- Что такое шебанг (shebang) в Bash
- Директива переводчика Shebang
- Использование Shebang в сценариях Bash
- Пример сценария
- Преодоление Шебанга
- Выводы
- What is the Function of Shebang in Linux?
- python_script
- r_script
- How to make executable file
- python_script
- Large computer cluster
- What is Shebang in Linux Shell Scripting?
- What is shebang in shell scripting?
- Why the shebang matters in shell scripting?
- Importance of specifying shell interpreter with shebang
- Shebang is ignored if you explicitly specify shell
- How exactly the shebang work?
- Conclusion
- Использование Shebang в оболочке Bash
- Директива интерпретатора Shebang
- Использование Shebang в скриптах Bash
- Пример скрипта
- Переопределение Shebang
- Заключение
- Shebang
- Contents
- Starting a Script With #!
- Ignoring An Interpreter Line (shebang)
- /bin/sh
- An example of /bin/sh script
- /usr/bin/env bash
Что такое шебанг (shebang) в Bash
Если вы изучаете сценарии Bash, читая чужой код, вы могли заметить, что первая строка в сценариях начинается с символа #! символы и путь к интерпретатору Bash.
Эта последовательность символов ( #! ) Называется shebang и используется для указания операционной системе, какой интерпретатор использовать для анализа остальной части файла.
Директива переводчика Shebang
Директива интерпретатора Shebang имеет следующую форму:
- Директива должна быть первой строкой в скрипте.
- Директива должна начинаться с shebang #!
- Пробел после символов shebang необязателен.
- Интерпретатор — это полный путь к двоичному файлу (например, /bin/sh , /bin/bash ).
- Аргументы интерпретатора необязательны.
- #!/bin/bash — использует bash для анализа файла.
- #!/usr/bin/env perl — Использует команду env для поиска пути к исполняемому файлу perl .
- #!/usr/bin/python Выполняет файл с использованием двоичного файла python .
Использование Shebang в сценариях Bash
Если shebang не указан и пользователь, выполняющий сценарий Bash, использует другую оболочку, сценарий будет проанализирован любым интерпретатором по умолчанию, используемым этой оболочкой. Например, интерпретатором по умолчанию для bash является bash а для zsh — sh . Чтобы ваш скрипт всегда интерпретировался с помощью Bash, вам необходимо указать путь к исполняемому файлу с помощью shebang.
Есть два способа использовать директиву Shebang и установить интерпретатор.
- Используя абсолютный путь к двоичному файлу bash:
Преимущество использования второго подхода заключается в том, что он будет искать исполняемый файл bash в $PATH окружения $PATH . Если существует более одного пути к bash , скрипт будет использовать первый из них.
При использовании первого параметра для добавления параметра в оболочку Bash передайте его интерпретатору. Например, чтобы запустить сценарий в режиме отладки, вы должны использовать #!/bin/bash -x . Если вы используете метод env вам нужно использовать set для объявления опции. Чтобы включить режим отладки, вы должны добавить set -x после строки shebang.
Пример сценария
Давайте создадим простой скрипт с помощью shebang, который напечатает «Hello, World». Откройте текстовый редактор и вставьте следующую строку:
Чтобы иметь возможность запускать скрипт без указания интерпретатора из командной строки, вам необходимо сделать файл исполняемым :
Теперь, если вы можете запустить сценарий, набрав ./ а затем имя сценария:
Преодоление Шебанга
Если по какой-то причине вы хотите переопределить интерпретатор, установленный в строке Shebang, вам необходимо запустить сценарий, явно указав желаемую оболочку.
Например, чтобы запустить сценарий, в котором #!/bin/sh указан в строке Shebang, используя оболочку bash вы должны ввести:
Учтите, что переопределять интерпретатор оболочки не рекомендуется, поскольку это может привести к неожиданному поведению сценария.
Выводы
К настоящему времени вы должны хорошо понимать, что такое Shebang и как использовать его в ваших сценариях Bash.
Если у вас есть какие-либо вопросы или отзывы, не стесняйтесь оставлять комментарии.
Источник
What is the Function of Shebang in Linux?
The #! characters form a magic number. We embed these magic number in any scripts under UNIX / Linux operating systems to tell the kernel what interpreter to execute, to read our script. Like Linux shell, Python, Perl and R interpreters. You might have noticed all Linux shell and Perl / python script starts with the below line:
Now we will write a program file for Python language. we can execute this program by calling the interpreter directly without adding shebang line like below.
python_script
For executing the code, we will mention python before name of the file.
