- Microsoft Windows
- Microsoft’s Windows operating system
- Workstation computers
- Living in cyberspace
- Ever smaller computers
- Embedded systems
- Handheld digital devices
- The Evolution of Microsoft Windows Operating System
- The History of Microsoft Windows Operating System
- Windows 1.0
- Windows 2.0
- Windows 3.0
- Windows 3.1
- Windows 95
- Windows 98
- Windows Me
- Windows 2000 Professional
- Windows XP
- Windows Vista
- Windows 7
- Windows 8
- Windows 8.1
- Windows 10
Microsoft Windows
Our editors will review what you’ve submitted and determine whether to revise the article.
Microsoft Windows, also called Windows and Windows OS, computer operating system (OS) developed by Microsoft Corporation to run personal computers (PCs). Featuring the first graphical user interface (GUI) for IBM-compatible PCs, the Windows OS soon dominated the PC market. Approximately 90 percent of PCs run some version of Windows.
The first version of Windows, released in 1985, was simply a GUI offered as an extension of Microsoft’s existing disk operating system, or MS-DOS. Based in part on licensed concepts that Apple Inc. had used for its Macintosh System Software, Windows for the first time allowed DOS users to visually navigate a virtual desktop, opening graphical “windows” displaying the contents of electronic folders and files with the click of a mouse button, rather than typing commands and directory paths at a text prompt.
Subsequent versions introduced greater functionality, including native Windows File Manager, Program Manager, and Print Manager programs, and a more dynamic interface. Microsoft also developed specialized Windows packages, including the networkable Windows for Workgroups and the high-powered Windows NT, aimed at businesses. The 1995 consumer release Windows 95 fully integrated Windows and DOS and offered built-in Internet support, including the World Wide Web browser Internet Explorer.
With the 2001 release of Windows XP, Microsoft united its various Windows packages under a single banner, offering multiple editions for consumers, businesses, multimedia developers, and others. Windows XP abandoned the long-used Windows 95 kernel (core software code) for a more powerful code base and offered a more practical interface and improved application and memory management. The highly successful XP standard was succeeded in late 2006 by Windows Vista, which experienced a troubled rollout and met with considerable marketplace resistance, quickly acquiring a reputation for being a large, slow, and resource-consuming system. Responding to Vista’s disappointing adoption rate, Microsoft in 2009 released Windows 7, an OS whose interface was similar to that of Vista but was met with enthusiasm for its noticeable speed improvement and its modest system requirements.
Windows 8 in 2012 offered a start screen with applications appearing as tiles on a grid and the ability to synchronize settings so users could log on to another Windows 8 machine and use their preferred settings. In 2015 Microsoft released Windows 10, which came with Cortana, a digital personal assistant like Apple’s Siri, and the Web browser Microsoft Edge, which replaced Internet Explorer. Microsoft also announced that Windows 10 would be the last version of Windows, meaning that users would receive regular updates to the OS but that no more large-scale revisions would be done.
The Editors of Encyclopaedia Britannica This article was most recently revised and updated by Amy Tikkanen, Corrections Manager.
Microsoft’s Windows operating system
In 1985 Microsoft came out with its Windows operating system, which gave PC compatibles some of the same capabilities as the Macintosh. Year after year, Microsoft refined and improved Windows so that Apple, which failed to come up with a significant new advantage, lost its edge. IBM tried to establish yet another operating system, OS/2, but lost the battle to Gates’s company. In fact, Microsoft also had established itself as the leading provider of application software for the Macintosh. Thus Microsoft dominated not only the operating system and application software business for PC-compatibles but also the application software business for the only nonstandard system with any sizable share of the desktop computer market. In 1998, amid a growing chorus of complaints about Microsoft’s business tactics, the U.S. Department of Justice filed a lawsuit charging Microsoft with using its monopoly position to stifle competition.
