- Linux Operating System | CLI (Command Line Interface) and GUI (Graphic User Interface)
- Графические интерфейсы Linux
- Budgie — графическая оболочка
- Cinnamon — среда рабочего стола
- Enlightenment
- GNOME — среда рабочего стола
- KDE (Plasma) — среда рабочего стола
- LXDE — lightweight desktop environment
- LXQt — легковесная среда рабочего стола
- MATE — продолжение развития классического Gnome
- Openbox — быстрый оконный менеджер
- Window Maker
- Run Linux GUI apps on the Windows Subsystem for Linux (preview)
- Install support for Linux GUI apps
- Prerequisites
- Fresh install — No prior WSL installation
- Existing WSL install
- Run Linux GUI apps
- Update the packages in your distribution
- Install Gedit
- Install GIMP
- Install Nautilus
- Install VLC
- Install X11 apps
- Install Google Chrome for Linux
- Install Microsoft Teams for Linux
- Install Microsoft Edge browser for Linux
- What is GUI in Linux OS?
- What is GUI in Linux?
- What is GUI explain?
- Which Linux has GUI?
- What is GUI and its uses?
- How does Linux GUI work?
- Does Linux use GUI?
- What is GUI explain with example?
- What are the types of GUI?
- Where are GUI used?
- What are the 2 Linux desktops?
- How do I switch to GUI in Linux?
- How do I start GUI in Linux?
- How does GUI work?
- How GUI is created?
- Why is GUI important?
Linux Operating System | CLI (Command Line Interface) and GUI (Graphic User Interface)
Linux actually means the kernel of the system, which is the sole controller of whatever happens on the computer system. When we talk or say that x “runs Linux” we usually refer to the system kernel and set of the tools that are used with it. Each of the present components will be checked so that we understand exactly what functions each does.
