- Directory
- Overview of a directory and path
- Overview of a Linux directory path
- How do I list or view directories?
- How to change a directory
- How to make a directory
- How to delete a directory
- What is the purpose of a directory?
- What type of files can be stored in a directory?
- Invalid directory characters
- How are files different than a directory?
- Does a directory have an extension?
- Current directory
- Windows current directory
- MS-DOS and Windows command line current directory
- Show the current directory in Linux and Unix
- How to list files in the current directory
- What is the current directory in a batch file?
- 9 Answers 9
- %__CD__% , %CD% , %=C:%
- Get current batchfile directory
- 4 Answers 4
- What are “.” and “..” in Windows’ directory?
- 3 Answers 3
Directory
A directory is a location for storing files on your computer. Directories are found in a hierarchical file system, such as Linux, MS-DOS, OS/2, and Unix.
Pictured is an example of output from the Windows/DOS tree command. It shows all the local and subdirectories (e.g., the «big» directory in the «cdn» directory). When looking at this overview, the current directory is the root directory of the C: drive. It’s called the «root» directory because there is nothing beneath it, and the other directories «branch» from it. If you are using an operating system with multiple user accounts, the directory may also be referred to as a home directory.
In a GUI such as Microsoft Windows, directories are referred to as folders. However, a directory and folder are synonymous.
Overview of a directory and path
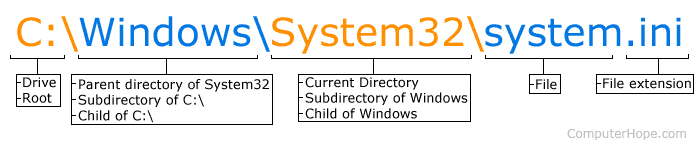
Below is an example of what a directory path would look like in MS-DOS.
In the picture, C: is the drive letter and the current directory is System32, which is a subdirectory of the Windows directory.
Overview of a Linux directory path
Below is an example of what a directory path may look like in a Linux or Unix variant.
In the above example, the current directory is bin, and it is a subdirectory of the usr directory. The beginning forward slash is the root directory.
How do I list or view directories?
To see directories and files in the current MS-DOS directory, use the dir command. In Linux to view directories and files in the current directory, you’d use the ls command.
- See the dir command page for further information and examples on this command.
- See the ls command page for information and examples on this command.
Both of the above commands also have switches that can be added to them to only view directories and not directories and files.
How to change a directory
To change a directory in MS-DOS, Linux, Unix, and most other command line operating systems, use the «cd» command.
How to make a directory
To make a directory in MS-DOS, Linux, Unix, and most other command line operating systems, use the «mkdir» command.
How to delete a directory
To remove a directory in MS-DOS, use the «rmdir» command. In Linux and Unix, use the «rm -r» command.
What is the purpose of a directory?
A directory is used to store, organize, and separate files and directories on a computer. For example, you could have a directory to store pictures and another directory to store all your documents. By storing specific types of files in a folder, you could quickly get to the type of file you wanted to view. In other words, if only pictures were in a pictures directory, it’s easier to find a picture than a directory containing all types of files.
Directories are also used as a place to store programs. For example, when you install a program, its files are stored in a unique directory that may contain subdirectories and tens, hundreds, or thousands of files related to that program. By storing a program in its own directory, it helps prevent files with the same name from getting overwritten, modified, or deleted by other programs.
What type of files can be stored in a directory?
A directory can contain one or more files of any type and can even store other directories that contain files.
Invalid directory characters
Below is a listing of reserved characters that cannot be used when creating a file or directory on most operating systems. When creating directories, if any of these characters are used, you’ll receive an error or encounter other problems.
How are files different than a directory?
A directory is an area on the computer containing other directories and files and helps keep the computer organized. Files can be contained within a directory and contain information used by the operating system or other programs on the computer. See our file page for further information on files.
Does a directory have an extension?
No. A directory does not have an extension like a file.
Current directory
Alternatively referred to as the working directory or current working directory (CWD), the current directory is the directory or folder where you are currently working. The following sections contain some common use examples involving the current working directory.
