- Создание и управление FQDN именем сервера 3CX
- Введение
- FQDN имя от компании 3CX
- Ваше собственное FQDN имя
- Изменение FQDN имени
- Заключение
- What Does FQDN Mean?
- FQDN Examples
- More Information on FQDN
- Partially Qualified Domain Name (PQDN)
- What is FQDN (Fully Qualified Domain Name)?
- Hostname
- Domain Name
- FQDN = Host Name + Domain Name
- Automatic WWW Host name
- Partially Qualified Domain Name
- What is FQDN? What does FQDN do?
- How to make a FQDN lookup?
- Why do you need FQDN?
- Conclusion
- Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) explained
- Structure of the FQDN
- Example of an FQDN
Создание и управление FQDN именем сервера 3CX
Введение
В этой статье мы поясним принципы создания и управления FQDN именем сервера 3CX. Это поможет вам лучше спланировать инсталляцию системы и избежать многих проблем в будущем.
Как вы, возможно уже знаете, при первоначальной инсталляции 3CX v15 ваш лицензионный ключ привязывается к FQDN имени, выбранном администратором в мастере первоначальной конфигурации. Поэтому продумайте удобное FQDN имя еще до начала установки!
FQDN имя от компании 3CX
Начиная с 3CX v15, при условии, что у вас активна подписка на обновления, вы можете воспользоваться DNS сервером 3CX. DNS 3CX (фактически, это DNS инфраструктура Google) предоставляет следующие возможности:
- Поддерживает публичное FQDN имя вашего сервера в одном из принадлежащих 3CX доменов верхнего уровня.
- Реализует функцию Dynamic DNS, то есть, при смене публичного IP адреса сервера, изменение DNS записи происходит автоматически.
Кроме сервиса DNS, 3CX предоставляет бесплатные доверенные SSL сертификаты безопасности от организации Let’s Encrypt, которые используются для подключений клиентов к серверу, видеоконференции и других важных функций.
Как было сказано, выбранное имя сервера привязывается к лицензионному ключу. Если вы получили бесплатный ключ PBX Edition Key и хотите просто протестировать 3CX, не выбирайте ваше основное имя (например, имя вашей компании), а используйте тестовое. Например, test-company.3cx.ru, а не company.3cx.ru.
C другой стороны, домен верхнего уровня изменить можно. Т.е. вы можете “переехать” с FQDN company.3cx.eu на company.3cx.ru. Имя хоста должно быть уникально в выбранном домене. Поэтому, если имя company.3cx.ru уже занято, вам придется выбирать другое. Имена резервируются по принципу первой заявки, поэтому поспешите с переходом на 3CX v15, чтобы успеть получить красивое имя.
Внимание: 3CX оставляет за собой право отменить регистрацию любого FQDN имени, если оно нарушает патентные права или содержит оскорбительные слова. Также 3CX не может переназначить имя для вас, если оно уже зарегистрировано на другую компанию.
Ваше собственное FQDN имя
Если вы планируете использовать собственное имя сервера, например, хост в вашем корпоративном домене, заранее подготовьте доверенный SSL сертификат для этого имени. Вы укажете его в мастере первоначальной настройки системы. В этом случае 3CX не выдает и не поддерживает для вас сертификат Let’s Encrypt.
Затем ваш лицензионный ключ будет привязан к собственному FQDN имени. Однако, тут есть одна особенность, связанная с работой сервиса 3CX Webmeeting: если ваше FQDN имя имеет вид pbx.company.com, портал Webmeeting автоматически генерирует для вас URL pbxcompany.3cx.*. Убедитесь, что такое имя еще не занято другим пользователем!
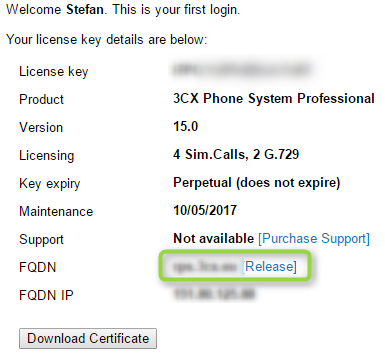
Изменение FQDN имени
Для коммерческих и бесплатных лицензий – зайдите в портал с вашими учетными данными и нажмите Release. Ключ будет отвязан от FQDN.
Заключение
Повторим основные принципы использования FQDN имени в инсталляциях 3CX:
- Первоначальная настройка системы привязывает FQDN сервера к лицензионному ключу
- Если оказалось, что выбранное имя уже кем-то занято:
- Появится ошибка Error creating FQDN: FQDN already in use. Please choose another one.
- Выберите другое свободное FQDN имя
What Does FQDN Mean?
An FQDN, or a Fully Qualified Domain Name, is written with the hostname and the domain name, including the top-level domain, in that order: [hostname].[domain].[tld].