The Linux based kernel can run a wide variety of software across many different hardware-based platforms. A computer can act as a server, which means it primarily handles data on other’s behalf or can act like a desktop, which means a user will be interacting with it directly. The system can run software or it can be used as a development PC in the process of creating any software. Linux can perform multiple roles as there is no special allocation to Linux about the role of the system; it’s only a matter of configuring the present applications and how do they execute.
Command Line Interface (CLI):
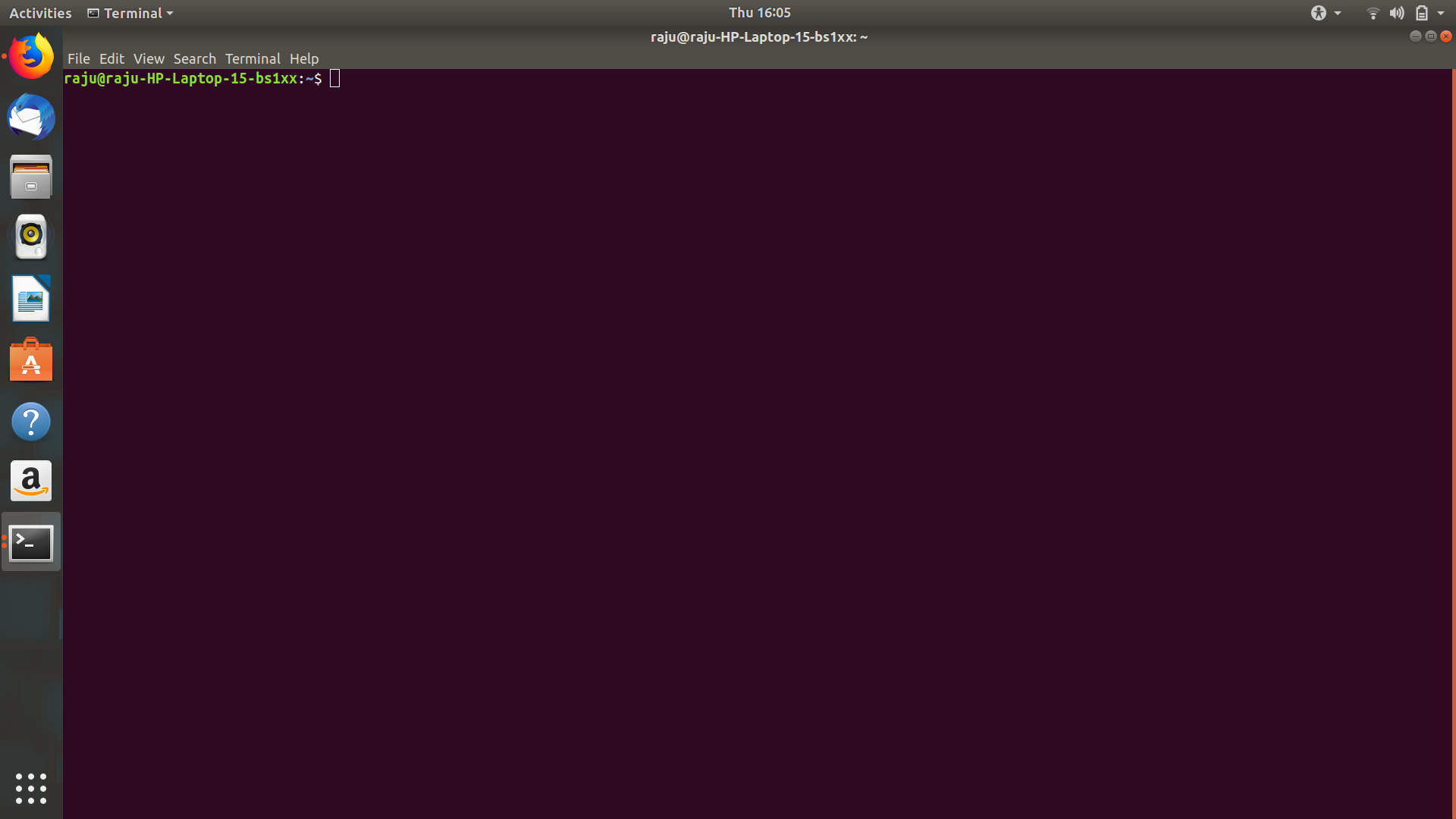
The Command Line Interface (CLI), is a non-graphical, text-based interface to the computer system, where the user types in a command and the computer then successfully executes it. The Terminal is the platform or the IDE that provides the command line interface (CLI) environment to the user.
The CLI terminal accepts the commands that the user types and passes to a shell. The shell then receives and interprets what the user has typed into the instructions that can be executed by the OS (Operating System). If the output is produced by the specific command, then this text is displayed in the terminal. If any of the problems with the commands are found, then some error message is displayed.
Graphical and the non-Graphic Interface:
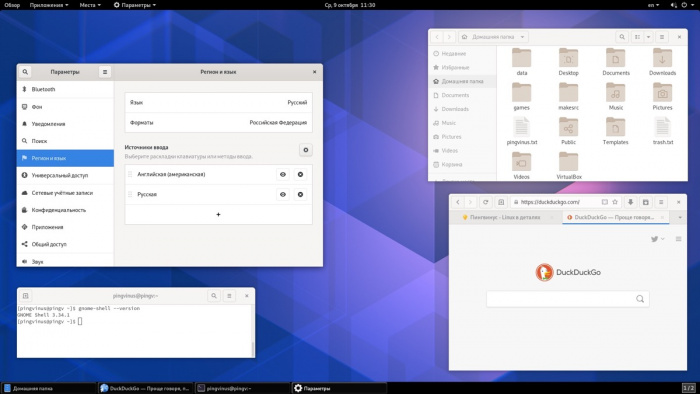
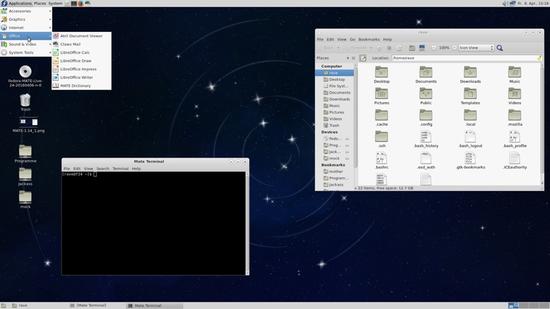
Linux has two approaches: graphically and non-graphically. In graphical mode, The actual applications live in windows that we can resize and move around according to our needs. we have the menu and tools to help us find what we’re looking for. This is the point where we’ll use a required web browser, our graphics editing tools, and our emails. Here we can see some example of the graphical desktop, with a menu bar of popular applications to the left.
