general purpose instrucion:
- Arithmetic, logical instructions: 32 bit (Note that this violates old concept of word size since multiply and divide takes more than one cycle)
- Branch, jump instructions: 32 bit for indirect addressing, 16-bit for immediate (Again Intel isn’t a great example because of CISC ISA and there is enough complexity here)
- Move, load, store: 32 bit for indirect, 16 bit for immediate (These instructions may take several cycles, so old definition of word size does not hold)
Second, bus and memory access sizes in hardware architecture:
- Logical address size before virtual address translation: 32 bit
- Virtual address size: 64-bit
- Physical address size post translation: 36 bit (system bus address bus)
- System bus data bus size: 256 bit
So from all the above sizes, most people intuitively called this a 32-bit CPU (despite no clear consensus on ALU word size and address bit size).
Interesting point to note here is that in olden days (70s and 80s) there were CPU architectures whose ALU word size was very different from it’s memory access size. Also note that we haven’t even dealt with the quirks in non-general purpose instructions.
Note on Intel x86_64
Contrary to popular belief, x86_64 is not a 64-bit architecture in the truest sense of the word. It is a 32 bit architecture which supports extension instructions which can do 64 bit operations. It also supports a 64-bit logical address size. Intel themselves call this ISA IA32e (IA32 extended, with IA32 being their 32-bit ISA).
References
The main difference between 32-bit processors and 64-bit processors is the speed they operate. 64-bit processors can come in dual core, quad core, and six core versions for home computing (with eight core versions coming soon). Multiple cores allow for increase processing power and faster computer operation. Software programs that require many calculations to function operate faster on the multi-core 64-bit processors, for the most part. It is important to note that 64-bit computers can still use 32-bit based software programs, even when the Windows operating system is a 64-bit version.
Another big difference between 32-bit processors and 64-bit processors is the maximum amount of memory (RAM) that is supported. 32-bit computers support a maximum of 3-4GB of memory, whereas a 64-bit computer can support memory amounts over 4 GB. This is important for software programs that are used for graphical design, engineering design or video editing, where many calculations are performed to render images, drawings, and video footage.
One thing to note is that 3D graphic programs and games do not benefit much, if at all, from switching to a 64-bit computer, unless the program is a 64-bit program. A 32-bit processor is adequate for any program written for a 32-bit processor. In the case of computer games, you’ll get a lot more performance by upgrading the video card instead of getting a 64-bit processor.
In the end, 64-bit processors are becoming more and more commonplace in home computers. Most manufacturers build computers with 64-bit processors due to cheaper prices and because more users are now using 64-bit operating systems and programs. Computer parts retailers are offering fewer and fewer 32-bit processors and soon may not offer any at all.