Workstation computers
While the personal computer market grew and matured, a variation on its theme grew out of university labs and began to threaten the minicomputers for their market. The new machines were called workstations. They looked like personal computers, and they sat on a single desktop and were used by a single individual just like personal computers, but they were distinguished by being more powerful and expensive, by having more complex architectures that spread the computational load over more than one CPU chip, by usually running the UNIX operating system, and by being targeted to scientists and engineers, software and chip designers, graphic artists, moviemakers, and others needing high performance. Workstations existed in a narrow niche between the cheapest minicomputers and the most powerful personal computers, and each year they had to become more powerful, pushing at the minicomputers even as they were pushed at by the high-end personal computers.
The most successful of the workstation manufacturers were Sun Microsystems, Inc., started by people involved in enhancing the UNIX operating system, and, for a time, Silicon Graphics, Inc., which marketed machines for video and audio editing.
The microcomputer market now included personal computers, software, peripheral devices, and workstations. Within two decades this market had surpassed the market for mainframes and minicomputers in sales and every other measure. As if to underscore such growth, in 1996 Silicon Graphics, a workstation manufacturer, bought the star of the supercomputer manufacturers, Cray Research, and began to develop supercomputers as a sideline. Moreover, Compaq Computer Corporation—which had parlayed its success with portable PCs into a perennial position during the 1990s as the leading seller of microcomputers—bought the reigning king of the minicomputer manufacturers, Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC). Compaq announced that it intended to fold DEC technology into its own expanding product line and that the DEC brand name would be gradually phased out. Microcomputers were not only outselling mainframes and minis, they were blotting them out.
Living in cyberspace
Ever smaller computers
Embedded systems
One can look at the development of the electronic computer as occurring in waves. The first large wave was the mainframe era, when many people had to share single machines. (The mainframe era is covered in the section The age of Big Iron.) In this view, the minicomputer era can be seen as a mere eddy in the larger wave, a development that allowed a favoured few to have greater contact with the big machines. Overall, the age of mainframes could be characterized by the expression “Many persons, one computer.”
The second wave of computing history was brought on by the personal computer, which in turn was made possible by the invention of the microprocessor. (This era is described in the section The personal computer revolution.) The impact of personal computers has been far greater than that of mainframes and minicomputers: their processing power has overtaken that of the minicomputers, and networks of personal computers working together to solve problems can be the equal of the fastest supercomputers. The era of the personal computer can be described as the age of “One person, one computer.”
Since the introduction of the first personal computer, the semiconductor business has grown to more than a quarter-trillion-dollar worldwide industry. However, this phenomenon is only partly ascribable to the general-purpose microprocessor, which accounts for about one-sixth of annual sales. The greatest growth in the semiconductor industry has occurred in the manufacture of special-purpose processors, controllers, and digital signal processors. These computer chips are increasingly being included, or embedded, in a vast array of consumer devices, including pagers, mobile telephones, music players, automobiles, televisions, digital cameras, kitchen appliances, video games, and toys. While the Intel Corporation may be safely said to dominate the worldwide microprocessor business, it has been outpaced in this rapidly growing multibillion-dollar industry by companies such as Motorola, Inc.; Hitachi, Ltd.; Texas Instruments Incorporated; NEC Corporation; and Lucent Technologies Inc. This ongoing third wave may be characterized as “One person, many computers.”
Handheld digital devices
The origins of handheld digital devices go back to the 1960s, when Alan Kay, a researcher at Xerox’s Palo Alto Research Center (PARC), promoted the vision of a small, powerful notebook-style computer that he called the Dynabook. Kay never actually built a Dynabook (the technology had yet to be invented), but his vision helped to catalyze the research that would eventually make his dream feasible.
It happened by small steps. The popularity of the personal computer and the ongoing miniaturization of the semiconductor circuitry and other devices first led to the development of somewhat smaller, portable—or, as they were sometimes called, luggable—computer systems. The first of these, the Osborne 1, designed by Lee Felsenstein, an electronics engineer active in the Homebrew Computer Club in San Francisco, was sold in 1981. Soon most PC manufacturers had portable models. At first these portables looked like sewing machines and weighed in excess of 20 pounds (9 kg). Gradually they became smaller (laptop-, notebook-, and then sub-notebook-size) and came with more powerful processors. These devices allowed people to use computers not only in the office or at home but also while traveling—on airplanes, in waiting rooms, or even at the beach.
