- Desktop
- Design concepts
- Guidelines
- Windows
- Editions of Windows
- Windows Home
- Windows Pro
- Business editions
- Why is Microsoft Windows called Windows?
- Microsoft Windows help pages
- Related pages
- Desktop
- What icons and items are found on the Windows desktop?
- Should I capitalize the word «desktop» in my writing?
- Related pages
- Microsoft Windows
Desktop
This design guide was created for Windows 7 and has not been updated for newer versions of Windows. Much of the guidance still applies in principle, but the presentation and examples do not reflect our current design guidance.
The desktop is the user’s work area for their programs. It’s not a way to promote awareness of your program or its brand. Don’t abuse it!
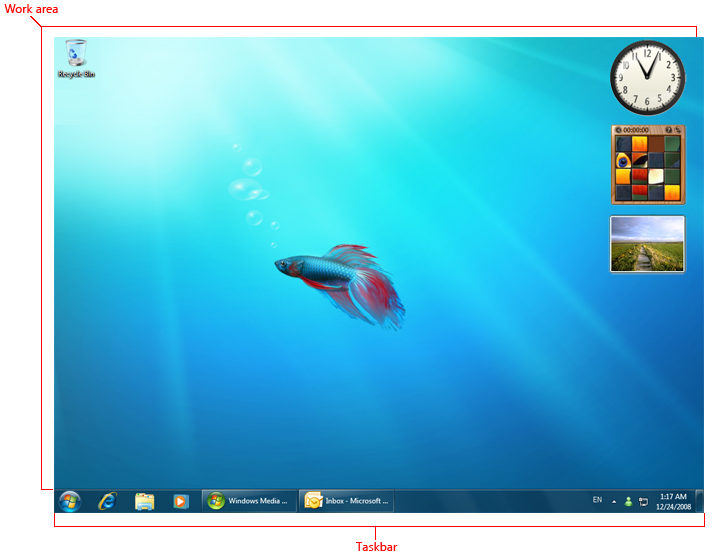
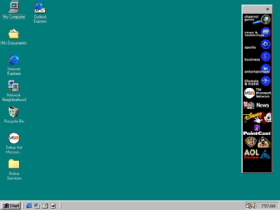
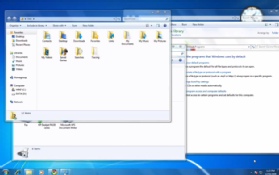
The desktop is the onscreen work area provided by Microsoft Windows, analogous to a physical desktop. It consists of a work area and taskbar. The work area may span multiple monitors.
A typical Windows desktop.
The active monitor is the monitor where the active program is running. The default monitor is the one with the Start menu, taskbar, and notification area.
Design concepts
The Windows desktop has the following program access points:
- Work area. The onscreen area where users can perform their work, as well as store programs, documents, and their shortcuts. While technically the desktop includes the taskbar, in most contexts it refers just to the work area.
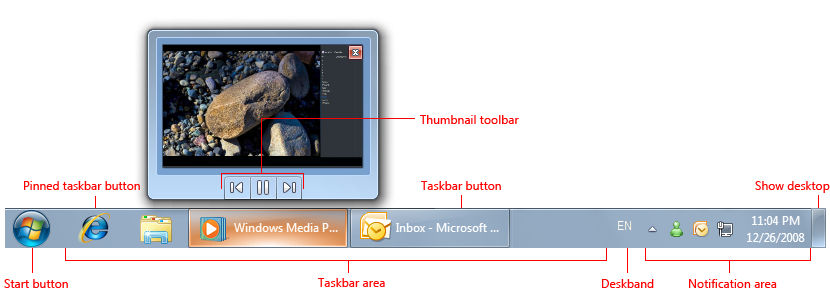
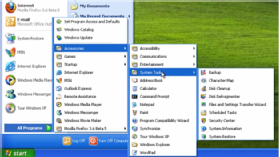
- Start button. The access point for all programs and special Windows places (Documents, Pictures, Music, Games, Computer, Control Panel), with «most recently used» lists for quick access to recently used programs and documents.
- Quick Launch. Removed from Windows 7. A direct access point for programs selected by the user.
- Taskbar. The access point for running programs that have desktop presence. While technically the taskbar spans the entire bar from the Start button to the notification area, in most contexts taskbar refers to the area in between, containing the taskbar buttons. This area is sometimes referred to as the taskband.
