- Best practices for configuring Windows Defender Firewall
- Keep default settings
- Understand rule precedence for inbound rules
- Create rules for new applications before first launch
- Inbound allow rules
- Known issues with automatic rule creation
- Establish local policy merge and application rules
- Know how to use «shields up» mode for active attacks
- Create outbound rules
- Document your changes
- Защитник Windows брандмауэра с расширенными мерами безопасности Windows Defender Firewall with Advanced Security design guide
- Об этом руководстве About this guide
- В этом разделе In this section
- Терминология, используемая в этом руководстве Terminology used in this guide
Best practices for configuring Windows Defender Firewall
Applies to
Windows operating systems including WindowsВ 10
Windows Server Operating Systems
Windows Defender Firewall with Advanced Security provides host-based, two-way network traffic filtering and blocks unauthorized network traffic flowing into or out of the local device. Configuring your Windows Firewall based on the following best practices can help you optimize protection for devices in your network. These recommendations cover a wide range of deployments including home networks and enterprise desktop/server systems.
To open Windows Firewall, go to theВ StartВ menu, selectВ Run, typeВ WF.msc, and then selectВ OK. See also Open Windows Firewall.
Keep default settings
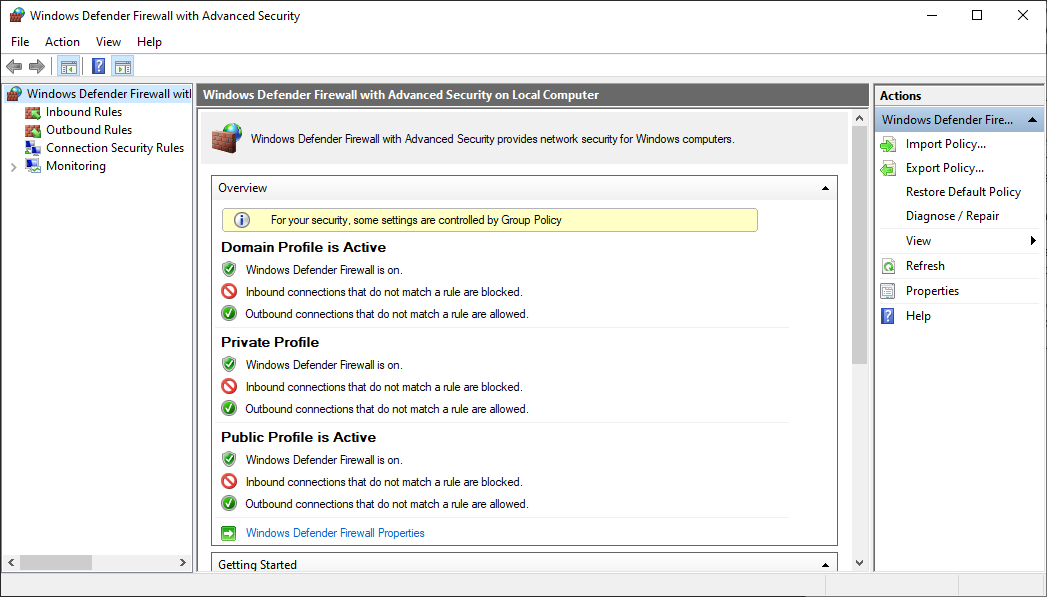
When you open the Windows Defender Firewall for the first time, you can see the default settings applicable to the local computer. The Overview panel displays security settings for each type of network to which the device can connect.
Figure 1: Windows Defender Firewall
Domain profile: Used for networks where there is a system of account authentication against a domain controller (DC), such as an Azure Active Directory DC
Private profile: Designed for and best used in private networks such as a home network
Public profile: Designed with higher security in mind for public networks like Wi-Fi hotspots, coffee shops, airports, hotels, or stores
View detailed settings for each profile by right-clicking the top-level Windows Defender Firewall with Advanced Security node in the left pane and then selecting Properties.