As the size of computers continued to shrink and microprocessors became more and more powerful, researchers and entrepreneurs explored new possibilities in mobile computing. In the late 1980s and early ’90s, several companies came out with handheld computers, called personal digital assistants (PDAs). PDAs typically replaced the cathode-ray-tube screen with a more compact liquid crystal display, and they either had a miniature keyboard or replaced the keyboard with a stylus and handwriting-recognition software that allowed the user to write directly on the screen. Like the first personal computers, PDAs were built without a clear idea of what people would do with them. In fact, people did not do much at all with the early models. To some extent, the early PDAs, made by Go Corporation and Apple, were technologically premature; with their unreliable handwriting recognition, they offered little advantage over paper-and-pencil planning books.
The potential of this new kind of device was realized in 1996 when Palm Computing, Inc., released the Palm Pilot, which was about the size of a deck of playing cards and sold for about $400—approximately the same price as the MITS Altair, the first personal computer sold as a kit in 1974. The Pilot did not try to replace the computer but made it possible to organize and carry information with an electronic calendar, telephone number and address list, memo pad, and expense-tracking software and to synchronize that data with a PC. The device included an electronic cradle to connect to a PC and pass information back and forth. It also featured a data-entry system called “graffiti,” which involved writing with a stylus using a slightly altered alphabet that the device recognized. Its success encouraged numerous software companies to develop applications for it.
In 1998 this market heated up further with the entry of several established consumer electronics firms using Microsoft’s Windows CE operating system (a stripped-down version of the Windows system) to sell handheld computer devices and wireless telephones that could connect to PCs. These small devices also often possessed a communications component and benefited from the sudden popularization of the Internet and the World Wide Web. In particular, the BlackBerry PDA, introduced by the Canadian company Research in Motion in 2002, established itself as a favourite in the corporate world because of features that allowed employees to make secure connections with their company’s databases.
In 2001 Apple introduced the iPod, a handheld device capable of storing 1,000 songs for playback. Apple quickly came to dominate a booming market for music players. The iPod could also store notes and appointments. In 2003 Apple opened an online music store, iTunes Store, and in the following software releases added photographs and movies to the media the iPod could handle. The market for iPods and iPod-like devices was second only to cellular telephones among handheld electronic devices.
While Apple and competitors grew the market for handheld devices with these media players, mobile telephones were increasingly becoming “smartphones,” acquiring more of the functions of computers, including the ability to send and receive e-mail and text messages and to access the Internet. In 2007 Apple once again shook up a market for handheld devices, this time redefining the smartphone market with its iPhone. The touch-screen interface of the iPhone was in its way more advanced than the graphical user interface used on personal computers, its storage rivaled that of computers from just a few years before, and its operating system was a modified version of the operating system on the Apple Macintosh. This, along with synchronizing and distribution technology, embodied a vision of ubiquitous computing in which personal documents and other media could be moved easily from one device to another. Handheld devices and computers found their link through the Internet.
The Evolution of Microsoft Windows Operating System
Published on August 19, 2015 By Amit Kumar
We all know that Microsoft Windows Operating System is the most popular and most used operating systems in Desktop and laptop computers. But, do you know about the evolution and history of Windows?
The Microsoft Windows is just like “one man army” in the field of operating systems because the company is efficiently providing Windows operating system services from past 30 years and people are happy with it. Even after independently ruling the operating system industry from years, the Microsoft Windows is still the most powerful and beneficial OS provider.
In this high technology era, the expectations of people have extremely grown up and they are ready to grab all the advanced services quickly. But Microsoft Windows Operating System is still the king of the game. For the example, you can see the Microsoft’s newly released Windows operating system “Windows 10“.
Windows 10 is the most advanced, full with features, fast and attractive operating system of Windows. If you are using Windows operating system from years, but still not familiar with the History of Microsoft windows operating system then you must take advantage from the below-mentioned glimpse of Microsoft Windows Operating System history.
