- 990x.top
- Простой компьютерный блог для души)
- DnsCache — что это за служба? (DNS-клиент)
- DnsCache — что это такое?
- Что такое DNS простыми словами?
- Как очистить кэш DNS?
- DnsCache — как отключить службу?
- Заключение
- Просмотр или очистка ДНС кэша в Windows – инструкция
- Содержание:
- Просмотр ДНС кэша в Windows
- Очистка ДНС кэша в Windows
- DNS Caching and How It Makes Your Internet Better
- Checking a local copy is faster than searching remotely every time
- The Purpose of a DNS Cache
- How a DNS Cache Works
- What Is DNS Cache Poisoning?
- DNS Flushing: What It Does and How to Do It
- How to Clear Windows DNS Cache (Server & Workstations)
- Clear DNS Cache on Windows 10
- Step 1: Open command prompt
- Step 2: Enter the following command
- Step 3: View DNS Resolver cache (Optional)
- Clear DNS Cache on Windows DNS Server
- Clear DNS Cache Using PowerShell
990x.top
Простой компьютерный блог для души)
DnsCache — что это за служба? (DNS-клиент)
Приветствую друзья! Сегодня мы постараемся разобраться с службой DnsCache, я найду максимум информации и напишу все простыми словами.
DnsCache — что это такое?
Служба кэширования DNS на стороне клиента. Клиент — имеется ввиду обычный домашний компьютер.
Отображаемое название — DNS-клиент.
Если службу отключить, то сетевой трафик для DNS-запросов увеличится. На самом деле для домашнего ПК это не так критично, просто будет отправляться больше запросов, другими словами — немного больше будет расходоваться интернета.
Зачем нужна? Служба оптимизирует производительность разрешения имен DNS за счет хранения ранее разрешенных имен в памяти. Простыми словами — это кэш, то есть зачем Windows узнавать одни и те же DNS-данные повторно? Когда она их может заносить в кэш и при необходимости — уже оттуда брать данные. В результате экономится время и трафик.
DnsCache работает под процессом svchost.exe, который запускается из этой папки с таким параметром:
C:\Windows\system32\svchost.exe -k NetworkService
Что такое DNS простыми словами?
Ребята, все очень просто, смотрите — мы посещаем сайты. У каждого сайта есть название. Однако название — это для нас, чтобы нам было легче и удобнее запомнить. Программы общаются не к названиям сайтов, а к их IP-адресам. Чтобы узнать какой IP-адрес скрывается за сайтом — и нужен сервер DNS (Domain Name System).
А теперь покажу на примере (образно говоря):
- Вы вводите в браузере Хроме сайт, например microsoft.com.
- При помощи DNS-сервера Хром узнает IP-адрес сервера, где расположен сайт microsoft.com.
- Хром посылает запрос к этому серверу, мол хотим получить сайт microsoft.com, сервер отвечает — просто выдает запрашиваемую страницу и браузер показывает ее вам.
Чтобы не запрашивать каждый раз IP-адрес можно воспользоваться DNS-кэшем, работу которого и осуществляет служба DnsCache (DNS-клиент).
Как очистить кэш DNS?
Оказывается этот кэш можно очистить.
Нужно просто открыть командную строку от администратора, если у вас Windows 10 то достаточно зажать Win + X и выбрать соответствующий пункт. Потом вставьте такую команду:

Когда нужно чистить этот кэш? Например если у вас странные проблемы с интернетом, неработают некоторые сайты, то можно попробовать очистить DNS-кэш. Иногда стоит чистить в целях приватности/конфиденциальности, чтобы вообще не было никаких данных о посещенных сайтах.
DnsCache — как отключить службу?
- Службу отключать нужно только если вы уверены в этом.
- Однако даже при отключенной службе в теории никаких проблем не будет, возможно интернет будет чуточку медленнее работать (думаю будет незаметно).
На самый крайний случай перед отключением можно создать точку восстановления.
Отключить службу можно обычным способом или через командную строку. Да, конечно можно еще задействовать реестр, но здесь нет смысла — служба спокойно отключается и обычными способами.
