- Увеличить Max Open File Limit в Unix/Linux
- Увеличить Max Open File Limit в Unix/Linux
- Увеличить Max Open File Limit в Unix/Linux
- Увеличить Max Open File Limit в Linux
- Увеличить Max Open File Limit в Mac OS X
- Увеличюем nginx worker_rlimit_nofile в nginx ( на уровне Nginx)
- Включение ограничений на основе PAM в Unix/Lixux
- How to Increase Number of Open Files Limit in Linux
- Find Linux Open File Limit
- Check Hard Limit in Linux
- Check Soft Limits in Linux
- How to Check System wide File Descriptors Limits in Linux
- Set User Level Open File limits in Linux
- Final thoughts
- If You Appreciate What We Do Here On TecMint, You Should Consider:
- Исправляем ошибку “Too many open files“ в Linux
- Ошибка: Too many open files и лимиты на количество открытых файлов в Linux
- Настройки лимитов ограничения на количество одновременно открытых файлов в Linux
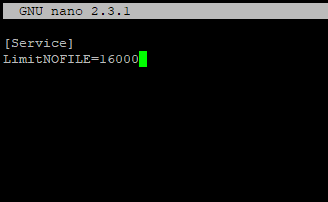
- Увеличить лимита открытых файловых дескрипторов для отдельного сервиса
- Увеличение максимального количества открытых файлов для Nginx и Apache
- Лимиты file-max для текущей сессии
- How to set ulimit and file descriptors limit on Linux Servers
- To see what is the present open file limit in any Linux System
- ulimit command :
- How to fix the problem when limit on number of Maximum Files was reached ?
- Set User level resource limit via limit.conf file
Увеличить Max Open File Limit в Unix/Linux
Увеличить Max Open File Limit в Unix/Linux
Несколько раз я сталкивался с ошибкой «Too many open files»(Слишком много открытых файлов) на сервере с высокой нагрузкой. Это означает, что сервер исчерпывает ресурс на максимальный предел открытых файлов (max open file limit). Теперь вопрос в том, как я могу увеличить лимиты открытых файлов на Linux? Да все очень просто, в своей статье «Увеличить Max Open File Limit в Unix/Linux» покажу как это выполняется.
Увеличить Max Open File Limit в Unix/Linux
Приведу команды на различные Unix/Linux ОС
Увеличить Max Open File Limit в Linux
Для начала проверим какой предел установлен в ОС:
Увеличиваем данный предел в Linux
Мы можем увеличить лимиты для открытых файлов:
-===ВРЕМЕННО===-
Если есть необходимость увеличить лимит временно (для тестирования, например), то можно это сделать так:
Вот еще один пример:
-===ПОСТОЯННО===-
Если есть необходимость увеличить лимит навсегда, то можно это сделать так:
Эти настройки будут сохраняться даже после перезагрузки системы. После добавления конфигурации в файл, выполните следующую команду, чтобы изменения вступили в силу:
Настройка лимитов для каждого пользователя
Проверка установленных лимитов
Используйте следующую команду, чтобы увидеть максимальное чисто для открытых файлов:
Подключаемся от пользователя (у меня это nginx):
Проверяем параметры Hard лимитов :
В консоле, можно ввести данную команду (очень удобно отображает):
Проверяем параметры лимитов Soft :
Увеличить Max Open File Limit в Mac OS X
Выполним проверку лимитов с помощью:
- Первый аргумент — soft limit.
- Второй аргумент — hard limit.