Maintain the default settings in Windows Defender Firewall whenever possible. These settings have been designed to secure your device for use in most network scenarios. One key example is the default Block behavior for Inbound connections.
Figure 2: Default inbound/outbound settings
To maintain maximum security, do not change the default Block setting for inbound connections.
Understand rule precedence for inbound rules
In many cases, a next step for administrators will be to customize these profiles using rules (sometimes called filters) so that they can work with user apps or other types of software. For example, an administrator or user may choose to add a rule to accommodate a program, open a port or protocol, or allow a predefined type of traffic.
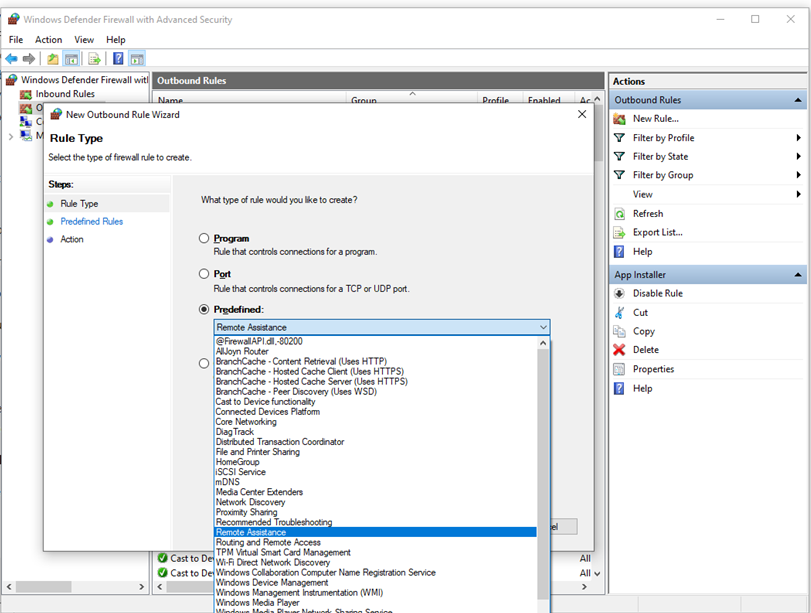
This can be accomplished by right-clicking either Inbound Rules or Outbound Rules, and selecting New Rule. The interface for adding a new rule looks like this:
Figure 3: Rule Creation Wizard
This article does not cover step-by-step rule configuration. See the Windows Firewall with Advanced Security Deployment Guide for general guidance on policy creation.
In many cases, allowing specific types of inbound traffic will be required for applications to function in the network. Administrators should keep the following rule precedence behaviors in mind when allowing these inbound exceptions.
Explicitly defined allow rules will take precedence over the default block setting.
Explicit block rules will take precedence over any conflicting allow rules.
More specific rules will take precedence over less specific rules, except in the case of explicit block rules as mentioned in 2. (For example, if the parameters of rule 1 includes an IP address range, while the parameters of rule 2 include a single IP host address, rule 2 will take precedence.)
Because of 1 and 2, it is important that, when designing a set of policies, you make sure that there are no other explicit block rules in place that could inadvertently overlap, thus preventing the traffic flow you wish to allow.
A general security best practice when creating inbound rules is to be as specific as possible. However, when new rules must be made that use ports or IP addresses, consider using consecutive ranges or subnets instead of individual addresses or ports where possible. This avoids creation of multiple filters under the hood, reduces complexity, and helps to avoid performance degradation.
Windows Defender Firewall does not support traditional weighted, administrator-assigned rule ordering. An effective policy set with expected behaviors can be created by keeping in mind the few, consistent, and logical rule behaviors described above.
Create rules for new applications before first launch
Inbound allow rules
When first installed, networked applications and services issue a listen call specifying the protocol/port information required for them to function properly. As there is a default block action in Windows Defender Firewall, it is necessary to create inbound exception rules to allow this traffic. It is common for the app or the app installer itself to add this firewall rule. Otherwise, the user (or firewall admin on behalf of the user) needs to manually create a rule.