Используя командную строку. Запустите командную строку от имени администратора, в Windows 10 это сделать просто — Win + X > выбираем соответствующий пункт. Теперь указываем две команды, первая — для остановки работы:
net stop dnscache
Вторая — для того чтобы служба после перезагрузки снова не запустилась:
sc config «dnscache» start= disabled
Отключение через список служб. Здесь тоже все просто:
- Зажмите Win + R, появится окошко Выполнить, вставьте команду services.msc и нажмите ОК.
- Откроется список служб — найдите здесь DNS-клиент, нажмите два раза.
- Появится окошко свойств: в меню Тип запуска выберите Отключена, а также нажмите на Остановить.

Заключение
- DnsCache — служба кэширования DNS-записей.
- Обычно отключать службу не нужно, но в целях эксперимента — можно попробовать. Может сайты будут чуть дольше открываться, но все равно маловероятно.
Вообще при проблемах с DNS рекомендуется ставить сервера от Google Public DNS — это 8.8.8.8 и 8.8.4.4 .
Просмотр или очистка ДНС кэша в Windows – инструкция
Приветствую!
Кэш DNS используется операционной системой для того, чтобы ускорить доступ к просматриваемым в браузере сайтам, Интернет сервисам и т.д. Однако данный функционал может приводить к проблемам, к примеру, при попытке посмотреть тот или иной сайт, в браузере может выводиться ошибка DNS_PROBE_FINISHED_NXDOMAIN, а в некоторых случаях и ERR_NAME_NOT_RESOLVED.
Конечно, не всегда кэш DNS виноват в возникновении данных проблем, но для решения оных первым делом стоит прибегнуть к очистке данного кэша.
Давайте посмотрим, как просмотреть кэш ДНС, очистить его.
Содержание:
Просмотр ДНС кэша в Windows
Процедура эта довольно проста.
- Первым делом необходимо открыть командную строку от имени администратора.
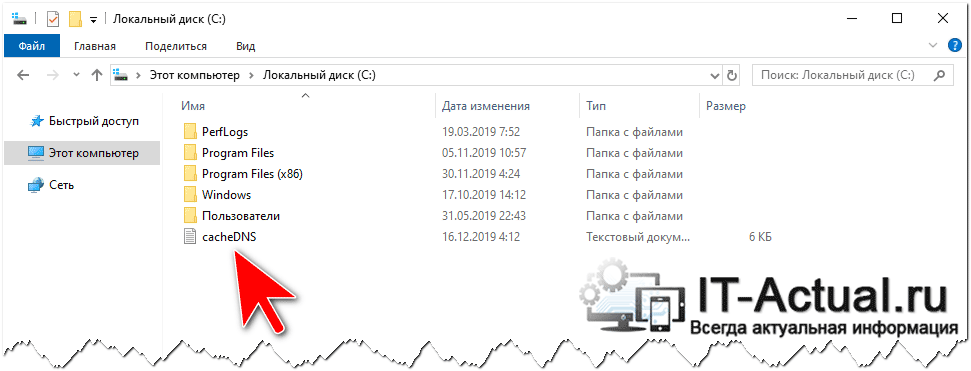
- Как только будет открыто указанное в первом шаге окно, в него необходимо ввести следующую команду:
И нажать клавишу Enter, дабы введённая команда была отработана.
Команда будет отработана очень быстро и по результатам её работы в корне диска «C» будет создан текстовый файл, в котором будет находиться информация о текущем сохранённом кэше ДНС. Будут приведены посещённые домены сайтов и IP адреса серверов, с которых эти сайты загружаются.
Очистка ДНС кэша в Windows
Теперь давайте посмотрим, как произвести молниеносно очистку всего ДНС кэша в Windows. Используемая версия операционной системы не имеет значения, инструкция является полностью универсальной.
- Дабы произвести очистку кэша ДНС, следует открыть командную строку, причём она должна быть открыта именно от имени администратора. О том, как это сделать, рассказано чуть выше. А именно в первом шаге инструкции по просмотре ДНС кэша.
- И так, открыв окно командной строки, далее следует ввести туда команду:
И для её выполнения нажать клавишу Enter.