Можно прописать в файл:
Увеличюем nginx worker_rlimit_nofile в nginx ( на уровне Nginx)
В nginx также можно увеличить лимиты с директивой worker_rlimit_nofile, которая позволяет увеличить этот лимит, если это не хватает данного ресурса на лету на уровне процесса:
И прописываем (редактируем):
После чего, проверяем конфигурацию nginx и перезапускаем его:
Save and close the file. Reload nginx web server, enter:
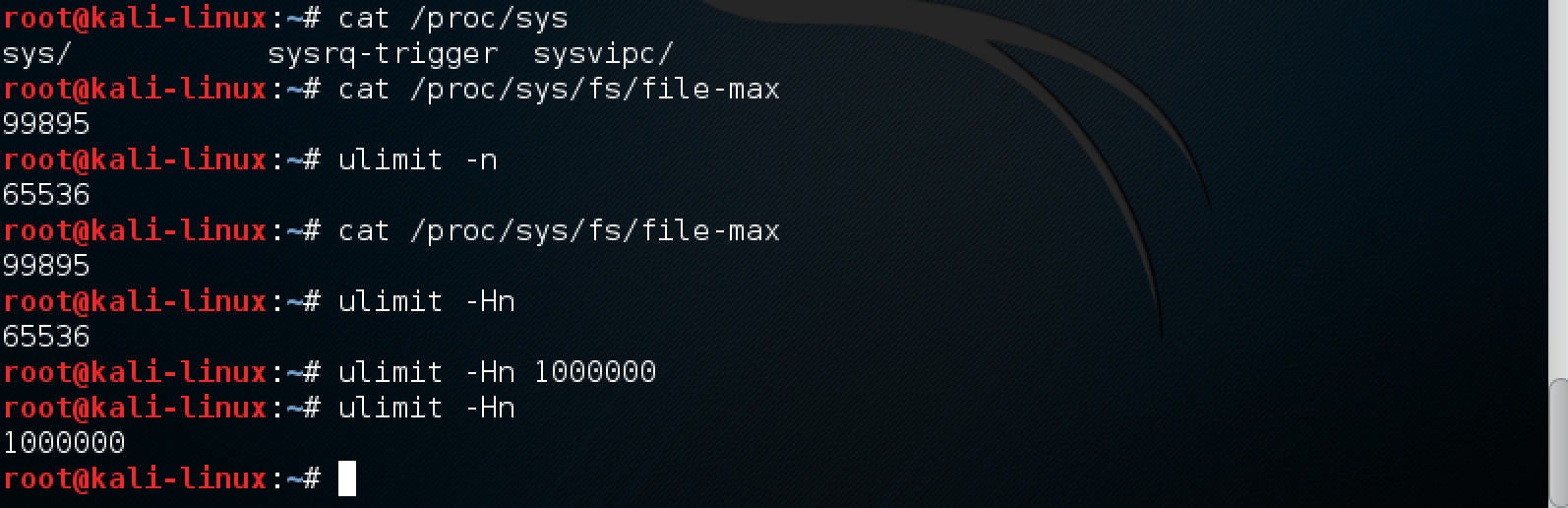
В комментариях писали что нельзя установить данные лимиты для Kali Linux. Вот, решил показать наглядный пример:
ulimit в Kali Linux
Включение ограничений на основе PAM в Unix/Lixux
Для Debian/Ubuntu
Редактируем файл (Debian/Ubuntu):
Открываем еще один файл:
И, приводим к виду:
И выполняем рестарт:
Для CentOS/RedHat/Fedora
Редактируем файл (Debian/Ubuntu):
Открываем еще один файл:
И, приводим к виду:
И выполняем рестарт:
У меня все! Статья «Увеличить Max Open File Limit в Unix/Linux», завершено.
Источник
How to Increase Number of Open Files Limit in Linux
In Linux, you can change the maximum amount of open files. You may modify this number by using the ulimit command. It grants you the ability to control the resources available for the shell or process started by it.
In this short tutorial we will show you how to check your current limit of open files and files descriptions, but to do so, you will need to have root access to your system.
First, Lets see how we can find out the maximum number of opened file descriptors on your Linux system.
Find Linux Open File Limit
The value is stored in:
The number you will see, shows the number of files that a user can have opened per login session. The result might be different depending on your system.
For example on a CentOS server of mine, the limit was set to 818354, while on Ubuntu server that I run at home the default limit was set to 176772.
If you want to see the hard and soft limits, you can use the following commands:
Check Hard Limit in Linux
Check Soft Limits in Linux
To see the hard and soft values for different users, you can simply switch user with “su” to the user which limits you want to check.
How to Check System wide File Descriptors Limits in Linux
If you are running a server, some of your applications may require higher limits for opened file descriptors. A good example for such are MySQL/MariaDB services or Apache web server.
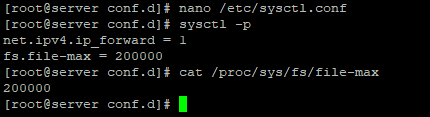
You can increase the limit of opened files in Linux by editing the kernel directive fs.file-max . For that purpose, you can use the sysctl utility.