Windows current directory
While in Windows Explorer, the current working directory is shown at the top of the Explorer window in a file address bar. For example, if you were in the System32 folder, you would see «C:\Windows\System32» or «Computer > C:>Windows\System32» depending on your version of Windows. In this example, System32 is the current directory.
While in Windows a directory is more properly referred to as a folder and not a directory.
MS-DOS and Windows command line current directory
In the MS-DOS or Windows command line, the current working directory is displayed as the prompt. For example, if the prompt was «C:\Windows\System32>» the «System32» directory is the current directory, «Windows» is the parent directory, and «C:\» is the drive (root directory). To list the files in the current directory use the dir command, and if you want to change the current directory, use the cd command.
You can use the chdir command by itself to print the current directory in MS-DOS and the Windows command line.
Show the current directory in Linux and Unix
Depending on your Linux or Unix variant and its shell, the current directory may be shown as the prompt or when using the pwd (print working directory) command.
How to list files in the current directory
To list the files and directories in the current directory depends on your operating system. If you’re using Microsoft Windows or MS-DOS, you can use the dir command to list the files and directories in the current directory. If you’re using Linux, you can use the ls command to list the files and directories in the current directory.
What is the current directory in a batch file?
I want to create a few batch files to automate a program.
My question is when I create the batch file, what is the current directory? Is it the directory where the file is located or is it the same directory that appears in the command prompt, or something else?
9 Answers 9
From within your batch file:
dp0 refers to the full path to the batch file’s directory (static)
%
f0 both refer to the full path to the batch directory and file name (static).
dp0 will always give the full path to the executing batch file. – dbenham Jun 12 ’13 at 11:19
dp0 gives the full path to the directory that the executing batch file is in. %
dpnx0 (which is equivalent to %
f0) gives the full path to the batch file. See robvanderwoude.com/parameters.php for more details. – deadlydog Jul 11 ’13 at 20:08
dp0 is the working directory not the batch files directory, Found this out the hard way. – trampster Jan 29 ’18 at 22:44
dp0 gives the batch file directory with trailing slash. – icc97 Feb 27 ’18 at 9:10
It usually is the directory from which the batch file is started, but if you start the batch file from a shortcut, a different starting directory could be given. Also, when you’r in cmd, and your current directory is c:\dir3 , you can still start the batch file using c:\dir1\dir2\batch.bat in which case, the current directory will be c:\dir3 .
In a batch file, %cd% is the most commonly used command for the current directory, although you can set your own variable:
So say you were wanting to open Myprog.exe. If it was in the same folder, you would use the command:
That would open Myprog from the current folder.
The other option is to make a directory in C: called AutomatePrograms. Then, you transfer your files to that folder then you can open them using the following command:
dp0 is more consistent. – icc97 Feb 27 ’18 at 9:14
Say you were opening a file in your current directory. The command would be:
I hope I answered your question.
It is the directory from where you run the command to execute your batch file.
As mentioned in the above answers you can add the below command to your script to verify:
It is the directory from where you start the batch file. E.g. if your batch is in c:\dir1\dir2 and you do cd c:\dir3 , then run the batch, the current directory will be c:\dir3 .
Just my 2 cents. The following command fails if called from batch file (Windows 7) placed on pendrive:
But this does the job:
dp0 – Ammar Mohammad Aug 3 ’19 at 12:49
%__CD__% , %CD% , %=C:%
There’s also another dynamic variable %__CD__% which points to the current directory but alike %CD% it has a backslash at the end. This can be useful if you want to append files to the current directory.
With %=C:% %=D:% you can access the last accessed directory for the corresponding drive. If the variable is not defined you haven’t accessed the drive on the current cmd session.
Get current batchfile directory
Firstly, I saw this topic but I couldn’t understand that.
Question :
There is a batch file in D:\path\to\file.bat with following content :
It must be D:\path\to
What am I doing wrong?
4 Answers 4
System read-only variable %CD% keeps the path of the caller of the batch, not the batch file location.