In Graphical Mode (GUI), we can have many shells open, it is a good thing when we are performing some tasks on multiple/remote computers. We can even log in with our username/id and password/keys through the GUI.
After successfully logging in, we are taken to the OS desktop where we can use the installed applications.
Non-graphical mode actually starts off with a text-based login, As shown below. We are generally prompted for our username/ID and after entering that, we are then prompted for our password. If the login is successful, then we are taken straight to an execution shell.
In command line interface or the CLI, there are none of the windows present to move around. Even though we have specific text editors, dedicated web browsers, and email clients, they are basically just texts. This is how UNIX got its start before the graphical environments became the norm. Most servers will be running in command line mode (CLI) too because a GUI is a waste of resources and dataspace. For example:
Источник
Графические интерфейсы Linux
В данном разделе сайта публикуется информация о графических интерфейсах операционной системы Linux. Интерфейсы разделены на две группы: среды рабочего стола и оконные менеджеры.
Среда рабочего стола Linux (Desktop Environment) — это комплексная готовая к работе оболочка. Обычно среда рабочего стола включает панель задач, функциональные меню, менеджер входа в систему, программы настройки, базовые программы и другие функциональные элементы, включая оконный менеджер.
Оконный менеджер Linux (Window Manager) — это программа, которая занимается отрисовкой окон, позволяет перемещать и изменять размер окна, обрабатывает действия пользователя, которые он делает в окне программы. Оконный менеджер может работать независимо или быть в составе среды рабочего стола.
Budgie — графическая оболочка
Budgie — графическая оболочка, которая была написана с нуля, но использует технологии GNOME.
Cinnamon — среда рабочего стола
Cinnamon — самостоятельная среда рабочего стола, являющаяся ответвлением от Gnome 3, но имеющая дизайн в стиле классического Gnome.
Enlightenment
Enlightenment (или просто E) — легковесный оконный менеджер (пользовательское окружение) не требовательный к ресурсам компьютера, потребляет очень мало оперативной памяти.
GNOME — среда рабочего стола
GNOME (GNU Network Object Model Environment) — популярная среда рабочего стола для Linux. Включает в себя набор утилит для настройки среды, прикладное программное обеспечение, системные утилиты и другие компоненты.
KDE (Plasma) — среда рабочего стола
KDE — полнофункциональная среда рабочего стола. В рамках проекта KDE разрабатывается большое количество приложений для повседневных нужд. KDE использует библиотеки Qt.
LXDE — lightweight desktop environment
LXDE (Lightweight X11 Desktop Environment) — быстрая легковесная среда рабочего стола, не требовательная к ресурсам компьютера. В качестве оконного менеджера используется Openbox. Окна и меню открываются без задержек, интерфейс отзывчивый и не вызывает раздражения.
LXQt — легковесная среда рабочего стола
LXQt — легковесная среда рабочего стола, использующая библиотеки (фреймворк) Qt.
MATE — продолжение развития классического Gnome
MATE — среда рабочего стола, которая является продолжением развития Gnome 2. MATE является сбалансированной средой с хорошим набором программ и утилит и приятным классическим интерфейсом.
Openbox — быстрый оконный менеджер
Openbox — легковесный оконный менеджер с простым минималистским интерфейсом. Данный оконный менеджер не требователен к системным ресурсам и работает очень быстро. При клике правой кнопкой мыши вызывается главное меню Openbox, через которое можно вызывать любые программы. Openbox хорошо настраивается и поддерживает темы оформления.
Window Maker
Window Maker — менеджер окон для Linux. Главными элементами интерфеса в Window Maker являются функциональные кнопки на рабочем столе и меню, вызываемое при клике правой кнопкой мыши по рабочему столу. Работает быстро, хорошо настраивается.