For example, to increase open file limit to 500000, you can use the following command as root:
You can check the current value for opened files with the following command:
With the above command the changes you have made will only remain active until the next reboot. If you wish to apply them permanently, you will have to edit the following file:
Add the following line:
Of course, you can change the number per your needs. To verify the changes again use:
Users will need to logout and login again for the changes to take effect. If you want to apply the limit immediately, you can use the following command:
Set User Level Open File limits in Linux
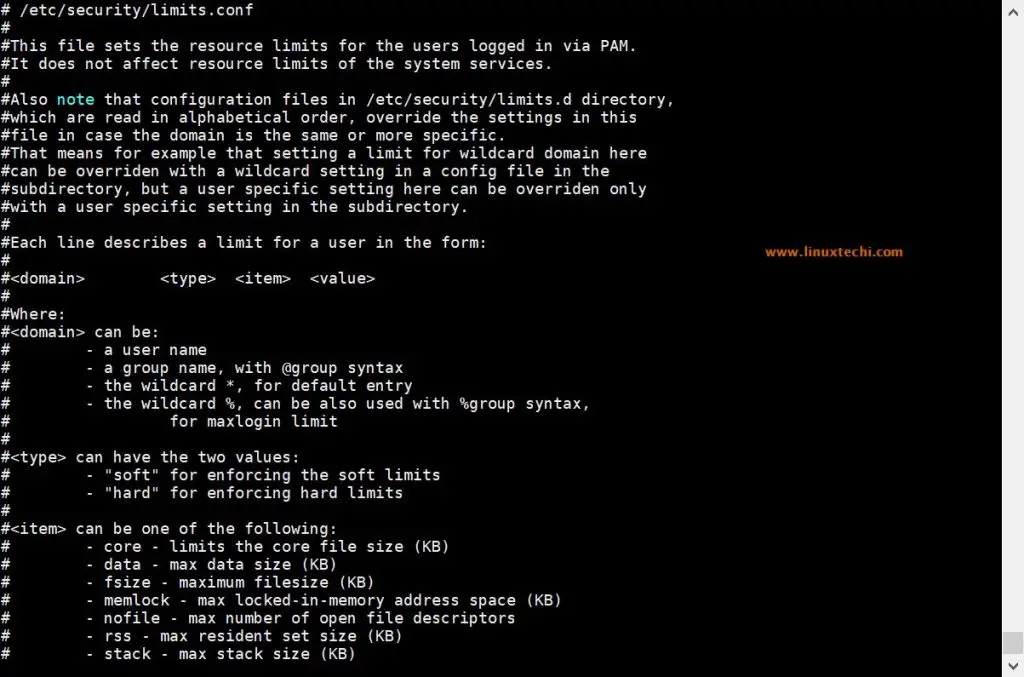
The above examples, showed how to set global limits, but you may want to apply limits per user basis. For that purpose, as user root, you will need to edit the following file:
If you are a Linux administrator, I suggest you that you become very familiar with that file and what you can do to it. Read all of the comments in it as it provides great flexibility in terms of managing system resources by limiting users/groups on different levels.
The lines that you should add take the following parameters:
Here is an example of setting a soft and hard limits for user marin:
Final thoughts
This brief article showed you a basic example of how you can check and configure global and user level limits for maximum number of opened files.
While we just scratched the surface, I highly encourage you to have a more detailed look and read regarding /etc/sysctl.conf and /etc/security/limits.conf and learn how to use them. They will be of great help for you one day.
If You Appreciate What We Do Here On TecMint, You Should Consider:
TecMint is the fastest growing and most trusted community site for any kind of Linux Articles, Guides and Books on the web. Millions of people visit TecMint! to search or browse the thousands of published articles available FREELY to all.
If you like what you are reading, please consider buying us a coffee ( or 2 ) as a token of appreciation.
We are thankful for your never ending support.
Источник
Исправляем ошибку “Too many open files“ в Linux
Очень часто при работе на высоконагруженных Linux серверах могут возникать ошибки “too many open files». Это означает, что программа открыла слишком много файлов (читай файловых дескрипторов) и не может открыть новые. В Linux ограничения “max open file limit“ установлены по умолчанию для каждого процесса и пользователя, и они не слишком высокие.
В данной статье мы рассмотрим, как проверить текущие ограничения по количеству открытых файлов, как его изменить эту настройку для всего сервера, для отдельных сервисов и для сеанса.
Ошибка: Too many open files и лимиты на количество открытых файлов в Linux
Для начала разберемся, где мы можем наблюдать ошибку “too many open files“. Чаще всего эта ошибка встречается на серверах с установленным веб-серверов NGINX/httpd, сервером БД (MySQL/MariaDB/PostgreSQL), при чтении большого количества логов. Например, когда веб-серверу Nginx не хватает лимита для открытия файлов, вы получите ошибку:
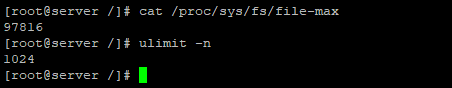
Максимально количество файловых дескрипторов, которые могут быть открыты в вашей системе можно узнать так:
Ограничение на количество открытых файлов для текущего пользователя – 1024. Можно проверить так:
Есть два типа ограничений: Hard и Soft. Пользователь может изменить лимит для soft ограничения (но значение soft не может превышать hard). Hard ограничение можно изменить только от привилегированного пользователя.
