- What is Operating System? Types of OS, Features and Examples
- What is an Operating System?
- History Of OS
- Examples of Operating System with Market Share
- Types of Operating System (OS)
- Batch Operating System
- Multi-Tasking/Time-sharing Operating systems
- Real time OS
- Distributed Operating System
- Network Operating System
- Mobile OS
- Functions of Operating System
- Features of Operating System (OS)
- Advantage of using Operating System
- Disadvantages of using Operating System
- What is a Kernel?
- Features of Kennel
- Types of Kernels
- Microsoft Windows
- Microsoft Windows
What is Operating System? Types of OS, Features and Examples
What is an Operating System?
An Operating System (OS) is a software that acts as an interface between computer hardware components and the user. Every computer system must have at least one operating system to run other programs. Applications like Browsers, MS Office, Notepad Games, etc., need some environment to run and perform its tasks.
The OS helps you to communicate with the computer without knowing how to speak the computer’s language. It is not possible for the user to use any computer or mobile device without having an operating system. 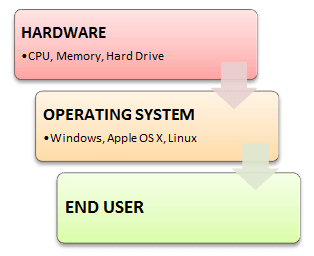
History Of OS
- Operating systems were first developed in the late 1950s to manage tape storage
- The General Motors Research Lab implemented the first OS in the early 1950s for their IBM 701
- In the mid-1960s, operating systems started to use disks
- In the late 1960s, the first version of the Unix OS was developed
- The first OS built by Microsoft was DOS. It was built in 1981 by purchasing the 86-DOS software from a Seattle company
- The present-day popular OS Windows first came to existence in 1985 when a GUI was created and paired with MS-DOS.
Examples of Operating System with Market Share
Following are the examples of Operating System with the latest Market Share
| OS Name | Share |
| Windows | 40.34 |
| Android | 37.95 |
| iOS | 15.44 |
| Mac OS | 4.34 |
| Linux | 0.95 |
| Chrome OS | 0.14 |
| Windows Phone OS | 0.06 |
Types of Operating System (OS)
Following are the popular types of Operating System:
- Batch Operating System
- Multitasking/Time Sharing OS
- Multiprocessing OS
- Real Time OS
- Distributed OS
- Network OS
- Mobile OS
Batch Operating System
Some computer processes are very lengthy and time-consuming. To speed the same process, a job with a similar type of needs are batched together and run as a group.
The user of a batch operating system never directly interacts with the computer. In this type of OS, every user prepares his or her job on an offline device like a punch card and submit it to the computer operator.
Multi-Tasking/Time-sharing Operating systems
Time-sharing operating system enables people located at a different terminal(shell) to use a single computer system at the same time. The processor time (CPU) which is shared among multiple users is termed as time sharing.
Real time OS
A real time operating system time interval to process and respond to inputs is very small. Examples: Military Software Systems, Space Software Systems are the Real time OS example.
Distributed Operating System
Distributed systems use many processors located in different machines to provide very fast computation to its users.
Network Operating System
Network Operating System runs on a server. It provides the capability to serve to manage data, user, groups, security, application, and other networking functions.
Mobile OS
Mobile operating systems are those OS which is especially that are designed to power smartphones, tablets, and wearables devices.
Some most famous mobile operating systems are Android and iOS, but others include BlackBerry, Web, and watchOS.
Functions of Operating System
Below are the main functions of Operating System: 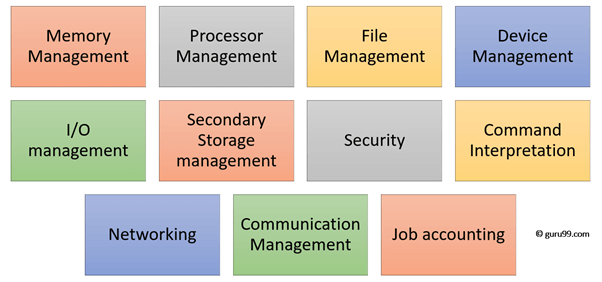
In an operating system software performs each of the function:
- Process management:- Process management helps OS to create and delete processes. It also provides mechanisms for synchronization and communication among processes.