Also we will write a program file for R language. we can execute this program by calling the interpreter directly without adding shebang line like below.
r_script
For executing the code, we will mention Rscript before name of the file.
How to make executable file
to make executable file we should add shebang line #!/usr/bin/python to the top of script and changing the mode of the file to be executable.
python_script
To make the file is executable, type the command below.
Now we can just run the file and it will be interpreted by python.
Large computer cluster
The path /usr/bin/python will probably work for most default systems but might not work on things like a large computer cluster. So we will use the program env to get the right interperter.
We can do the same for any program like Rscript as well.
Источник
What is Shebang in Linux Shell Scripting?
You’ll often come across shell scripts that start with:
This #! is called shebang or hashbang. The shebang plays an important role in shell scripting, specially while dealing with different types of shell.
In this tutorial, you’ll learn:
- What is Shebang?
- How does it play an important role in shell scripting?
What is shebang in shell scripting?
The shebang is the combination of the # (pound key) and ! (exclamation mark). This character combination has a special meaning when it is used in the very first line of the script. It is used to specify the interpreter with which the given script will be run by default.
So, if the first line of a script is:
It means the interpreter should be bash shell. If the first line is:
It means the interpreter to be used is Z shell.
The #! is surely special because # is used for comments in shell scripts but here it has a special meaning.
Why the shebang matters in shell scripting?
Here’s the thing. The shebang followed by the executable of the shell is not mandatory for a script.
If you write a simple script like this:
And give it execute permission and run it with the . operator, it will be run by your login shell.
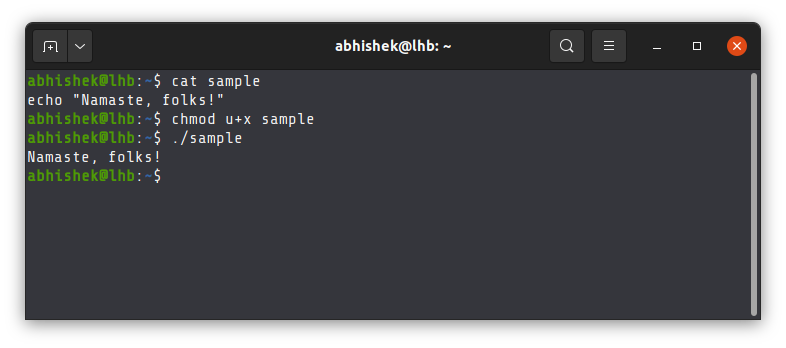
Then why do shell scripts include #!/bin/bash line at the beginning of the script?
Because there are several shells available for Linux and UNIX systems. While these shells have mostly common syntax, they do have different syntax or different way of handling things.
This is why it becomes important to specify the correct shell interpreter in the script, otherwise some scripts may produce different results when run in different shells.
Let me show that to you with a simple example.
Importance of specifying shell interpreter with shebang
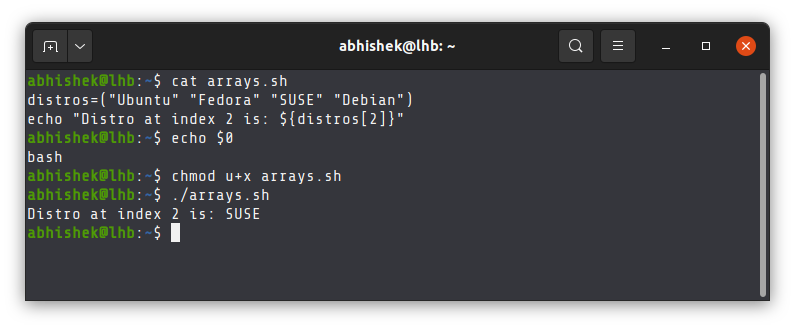
I have written a sample shell script with an array of distributions. The script then displays the distro at index 2.
I have not added the shebang line to specify any shell interpreter. This means when I execute this script, it will be run by the default shell (bash in my case):
Can you guess the output of the script?
It shows SUSE at index 2 because array index start at 0 in Bash and many other programming and scripting languages. BUT that’s not the case in Z shell. In Z shell, array index starts at 1.
