- 6 Best Free Linux Task Managers
- Use Task Manager Equivalent in Linux
- System Monitor: The Task Manager of Linux distributions
- Best Task Managers for Linux
- Pre-installed Task Managers
- Pstree
- Glances
- Conclusion
- About the author
- Nitesh Kumar
- 6 best task managers for Linux
- CLI-based Linux Task Managers
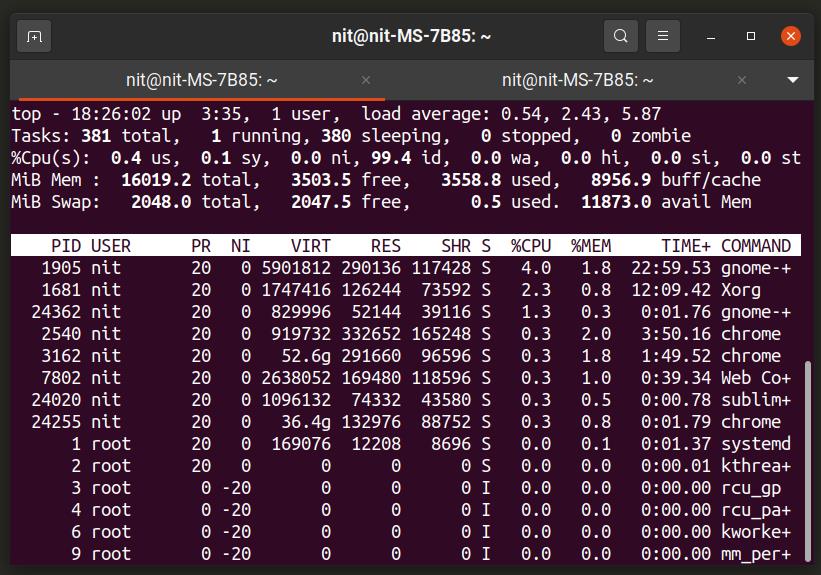
- 1. Top
- 2. Glances
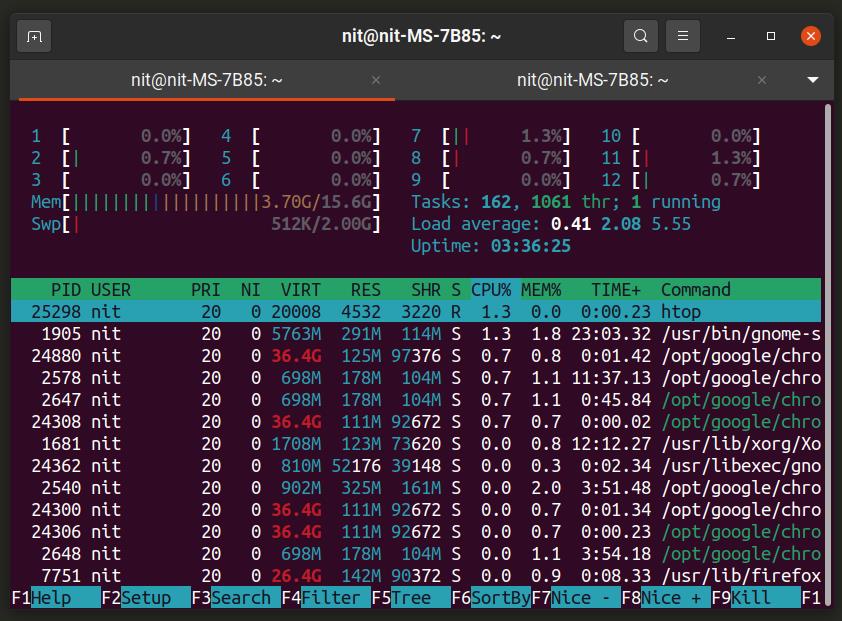
- 3. Htop
- GUI-based Linux Task Managers
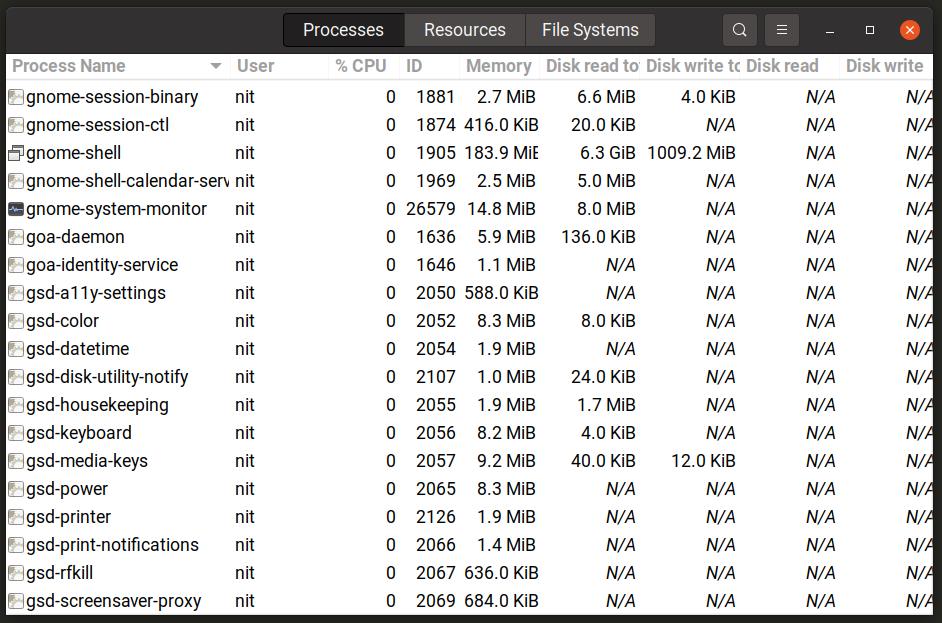
- 1. Gnome System Monitor
- 2. Mate System Monitor
- 3. KSysGuard
- Conclusion
6 Best Free Linux Task Managers
A task manager is software which enables users to compile a list of tasks to be completed. This list is also known as a to-do list or things-to-do. For the purposes of this article, the term ‘task manager’ should not be confused with monitoring software which provides information about programs and processes running on a computer.
The list of activities that may form a to-do list include chores, grocery lists, reminders for important events (such as purchasing wedding presents or birthday gifts), self management, software development, project / business management, and so on. Task managers help to organise your day, ensuring that you know in an instant what you need to do.
Linux has a large range of open source task managers, in part because many of them have a limited feature set and hence are relatively quick to code. This feature selects our personal favorites, including both console based applications and software sporting an attractive graphical user interface. There are also many web based task managers available, which we will cover in a forthcoming article.
To be productive, you may need more than a task manager. Our features on Productivity Tools and Personal Information Managers help to organize your day in other ways.
To provide an insight into the quality of software that is available, we have compiled a list of 6 proficient task managers. Hopefully, there will be something of interest here for anyone who wants to avoid that sinking feeling of remembering (albeit too late) something important that needs to be actioned. And this Group Test would not be complete without our legendary rating chart.