- Memory management:- Memory management module performs the task of allocation and de-allocation of memory space to programs in need of this resources.
- File management:- It manages all the file-related activities such as organization storage, retrieval, naming, sharing, and protection of files.
- Device Management: Device management keeps tracks of all devices. This module also responsible for this task is known as the I/O controller. It also performs the task of allocation and de-allocation of the devices.
- I/O System Management: One of the main objects of any OS is to hide the peculiarities of that hardware devices from the user.
- Secondary-Storage Management: Systems have several levels of storage which includes primary storage, secondary storage, and cache storage. Instructions and data must be stored in primary storage or cache so that a running program can reference it.
- Security:- Security module protects the data and information of a computer system against malware threat and authorized access.
- Command interpretation: This module is interpreting commands given by the and acting system resources to process that commands.
- Networking: A distributed system is a group of processors which do not share memory, hardware devices, or a clock. The processors communicate with one another through the network.
- Job accounting: Keeping track of time & resource used by various job and users.
- Communication management: Coordination and assignment of compilers, interpreters, and another software resource of the various users of the computer systems.
Features of Operating System (OS)
Here is a list important features of OS:
- Protected and supervisor mode
- Allows disk access and file systems Device drivers Networking Security
- Program Execution
- Memory management Virtual Memory Multitasking
- Handling I/O operations
- Manipulation of the file system
- Error Detection and handling
- Resource allocation
- Information and Resource Protection

Advantage of using Operating System
- Allows you to hide details of hardware by creating an abstraction
- Easy to use with a GUI
- Offers an environment in which a user may execute programs/applications
- The operating system must make sure that the computer system convenient to use
- Operating System acts as an intermediary among applications and the hardware components
- It provides the computer system resources with easy to use format
- Acts as an intermediator between all hardware’s and software’s of the system
Disadvantages of using Operating System
- If any issue occurs in OS, you may lose all the contents which have been stored in your system
- Operating system’s software is quite expensive for small size organization which adds burden on them. Example Windows
- It is never entirely secure as a threat can occur at any time
What is a Kernel?
The kernel is the central component of a computer operating systems. The only job performed by the kernel is to the manage the communication between the software and the hardware. A Kernel is at the nucleus of a computer. It makes the communication between the hardware and software possible. While the Kernel is the innermost part of an operating system, a shell is the outermost one.
Features of Kennel
- Low-level scheduling of processes
- Inter-process communication
- Process synchronization
- Context switching
Types of Kernels
There are many types of kernels that exists, but among them, the two most popular kernels are:
1.Monolithic
A monolithic kernel is a single code or block of the program. It provides all the required services offered by the operating system. It is a simplistic design which creates a distinct communication layer between the hardware and software.
2. Microkernels
Microkernel manages all system resources. In this type of kernel, services are implemented in different address space. The user services are stored in user address space, and kernel services are stored under kernel address space. So, it helps to reduce the size of both the kernel and operating system.
Microsoft Windows
Our editors will review what you’ve submitted and determine whether to revise the article.
Microsoft Windows, also called Windows and Windows OS, computer operating system (OS) developed by Microsoft Corporation to run personal computers (PCs). Featuring the first graphical user interface (GUI) for IBM-compatible PCs, the Windows OS soon dominated the PC market. Approximately 90 percent of PCs run some version of Windows.
The first version of Windows, released in 1985, was simply a GUI offered as an extension of Microsoft’s existing disk operating system, or MS-DOS. Based in part on licensed concepts that Apple Inc. had used for its Macintosh System Software, Windows for the first time allowed DOS users to visually navigate a virtual desktop, opening graphical “windows” displaying the contents of electronic folders and files with the click of a mouse button, rather than typing commands and directory paths at a text prompt.