Для вывода Soft -граничения выполните:
Для вывода Hard-ограничения:
Настройки лимитов ограничения на количество одновременно открытых файлов в Linux
Чтобы разрешить всем сервисам открывать большее количество файлов, можно изменить лимиты на уровне всей ОС Linux. Чтобы новые настройки работали постоянно и не сбрасывались при перезапуске сервера или сессии, нужно поправить файл /etc/security/limits.conf. Добавьте строки:
Ели вы используете Ubuntu, нужно прописать строку:
Данный параметр добавляет возможность загрузки ограничений при авторизации пользователя.
После изменений, перезапустите терминал и проверьте значение лимита max_open_files:
Увеличить лимита открытых файловых дескрипторов для отдельного сервиса
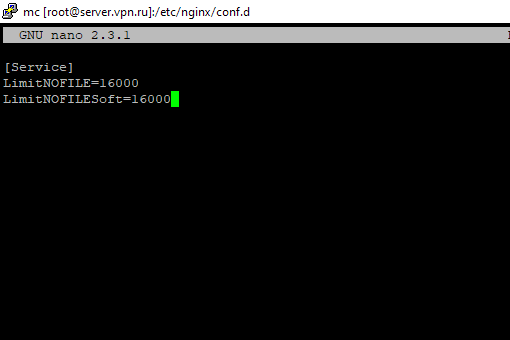
Вы можете изменить лимит на количество открытых файловых дескрипторов для конкретного сервиса, а не для всей системы. Рассмотрим на примере apache. Чтобы изменить значения, откройте настройки службы через systemctl: # systemctl edit httpd.service Добавьте необходимые лимиты, например:
После изменения, нужно обновить конфигурацию сервиса и перезапустить его:
# systemctl daemon-reload
# systemctl restart httpd.service
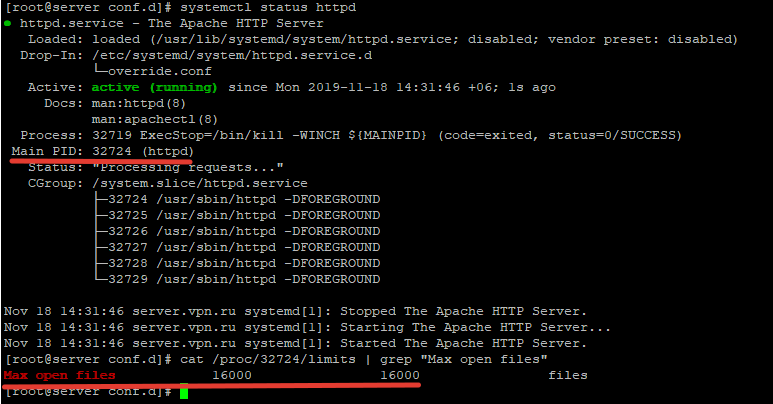
Чтобы проверить, изменились ли значения, нужно получить PID сервиса:
# systemctl status httpd.service
Например, вы определил PID сервиса 32724:
# cat /proc/32724/limits | grep «Max open files”
Так вы изменили значения Max open files для конкретного сервиса.
Увеличение максимального количества открытых файлов для Nginx и Apache
При изменении ограничения на количество открытых файлов для веб-сервера, нужно также поправить конфигурационный файл службы. Например, для Nginx в файле конфигурации /etc/nginx/nginx.conf, нужно прописать/изменить значение в директиве:
После чего выполнить рестарт Nginx.
Для apache, нужно создать директорию:
После этого создайте файл limit_nofile.conf:
И добавьте в него:
Не забудьте перезапустить сервис httpd.
Лимиты file-max для текущей сессии
Чтобы изменить лимиты на открытые файлы в рамках вашей сессии терминала, выполните команду:
При закрытии терминала и создания новой сессии, лимиты вернуться к начальным значениям, указанным в файле /etc/security/limits.conf.
Чтобы изменить общее значение в системе /proc/sys/fs/file-max, измените значение fs.file-max в /etc/sysctl.conf:
В данной статье мы разобрались, как решить проблему с недостаточным лимитом для открытых файловых дескрипторов в Linux и рассмотрели несколько вариантов изменения лимитов на сервере.
Источник
How to set ulimit and file descriptors limit on Linux Servers
Introduction: Challenges like number of open files in any of the production environment has become common now a day. Since many applications which are Java based and Apache based, are getting installed and configured, which may lead to too many open files, file descriptors etc. If this exceeds the default limit that is set, then one may face access control problems and file opening challenges. Many production environments come to standstill kind of situations because of this.