Related tips you might like »»
The History of Microsoft Windows Operating System
Most of us know very well about the founder of Windows operating system and the most popular Windows operating system by Microsoft. But very few of us know – What was Microsoft’s first operating system? And, In Microsoft windows how many types of operating systems are there?
In this Microsoft Windows guide, I am going to explain about the evolution of Microsoft Windows Operating System over 30 years. So, let’s have a look at the glimpse of Microsoft Windows Operating System history:
In 1983, Microsoft announced the development of Windows operating system, a graphical user interface (GUI) for its own operating system (MS-DOS). Over 30 years later a lot of things has changed, let’s start observing the things:
Windows 1.0
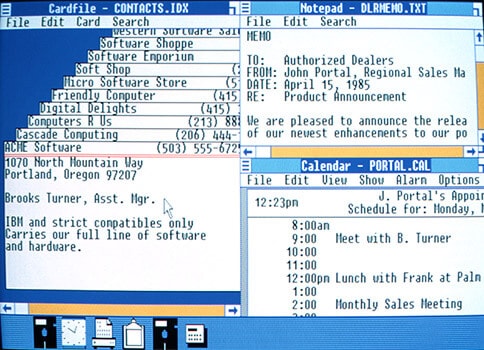
The first version of Microsoft Windows (Windows 1.0) was released on November 20, 1985. It was one of the most surprising moments for all computer users because now they were able to move a mouse to point and click their way through the screen in the place of typing MS‑DOS commands.
Windows 1.0 was introduced with several basic programs like MS‑DOS file management, Paint, Windows Writer, Notepad, Calculator, and a calendar, card file, and clock etc. Even a game called “Reversi” was also included with the Microsoft’s first Windows operating system.
Windows 2.0
Just after the two years, Microsoft released Windows 2.0 on December 9, 1987. The second version of Windows was introduced with desktop icons and expanded memory. Along with the Windows 2’s improved graphics support, now users were able to overlap windows, manage the screen layout, and use keyboard shortcuts etc to speed up their work.
The most interesting thing, Control Panel made its first appearance in Windows 2.0 operating system.
Windows 3.0
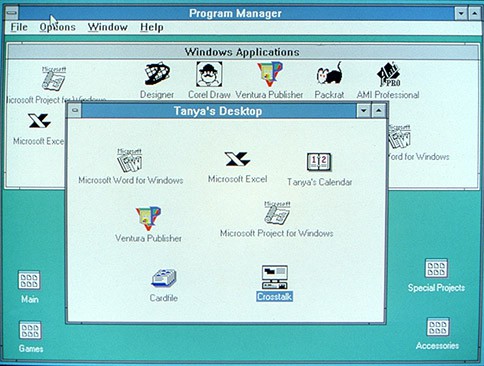
After launching two successful versions of Windows, Microsoft made an announcement about its third operating system (Windows 3.0) on May 22, 1990. This new Windows operating system was quite popular because of its good performance, advanced graphics with 16 colors, and improved icons.
Windows 3.0 was released with full support for the Intel 386 processor, Program Manager, File Manager, and Print Manager etc. With this OS, all the programs were running noticeably faster in comparison to other older versions of Windows.
Windows 3.1
Windows 3.1 was released in 1992. Basically, Windows 3.1 was the updated version of Windows 3.0. People felt attracted towards it because Windows 3.1 required only 1MB of RAM to run and allowed all supported MS-DOS programs to be controlled with a mouse.
Addition to all these things, Windows 3.1 operating system was also the first Windows version to be distributed on a CD-ROM. Microsoft Minesweeper’s appearance was another interesting thing.
Windows 95
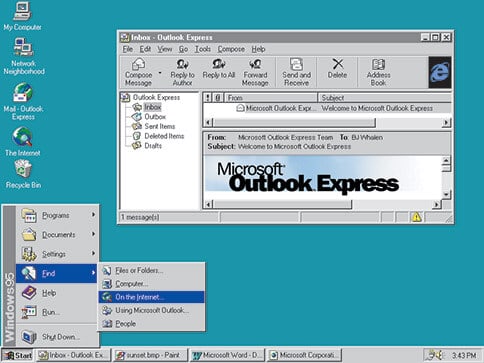
After the three years of accurate observations of users activities, Microsoft released the new version of Windows called “Windows 95” on August 24, 1995. Windows 95 was the first Windows operating system that came with a Start button and Start menu.