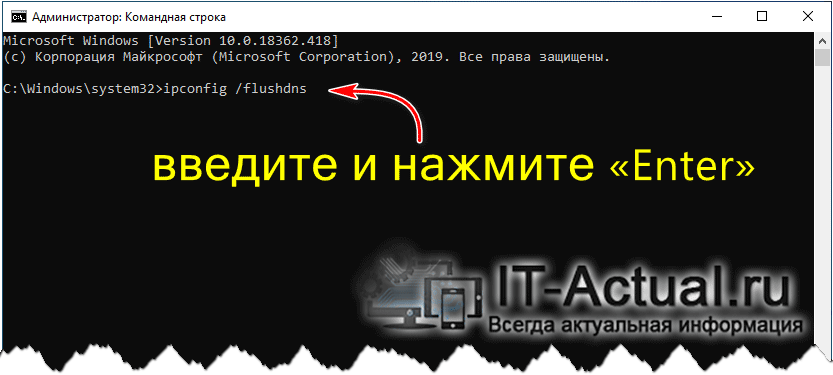
Вот так, весьма и весьма не сложно осуществляется просмотр кэшированных в Виндовс (причём любой версии) DNS записей, а также осуществляется при необходимости полная очистка операционной системы от этих данных.
И да, опасаться процедуры очистки не стоит, никакие важные системные или пользовательские данные в процессе выполнения данной процедуры не удаляются.
В свою очередь, Вы тоже можете нам очень помочь.
Просто поделитесь статьей в социальных сетях и мессенджерах с друзьями.
Поделившись результатами труда автора, вы окажете неоценимую помощь как ему самому, так и сайту в целом. Спасибо!
DNS Caching and How It Makes Your Internet Better
Checking a local copy is faster than searching remotely every time
A DNS cache (sometimes called a DNS resolver cache) is a temporary database, maintained by a computer’s operating system, that contains records of all the recent visits and attempted visits to websites and other internet domains.
In other words, a DNS cache is just a memory of recent DNS lookups that your computer can quickly refer to when it’s trying to figure out how to load a website.
The information in this article applies to home users who haven’t changed their DNS settings.
The Purpose of a DNS Cache
The internet relies on the Domain Name System to maintain an index of all public websites and their corresponding IP addresses. You can think of it as a phone book.
With a phone book, we don’t have to memorize everyone’s phone number, which is the only way phones can communicate: with a number. In the same way, DNS is used so we can avoid having to memorize every website’s IP address, which is the only way network equipment can communicate with websites.
This is what happens behind the curtain when you ask your web browser to load a website.
You type in a URL like lifewire.com and your web browser asks your router for the IP address. The router has a DNS server address stored, so it asks the DNS server for the IP address of that hostname. The DNS server finds the IP address that belongs to lifewire.com and then is able to understand what website you’re asking for, after which your browser can then load the appropriate page.
This happens for every website you want to visit. Every time you visit a website by its hostname, the web browser initiates a request out to the internet, but this request cannot be completed until the site’s name is «converted» into an IP address.
The problem is that even though there are tons of public DNS servers your network can use to try to speed up the conversion/resolution process, it’s still quicker to have a local copy of the «phone book,» which is where DNS caches come into play.
The DNS cache attempts to speed up the process even more by handling the name resolution of recently visited addresses before the request is sent out to the internet
There are actually DNS caches at every hierarchy of the «lookup» process that ultimately gets your computer to load the website. The computer reaches your router, which contacts your ISP, which might hit another ISP before ending up at what’s called the «root DNS servers.» Each of those points in the process has a DNS cache for the same reason, which is to speed up the name resolution process.
How a DNS Cache Works
Before a browser issues its requests to the outside network, the computer intercepts each one and looks up the domain name in the DNS cache database. The database contains a list of all recently accessed domain names and the addresses that DNS calculated for them the first time a request was made.
The contents of a local DNS cache can be viewed on Windows using the command ipconfig /displaydns, with results similar to this:
In DNS, the «A» record is the portion of the DNS entry that contains the IP address for the given host name. The DNS cache stores this address, the requested website name, and several other parameters from the host DNS entry.
What Is DNS Cache Poisoning?
A DNS cache becomes poisoned or polluted when unauthorized domain names or IP addresses are inserted into it.