Luckily, we have “ulimit” command in any of the Linux based server, by which one can see/set/get number of files open status/configuration details. This command is equipped with many options and with this combination one can set number of open files. Following are step-by-step commands with examples explained in detail.
To see what is the present open file limit in any Linux System
To get open file limit on any Linux server, execute the following command,
The above number shows that user can open ‘146013’ file per user login session.
This clearly indicates that individual Linux operating systems have different number of open files. This is based on dependencies and applications which are running in respective systems.
ulimit command :
As the name suggests, ulimit (user limit) is used to display and set resources limit for logged in user.When we run ulimit command with -a option then it will print all resources’ limit for the logged in user. Now let’s run “ulimit -a” on Ubuntu / Debian and CentOS systems,
Ubuntu / Debian System,
CentOS System
As we can be seen here different OS have different limits set. All these limits can be configured/changed using “ulimit” command.
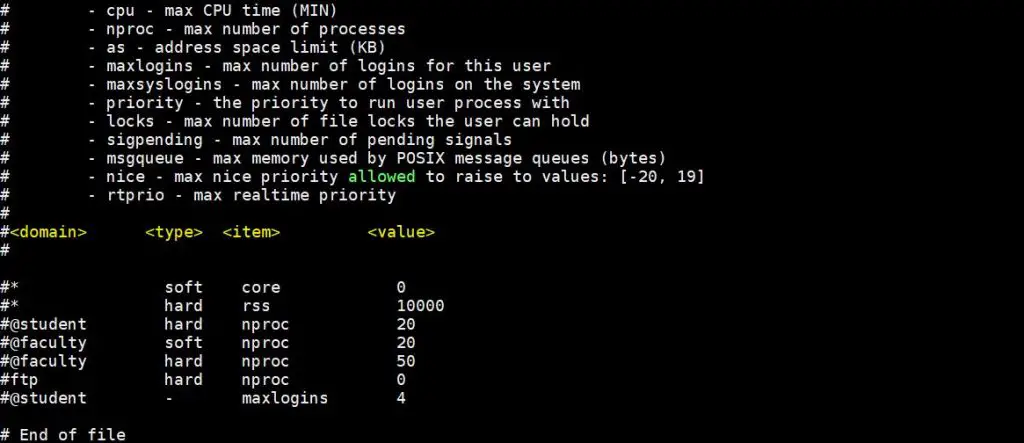
To display the individual resource limit then pass the individual parameter in ulimit command, some of parameters are listed below:
- ulimit -n –> It will display number of open files limit
- ulimit -c –> It display the size of core file
- umilit -u –> It will display the maximum user process limit for the logged in user.
- ulimit -f –> It will display the maximum file size that the user can have.
- umilit -m –> It will display the maximum memory size for logged in user.
- ulimit -v –> It will display the maximum memory size limit
Use below commands check hard and soft limits for number of open file for the logged in user
How to fix the problem when limit on number of Maximum Files was reached ?
Let’s assume our Linux server has reached the limit of maximum number of open files and want to extend that limit system wide, for example we want to set 100000 as limit of number of open files.
Use sysctl command to pass fs.file-max parameter to kernel on the fly, execute beneath command as root user,
Above changes will be active until the next reboot, so to make these changes persistent across the reboot, edit the file /etc/sysctl.conf and add same parameter,
save and exit file,
Run the beneath command to make above changes into effect immediately without logout and reboot.
Now verify whether new changes are in effect or not.
Use below command to find out how many file descriptors are currently being utilized:
Note:- Command “sysctl -p” is used to commit the changes without reboot and logout.
Set User level resource limit via limit.conf file
“/etc/sysctl.conf” file is used to set resource limit system wide but if you want to set resource limit for specific user like Oracle, MariaDB and Apache then this can be achieved via “/etc/security/limits.conf” file.
Sample Limit.conf is shown below,
Let’s assume we want to set hard and soft limit on number of open files for linuxtechi user and for oracle user set hard and soft limit on number of open process, edit the file “/etc/security/limits.conf” and add the following lines
Save & exit the file.
Note: In case you want to put resource limit on a group instead of users, then it can also be possible via limit.conf file, in place of user name , type @ and rest of the items will be same, example is shown below,
Verify whether new changes are in effect or not,
Note: Other majorly used command is “ lsof ” which is used for finding out “how many files are opened currently”. This command is very helpful for admins.
Conclusion:
As mentioned in the introduction section “ulimit” command is very powerful and helps one to configure and make sure application installations are smoother without any bottlenecks. This command helps in fixing many of the number of file limitations in Linux based servers.
Источник