Источник
Run Linux GUI apps on the Windows Subsystem for Linux (preview)
You can now preview Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) support for running Linux GUI applications (X11 and Wayland) on Windows in a fully integrated desktop experience.
WSL 2 enables Linux GUI applications to feel native and natural to use on Windows.
- Launch Linux apps from the Windows Start menu
- Pin Linux apps to the Windows task bar
- Use alt-tab to switch between Linux and Windows apps
- Cut + Paste across Windows and Linux apps
You can now integrate both Windows and Linux applications into your workflow for a seamless desktop experience.
Install support for Linux GUI apps
Prerequisites
You will need to be on Windows 11 Build 22000 or higher to access this feature. You can join the Windows Insiders Program to get the latest preview builds.
Installed driver for vGPU
To run Linux GUI apps, you should first install the preview driver matching your system below. This will enable you to use a virtual GPU (vGPU) so you can benefit from hardware accelerated OpenGL rendering.
Fresh install — No prior WSL installation
If you have not already done so, install WSL and set up a user name and password for your Linux distribution.
Open a command prompt with administrator privileges.
Select Start, type PowerShell, right-click Windows PowerShell, and then select Run as administrator.
Run this command and reboot your machine when prompted:
Once your machine has finished rebooting, installation will continue and you will be asked to enter a username and password. This will be your Linux credential for the Ubuntu distribution.
You’re now ready to begin using Linux GUI apps on WSL!
Existing WSL install
If you already have WSL installed on your machine, you can update to the latest version that includes Linux GUI support by running the update command from an elevated command prompt.
Select Start, type PowerShell, right-click Windows PowerShell, and then select Run as administrator.
Enter the WSL update command:
You will need to restart WSL for the update to take effect. You can restart WSL by running the shutdown command in PowerShell.
Linux GUI apps are only supported with WSL 2 and will not work with a Linux distribution configured for WSL 1. Read about how to change your distribution from WSL 1 to WSL 2.
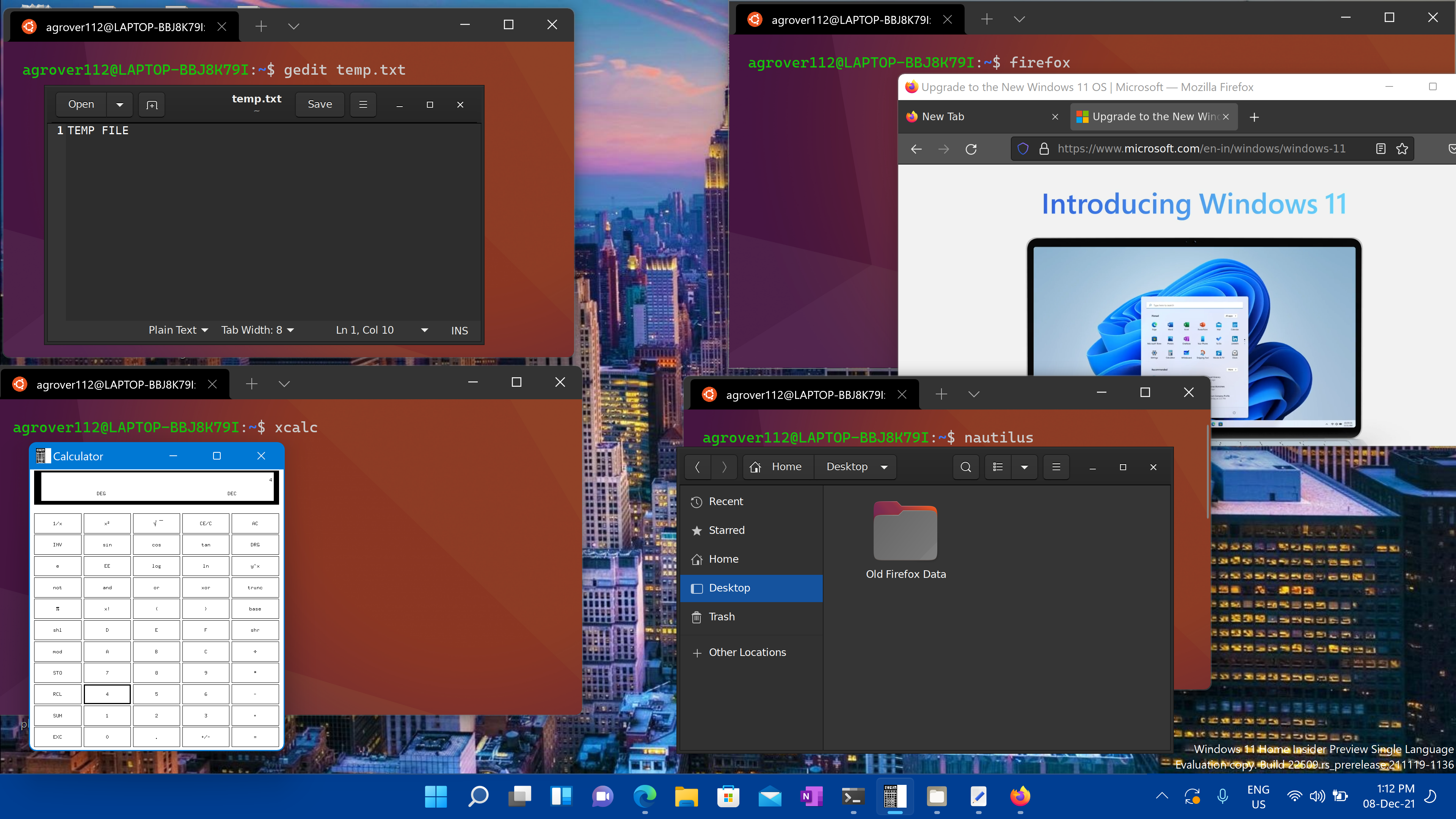
Run Linux GUI apps
