Computing Support Assistant
Organizations that have a large number of computers normally have a technical support department of some kind. The computing support assistant in these departments has a range of responsibilities, including the purchase and installation of computer hardware and software, settingup, managing and maintaining network systems, troubleshooting computing problems, and designing and adapting software. He also trains users in the use of both equipment and software.
The person being interviewed in this unit is a Computing Support Assistant and is likely to be involved with basic troubleshooting problems. Problems can occur in any area but printing problems are very common. This is probably because printers are partly mechanical and the moving parts are more likely to give problems. The alignment and condition of the paper is important, and it is not uncommon for the paper to get stuck in the mechanism causing what is known as a paper jam.
General purpose office programs, such as word processors, spreadsheets, and databases usually have a large number of features, many of which are rarely used. Users often need help to find out how to operate these features. In PC systems it is also possible for memory problems to occur, particularly if the user is using a large number of programs at the same time. Memory problems can cause the computer to stop functioning. When this happens, the computer is said to have hung or frozen, although the term frozen usually refers to the display screen.
It is important for the computing support staff to be able to communicate with users as well as keep up to date with current technical knowledge about hardware and software. Computing is changing at an accelerating pace and it is difficult for support assistant to keep up with all the changes. Ways that this computing support assistant uses to keep in touch with developments include attending courses, using the Internet, and reading current magazines.
10 Interview: Computing Support Assistant
Task 1 Anne works in a large insurance company. She’s a computing support
assistant. She looks after people and their computers, and she helps with any problems people have. What sort of problems do you think they might have?
| Language work: Adverbs of frequency |
| Study these extracts from the interview. |
| I: Are you ever bored? A: No, not really, because it’s never the same things over and over again; it’s different each time. |
| A: People have problems with the hardware, often with printers . paper jamming. They also have problems finding options in the programs. Mostly with word-processing. I: Are there any other hardware problems? A: Occasionally a computer freezes, it hangs or freezes. It’s usually a memory problem. I: Is it always the machine or is it sometimes the user? A: Sometimes it’s the user. The printer isn’t switched on, or there’s no paper in it. |
| The words in italics tell us how often something happens. For example: I: How often does a computer crash? A: Sometimes, not very often. |
| We can grade these words from always to never like this: always almost always usually often sometimes occasionally almost never never |
Task 4 This table shows the number of hardware and software problems Anne had last year. Describe how often these problems happened, using the adverbs above.
Example There were sometimes problems with the network
| Printers |
| Monitors |
| Cabling |
| Scanners |
| Network |
| Spreadsheet |
| Database |
| Word processing |
Computing words and abbreviations
Task 5 Put the devices from the list into these sets.
| CD-ROM disk | laser printer |
| digital camera | lightpen |
| dot-matrix printer | magneto-optical disk |
| fixed hard disk | magnetic tape |
| floppy disk | microphone |
| inkjet printer | monitor |
| joystick | removable hard disk |
| keyboard | scanner |
Task 6 Match each definition (1-8) with the correct feature (a-h).
1 This is a window which appears when information about a choice is needed or when options have to be selected.
2 This indicates the amount of space between the dots which make up the image on a monitor.
3 This is part of a screen which is used to select an action, usually by clicking the mouse button over it.
4 This is a measure of the number of dots which make up the image on a monitor.
5 This shows a list of choices which the user can select from using the pointer.
6 This is part of a dialog box where the user can type file names and other information.
7 This is the speed at which the monitor refreshes the image on the screen.
8 This is a small picture on the screen which represents a program, folder, or file.
| a | aperture grill pitch | e | drop-down list box |
| b | command button | f | maximum resolution |
| с | dialog box | g | refresh rate |
| d | icon | h | text box |
Task 7 Answer these questions about the interview with full sentences. Then link your answers to make a short paragraph about Anne.
1 What kind of work does Anne do?
2 What does she like most about the job?
3 What kinds of problems do people have with hardware?
4 Why do computers freeze?
5 How does she keep up with new developments in computing?
6 What kinds of courses does she go on?
| | | следующая лекция ==> | |
| Everyday uses of computers | | | The Internet 1: email and newsgroups |
Дата добавления: 2016-04-26 ; просмотров: 1592 ; ЗАКАЗАТЬ НАПИСАНИЕ РАБОТЫ
About the Microsoft Support and Recovery Assistant
The Microsoft Support and Recovery Assistant works by running tests to figure out what’s wrong and offers the best solution for the identified problem. It can currently fix Office, Microsoft 365, or Outlook problems. If the Microsoft Support and Recovery Assistant can’t fix a problem for you, it will suggest next steps and help you get in touch with Microsoft support.
To download the Microsoft Support and Recovery Assistant follow these steps:
Click the button below to download the Microsoft Support and Recovery Assistant.

Note: By downloading this app, you agree to the terms of the Microsoft Services Agreement and Privacy Statement
Follow the steps below to download the Microsoft Support and Recovery Assistant according to your browser.
Tip: The tool may take a few minutes to download and install.
Edge or Internet Explorer
At the bottom of the browser window, select Run to launch the SetupProd.exe.
In the lower-lower left corner right-click SetupProd.exe > Open.
In the pop-up window, select Save File.
Next, from the upper-right of the FireFox browser window, select the downloads arrow and then select SetupProd.exe.
Read the Microsoft Services Agreement, and then click I agree.
Choose the app you are having problems with and click Next.
Choose the problem you’re having from the list and click Next.