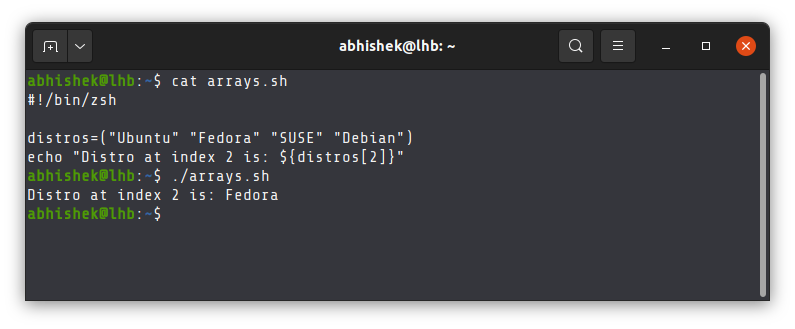
I have Z shell installed on my system. I change the script and add the shebang line to specify that the script should be run by Z shell by default.
Can you guess the output when I run the script now?
Do you notice the difference now? It’s the same script but the addition of the shebang line made the difference.
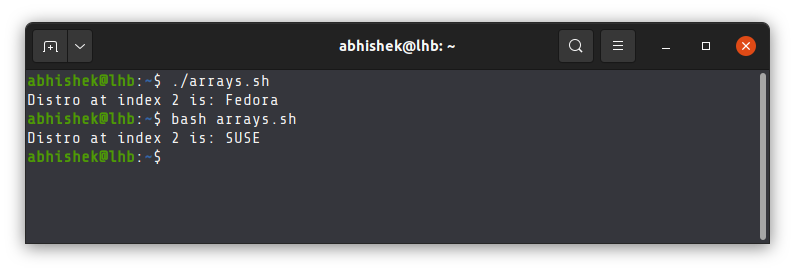
And this is why specifying the correct shell interpreter with shebang operator is important. As a sysadmin, you might write shell scripts keeping a specific shell in mind, be it bash, ksh or zsh. But you cannot be sure that the system that will run the script will have the same default shell as yours. Now things make sense, right?
Shebang is ignored if you explicitly specify shell
Why am I stressing on «default» shell? Because the shebang specifies the interpreter to run the script with.
You may, however, specify the shell explicitly and in such cases, the shebang line will be ignored.
How exactly the shebang work?
When you use the shebang in the first line of a script, you are telling the shell to run the given script with the specified command.
Basically, #!/bin/zsh is equivalent to:
I have told you that if the first line of a script starts with shebang, it means you are specifying the shell interpreter.
That’s only partially true. Actually, that’s the purpose of the shebang character. But it’s not necessary that shebang line must have executable of a shell. It can be anything.
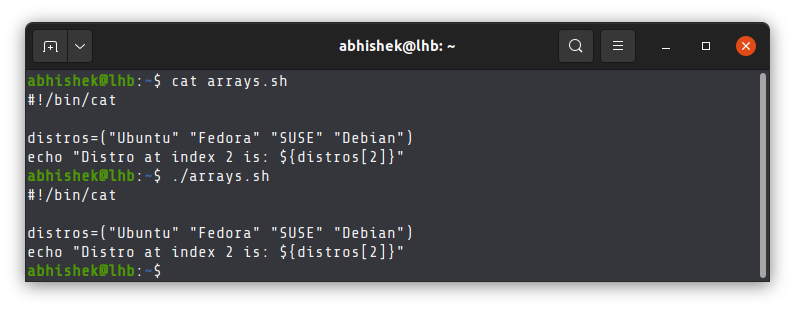
For example, I am going to replace #!/bin/zsh with #!/bin/cat . /bin/cat is the executable of the cat command.
This means that now this script will run with cat command and display the content of the script.
It will work as long as it points to an executable command. If you put some random stuff, it will throw error.
I change the shebang line to:
Clearly, it does not point to the executable of any command and thus it throws a bad interpreter error.
Conclusion
Let me answer a few more questions before ending this article:
- It is important that there is no space between # and ! . You CANNOT use it like this: # !/bin/bash .
- Most system allow special between #! and /bin/bash however it is a good practice to avoid space between #! and /bin/bash .
- #! has to be on the first line, otherwise the shebang line will be treated as comment. You cannot even have a blank line before it.
I hope you have a better understand on why #! is used in the beginning of shell scripts in Linux. Feel free to leave a comment if you have questions or suggestions.
Источник
Использование Shebang в оболочке Bash
Эта последовательность символов ( #!) называется shebang и используется, чтобы сообщить операционной системе, какой интерпретатор использовать для анализа остальной части файла.