Now, let’s explore the 6 task managers at hand. For each title we have compiled its own portal page, a full description with an in-depth analysis of its features, screenshots, together with links to relevant resources.
Источник
Use Task Manager Equivalent in Linux
Last updated April 11, 2020 By Abhishek Prakash 9 Comments
These are some of the most frequently asked questions from Linux beginners: “Is there a task manager for Linux?” “How do you open the task manager on Linux?” “Where do I find the Ubuntu task manager?”
People who are coming from Windows know how useful the task manager is. You press Ctrl+Alt+Del to get to the task manager in Windows. This task manager shows you all the running processes and their memory consumption. You can choose to end a process from this task manager application.
When you’re just starting out with Linux, you may look for a task manager equivalent on Linux as well. An expert Linux user prefers the command-line way to find processes and memory consumption, etc., but you don’t have to go that way, at least not when you’re just starting out with Linux.
All the major Linux distributions have a task manager equivalent. Usually, it’s called System Monitor, but it actually depends on your Linux distribution and the desktop environment it uses.
In this article, we’ll see how to find and use the task manager on Ubuntu and other Linux distributions that use GNOME as the desktop environment.
System Monitor: The Task Manager of Linux distributions
If you’re using the GNOME desktop, press the Super key (Windows key) and look for System Monitor. In other desktop environments, search for System Monitor in the menu.
This will start the GNOME System Monitor. It shows you all the running processes and their memory consumption.
You can select a process and click on End process to kill it. You can also select multiple entries here and kill the processes in one click.
You can also see some statistics about your system in the Resources tab, such as CPU consumption per core basis, memory usage, network usage, etc.