The most exciting thing, Windows 95 was built with Internet support, dial-up networking, and new Plug and Play capacities that allow installing hardware and software easily.
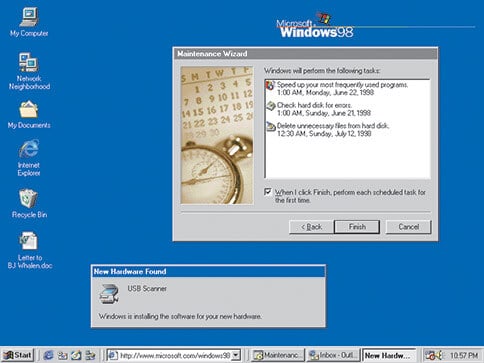
Windows 98
Windows 98 was the last version of Windows based on MS‑DOS which was released on June 25, 1998. It was designed specifically for consumers. Windows 98 was the first version of Windows that introduced back and forward navigation buttons and the address bar in Windows Explorer, among all other things.
Along with the support for reading DVD discs and universal serial bus (USB) devices, it came with many other improved features that help users to open and close programs more quickly.
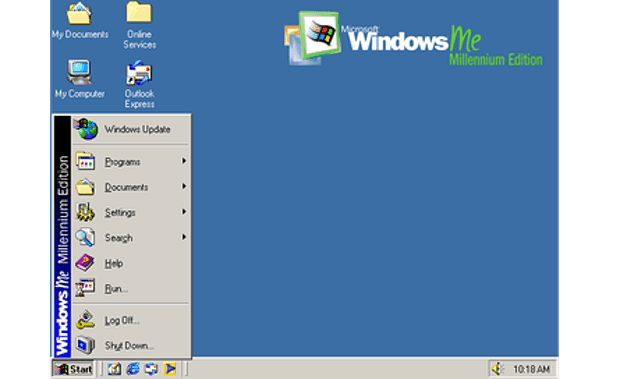
Windows Me
Technically, Windows Me (released on September 2000) was specially designed for home computer use. It provides countless music, video, and home networking enhancements and reliability improvements compared to all previous versions of Windows. Also, the Windows Me Edition was the last Windows operating system to be based on Windows 95 code-base.
Windows Me landed with many helpful features like System Restore, Movie Maker, Microsoft Windows Media Player 7 technologies etc.
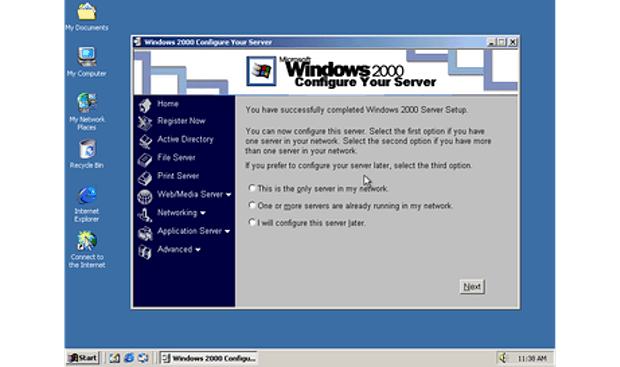
Windows 2000 Professional
Windows 2000 Professional is the enterprise twin of Windows Me which was released on February 2000. It was based on Microsoft’s business-oriented system Windows NT Workstation 4.0 and later it became the basis for Windows XP.
Actually, Windows 2000 Professional is specially designed to replace all other old versions of Windows including Windows 95, Windows 98, and Windows NT Workstation 4.0 on all business computer desktops and laptops.