- Deskbands. Not recommended. Minimized functional, long-running programs, such as the Language Bar. Programs that minimize to deskbands don’t display taskbar buttons when minimized.
- Notification area. A short-term source for notifications and status, as well as an access point for system- and program-related features that have no presence on the desktop.
The Windows desktop access points include the Start button, taskbar, and notification area. Note the thumbnail feature of the taskbar button.
The Windows desktop is a limited, shared resource that is the user’s entry point to Windows. Leave users in control. You should use its areas as intended—any other usage should be considered an abuse. Never view them as ways to promote awareness of your program or its brand.
For Windows 7, Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) and Independent Hardware Vendors (IHVs) can use Device Stage to design a customized, branded UI for the computer and devices, without cluttering users’ desktops. OEMs in particular can use Device Stage PC to feature custom programs, service offerings, and support. For more information, see the Microsoft Device Experience Development Kit.
If you do only one thing.
- Don’t abuse the desktop—keep users in control. If your target users are likely to use your program frequently, provide an option during setup to put a shortcut on the desktop, unselected by default.
Guidelines
If your users are very likely to use your program frequently, provide an option during setup to put a program shortcut on the desktop. Most programs won’t be used frequently enough to warrant offering this option.
Present the option unselected by default. Requiring users to select the option is important because once undesired icons are on the desktop, many users are reluctant to remove them. This can lead to unnecessary desktop clutter.
If users select the option, provide only a single program shortcut. If your product consists of multiple programs, provide a shortcut only to the main program.
Put only program shortcuts on the desktop. Don’t put the actual program or other types of files.
Correct:
Incorrect:
In the incorrect example, the program, not a shortcut, is copied to the desktop.
Choose a label that can be displayed without truncation. Users shouldn’t see an ellipsis.
Correct:
Incorrect:
In the incorrect example, the program shortcut label is so long that it is truncated.
Windows
Windows may refer to any of the following:
1. Microsoft Windows (also referred to as Windows or Win) is a graphical operating system developed and published by Microsoft. It provides a way to store files, run software, play games, watch videos, and connect to the Internet.
Microsoft Windows was first introduced with version 1.0 on November 10, 1983. Over a dozen versions of Windows were released after that, including the current version, Windows 10.
Editions of Windows
Starting with Windows XP, Microsoft has published various editions of Windows. Each of these Windows editions has the same core operating system, but some editions have additional features, at an additional cost.
The two most common editions of Windows for home computers are Windows Home and Windows Professional.
Windows Home
Windows Home (also called Win Home) is the basic edition of Windows. It provides all the fundamental functions of Windows, such as connecting to the Internet, browsing the web, watching videos, using office software, and playing video games. It is the least expensive edition of Windows, and it comes preinstalled on many new computers.
Windows Pro
Windows Professional (also called Windows Pro, or Win Pro) is an enhanced Windows edition, for power users, and small to medium sized businesses. It includes all the features of Windows Home, plus the following:
- Remote Desktop — allows you to remotely control another Windows computer connected to the Internet.
- Bitlocker — Microsoft’s integrated file encryption.
- Trusted Boot — provides encryption of the boot loader, protecting the computer against rootkits.
- Hyper-V — a Windows hypervisor for running virtual machines, equivalent to third-party software, such as VirtualBox.
- Windows Sandbox — provides a lightweight, sandboxed Windows 10 instance. You can use this isolated «Windows within Windows» environment to safely run suspicious or untrusted software. Windows Sandbox requires a Windows Insider build of Windows 10 Pro or Enterprise.
- Group policy management — Administrators can define group policies, for managing multiple Windows users in a business or organization.
- Support for more than 128 GB of RAM.
- Greater Windows Update installation options, including more flexible scheduling and postponement for up to 35 days.
Business editions
Windows Professional for Workstations and Windows Enterprise provide advanced features for professional studios and large businesses. For more information, refer to the side-by-side comparison in the official Microsoft Windows business edition comparison chart.
Why is Microsoft Windows called Windows?
Before the release of Microsoft Windows, Microsoft users were used to the single task command line operating system MS-DOS. Because Microsoft names most of its products with one word, it needed a word that best described its new GUI operating system. Microsoft chose «Windows» because of the multiple windows that allow different tasks and programs to run at the same time. Because you cannot trademark a common name like «Windows,» it’s officially known as «Microsoft Windows». The first version of Microsoft Windows was version 1.0, released in 1985.