Occasionally a cache may become corrupted because of technical glitches or administrative accidents, but DNS cache poisoning is typically associated with computer viruses or other network attacks that insert invalid DNS entries into the cache.
Poisoning causes client requests to be redirected to the wrong destinations, usually malicious websites or pages full of advertisements.
For example, if the docs.google.com record from above had a different «A» record, then when you entered docs.google.com in your web browser, you’d be taken somewhere else.
This poses a massive problem for popular websites. If an attacker redirects your request for Gmail.com, for example, to a website that looks like Gmail but isn’t, you might end up suffering from a phishing attack like whaling.
DNS Flushing: What It Does and How to Do It
When troubleshooting cache poisoning or other internet connectivity problems, a computer administrator may wish to flush (i.e. clear, reset, or erase) a DNS cache.
Since clearing the DNS cache removes all the entries, it deletes any invalid records too and forces your computer to repopulate those addresses the next time you try accessing those websites. These new addresses are taken from the DNS server your network is set up to use.
So, to use the example above, if the Gmail.com record was poisoned and redirecting you to a strange website, flushing the DNS is a good first step to getting the regular Gmail.com back again.
In Microsoft Windows, you can flush the local DNS cache using the ipconfig /flushdns command in a Command Prompt. You know it works when you see the Windows IP configuration successfully flushed the DNS Resolver Cache or Successfully flushed the DNS Resolver Cache message.
Through a command terminal, macOS users should use dscacheutil -flushcache but know that there is not a «successful» message after it runs, so you’re not told if it worked. In some cases, Mac users will also have to kill the DNS responder (sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder.) Linux users should enter the /etc/rc.d/init.d/nscd restart command. The exact command will vary based on your Linux distribution, though.
A router can have a DNS cache as well, which is why rebooting a router is often a troubleshooting step. For the same reason you might flush the DNS cache on your computer, you can reboot your router to clear the DNS entries stored in its temporary memory.
How to Clear Windows DNS Cache (Server & Workstations)
Having DNS resolution problems? Do you need to clear the DNS cache on a Windows 10 computer or Server?
Then you’re in the right place.
In this post, I’ll show you how to quickly clear the DNS cache using the command line, Windows Server DNS console and PowerShell.
Clear DNS Cache on Windows 10
This also works on older Windows operating systems.
Step 1: Open command prompt
Click the Windows start button and type cmd
Click on Command Prompt to open
Step 2: Enter the following command
With command prompt open type:
That’s it for flushing the local cache. If you want to check the local cache then move on to step 3.
Step 3: View DNS Resolver cache (Optional)
This is another simple command just type:
This will display all the local cache entries.
RECOMMENDED: SOLARWINDS IP ADDRESS TRACKER (FREE TOOL)
Scan, detect and easily manage IP addresses with the Free IP address tracker by SolarWinds. By using this FREE tool you can save time by eliminating the need to manually track IP address information.
In addition, it helps to detect IP conflicts on your subnet. Download your FREE copy of IP Address Tracker.
Clear DNS Cache on Windows DNS Server
Maybe it’s not a local client issue, maybe your server has a bad cache entry. Follow these steps to clear the cache on your Windows Server.
In this example, I’m using Windows Server 2016.
This is super easy, just open the DNS console, right-click the DNS server and select clear cache
Clear DNS Cache Using PowerShell
To clear the client cache using PowerShell use this command:
To clear the local DNS server cache use this command:
To clear the DNS cache on a specific DNS server use this command. Change -ComputerName to the name of the server you want to clear
Clear-DnsServerCache –ComputerName “DC1” -Force
If you still have DNS issues then check out my guide on using nslookup to test DNS, it includes 8 tips for troubleshooting DNS problems.
Leave a comment below
Recommended Tool: SolarWinds Server & Application Monitor
This utility was designed to Monitor Active Directory and other critical services like DNS & DHCP. It will quickly spot domain controller issues, prevent replication failures, track failed logon attempts and much more.
What I like best about SAM is it’s easy to use dashboard and alerting features. It also has the ability to monitor virtual machines and storage.

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/headshot-00415ba557444a8a9b6bb139498b97c5.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/what-is-a-dns-cache-817514-289185cfa826431e91eeef1295481625.png)