Subsequent versions introduced greater functionality, including native Windows File Manager, Program Manager, and Print Manager programs, and a more dynamic interface. Microsoft also developed specialized Windows packages, including the networkable Windows for Workgroups and the high-powered Windows NT, aimed at businesses. The 1995 consumer release Windows 95 fully integrated Windows and DOS and offered built-in Internet support, including the World Wide Web browser Internet Explorer.
With the 2001 release of Windows XP, Microsoft united its various Windows packages under a single banner, offering multiple editions for consumers, businesses, multimedia developers, and others. Windows XP abandoned the long-used Windows 95 kernel (core software code) for a more powerful code base and offered a more practical interface and improved application and memory management. The highly successful XP standard was succeeded in late 2006 by Windows Vista, which experienced a troubled rollout and met with considerable marketplace resistance, quickly acquiring a reputation for being a large, slow, and resource-consuming system. Responding to Vista’s disappointing adoption rate, Microsoft in 2009 released Windows 7, an OS whose interface was similar to that of Vista but was met with enthusiasm for its noticeable speed improvement and its modest system requirements.
Windows 8 in 2012 offered a start screen with applications appearing as tiles on a grid and the ability to synchronize settings so users could log on to another Windows 8 machine and use their preferred settings. In 2015 Microsoft released Windows 10, which came with Cortana, a digital personal assistant like Apple’s Siri, and the Web browser Microsoft Edge, which replaced Internet Explorer. Microsoft also announced that Windows 10 would be the last version of Windows, meaning that users would receive regular updates to the OS but that no more large-scale revisions would be done.
The Editors of Encyclopaedia Britannica This article was most recently revised and updated by Amy Tikkanen, Corrections Manager.
Microsoft Windows
Windows is Microsoft’s flagship operating system (OS), the de facto standard for home and business computers. The graphical user interface (GUI)-based OS was introduced in 1985 and has been released in many versions since then, as described below. Microsoft got its start with the partnership of Bill Gates and Paul Allen in 1975. Gates and Allen co-developed Xenix (a version of Unix) and also collaborated on a BASIC interpreter for the Altair 8800. The company was incorporated in 1981.
Microsoft gained prominence in the tech field with the release of MS-DOS, a text-based command-line-driven operating system. DOS was mostly based on a purchased intellectual property, QDOS. GUI-based operating systems of that time included Xerox’s Alto, released in 1979, and Apple’s LISA and Macintosh systems, which came later. Die-hard fans of MS-DOS referred to such systems as WIMPs, which stood for «windows, icons, mouse and pull-down menus (or pointers).»
However, Gates saw the potential in GUI-based systems and started a project he called Interface Manager. Gates thought he could bring the GUI to a wider audience at a lower cost than the $9,000 LISA. The rest of Microsoft supported this idea, and, in a somewhat ironic move, the project team selected «Windows» as the name of the new operating system.
Microsoft announced the impending release of Windows 1.0 in 1983. The company used some features it licensed from Apple for portions of its interface. Microsoft released Windows 1.0 in 1985. Apple sued Microsoft and Hewlett-Packard for $5.5 billion in 1988 claiming it did not give the companies authorization to use certain GUI elements. In 1992, a federal court concluded Microsoft and Hewlett-Packard did not go beyond the 1985 agreement. Apple appealed that decision, which was upheld in 1994.
Competitors to Windows include Apple’s macOS and the open source Linux operating system from Linus Torvalds. The free price gives Linux an edge in availability, while macOS is known for its stability and user experience. However, Microsoft Windows continues to maintain its dominance — a June 2018 report from the NetMarketShare site shows Windows installed on nearly 88% of desktops and laptops — with a steady rollout of new versions to support advances in hardware.
Like many early versions of Microsoft’s GUI operating systems, Windows 1.0 was essentially a program that ran on top of DOS. Microsoft did not release the system until two years after its first announcement, leading to suggestions that Windows was vaporware. The release was a shaky start for the tech giant. Users found the software unstable. However, the point-and-click interface made it easier for new users to operate a computer. The user-friendly nature of Windows also drew interest from customers who might have been intimidated by a command-line interface. Windows 1.0 offered many of the common components found in today’s graphical user interface, such as scroll bars and «OK» buttons.