Microsoft Windows help pages
Related pages
2. In general, a window is a fundamental part of a computer GUI (graphical user interface). A window is an area of the display containing a single running application. The window can be moved, resized, hidden, or maximized as desired by the user. The Microsoft Windows operating system is named after this UI element.
3. Regarding Unix-like operating systems, such as Linux or BSD, Windows may refer to the X Window System.
Desktop
A desktop may refer to any of the following:
1. A desktop is a term commonly used to describe a desktop computer or system unit.
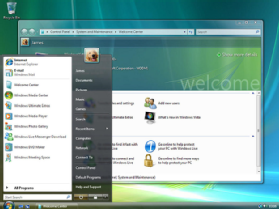
2. When referring to an operating system or GUI (graphical user interface), the desktop is a system of organization of icons on a screen. The Microsoft Windows desktop was first introduced with Microsoft Windows 95 and included with every version of Windows since then. The image below is an example of the Microsoft Windows 7 desktop.
In this example, there are no icons on the desktop, and the wallpaper is a blue screen with the Windows 7 logo. Also, the taskbar is at the bottom of the desktop and contains the Start, taskbar icons, Windows Notification Area, and the time and date.
If you’re more familiar with a smartphone or tablet, you can think of the desktop as the home screen.
You can get to the Windows desktop at any time by pressing the Windows key and D at the same time or using Aero Peek.
What icons and items are found on the Windows desktop?
Some of the most common icons on the desktop include those for My Computer, Recycle Bin, your Internet browser (e.g., Internet Explorer), and My Documents. On the Windows desktop, you can find the Windows Start menu through the Start on the taskbar, and the Windows Notification Area.
If some or all of these icons are missing on the desktop, you can change which icons are displayed. Click the link below and follow the steps to show, or hide, these icons.
The date and time are also shown on the desktop, in the notification area on the taskbar. If the date and time are incorrect, you can change the date and time from the desktop.
Should I capitalize the word «desktop» in my writing?
Unless at the beginning of a sentence, «desktop» should be written as all lowercase when referring to part of a GUI operating system.
Other words that contain the word desktop, such as «Active Desktop» and «Remote Desktop» are capitalized. Settings and options may also capitalize desktop in their description.
Related pages
3. With software, a desktop is a Graphical User Interface metaphor in a desktop environment for the interaction between the user and the operating system.
4. Desktops is a Windows Sysinternals utility that allows users to manage applications on up to four virtual desktops, all accessible using the tray icon interface.
Microsoft Windows
Windows is Microsoft’s flagship operating system (OS), the de facto standard for home and business computers. The graphical user interface (GUI)-based OS was introduced in 1985 and has been released in many versions since then, as described below. Microsoft got its start with the partnership of Bill Gates and Paul Allen in 1975. Gates and Allen co-developed Xenix (a version of Unix) and also collaborated on a BASIC interpreter for the Altair 8800. The company was incorporated in 1981.
Microsoft gained prominence in the tech field with the release of MS-DOS, a text-based command-line-driven operating system. DOS was mostly based on a purchased intellectual property, QDOS. GUI-based operating systems of that time included Xerox’s Alto, released in 1979, and Apple’s LISA and Macintosh systems, which came later. Die-hard fans of MS-DOS referred to such systems as WIMPs, which stood for «windows, icons, mouse and pull-down menus (or pointers).»
However, Gates saw the potential in GUI-based systems and started a project he called Interface Manager. Gates thought he could bring the GUI to a wider audience at a lower cost than the $9,000 LISA. The rest of Microsoft supported this idea, and, in a somewhat ironic move, the project team selected «Windows» as the name of the new operating system.
Microsoft announced the impending release of Windows 1.0 in 1983. The company used some features it licensed from Apple for portions of its interface. Microsoft released Windows 1.0 in 1985. Apple sued Microsoft and Hewlett-Packard for $5.5 billion in 1988 claiming it did not give the companies authorization to use certain GUI elements. In 1992, a federal court concluded Microsoft and Hewlett-Packard did not go beyond the 1985 agreement. Apple appealed that decision, which was upheld in 1994.
Competitors to Windows include Apple’s macOS and the open source Linux operating system from Linus Torvalds. The free price gives Linux an edge in availability, while macOS is known for its stability and user experience. However, Microsoft Windows continues to maintain its dominance — a June 2018 report from the NetMarketShare site shows Windows installed on nearly 88% of desktops and laptops — with a steady rollout of new versions to support advances in hardware.