If there are no active application or administrator-defined allow rule(s), a dialog box will prompt the user to either allow or block an application’s packets the first time the app is launched or tries to communicate in the network.
If the user has admin permissions, they will be prompted. If they respond No or cancel the prompt, block rules will be created. Two rules are typically created, one each for TCP and UDP traffic.
If the user is not a local admin, they will not be prompted. In most cases, block rules will be created.
In either of the scenarios above, once these rules are added they must be deleted in order to generate the prompt again. If not, the traffic will continue to be blocked.
The firewall’s default settings are designed for security. Allowing all inbound connections by default introduces the network to various threats. Therefore, creating exceptions for inbound connections from third-party software should be determined by trusted app developers, the user, or the admin on behalf of the user.
Known issues with automatic rule creation
When designing a set of firewall policies for your network, it is a best practice to configure allow rules for any networked applications deployed on the host. Having these rules in place before the user first launches the application will help ensure a seamless experience.
The absence of these staged rules does not necessarily mean that in the end an application will be unable to communicate on the network. However, the behaviors involved in the automatic creation of application rules at runtime requires user interaction.
To determine why some applications are blocked from communicating in the network, check for the following:
A user with sufficient privileges receives a query notification advising them that the application needs to make a change to the firewall policy. Not fully understanding the prompt, the user cancels or dismisses the prompt.
A user lacks sufficient privileges and is therefore not prompted to allow the application to make the appropriate policy changes.
Local Policy Merge is disabled, preventing the application or network service from creating local rules.
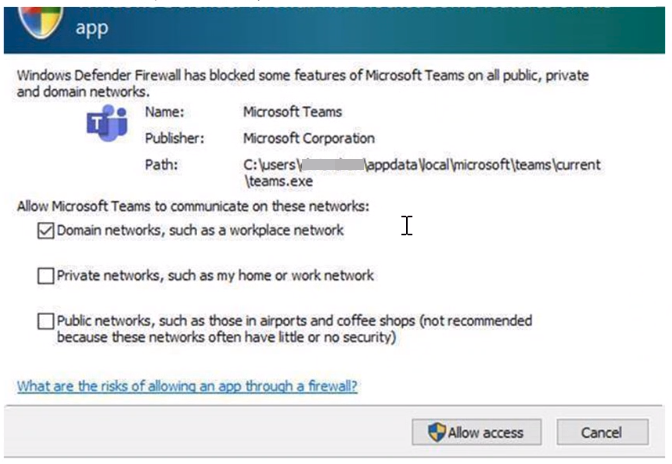
Figure 4: Dialog box to allow access
Establish local policy merge and application rules
Firewall rules can be deployed:
- Locally using the Firewall snap-in (WF.msc)
- Locally using PowerShell
- Remotely using Group Policy if the device is a member of an Active Directory Name, System Center Configuration Manager (SCCM), or Intune (using workplace join)
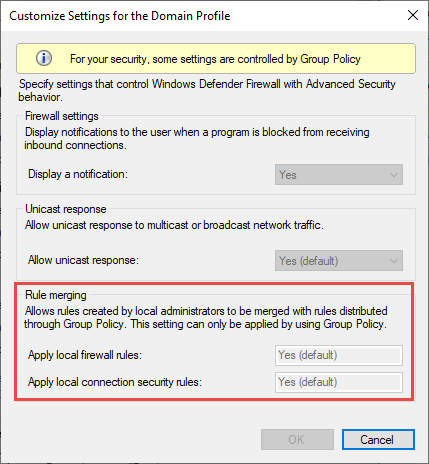
Rule merging settings control how rules from different policy sources can be combined. Administrators can configure different merge behaviors for Domain, Private, and Public profiles.
The rule merging settings either allow or prevent local admins from creating their own firewall rules in addition to those obtained from Group Policy.