Директива интерпретатора Shebang
Директива интерпретатора Shebang имеет следующий вид:
- Директива должна быть первой строкой в скрипте.
- Директива должна начинаться с Shebang #!
- Пробел после символов Shebang не является обязательным.
- Интерпретатор – это полный путь к двоичному файлу (например /bin/sh, /bin/bash).
- Аргументы интерпретатора являются необязательными.
- #!/bin/bash- Использует bash для разбора файла.
- #!/usr/bin/env perl- Использует команду env, чтобы найти путь к исполняемому файлу perl.
- #!/usr/bin/python – Выполняет файл, используя двоичный файл python.
Использование Shebang в скриптах Bash
Если shebang не указан и пользователь, выполняющий сценарий Bash, использует другую оболочку, сценарий будет проанализирован любым интерпретатором по умолчанию, который используется этой оболочкой. Например, интерпретатор по умолчанию для bashis bash и for zshis sh. Чтобы ваш скрипт всегда интерпретировался с помощью Bash, вам необходимо указать путь к исполняемому файлу с помощью shebang.
Есть два способа использовать директиву Shebang и установить интерпретатор.
- Используя абсолютный путь к двоичному файлу bash:
Используя утилиту env:
Преимущество использования второго подхода состоит в том, что он будет искать исполняемый файл bash в пользовательской переменной среды $PATH. Если существует более одного пути bash, первый будет использоваться сценарием.
При использовании первой опции для добавления опции в поставку оболочки Bash передайте ее интерпретатору. Например, чтобы запустить скрипт в режиме отладки, вы бы использовали #!/bin/bash -x. Если вы используете метод env, вам нужно использовать set для объявления опции. Чтобы включить режим отладки, вы должны добавить set -x после строки shebang.
Пример скрипта
Давайте создадим простой скрипт с использованием shebang, который выведет «Hello, World». Откройте ваш текстовый редактор и вставьте следующую строку:
Чтобы иметь возможность запускать скрипт без указания интерпретатора из командной строки, вам нужно сделать файл исполняемым:
Теперь, если вы можете запустить скрипт, набрав ./ после имени скрипта:
Переопределение Shebang
Если по какой-то причине вы хотите переопределить набор интерпретаторов в строке Shebang, вам нужно запустить скрипт, явно указав требуемую оболочку.
Например, чтобы запустить сценарий, #!/bin/sh указанный в строке Shebang, с помощью оболочки bash, введите:
Обратите внимание, что не стоит переопределять интерпретатор оболочки, так как это может привести к неожиданному поведению скрипта.
Заключение
К настоящему времени вы должны хорошо понимать, что такое Shebang и как использовать его в ваших скриптах Bash.
Если у вас есть какие-либо вопросы или отзывы, не стесняйтесь оставлять комментарии.
Если вы нашли ошибку, пожалуйста, выделите фрагмент текста и нажмите Ctrl+Enter.
Источник
Shebang
The #! syntax used in scripts to indicate an interpreter for execution under UNIX / Linux operating systems. Most Linux shell and perl / python script starts with the following line:
Contents
Starting a Script With #!
- It is called a shebang or a «bang» line.
- It is nothing but the absolute path to the Bashinterpreter.
- It consists of a number sign and an exclamation point character (#!), followed by the full path to the interpreter such as /bin/bash.
- All scripts under Linux execute using the interpreter specified on a first line [1] .
- Almost all bash scripts often begin with #!/bin/bash (assuming that Bash has been installed in /bin)
- This ensures that Bash will be used to interpret the script, even if it is executed under another shell [2] .
- The shebang was introduced by Dennis Ritchie between Version 7 Unix and 8 at Bell Laboratories. It was then also added to the BSD line at Berkeley [3] .
Ignoring An Interpreter Line (shebang)
- If you do not specify an interpreter line, the default is usually the /bin/sh. But, it is recommended that you set #!/bin/bash line.
/bin/sh
For a system boot script, use /bin/sh:
sh is the standard command interpreter for the system. The current version of sh is in the process of being changed to conform with the POSIX 1003.2 and 1003.2a specifications for the shell.
An example of /bin/sh script
For a typical script use the #!/bin/bash shell.
/usr/bin/env bash
The /usr/bin/env run a program such as a bash in a modified environment. It makes your bash script portable. The advantage of #!/usr/bin/env bash is that it will use whatever bash executable appears first in the running user’s $PATH variable.
Источник