1987: Windows 2.0 and 2.11
Windows 2.0 was faster, more stable and had more GUI features in common with the Apple LISA. The system introduced the control panel and ran the first versions of Excel and Word. Windows 2.0 supported extended memory, and Microsoft updated it for compatibility with Intel’s 80386 processor. It was during this time that Microsoft became the largest software vendor in the world, just as computers were becoming more commonplace. The fact that Windows systems were user-friendly and relatively affordable was a contributing factor to the growing PC market.
Microsoft optimized the Windows 3.0 operating system, which still ran on top of DOS, for the 386 processor for a more responsive system. Windows 3.0 supported 16 colors and included the casual games familiar to most Windows users: Solitaire, Minesweeper and Hearts. Games that required more processing power still ran directly on MS-DOS. Exiting to DOS gave games direct hardware access made more system resources available that otherwise would have gone to Windows. Microsoft offered Windows 3.1 as a paid sub-release in 1993. Windows 3.1 features included support for TrueType fonts and peer-to-peer networking.
Windows NT’s release marked the completion of a side project to build a new, advanced OS. NT was 32-bit and had a hardware abstraction layer. DOS was available through the command prompt, but it did not run the Windows OS. Microsoft designed NT as a workstation OS for businesses rather than home users. The system introduced the Start button.
Windows 95 introduced the Windows operating system to a wider audience with a marketing campaign that featured The Rolling Stones song «Start Me Up» to celebrate the Start button’s arrival to the masses. Windows 95 facilitated hardware installation with its Plug and Play feature. Microsoft also unveiled 32-bit color depth, enhanced multimedia capabilities and TCP/IP network support.
Microsoft improved speed and Plug and Play hardware support in Windows 98. The company also debuted USB support and the Quick Launch bar in this release. DOS gaming began to wane as Windows gaming technology improved. The popularity of the OS made it an attractive target for malware. Microsoft integrated web technology into the Windows user interface and built its own web browser into the desktop. This feature was one of the defining issues in the U.S. Justice Department’s antitrust suit against Microsoft in the 1990s.
Windows ME (Millennium Edition) was the last use of the Windows 95 codebase. Its most notable new feature was System Restore. Many customers found this release to be unstable, and it was acknowledged as a poor release by Steve Ballmer and Microsoft. Some critics said ME stood for «mistake edition.»
Microsoft released the professional desktop OS Windows 2000 the same year. Microsoft based this OS on the more stable Windows NT code. Some home users installed Windows 2000 for its greater reliability. Microsoft updated Plug and Play support, which spurred home users to switch to this OS.
Microsoft delivered Windows XP as the first NT-based system with a version aimed squarely at the home user. Home users and critics rated XP highly. The system improved Windows appearance with colorful themes and provided a more stable platform.
Microsoft virtually ended gaming in DOS with this release. DirectX-enabled features in 3D gaming that OpenGL had difficulties with. XP offered the first Windows support for 64-bit computing, but it was not very well supported, lacking drivers and applications to run.
Microsoft hyped Windows Vista after the company spent a lot of resources to develop a more polished appearance. Vista had interesting visual effects but the OS was slow to start and run. The 32-bit version, in particular, didn’t enable enough RAM for the memory-hungry OS to operate properly.
Microsoft tightened licensing rights and made it more work to activate Windows. The company also peeled back user control of the operating system’s internal workings.
Microsoft lost market share to Apple and Linux variants. Vista’s flaws — coupled with the fact that many older computers lacked the resources to run the system — led to many home and business users staying with XP.
Microsoft built Windows 7 on the Vista kernel. Windows 7 picked up Vista’s visual capabilities but featured more stability. To many end users, the biggest changes between Vista and Windows 7 were faster boot times, new user interface and the addition of Internet Explorer 8.
With true 64-bit support and more Direct X features, Windows 7 proved to be a popular release for Windows users.