Figure 5: Rule merging setting
In the firewall configuration service provider, the equivalent setting is AllowLocalPolicyMerge. This setting can be found under each respective profile node, DomainProfile, PrivateProfile, and PublicProfile.
If merging of local policies is disabled, centralized deployment of rules is required for any app that needs inbound connectivity.
Admins may disable LocalPolicyMerge in high security environments to maintain tighter control over endpoints. This can impact some apps and services that automatically generate a local firewall policy upon installation as discussed above. For these types of apps and services to work, admins should push rules centrally via group policy (GP), Mobile Device Management (MDM), or both (for hybrid or co-management environments).
Firewall CSP and Policy CSP also have settings that can affect rule merging.
As a best practice, it is important to list and log such apps, including the network ports used for communications. Typically, you can find what ports must be open for a given service on the app’s website. For more complex or customer application deployments, a more thorough analysis may be needed using network packet capture tools.
In general, to maintain maximum security, admins should only push firewall exceptions for apps and services determined to serve legitimate purposes.
The use of wildcard patterns, such as C:*\teams.exe is not supported in application rules. We currently only support rules created using the full path to the application(s).
Know how to use «shields up» mode for active attacks
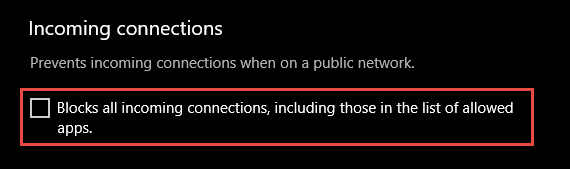
An important firewall feature you can use to mitigate damage during an active attack is the «shields up» mode. It is an informal term referring to an easy method a firewall administrator can use to temporarily increase security in the face of an active attack.
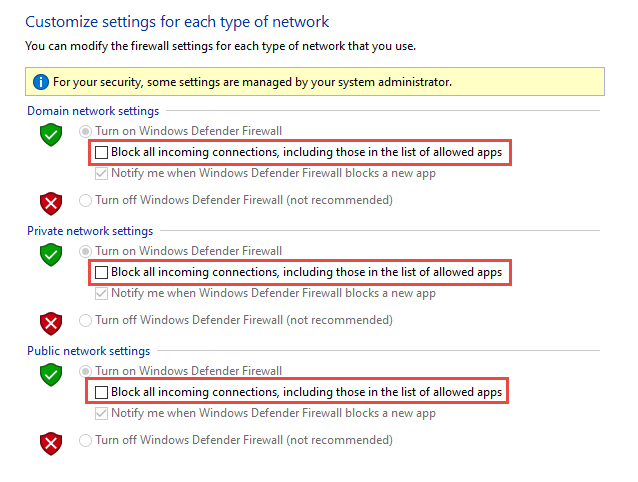
Shields up can be achieved by checking Block all incoming connections, including those in the list of allowed apps setting found in either the Windows Settings app or the legacy file firewall.cpl.
Figure 6: Windows settings App/Windows Security/Firewall Protection/Network Type
Figure 7: Legacy firewall.cpl
By default, the Windows Defender Firewall will block everything unless there is an exception rule created. This setting overrides the exceptions.
For example, the Remote Desktop feature automatically creates firewall rules when enabled. However, if there is an active exploit using multiple ports and services on a host, you can, instead of disabling individual rules, use the shields up mode to block all inbound connections, overriding previous exceptions, including the rules for Remote Desktop. The Remote Desktop rules remain intact but remote access will not work as long as shields up is activated.
Once the emergency is over, uncheck the setting to restore regular network traffic.
Create outbound rules
What follows are a few general guidelines for configuring outbound rules.
The default configuration of Blocked for Outbound rules can be considered for certain highly secure environments. However, the Inbound rule configuration should never be changed in a way that Allows traffic by default.
It is recommended to Allow Outbound by default for most deployments for the sake of simplification around app deployments, unless the enterprise prefers tight security controls over ease-of-use.