You can watch this video to see it in action:
There are more ways to manage tasks
That was the graphical way. If you want to go the command line way, just run the top command in terminal and you can see all the running processes and their memory consumption. You can easily kill processes in the Linux command line.
If you want a command-line based task manager on Linux, I recommend using htop. You can see running processes, memory usage, and more, and you can easily use hotkeys to end processes. And it looks good as well.
This is all you need to know about task manager equivalents on Linux. I hope you found this quick tutorial helpful. If you have questions or suggestions, feel free to comment.
Like what you read? Please share it with others.
Источник
Best Task Managers for Linux
Top is a command line tool to show resource consumption of various processes and tasks running on your Linux system. It comes installed by default on almost all Linux distributions and it can show overall usage of system resources as well. It also features an option to tweak priority (niceness) of running processes. Top is really useful if you want to identify processes that are eating up system resources and if you want to do a comparison between different applications. Top presents data is in a nice tabular form.
To run Top, execute the following command:
You can learn more about Top using the following two commands:
Htop is a command line task manager that works similar to the “top” application mentioned above. However, it comes with a lot of extra features and interactivity that will allow you to use some advanced functions. Based on the ncurses library, Htop can also show you colored output for better readability. The bottom row in Htop shows keyboard shortcuts for changing settings and filtering the results. You can also use Htop to change resource consumption priority of processes.
You can install Htop in Ubuntu by using the command mentioned below:
Htop can be installed from the package manager shipped with your Linux distribution. You can also download it from its homepage.
To run Htop, use the following command:
You can learn more about Htop using the following two commands:
Pre-installed Task Managers
A dedicated task management utility is included in the application stack of most Linux based desktop environments. If you are using GNOME, KDE, Xfce, MATE, LXDE, and LXQt based desktop environments, you will get a task management tool available by default as a pre-installed application. You can run this tool from the application launcher to start managing the tasks. Usually you can find these task management applications by searching for the term “system monitor” or “task manager” in the application launcher and package manager of your Linux distribution.
If for some reason one of these these task managers are is not available by default on your Linux distribution, you can install it by searching for “KSysGuard”, “Gnome System Monitor”, “Mate System Monitor”, “LXTask”, “XFCE4 Task Manager” terms in the package manager.
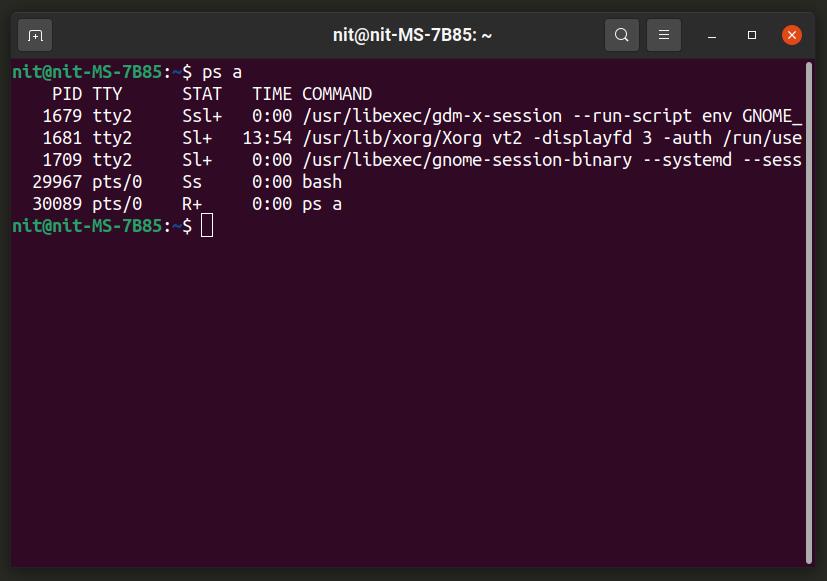
Ps is another useful tool that comes pre-installed by default on almost all Linux distributions. While it is not as advanced as Top and Htop, it is good enough if you just want to find the process ID (PID) of a certain task to further run any commands on it.
You won’t need to install “ps” in your Linux distribution. However, if for some reason it is not available, you can search for it in the package manager.