Microsoft released Windows 8 with a number of enhancements and debuted its tile-based Metro user interface. Windows 8 took better advantage of multicore processing, solid-state drives (SSD), touchscreens and other alternate input methods. Users found the switching from the traditional desktop to the tile-based interface awkward. Even after Microsoft’s UI and other updates in 8.1, Windows 8 trailed not just Windows 7 but XP in user numbers into 2014.
Microsoft announced Windows 10 in September 2014, skipping Windows 9. Version 10 includes the Start menu, which was absent from Windows 8. A responsive design feature called Continuum adapts the interface depending on whether the user works with a touchscreen or a keyboard and mouse for input. New features like an onscreen back button simplified touch input. Microsoft designed the OS to have a consistent interface across devices including PCs, laptops and tablets.
Microsoft did not implement many security methods in its operating systems until Windows NT and XP. For example, the default user on a Windows computer received administrator privileges until Vista.
Consumer editions of early versions of Windows did not have security measures built in since Microsoft designed the OS for single users without network connections. The company integrated security features in Windows NT, but they weren’t in the forefront of Microsoft’s design.The combination of lack of security and widespread popularity made Windows systems a target for malicious programs, such as viruses or system exploits.
Microsoft began to release monthly patches every second Tuesday of the month, known as Patch Tuesday, in 2003. Patches to update critical issues may be released on a faster schedule, known as out-of-band patches.
Windows Vista added User Account Control, a privilege evaluation feature based on a token system. The token allowed users only the most basic privileges, such as the ability to execute tasks that may modify system data. When an administrator logged on, they received two tokens — one that a standard user would receive and another that allowed administrator-level tasks.
Microsoft released its Windows Defender security application as a beta program for Windows XP in 2005. Windows Defender protects systems from spyware threats. Microsoft included Defender in later versions of Windows, such as Windows 10. Microsoft further buttressed system security with Windows Defender Credential Guard for virtualization-based security, System Guard to protect firmware components and configurations and Application Guard to protect against malware and hacking threats in the Microsoft Edge browser.
Starting with Windows XP, Microsoft separated Windows to give different features to distinct audiences. Windows 10, for example, has multiple editions including Windows 10 Home, Pro and Enterprise editions.
Microsoft makes its consumer operating systems for users in an ordinary household setting. Enterprise operating system is designed for large organizations in a business setting. The enterprise software tends to have more customization abilities and features that an organization can utilize, such as security or language packs.
Microsoft designed Windows 10 Home for consumers and tailored to operate on PCs, tablets and 2-in-1 devices. Microsoft built Windows 10 Pro as a baseline OS for any business, while it developed Windows 10 Enterprise for businesses with higher security needs.
Security features differ from Windows 10 Home, Pro and Enterprise editions. Windows 10 Home includes basic security features such as Windows Defender, Device Encryption and Windows Information Protection. Windows 10 Pro adds more security features such as Bitlocker, Windows Defender System Guard, Windows Defender Exploit Guard and Windows Defender Antivirus. Windows 10 Enterprise is identical in features and functionality to Pro but adds more security features such as Windows Defender Credential Guard, Windows Defender Application Guard and Windows Defender Application Control.
MacOS is a GUI-based OS developed and owned by Apple. MacOS is the primary OS for Apple computers. Apple introduced macOS in 1984. The company released a consumer version in 2001 with macOS X 10.0, which drew praise for its user interface, but criticism for its performance.
After macOS X 10.0, Apple developed newer versions of macOS X from 10.0-10.14. Earlier versions were named after big cats, such as Tiger, Puma, Snow Leopard and Mountain Lion. MacOS 10.4.4, or Tiger, was a notable update, which improved performance with graphics processing and file searching. Later versions of MacOS X were then named after California landmarks such as Yosemite, Sierra or Mojave.
Linux is an open source OS built on a Linux kernel. Released in 1991, Linux loads and unloads its kernel at runtime, meaning the user can add software or hardware to a Linux system without rebooting.
Linux is used in consumer and enterprise settings. A well-known consumer-based Linux OS, for example, is Android, which has a large install base on mobile devices. Enterprises can use server versions of Linux for enterprise use, such as virtual machines.