Like many early versions of Microsoft’s GUI operating systems, Windows 1.0 was essentially a program that ran on top of DOS. Microsoft did not release the system until two years after its first announcement, leading to suggestions that Windows was vaporware. The release was a shaky start for the tech giant. Users found the software unstable. However, the point-and-click interface made it easier for new users to operate a computer. The user-friendly nature of Windows also drew interest from customers who might have been intimidated by a command-line interface. Windows 1.0 offered many of the common components found in today’s graphical user interface, such as scroll bars and «OK» buttons.
1987: Windows 2.0 and 2.11
Windows 2.0 was faster, more stable and had more GUI features in common with the Apple LISA. The system introduced the control panel and ran the first versions of Excel and Word. Windows 2.0 supported extended memory, and Microsoft updated it for compatibility with Intel’s 80386 processor. It was during this time that Microsoft became the largest software vendor in the world, just as computers were becoming more commonplace. The fact that Windows systems were user-friendly and relatively affordable was a contributing factor to the growing PC market.
Microsoft optimized the Windows 3.0 operating system, which still ran on top of DOS, for the 386 processor for a more responsive system. Windows 3.0 supported 16 colors and included the casual games familiar to most Windows users: Solitaire, Minesweeper and Hearts. Games that required more processing power still ran directly on MS-DOS. Exiting to DOS gave games direct hardware access made more system resources available that otherwise would have gone to Windows. Microsoft offered Windows 3.1 as a paid sub-release in 1993. Windows 3.1 features included support for TrueType fonts and peer-to-peer networking.
Windows NT’s release marked the completion of a side project to build a new, advanced OS. NT was 32-bit and had a hardware abstraction layer. DOS was available through the command prompt, but it did not run the Windows OS. Microsoft designed NT as a workstation OS for businesses rather than home users. The system introduced the Start button.
Windows 95 introduced the Windows operating system to a wider audience with a marketing campaign that featured The Rolling Stones song «Start Me Up» to celebrate the Start button’s arrival to the masses. Windows 95 facilitated hardware installation with its Plug and Play feature. Microsoft also unveiled 32-bit color depth, enhanced multimedia capabilities and TCP/IP network support.
Microsoft improved speed and Plug and Play hardware support in Windows 98. The company also debuted USB support and the Quick Launch bar in this release. DOS gaming began to wane as Windows gaming technology improved. The popularity of the OS made it an attractive target for malware. Microsoft integrated web technology into the Windows user interface and built its own web browser into the desktop. This feature was one of the defining issues in the U.S. Justice Department’s antitrust suit against Microsoft in the 1990s.
Windows ME (Millennium Edition) was the last use of the Windows 95 codebase. Its most notable new feature was System Restore. Many customers found this release to be unstable, and it was acknowledged as a poor release by Steve Ballmer and Microsoft. Some critics said ME stood for «mistake edition.»
Microsoft released the professional desktop OS Windows 2000 the same year. Microsoft based this OS on the more stable Windows NT code. Some home users installed Windows 2000 for its greater reliability. Microsoft updated Plug and Play support, which spurred home users to switch to this OS.
Microsoft delivered Windows XP as the first NT-based system with a version aimed squarely at the home user. Home users and critics rated XP highly. The system improved Windows appearance with colorful themes and provided a more stable platform.
Microsoft virtually ended gaming in DOS with this release. DirectX-enabled features in 3D gaming that OpenGL had difficulties with. XP offered the first Windows support for 64-bit computing, but it was not very well supported, lacking drivers and applications to run.
Microsoft hyped Windows Vista after the company spent a lot of resources to develop a more polished appearance. Vista had interesting visual effects but the OS was slow to start and run. The 32-bit version, in particular, didn’t enable enough RAM for the memory-hungry OS to operate properly.
Microsoft tightened licensing rights and made it more work to activate Windows. The company also peeled back user control of the operating system’s internal workings.
Microsoft lost market share to Apple and Linux variants. Vista’s flaws — coupled with the fact that many older computers lacked the resources to run the system — led to many home and business users staying with XP.
Microsoft built Windows 7 on the Vista kernel. Windows 7 picked up Vista’s visual capabilities but featured more stability. To many end users, the biggest changes between Vista and Windows 7 were faster boot times, new user interface and the addition of Internet Explorer 8.
With true 64-bit support and more Direct X features, Windows 7 proved to be a popular release for Windows users.