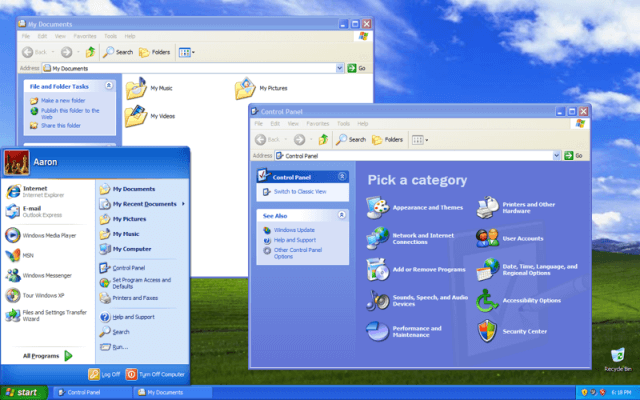
Windows XP
Concretely one of the best Microsoft’s Windows versions, Windows XP was released on October 2001. The redesigned look and feel with great accessibility and a unified Help and Support services center made this operating system more awesome. Windows XP was also the longest running Microsoft’s Windows operating system.
Windows XP was really quite stable, usable, and fast in all ways. It was available in 25 different languages. Navigation simplicity of the Start menu, taskbar, and Control Panel are more intuitive. Windows XP operating system has several editions like Windows XP 64-bit Edition (2001)| Windows XP Media Center Edition (2002) | Windows XP Tablet PC Edition (2002).
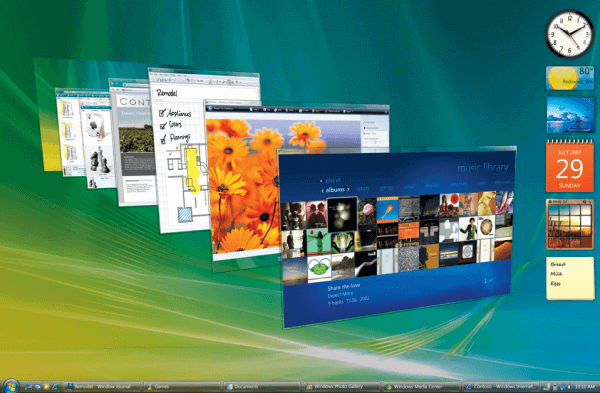
Windows Vista
After the 6 years long journey of Windows XP, Windows Vista was released in 2006. Windows Vista was specially security focused operating system which was available in 35 different languages. System design plays a big role in Windows Vista, many features like the taskbar, Start button, Search menu received a brand new look with this operating system.
Windows Vista was introduced with the new features like speech recognition, Windows DVD Maker and Photo Galler etc. Addition to these things, it was also the first Windows version to be distributed on DVD.
Windows 7
Windows 7 was first released in October 2009 along with some very interesting features such as faster booting, Device Stage, Windows PowerShell, less obtrusive User Account Control, multi-touch, and improved window management etc. Windows 7 operating system is available in six different editions:
- Windows 7 Starter (available worldwide)
- Windows 7 Home Basic
- Windows 7 Home Premium
- Windows 7 Professional
- Windows 7 Enterprise (available to volume-license business customers only)
- Windows 7 Ultimate (available to retail market with limited availability to OEMs)
Undoubtedly, Windows 7 is faster, more stable and easier to use. According to the Wikipedia’s usage share of operating systems list, Windows 7 is the most used Windows operating system on Desktop and laptop computers. In order to get more interesting guide related to Windows 7 operating system, check out our Windows 7 Tutorials section.
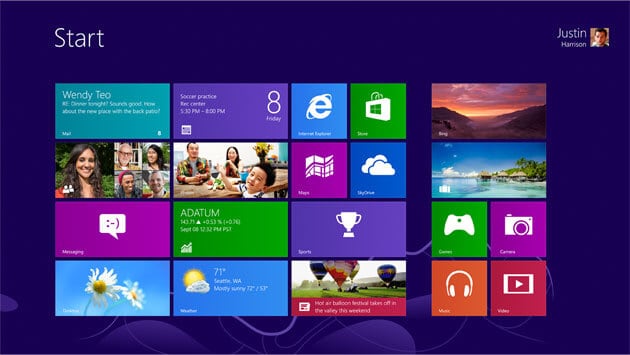
Windows 8
Windows 8 was Microsoft’s most good looking and colorful operating system released on October 2012. Windows 8 was the first version of Windows that come up with a totally new interface that works quite smoothly for both touch and mouse and keyboard. It features a Start screen (updated Start menu) with apps and tiles that connect to people, files, apps, and websites etc.