In high security environments, an inventory of all enterprise-spanning apps must be taken and logged by the administrator or administrators. Records must include whether an app used requires network connectivity. Administrators will need to create new rules specific to each app that needs network connectivity and push those rules centrally, via group policy (GP), Mobile Device Management (MDM), or both (for hybrid or co-management environments).
For tasks related to creating outbound rules, see Checklist: Creating Outbound Firewall Rules.
Document your changes
When creating an inbound or outbound rule, you should specify details about the app itself, the port range used, and important notes like creation date. Rules must be well-documented for ease of review both by you and other admins. We highly encourage taking the time to make the work of reviewing your firewall rules at a later date easier. AndВ neverВ create unnecessary holes in your firewall.
Защитник Windows брандмауэра с расширенными мерами безопасности Windows Defender Firewall with Advanced Security design guide
Область применения Applies to
- Windows 10 Windows 10
- Windows Server 2016 Windows Server 2016
Защитник Windows брандмауэром с расширенными мерами безопасности является брандмауэр хост-системы, который обеспечивает безопасность устройства двумя способами. Windows Defender Firewall with Advanced Security is a host firewall that helps secure the device in two ways. Во-первых, он может фильтровать сетевой трафик, разрешенный для ввода устройства из сети, а также контролировать сетевой трафик, который устройство может отправлять в сеть. First, it can filter the network traffic permitted to enter the device from the network, and also control what network traffic the device is allowed to send to the network. Во-Защитник Windows брандмауэр поддерживает IPsec, что позволяет требовать проверку подлинности с любого устройства, которое пытается связаться с устройством. Second, Windows Defender Firewall supports IPsec, which enables you to require authentication from any device that is attempting to communicate with your device. Если требуется проверка подлинности, устройства, которые не могут проверить подлинность, не могут взаимодействовать с устройством. When authentication is required, devices that cannot authenticate cannot communicate with your device. С помощью IPsec можно также зашифровать определенный сетевой трафик, чтобы предотвратить его чтение или перехват во время перехода между устройствами. By using IPsec, you can also require that specific network traffic be encrypted to prevent it from being read or intercepted while in transit between devices.
Интерфейс для Защитник Windows брандмауэра гораздо более гибок и гибок, чем пользовательский интерфейс, Защитник Windows панели управления брандмауэром. The interface for Windows Defender Firewall is much more capable and flexible than the consumer-friendly interface found in the Windows Defender Firewall Control Panel. Они взаимодействуют с одними и теми же службами, но обеспечивают разные уровни контроля над этими службами. They both interact with the same underlying services, but provide different levels of control over those services. Хотя панель управления Защитник Windows брандмауэра отвечает требованиям для защиты одного устройства в домашней среде, она не предоставляет достаточных функций централизованного управления или безопасности для защиты более сложного сетевого трафика в типичной корпоративной среде. While the Windows Defender Firewall Control Panel meets the needs for protecting a single device in a home environment, it does not provide enough centralized management or security features to help secure more complex network traffic found in a typical business enterprise environment.
Об этом руководстве About this guide
В этом руководстве вы можете выбрать или создать проект для развертывания Защитник Windows брандмауэра в корпоративной среде. This guide provides recommendations to help you to choose or create a design for deploying Windows Defender Firewall in your enterprise environment. В руководстве описываются некоторые распространенные цели использования брандмауэра Защитник Windows, а затем описаны цели, применимые к вашему сценарию, с проектами, представленными в этом руководстве. The guide describes some of the common goals for using Windows Defender Firewall, and then helps you map the goals that apply to your scenario to the designs that are presented in this guide.
Это руководство предназначено для ИТ-специалистов, которым назначена задача развертывания технологий брандмауэра и IPsec в сети организации для достижения целей безопасности организации. This guide is intended for the IT professional who has been assigned the task of deploying firewall and IPsec technologies on an organization’s network to help meet the organization’s security goals.