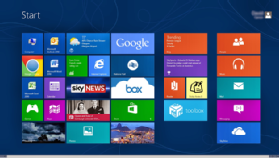
Microsoft released Windows 8 with a number of enhancements and debuted its tile-based Metro user interface. Windows 8 took better advantage of multicore processing, solid-state drives (SSD), touchscreens and other alternate input methods. Users found the switching from the traditional desktop to the tile-based interface awkward. Even after Microsoft’s UI and other updates in 8.1, Windows 8 trailed not just Windows 7 but XP in user numbers into 2014.
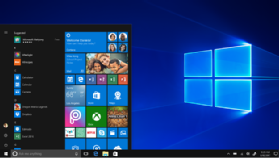
Microsoft announced Windows 10 in September 2014, skipping Windows 9. Version 10 includes the Start menu, which was absent from Windows 8. A responsive design feature called Continuum adapts the interface depending on whether the user works with a touchscreen or a keyboard and mouse for input. New features like an onscreen back button simplified touch input. Microsoft designed the OS to have a consistent interface across devices including PCs, laptops and tablets.
Microsoft did not implement many security methods in its operating systems until Windows NT and XP. For example, the default user on a Windows computer received administrator privileges until Vista.
Consumer editions of early versions of Windows did not have security measures built in since Microsoft designed the OS for single users without network connections. The company integrated security features in Windows NT, but they weren’t in the forefront of Microsoft’s design.The combination of lack of security and widespread popularity made Windows systems a target for malicious programs, such as viruses or system exploits.
Microsoft began to release monthly patches every second Tuesday of the month, known as Patch Tuesday, in 2003. Patches to update critical issues may be released on a faster schedule, known as out-of-band patches.
Windows Vista added User Account Control, a privilege evaluation feature based on a token system. The token allowed users only the most basic privileges, such as the ability to execute tasks that may modify system data. When an administrator logged on, they received two tokens — one that a standard user would receive and another that allowed administrator-level tasks.
Microsoft released its Windows Defender security application as a beta program for Windows XP in 2005. Windows Defender protects systems from spyware threats. Microsoft included Defender in later versions of Windows, such as Windows 10. Microsoft further buttressed system security with Windows Defender Credential Guard for virtualization-based security, System Guard to protect firmware components and configurations and Application Guard to protect against malware and hacking threats in the Microsoft Edge browser.
Starting with Windows XP, Microsoft separated Windows to give different features to distinct audiences. Windows 10, for example, has multiple editions including Windows 10 Home, Pro and Enterprise editions.
Microsoft makes its consumer operating systems for users in an ordinary household setting. Enterprise operating system is designed for large organizations in a business setting. The enterprise software tends to have more customization abilities and features that an organization can utilize, such as security or language packs.
Microsoft designed Windows 10 Home for consumers and tailored to operate on PCs, tablets and 2-in-1 devices. Microsoft built Windows 10 Pro as a baseline OS for any business, while it developed Windows 10 Enterprise for businesses with higher security needs.
Security features differ from Windows 10 Home, Pro and Enterprise editions. Windows 10 Home includes basic security features such as Windows Defender, Device Encryption and Windows Information Protection. Windows 10 Pro adds more security features such as Bitlocker, Windows Defender System Guard, Windows Defender Exploit Guard and Windows Defender Antivirus. Windows 10 Enterprise is identical in features and functionality to Pro but adds more security features such as Windows Defender Credential Guard, Windows Defender Application Guard and Windows Defender Application Control.
MacOS is a GUI-based OS developed and owned by Apple. MacOS is the primary OS for Apple computers. Apple introduced macOS in 1984. The company released a consumer version in 2001 with macOS X 10.0, which drew praise for its user interface, but criticism for its performance.
After macOS X 10.0, Apple developed newer versions of macOS X from 10.0-10.14. Earlier versions were named after big cats, such as Tiger, Puma, Snow Leopard and Mountain Lion. MacOS 10.4.4, or Tiger, was a notable update, which improved performance with graphics processing and file searching. Later versions of MacOS X were then named after California landmarks such as Yosemite, Sierra or Mojave.
Linux is an open source OS built on a Linux kernel. Released in 1991, Linux loads and unloads its kernel at runtime, meaning the user can add software or hardware to a Linux system without rebooting.
Linux is used in consumer and enterprise settings. A well-known consumer-based Linux OS, for example, is Android, which has a large install base on mobile devices. Enterprises can use server versions of Linux for enterprise use, such as virtual machines.