To run “ps”, use the following command (replace user name):
You can learn more about “ps” by using the following two commands:
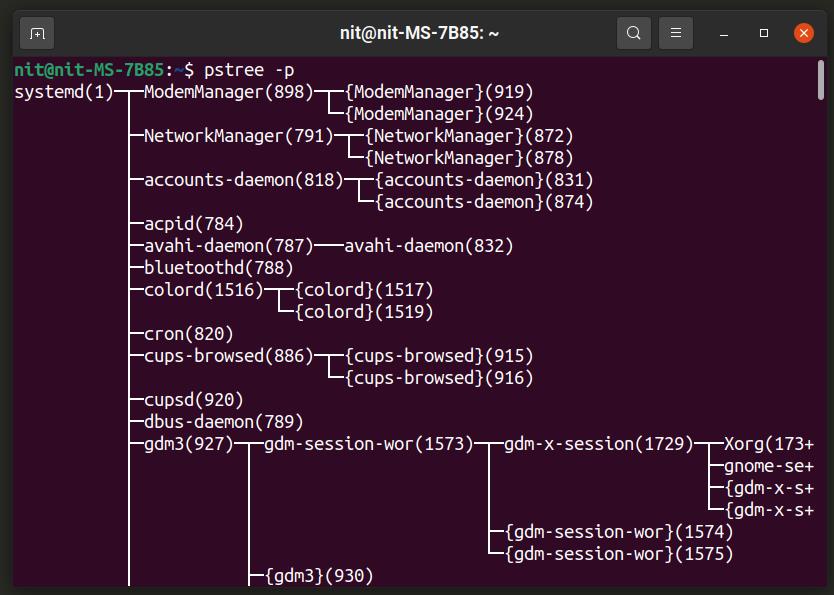
Pstree
Pstree works similar to the “ps” command, with a unique “tree view” feature . It can show processes and their child sub-processes in a tree format, allowing users to better monitor running tasks.
Pstree should come pre-installed on your Linux distribution. If not, then search for it in your package manager as it is included in repositories of all major Linux distributions.
To show processes and subprocesses along with their their process IDs, use the following command:
You can learn more about “pstree” using the following two commands:
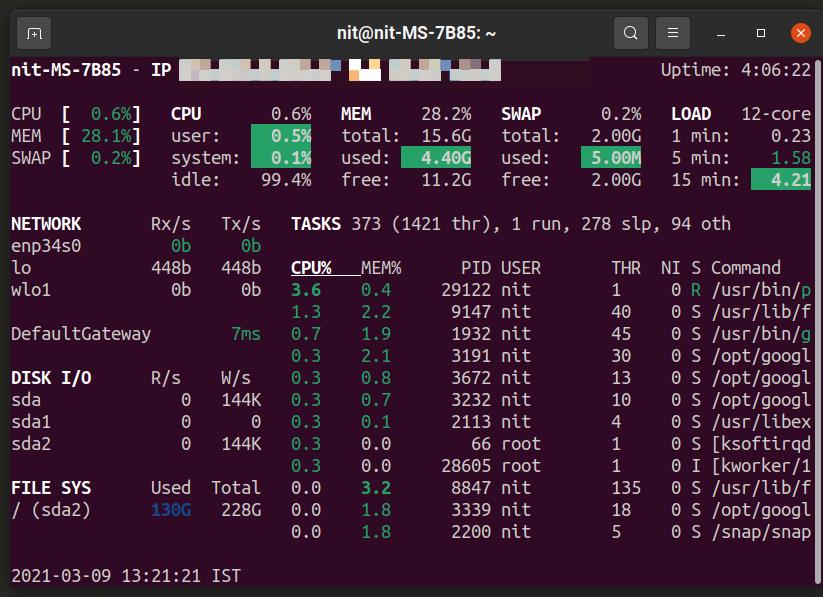
Glances
Glances is an open source and cross-platform process monitor tool written in Python. It features a ncurses and text based interface that can be viewed in a terminal emulator as well as a web based interface that can be viewed in any browser. The web based viewer requires a client-server setup, binaries for both are included in the official builds. Glances can show an overwhelming amount of information and it is much more powerful than other utilities mentioned in the article. You can customize it to show only limited information using its numerous command line options.
To install glances in Ubuntu, use the following command:
You can install Glances in other Linux distributions either from the package manager or you can follow official installation instructions available here.
To know more about Glances, using the following two commands:
Conclusion
Task management tools allow you to better control your system by providing useful information about resource consumption of individual processes. These tools are especially useful for system admins, application developers and gamers who routinely monitor process behavior.
About the author
Nitesh Kumar
I am a freelancer software developer and content writer who loves Linux, open source software and the free software community.