Защитник Windows брандмауэр должен быть частью комплексного решения для обеспечения безопасности, которое реализует различные технологии безопасности, такие как брандмауэры периметра, системы обнаружения вторжений, виртуальная частная сеть (VPN), проверка подлинности IEEE 802.1X для беспроводных и проводных подключений, а также правила безопасности подключений IPsec. Windows Defender Firewall should be part of a comprehensive security solution that implements a variety of security technologies, such as perimeter firewalls, intrusion detection systems, virtual private networking (VPN), IEEE 802.1X authentication for wireless and wired connections, and IPsec connection security rules.
Для успешного использования этого руководства необходимо хорошо понимать как возможности брандмауэра Защитник Windows, так и то, как доставлять параметры конфигурации на управляемые устройства с помощью групповой политики в Active Directory. To successfully use this guide, you need a good understanding of both the capabilities provided by Windows Defender Firewall, and how to deliver configuration settings to your managed devices by using Group Policy in Active Directory.
Цели реализации можно использовать для формирования одной из этих Защитник Windows брандмауэра с расширенными макетами безопасности или настраиваемого дизайна, объединяющего элементы из представленных здесь элементов: You can use the implementation goals to form one of these Windows Defender Firewall with Advanced Security designs, or a custom design that combines elements from those presented here:
Проектирование базовой политики брандмауэра. Basic firewall policy design. Ограничивает сетевой трафик, в который и из ваших устройств, передается только необходимый и авторизованный трафик. Restricts network traffic in and out of your devices to only that which is needed and authorized.
Разработка политики изоляции домена. Domain isolation policy design. Предотвращает получение незапрошенного сетевого трафика с устройств, которые не являются членами домена, устройствам, которые являются членами домена. Prevents devices that are domain members from receiving unsolicited network traffic from devices that are not domain members. Можно установить дополнительные «зоны» для поддержки особых требований некоторых устройств, например: Additional «zones» can be established to support the special requirements of some devices, such as:
«Граница зоны» для устройств, которые должны иметь возможность получать запросы от не изолированных устройств. A «boundary zone» for devices that must be able to receive requests from non-isolated devices.
«Зона шифрования» для устройств, которые хранят конфиденциальные данные, которые должны быть защищены во время передачи по сети. An «encryption zone» for devices that store sensitive data that must be protected during network transmission.
Разработка политики изоляции сервера. Server isolation policy design. Ограничивает доступ к серверу только ограниченной группой авторизованных пользователей и устройств. Restricts access to a server to only a limited group of authorized users and devices. Обычно настраивается в качестве зоны в проекте изоляции домена, но также может быть настроен как изолированный дизайн, обеспечивая многие преимущества изоляции домена от небольшого набора устройств. Commonly configured as a zone in a domain isolation design, but can also be configured as a stand-alone design, providing many of the benefits of domain isolation to a small set of devices.
Проектирование политики изоляции на основе сертификатов. Certificate-based isolation policy design. Этот дизайн дополняет один из предыдущих двух макетов и поддерживает любую из их возможностей. This design is a complement to either of the previous two designs, and supports any of their capabilities. Вместо проверки подлинности Kerberos V5, используемой по умолчанию в Active Directory, используются криптографические сертификаты, развернутые на клиентах и серверах. It uses cryptographic certificates that are deployed to clients and servers for authentication, instead of the Kerberos V5 authentication used by default in Active Directory. Это позволяет устройствам, которые не являются частью домена Active Directory, например устройствам под управлением операционных систем, кроме Windows, участвовать в решении изоляции. This enables devices that are not part of an Active Directory domain, such as devices running operating systems other than Windows, to participate in your isolation solution.