Basically, Windows 8 operating system is focused more on the touch screen than a keyboard and mouse. Windows 8 operating system is available in the following editions:
- Windows 8
- Windows 8 Pro
- Windows 8 Enterprise
- Windows RT
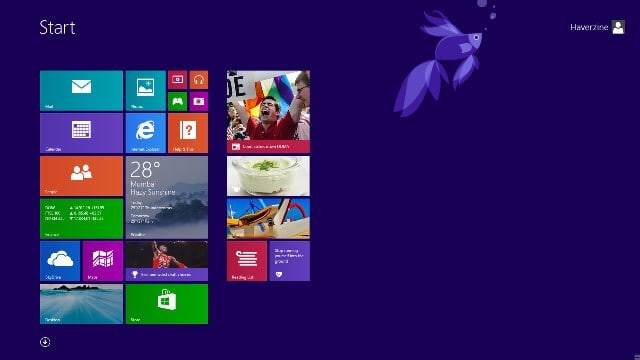
Windows 8.1
Windows 8.1 is the advanced version of Windows 8 operating system introduced in October 2013. It offers a powerful collection of Windows apps and cloud connectivity on most of the compatible devices. It comes up with some interesting improvements and new features like changes in user interface and desktop, apps, online services and functionality, security and hardware compatibility, hardware functionality etc.
Addition to all these changes, Windows 8.1 is also full with various new built-in apps such as Bing Food & Drink, Bing Health & Fitness, and some great utility apps like Reading List, Calculator, and Alarms etc. Windows 8.1 operating system is available in the following editions:
- Windows RT 8.1
- Windows 8.1 Edition
- Windows 8.1 Pro Edition
- Windows 8.1 Enterprise Edition
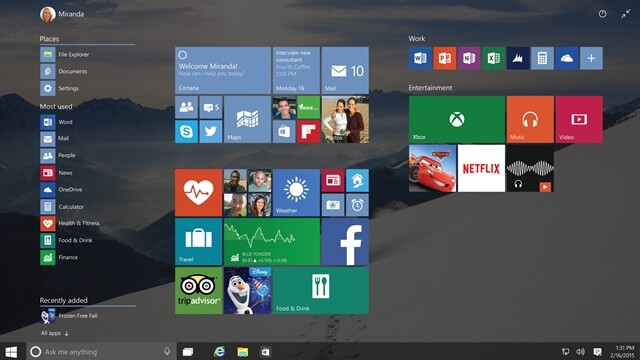
Windows 10
Windows 10 is the newly released (July 29, 2015) Windows operating system of the Microsoft. Windows 10 operating system is the most advanced version of Microsoft Windows which is introduced with a number of new features like Cortana, the Microsoft Edge, The Start menu, Windowed Windows Store apps, Virtual desktops/Task View, Action Center, Revamped core apps, The Xbox app, Continuum, Unified settings, and much more.
Actually, Windows 10 combines the strengths of Windows 8 with Windows 7 operating system. Microsoft Edge is the new Web browser of Windows 10 which is specially designed to be a lightweight web browser. Windows 10 operating system is available in the following editions:
- Windows 10 Home
- Windows 10 Pro
- Windows 10 Enterprise
- Windows 10 Enterprise 2015 LTSB
- Windows 10 Education
- Windows 10 Mobile
- Windows 10 Mobile Enterprise
- Windows 10 IoT Core
Windows 10 offering free upgrade to Windows 7 and Windows 8.1 users for the first year. So, if you are using a genuine version of Windows then you can easily upgrade to Windows 10 for free from Windows 7 or Windows 8.1 operating system. If you want perform a clean Windows 10 installation, you can do it by creating Windows 10 bootable USB flash drive.
Thus, you can see how amazingly Microsoft Windows operating system received the exclusive designs, features, new services, and well optimized structures. I am quite sure, you found the above mentioned glimpse of Microsoft Windows Operating System history useful for you.