Источник
6 best task managers for Linux
Whether you need a tool for killing an unresponsive app or for monitoring what’s going on in your system, you need a task manager app. This article focuses on the best free and open-source task manager available for Linux.
O ne of the essential tools in any Linux distribution is a Task Manager. It is a system monitor application that gives you a report of all programs running on your computer and the status of your RAM and CPU usage.
It also comes in handy when you need to kill/stop freezing processes or applications that are consuming too many system resources. With advanced task-manager tools, you can even change the scheduling priority.
There are many Linux task manager programs available in the market today. Furthermore, every Linux distribution comes with a preinstalled task manager program depending on the Desktop environment.
We have both CLI (Command Line) and GUI task-manager programs. With CLI, these programs run on the Linux terminal and give you a full report of all running applications. You can stop running programs by running a command like “kill 13356”, which means ; kill a process with id 13356 . For GUI task-managers, these programs provide the user with an interactive graphical user interface.
In this post, we will look at both CLI based task-managers and GUI based task-managers.
CLI-based Linux Task Managers
Most Linux users like command-line tools. Since you don’t need to load a GUI, these tools consume fewer system resources and load much faster. Also, if you are a server admin, you need to use a CLI based task manager.
1. Top
“top” is one of the most common task managers used by Linux users. Unlike other tools, the top task-manager comes preinstalled on all Linux distributions. You can launch it by just typing the word “top” on the terminal. It gives you a dynamic view of all the programs running on the computer with other parameters like; user running the process, process-id, CPU usage, memory(RAM) utilization, and more. You can kill running processes using the kill command and PID (process id); kill -p 13356 or kill -9 13356 if it’s a persistent process.
To navigate up and down the top window, use (alt + k) to scroll up and (alt + j) to scroll down. For beginners, type the command “man top,” and it will give you all details and guidelines to using top.

2. Glances
“glances” is a cross-platform task manager written in python. It makes use of open architecture in that, and developers can add their custom plugins. Unlike most other system monitoring tools, glances make use of a client-server architecture, which enables remote monitoring of a system. It is achieved via an interactive web UI, terminal (command line), or through an API (XML-RPC and RESTful).
With glances, you can also view additional information like; upload and download internet speeds, Disk read and write details, and the mounted disks/drives.

Glances use different colors to list the process running with “red,” indicating a process consuming much of the system resources.
3. Htop
“htop” is quite similar to Top only with several additional features. Unlike Top, Htop allows you to scroll both vertically and horizontally. You can, therefore, view all running processes together with their command-line parameters.
Htop also makes use of several Function keys displayed at the bottom, with each one performing different tasks. To start this system monitoring tool, type the command “htop” in the command-line. You can also add different parameters to this command.
E.g., htop -u –user=USERNAME, shows only the process under a particular user.
Other popular CLI task managers available are ps and, pstree.

GUI-based Linux Task Managers
We have looked at some of CLI based task managers, now let’s put our focus on GUI based system monitor tools. These tools come with an interactive user interface that displays all activities taking place in the system.
1. Gnome System Monitor
This tool is one of the many software by GNOME family. It comes available with all Linux distributions that make use of the GNOME desktop. At the top of this application, there are three primary tabs, Processes, Resources, and File Systems. You can navigate around by clicking on any of these buttons.
GNOME gives system information like all running processes and their properties, CPU-Memory-Network and swap memory usage, mounted disks, and available space.

2. Mate System Monitor
Just like the GNOME system monitor, the Mate task manager is a default tool for any Linux distributions using the Mate desktop environment. It allows you to monitor and manage all running processes on your system. It also generates a general view on Memory usage, CPU utilization, and network usage.
With the Mate system monitor, you can identify processes and kill or stop them in case. You can also change process priority as you wish.

3. KSysGuard
KSysGuard is the default system monitor tool for the KDE desktop environment. It supports both GUI and CLI user interaction.
With its advanced Client/Server architecture, KSysGuard can be used to monitor the system on a remote machine. KSysGuard is regarded as a powerful task manager since you can kill/stop any persistent/problematic process with ease.

Conclusion
In this post, we looked at both CLI and GUI based task managers. For experienced Linux users and network/system administrators, you can use command-line based task-managers.
These tools have the advantage of not using much system resources, and some of the parameters used can be passed using scripts like bash or python. Otherwise, you can go for GUI-based task managers.
Источник