В дополнение к описаниям и примерам для каждого проекта вы найдете рекомендации по сбору необходимых данных о вашей среде. In addition to descriptions and example for each design, you will find guidelines for gathering required data about your environment. Затем вы можете использовать эти рекомендации для планирования и разработки брандмауэра Защитник Windows с расширенным развертыванием безопасности. You can then use these guidelines to plan and design your Windows Defender Firewall with Advanced Security deployment. После прочтания этого руководства и завершения сбора, документирования и сопоставления требований организации у вас есть сведения, необходимые для начала развертывания брандмауэра Защитник Windows с помощью рекомендаций в руководстве по развертыванию брандмауэра Защитник Windows с расширенным развертыванием системы безопасности. After you read this guide, and finish gathering, documenting, and mapping your organization’s requirements, you have the information that you need to begin deploying Windows Defender Firewall using the guidance in the Windows Defender Firewall with Advanced Security Deployment Guide.
Вы можете найти Защитник Windows брандмауэра с помощью руководства по развертыванию advanced Security Deployment в указанных здесь расположениях. You can find the Windows Defender Firewall with Advanced Security Deployment Guide at these locations:
(Загружаемый документ Word) (Downloadable Word document)
В этом разделе In this section
| Статья Topic | Описание Description |
|---|---|
| Understanding the Защитник Windows firewall with Advanced Security Design Process Understanding the Windows Defender Firewall with Advanced Security Design Process | Узнайте, как начать работу с брандмауэром Защитник Windows с помощью процесса разработки advanced Security. Learn how to get started with the Windows Defender Firewall with Advanced Security design process. |
| Определение брандмауэра Защитник Windows безопасности с помощью расширенных целей развертывания системы безопасности Identifying Your Windows Defender Firewall with Advanced Security Deployment Goals | Узнайте, как определить брандмауэр Защитник Windows с целями реализации advanced Security. Learn how to identify your Windows Defender Firewall with Advanced Security implementation goals. |
| Сопоставление целей развертывания с брандмауэром Защитник Windows с расширенным дизайном безопасности Mapping Your Deployment Goals to a Windows Defender Firewall with Advanced Security Design | После завершения проверки существующего брандмауэра Защитник Windows с целями реализации advanced Security и определения целей, важных для конкретного развертывания, можно сопооставить эти цели с определенным брандмауэром Защитник Windows с расширенным дизайном безопасности. After you finish reviewing the existing Windows Defender Firewall with Advanced Security implementation goals and you determine which goals are important to your specific deployment, you can map those goals to a specific Windows Defender Firewall with Advanced Security design. |
| Проектирование брандмауэра Защитник Windows с помощью стратегии «Advanced Security» Designing a Windows Defender Firewall with Advanced Security Strategy | Чтобы выбрать наиболее эффективную разработку для защиты сети, необходимо тратить время на сбор основных сведений о текущей компьютерной среде. To select the most effective design for helping to protect the network, you must spend time collecting key information about your current computer environment. |
| Планирование брандмауэра Защитник Windows с расширенным дизайном безопасности Planning Your Windows Defender Firewall with Advanced Security Design | После сбора соответствующей информации в предыдущих разделах и понимания основ разработки, как описано выше в этом руководстве, можно выбрать дизайн (или сочетание макетов), которые соответствуют вашим потребностям. After you have gathered the relevant information in the previous sections, and understand the basics of the designs as described earlier in this guide, you can select the design (or combination of designs) that meet your needs. |
| Приложение A. Пример файлов шаблонов GPO для параметров, используемых в этом руководстве Appendix A: Sample GPO Template Files for Settings Used in this Guide | XML-файл, содержащий настраиваемые параметры реестра, можно импортировать в объект групповой политики (GPO) с помощью функции «Настройки» консоли управления групповыми политиками (GPMC). You can import an XML file containing customized registry preferences into a Group Policy Object (GPO) by using the Preferences feature of the Group Policy Management Console (GPMC). |
Терминология, используемая в этом руководстве Terminology used in this guide
В следующей таблице указаны и определены термины, используемые в этом руководстве. The following table identifies and defines terms used throughout this guide.