You can run the following commands from your Linux terminal to download and install these popular Linux applications. If you are using a different distribution than Ubuntu, it may use a different package manager than apt. Once the Linux application is installed, you can find it in your Start menu under the distribution name. For example: Ubuntu -> Microsoft Edge .
Update the packages in your distribution
Install Gedit
Gedit is the default text editor of the GNOME desktop environment.
To launch your bashrc file in the editor, enter: gedit
Install GIMP
GIMP is a free and open-source raster graphics editor used for image manipulation and image editing, free-form drawing, transcoding between different image file formats, and more specialized tasks.
To launch, enter: gimp
Install Nautilus
Nautilus, also known as GNOME Files, is the file manager for the GNOME desktop. (Similiar to Windows File Explorer).
To launch, enter: nautilus
Install VLC
VLC is a free and open source cross-platform multimedia player and framework that plays most multimedia files.
To launch, enter: vlc
Install X11 apps
X11 is the Linux windowing system and this is a miscellaneous collection of apps and tools that ship with it, such as the xclock, xcalc calculator, xclipboard for cut and paste, xev for event testing, etc. See the x.org docs for more info.
To launch, enter the name of the tool you would like to use. For example:
Install Google Chrome for Linux
To install the Google Chrome for Linux:
- Change directories into the temp folder: cd /tmp
- Use wget to download it: sudo wget https://dl.google.com/linux/direct/google-chrome-stable_current_amd64.deb
- Get the current stable version: sudo dpkg -i google-chrome-stable_current_amd64.deb
- Fix the package: sudo apt install —fix-broken -y
- Configure the package: sudo dpkg -i google-chrome-stable_current_amd64.deb
To launch, enter: google-chrome
Install Microsoft Teams for Linux
To install Microsoft Teams for Linux:
- Change directories into the temp folder: cd /tmp
- Use curl to download the package: sudo curl -L -o «./teams.deb» «https://teams.microsoft.com/downloads/desktopurl?env=production&plat=linux&arch=x64&download=true&linuxArchiveType=deb»
- Use apt to install it: sudo apt install ./teams.deb -y
To launch, enter: teams
Install Microsoft Edge browser for Linux
Find information on how to install the Microsoft Edge browser for Linux using the command line on the Edge Insider site. Select Get instructions under the Command line installation section of the page.