You can get the name of the batch script itself as typed by the user with %0 (e.g. scripts\mybatch.bat ). Parameter extensions can be applied to this so %
dp0 will return the Drive and Path to the batch script (e.g. W:\scripts\ ) and %
f0 will return the full pathname (e.g. W:\scripts\mybatch.cmd ).
You can refer to other files in the same folder as the batch script by using this syntax:
This can even be used in a subroutine, Echo %0 will give the call label but, echo «%
nx0″ will give you the filename of the batch script.
When the %0 variable is expanded, the result is enclosed in quotation marks.
dp0 will return path to batch location. echo %
f0 will return path to the batch with filename. – Stoleg Jun 12 ’13 at 12:03
dp0 ? – Ivailo Bardarov May 5 ’17 at 10:06
dp0 as first line of batch file and worked – mkb Oct 25 ’17 at 4:03
dp0″ rather than %
dp0 . Quotes will guarantee the path is taken as one token, even if there are spaces, and also protects against poison characters like & . – dbenham Dec 20 ’19 at 3:53
Within your .bat file:
You can now use the variable %mypath% to reference the file path to the .bat file. To verify the path is correct:
For example, a file called DIR.bat with the following contents
run from the directory g:\test\bat will echo that path in the DOS command window.
Here’s what I use at the top of all my batch files. I just copy/paste from my template folder.
Setting current batch file’s path to %batdir% allows you to call it in subsequent stmts in current batch file, regardless of where this batch file changes to. Using PUSHD allows you to use POPD to quickly set this batch file’s path to original %batdir%. Remember, if using %batdir%ExtraDir or %batdir%\ExtraDir (depending on which version used above, ending backslash or not) you will need to enclose the entire string in double quotes if path has spaces (i.e. «%batdir%ExtraDir»). You can always use PUSHD %
dp0. [https: // ss64.com/ nt/ syntax-args .html] has more on (%
Note that using (::) at beginning of a line makes it a comment line. More importantly, using :: allows you to include redirectors, pipes, special chars (i.e. | etc) in that comment.
Of course, Powershell does this and lots more.
What are “.” and “..” in Windows’ directory?
I am writing a program to list out all files in a directory on Windows. I simply use those File Management functions provided but I am curious about the result:
So technically, what are these «.» and «..» ? I recalled I use «cd ..» in cmd to exit to the upper directory. For «cd .», I don’t know what is it for.
3 Answers 3
«.» is the current directory.
«..» is the parent directory.
This is the same as Unix systems. From your output it looks like Windows is treating them as files.
In the past I’ve used the «.» to make sure that the command (what ever it might be) finds the file in the current directory. The following two statements should be identical:
but if you have some weird search rules that looks on the PATH or in C:\Windows first (for example) then they aren’t.
I’ve found these statements:
- Use a period as a directory component in a path to represent the current directory, for example «.\temp.txt». For more information, see Paths.
- Use two consecutive periods (..) as a directory component in a path to represent the parent of the current directory, for example «..\temp.txt». For more information, see Paths.
on the MSDN page on Naming Files, Paths, and Namespaces but there’s no explanation of what they actually are.
The Wikipedia page on Path as a little more information, but again doesn’t explain how these are actually stored.
The single dot represents the current working directory. The double dot represents the current working directory’s parent directory.
Neither of these represent a concrete ‘file’ in the underlying file system, but represent the directory’s location within the file system hierarchy. Although you don’t mention it, the ‘/’ symbol, on its own, is similar to these in that it generally represents the root of a particular file system. ie
will take you to the root of the current file system.
Rather, the ‘.’ and ‘..’ are references to available resources within the file system, and as such are pseudo-files or pseudo-references generated by the request for file information to the underlying file system and are included to aid navigation around the file system. They are generally OS independent ie. most OS systems respect their use.
You say you are ‘writing a program’. Many file management routines that retrieve directory listings include a switch or a method which ignores these pseudo-files when generating directory listings.
However, its normally easiest to write your program to iterate over the entries and ignore these directory entries if you don’t need them. Alternatively write your program to only list files, or even files of the specific type you are looking for. For example, use DOS type commands in Windows, executing
will show only files in the directory but not the ‘.’ and ‘..’ entries. while
would list only .txt files in the directory.