In this scenario, «qualified» means «specified» since the full location of the domain is specified in the name. The FQDN specifies the exact location of a host within DNS. If the name isn’t this specified, it’s called a partially qualified domain name, or PQDN. There’s more information on PQDNs at the bottom of this page.
An FQDN might also be called an absolute domain name since it provides the absolute path of the host.
FQDN Examples
A fully qualified domain name is always written in this format: [hostname].[domain].[tld]. For example, a mail server on the example.com domain may use the FQDN mail.example.com.
Here are some other examples of fully qualified domain names:
More Information on FQDN
Fully qualified domain names actually require a period at the end. This means www.microsoft.com. would be the acceptable way to enter that FQDN. However, most systems simply imply the period even if you don’t explicitly give it. Some web browsers might even let you enter the period at the end of an URL, but it’s not required.
Domain names that aren’t «fully qualified» will always have some sort of ambiguity about them. For example, p301srv03 can’t be an FQDN because there are any number of domains that might also have a server by that name. p301srv03.wikipedia.com and p301srv03.microsoft.com are just two examples—knowing only the hostname doesn’t do much for you.
Even microsoft.com isn’t fully qualified because we don’t know for sure what the hostname is, even if most browsers do automatically assume it’s www.
These domain names that aren’t fully qualified are actually called partially qualified domain names. The next section has more information on PQDNs.
Partially Qualified Domain Name (PQDN)
Another term that’s similar to FQDN is PQDN, or partially qualified domain name, which is just a domain name that isn’t fully specified. The p301srv03 example from above is a PQDN because while you know the hostname, you don’t know what domain it belongs to.
Partially qualified domain names are just used for convenience, but only in certain contexts. They’re for special scenarios when it’s easier to refer to the hostname without referencing the entire fully qualified domain name. This is possible because in those contexts, the domain is already known elsewhere, and so only the hostname is needed for a particular task.
For example, in DNS records, an administrator could refer to the fully qualified domain name like en.wikipedia.org or just shorten it and use the hostname of en. If it’s shortened, the rest of the system will understand that in that particular context, en is really referring to en.wikipedia.org.
However, you should understand that FQDN and PQDN are definitely not the same things. An FQDN provides the full absolute path of the host while the PQDN only gives a relative name that’s just a small portion of the full domain name.
What is FQDN (Fully Qualified Domain Name)?
We generally see the term FQDN or Fully Qualified Domain Name and generally, though that is is like secret magic that provides some information about the servers and hosts. No. The answer is no the FQDN provides no secret or magic. We use FQDN in order to specify hostnames in a hierarchical manner. Below we will look at how we calculate FQDN.
Hostname
The hostname is used to identify hosts with meaning full names. For example, when we set up the Windows operating system the Windows set the hostname of the computer with the created user name like IsmailPC. Of course, we can change this hostname whatever we want. The following list provides an example of hostnames.
Domain Name
A domain name is used to create a domain with a name. The Internet provides a consistent and unique domain name hierarchy. For example, poftut.com specifies this site which is a domain name. We can use domain names not just sites also other things like databases, services, etc.
FQDN = Host Name + Domain Name
Now we came to the real topic. We have learned the basics which creates FQDN. Fully qualified means the whole and domain name cames after that. Fully qualified domain name consist of Host name + Domain name . FQDN specifies the host whit out any extra description. For example:
Hostname: www
Domain name: poftut.com
FQDN: www.poftut.com
www.poftut.com specifies the host which provides www or web services.
Automatic WWW Host name
Normally while surfing the internet we can type URL as poftut.com. This is not a fully qualified domain name even does not provide the hostname. But the browser automatically add www as default as it expects from us to surf in poftut.com web site.
Partially Qualified Domain Name
Hostnames can be named as Partially Qualified Domain Names. Because hostnames do not provide the domain name. We can only use the hostname if we know or automatically add the domain name to the hostname. For example, if we are in the same domain we can use PQDN for communication and specification.
What is FQDN? What does FQDN do?
What is FQDN? What does it do? FQDN means Fully Qualified Domain Name. It is the fullest possible domain name of a host or a computer, on the internet.
FQDN, another hard-to-pronounce abbreviation. You don’t really need to know it to get a domain and set it up, but for the more curious of you, here it is.
FQDN means Fully Qualified Domain Name. It is the fullest possible domain name of a host or a computer, on the internet. Here you can see the syntax of it:
[hostname].[domain].[tld]
It can also include a subdomain. The subdomain is not the hostname. It is just a part of the domain.
Let’s see an example with Cloudns.net. We read it from right to left.
www.cloudns.net
First is “.net”, which is the top-level domain. Then it follows the domain name “cloudns”, and the last is the hostname “www.”.