Источник
What is GUI in Linux OS?
A GUI application or graphical application is basically anything that you can interact with using your mouse, touchpad or touch screen. … In a Linux distribution, a desktop environment provides the graphical interface for you to interact with your system.
What is GUI in Linux?
A graphical user interface (GUI) is a human-computer interface (i.e., a way for humans to interact with computers) that uses windows, icons and menus and which can be manipulated by a mouse (and often to a limited extent by a keyboard as well).
What is GUI explain?
A graphical user interface (GUI) is a type of user interface through which users interact with electronic devices via visual indicator representations.
Which Linux has GUI?
You’ll find GNOME as the default desktop in Ubuntu, Debian, Arch Linux, and other open source Linux distributions. As well, GNOME can be installed on Linux distros such as Linux Mint.
What is GUI and its uses?
A GUI uses windows, icons, and menus to carry out commands, such as opening, deleting, and moving files. Although a GUI operating system is primarily navigated using a mouse, a keyboard can also be used via keyboard shortcuts or the arrow keys.
How does Linux GUI work?
Typing “make menuconfig” when working with the source code for the Linux kernel opens and Ncurses interface for configuring the kernel. The core of most GUIs is a windowing system (sometimes called a display server). Most windowing systems use the WIMP structure (Windows, Icons, Menus, Pointer).
Does Linux use GUI?
Short answer: Yes. Both Linux and UNIX have GUI system. … Every Windows or Mac system has a standard file manager, utilities and text editor and help system. Similarly these days KDE and Gnome desktop manger are pretty standard on all UNIX platforms.
What is GUI explain with example?
Introduction to GUI. … It is the common user Interface that includes Graphical representation like buttons and icons and communication can be performed by interacting with these icons rather than the usual text-based or command-based communication. Understanding. A common example of a GUI is Microsoft operating systems.
What are the types of GUI?
There are four prevalent types of user interface and each has a range of advantages and disadvantages:
- Command Line Interface.
- Menu-driven Interface.
- Graphical User Interface.
- Touchscreen Graphical User Interface.
Where are GUI used?
The actions in a GUI are usually performed through direct manipulation of the graphical elements. Beyond computers, GUIs are used in many handheld mobile devices such as MP3 players, portable media players, gaming devices, smartphones and smaller household, office and industrial controls.
What are the 2 Linux desktops?
Best desktop environments for Linux distributions
- KDE. KDE is one of the most popular desktop environments out there. …
- MATE. MATE Desktop Environment is based on GNOME 2. …
- GNOME. GNOME is arguably the most popular desktop environment out there. …
- Cinnamon. …
- Budgie. …
- LXQt. …
- Xfce. …
- Deepin.
How do I switch to GUI in Linux?
To switch to the complete terminal mode in Ubuntu 18.04 and above, simply use the command Ctrl + Alt + F3 . To switch back to the GUI (Graphical User Interface) mode, use the command Ctrl + Alt + F2 .
How do I start GUI in Linux?
How to start GUI on redhat-8-start-gui Linux step by step instructions
- If you have not done so yet, install the GNOME desktop environment. …
- (Optional) Enable GUI to start after reboot. …
- Start GUI on RHEL 8 / CentOS 8 without the need for reboot by using the systemctl command: # systemctl isolate graphical.
How does GUI work?
How does it work? Edit. A GUI allows the user of a computer to communicate with the computer by moving a pointer around on a screen and clicking a button. … A program on the computer is constantly checking for the location of the pointer on the screen, any movement of the mouse, and any buttons pressed.
How GUI is created?
2 Answers. The operating system provides libraries that interface with the monitor/display. In short, GUI libraries such as Qt interact with those libraries of the operating system and creates an easier bridge for you, the programmer to interact with the monitor.
Why is GUI important?
Abstract. The Graphical User Interface (GUI) is an integral component of contemporary computer software. A stable and reliable GUI is necessary for correct functioning of software applications. Comprehensive verification of the GUI is a routine part of most software development life cycles.
Источник