Follow the directions the Microsoft Support and Recovery Assistant provides.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following operating systems are supported:
Windows 8 and Windows 8.1
Outlook in any of the following Office versions can be scanned:
Microsoft Microsoft 365 (2019, 2016, or 2013, 32-bit or 64-bit)
Microsoft Office 2019 (32-bit or 64-bit; Click-to-Run or MSI installations)
Microsoft Office 2016 (32-bit or 64-bit; Click-to-Run or MSI installations)
Microsoft Office 2013 (32-bit or 64-bit; Click-to-Run or MSI installations)
Microsoft Office 2010 (32-bit or 64-bit)
If you are running any edition of Windows 7, you must also have .NET Framework 4.5 installed. Windows 8 and later versions of Windows include at least .NET Framework 4.5.
The Microsoft Support and Recovery Assistant offers the best solution for these identified problems:
I get an error when I install Office
I can’t activate Office
I need to uninstall Office
Outlook won’t start
I can’t setup my Microsoft 365 email in Outlook
Outlook keeps asking for my password
Outlook keeps saying «Trying to connect. » or «Disconnected»
Shared mailboxes or shared calendars don’t work
I’m having problems with my calendar
Outlook stops responding
Outlook keeps crashing
I can’t send, receive, or find email
OneDrive for Business
I can’t sync my files with OneDrive
I can’t install OneDrive
Other Office apps
I can’t sign into Skype for Business
I can’t get email on my phone
I’m having trouble opening or signing in to Outlook on the web
I can’t install, connect, or enable Dynamics 365 for Outlook
The Teams Meeting option isn’t shown or the Teams Meeting add-in doesn’t load in Outlook
There are additional scenarios for Outlook on the web, Outlook for Mac, and Mobile devices, plus advanced diagnostics for Exchange Online and Outlook.
The Microsoft Support and Recovery Assistant offers automated fixes for many of the issues it detects. If you elect to perform an automated fix, the recovery actions that are performed by the fix are entered into the log file created by the Microsoft Support and Recovery Assistant. To view this log file and the recovery actions performed during a scenario, please follow these steps.
On the last screen of the scenario, check Open the log file folder after clicking Submit, complete the survey, and then select Submit.
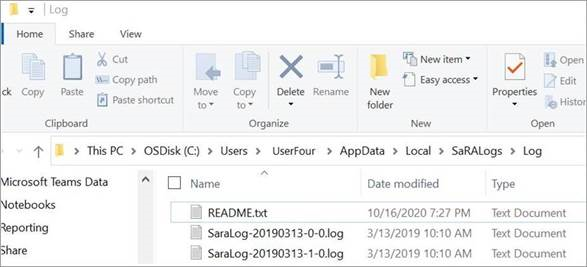
In the pop-up window, open the most recently created log file.
Search the log file for «Recovery,».
Repeat the search for «Recovery,» until you reach the end of the log file.
Note: The README.txt file includes a link to this article.
No. The following troubleshooting scenarios in the app can be run without a Microsoft account, or the work or school account you use with Office:
Outlook Advanced Diagnostics
Yes. If you’re an administrator and want to install and start the Microsoft Support and Recovery Assistant from a shared location on a network instead of the default internet location don’t use the download link in this article. Instead, follow the steps in this article on docs.microsoft.com: How to install and maintain Microsoft Support and Recovery Assistant (SaRA) from a network share.
We’re sorry, but we don’t have a version of the Microsoft Support and Recovery Assistant that can be installed on a Mac. However, the Outlook for Mac scenario in the app can troubleshoot some issues that occur on your Mac even though the app is installed on a Windows PC.
Yes. You’ll need an internet connection to download, install, and use the Microsoft Support and Recovery Assistant.
To uninstall the app from your computer, follow these steps:
Open the Control Panel.
Click Uninstall a Program.
Locate and select Microsoft Support and Recovery Assistant.
Select Remove the application from this computer, and then click OK.
When you reach the end of a scenario in the app you’re shown a screen where you’re asked if we fixed your problem. Select any of the top three options to have the remaining questions in the screen displayed. You can enter your feedback into the box at the bottom of the screen.
When you run the Microsoft Support and Recovery Assistant (SaRA) to identify or diagnose a particular issue, SaRA records anonymous information (Telemetry) about the actions and analysis that are performed by SaRA when a scenario is run. Microsoft uses the telemetry data to improve customer experiences and to monitor the health of the application. The amount of telemetry data collected differs with different scenarios.
A copy of the telemetry information is saved in a local log file by SaRA. To view the log file, follow these steps:
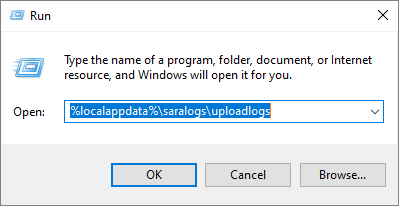
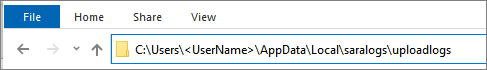
Telemetry data is collected and uploaded to the uploadlogs folder in the Local Disk ( C:). To access this folder, use one of the following methods:
Open the Run Command window ( Windows logo key + R,) and run the %localappdata%\saralogs\uploadlogs command as follows:
In File Explorer, type C:\Users\ \AppData\Local\saralogs\uploadlogs and press Enter as follows:
Note: is your Windows profile name in the system.
To view the information about a log file, double-click and open the file. For each scenario, a separate log file will be created and uploaded as the SaraTelemetry_ .log format.
The log files include comprehensive information such as SessionID, TimeStamp, and Office applications on the affected system. The collected information is completely anonymous, and it does not trace back to you in any form. The following is the definition of some fields that are collected as part of the telemetry data:
User GUID: A random GUID that is stored in SaRA settings. It may be used to identify usage trends of the Office application while keeping the data anonymous.
Client launch ID: A random GUID that is generated when the application is running.
Tenant ID: Represent the Office 365 Tenant information about the organization that is associated with this ID.