The hostname can show a specific service or protocol for the domain like “mail” or “ftp”.
The FQDN serves to show the exact location of an object inside the DNS hierarchy.
PQDN is Partially Qualified Domain Name. It is just a part of the complete domain name. Let’s use our domain name again. The PQDN is, for example, “cloudns.net”. In this one, we don’t have the host “www.”.
If you are searching for a fast and secure DNS service – the best choice is the Anycast DNS!
How to make a FQDN lookup?
You can perform a FQDN lookup on your computer with any of the popular OS.
Windows 10. Go to “control panel” and click “system.” You will see it next to the “Full Computer Name.”
MacOS – Open the terminal, type “hostname –f”, and then press the enter button. You will see the FQDN.
Linux – similar to the MacOS, open the terminal, but this time type “hostname –A”.
Why do you need FQDN?
You will need FQDN to make a device accessible on the internet. You will use it to configure your DNS and get an IP address.
Another use case is when you want to get an SSL certificate. Today, almost every site has one, and you need to provide the FQDN to obtain it.
Remote Access. The DNS server will perform a lookup in its registers and resolve the FQDN to the correspondent IP address.
Access a protocol or a service. If you want to use a FTP for example, you will need the Fully Qualified Domain Name or IP. Also, for setting up email for specific applications, you will need it.
Conclusion
Fully Qualified Domain Name is used all the time, even if you don’t see it directly. It is the full identifier of the domain names.
Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) explained
The term “fully qualified domain name”, FQDN for short, refers to the complete and unique address of an internet presence. It consists of the host name and the domain, and is used to locate specific hosts online and access them using name resolution.
The structure of an FQDN is predefined by the domain name system (DNS). The names of the individual levels in the domain name area are called “labels” and are separated from one another by dots. Each label must consist of 1 to 63 characters and the total FQDN may not exceed 255 characters in total. Only letters, numbers, or dashes can be used. Each label has to have either a letter or a number at the beginning.
The fully qualified domain name consists of three or more labels: The top level domain, the domain names, optional subdomains, and the host name. If a domain name doesn’t specify all of the labels that are required for the FQDN, then this is called a “Partially Qualified Domain Name” (PQDN). This often means that only the host name is given. The generic name or the FQDN and its IP address is the “Fully Qualified Host Name” (FQHN).
In the following, learn exactly how the fully qualified domain name is structured.
FQDN stands for fully qualified domain name. The FQDN represents the absolute address of the internet presence. “Fully qualified” refers to the unique identification that guarantees that all of the domain levels are specified. The FQDN contains the host name and domain, including the top level domain, and can be uniquely assigned to an IP address.
Structure of the FQDN
If you want to better understand the naming hierarchy of the FQDN, then it makes sense to look at the structure of an FQDN from right to left. The further right a label is located, the higher it lies in the tree diagram representation of the hierarchy. On the highest hierarchical level you’ll find the root label, also called the null label, or the “root” of the DNS system. It consists of a blank area, and so is only expressed by a period, or dot. In browsers today, it’s not necessary to enter this dot anymore, since the browser will add it itself.
On the next highest hierarchy level is the top level domain, for example “.com”, “.org”, or “.ca”. To resolve the address, the name server searches through the directory of the given TLD for the domain on the next hierarchy level. Once this is identified, the host whose host name is listed in the lowest label is contacted to access the given site.
Schematic representation of the structure of fully qualified domain names
Example of an FQDN
The following example clarifies the structure of a fully qualified domain name:
hosting.ionos.ca.
In a name server’s directory, the dot on the far right is always included in the FQDN.
The root label after the dot remains empty. The top level domain in our example is the country-specific top level domain “.ca”. Country-specific TLDs are also gathered under the abbreviation ccTLD for “country code top level domain”. These are different than generic TLDs like .com or .org, which are referred to as gTLD (for “generic top level domain”). After the top level domain comes the domain name, also called the “second level label” or “second level domain”. In our example, this is “IONOS”. On the far left, we have the host name as the third level label: In our example, “hosting”.
Between the second level domain and the host name you can add additional labels for subdomains that refer to the sub areas of the domain and are called “third level domains”, “fourth level domains”, and so on. Their number is only limited by the maximum allowed total length of 255 characters for the FQDN. One example: In the fictitious FQDN hosting.example.ionos.ca, “example” would be a subdomain of “ionos.ca” and “hosting” would again be the host name.
Register a domain name
Build your brand on a great domain, including SSL and a personal consultant!
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/tim-fisher-5820c8345f9b581c0b5a63cf.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/001_what-does-fqdn-mean-2625883-5c05cb5fc9e77c00010d6438.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/002_what-does-fqdn-mean-2625883-5c05cd0b46e0fb000166e0dd.jpg)




