- How To Manage Virtual Memory (Pagefile) In Windows 10
- Introduction to page files
- Functionality
- Physical extension of RAM
- Application requirements
- Support for system crash dumps
- Page files in Windows with large physical memory
- System committed memory
- How to increase Page File size or Virtual Memory in Windows 10
- Increase Page File size on Windows 10
- Page File location
- How to Change Pagefile Size and Location in Windows
- What is Pagefile
- Change Pagefile Size
- Change Pagefile Location
- What is the best Page File size for 64-bit versions of Windows 10?
- Best Page File size for 64-bit versions of Windows 10
- 1] Crash dump setting
- 2] Peak system commit charge
- 3] Quantity of infrequently accessed pages+
How To Manage Virtual Memory (Pagefile) In Windows 10
This tutorial was written by Tom’s Hardware Community member viveknayyar007. You can find a list of all their tutorials here.
Pagefile in Windows 10 is a hidden system file with the .SYS extension that is stored on your computer’s system drive (usually C:\). The Pagefile allows the computer to perform smoothly by reducing the workload of the physical memory, or RAM.
Simply put, every time you open more applications than the RAM on your PC can accommodate, the programs already present in the RAM are automatically transferred to the Pagefile. This process is technically called Paging. Because the Pagefile works as a secondary RAM, many times it is also referred to as Virtual Memory.
The minimum and maximum size of the Pagefile can be up to 1.5 times and 4 times of the physical memory that your computer has, respectively. For example, if your computer has 1GB of RAM, the minimum Pagefile size can be 1.5GB, and the maximum size of the file can be 4GB.
By default, Windows 10 automatically manages the Pagefile according to your computer’s configuration and the RAM present in it. However, if you ever face lagging while working on Windows 10, or you start getting the PAGE_FAULT_IN_NONPAGED_AREA or KERNEL_DATA_INPAGE_ERROR Blue Screen of Death (BSOD), managing the size of the Pagefile manually is the first thing you should look for.
Managing the Pagefile size manually in Windows 10 is simple. Here is how:
- Use an administrator account to log on to Windows 10.
- From the desktop screen, right-click the Start button to open its context menu.
Introduction to page files
A page file (also known as a «paging file») is an optional, hidden system file on a hard disk.
Functionality
Page files have the following functionalities.
Physical extension of RAM
Page files enable the system to remove infrequently accessed modified pages from physical memory to let the system use physical memory more efficiently for more frequently accessed pages.
Application requirements
Some products or services require a page file for various reasons. For specific information, check the product documentation.
For example, the following Windows servers requires page files:
- Windows Server domain controllers (DCs)
- DFS Replication (DFS-R) servers
- Certificate servers
- ADAM/LDS servers
This is because the algorithm of the database cache for Extensible Storage Engine (ESENT, or ESE in Microsoft Exchange Server) depends on the «\Memory\Transition Pages RePurposed/sec» performance monitor counter. A page file is required to make sure that the database cache can release memory if other services or applications request memory.
For Windows Server 2012 Hyper-V and Windows Server 2012 R2 Hyper-V, the page file of the management OS (commonly called the host OS) should be left at the default of setting of «System Managed» .
Support for system crash dumps
Page files can be used to «back» (or support) system crash dumps and extend how much system-committed memory (also known as “virtual memory”) a system can support.
For more information about system crash dumps, see system crash dump options.
Page files in Windows with large physical memory
When large physical memory is installed, a page file might not be required to support the system commit charge during peak usage. For example, 64-bit versions of Windows and Windows Server support more physical memory (RAM) than 32-bit versions support. The available physical memory alone might be large enough.
However, the reason to configure the page file size has not changed. It has always been about supporting a system crash dump, if it is necessary, or extending the system commit limit, if it is necessary. For example, when a lot of physical memory is installed, a page file might not be required to back the system commit charge during peak usage. The available physical memory alone might be large enough to do this. However, a page file or a dedicated dump file might still be required to back a system crash dump.
System committed memory
Page files extend how much «committed memory» (also known as «virtual memory») is used to store modified data.
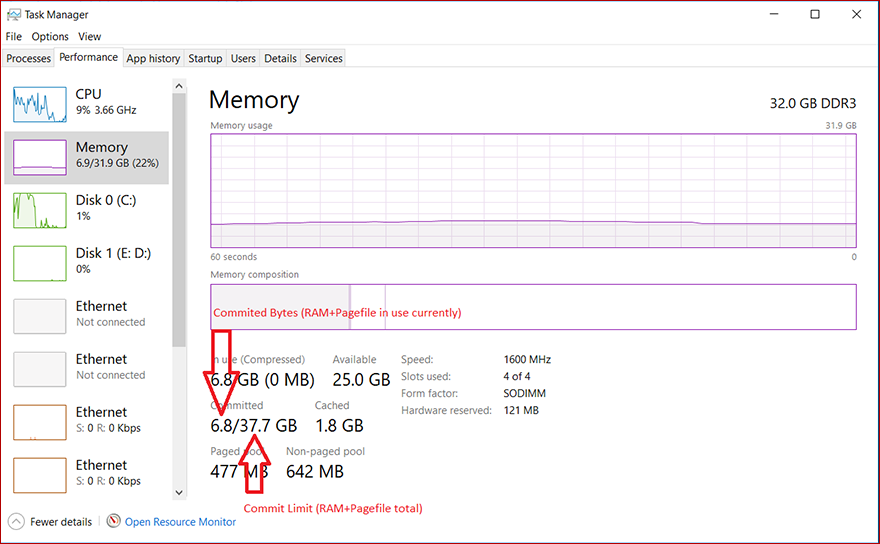
The system commit memory limit is the sum of physical memory and all page files combined. It represents the maximum system-committed memory (also known as the «system commit charge») that the system can support.
The system commit charge is the total committed or «promised» memory of all committed virtual memory in the system. If the system commit charge reaches the system commit limit, the system and processes might not get committed memory. This condition can cause freezing, crashing, and other malfunctions. Therefore, make sure that you set the system commit limit high enough to support the system commit charge during peak usage.
The system committed charge and system committed limit can be measured on the Performance tab in Task Manager or by using the «\Memory\Committed Bytes» and «\Memory\Commit Limit» performance counters. The \Memory% Committed Bytes In Use counter is a ratio of \Memory\Committed Bytes to \Memory\Commit Limit values.
System-managed page files automatically grow up to three times the physical memory or 4 GB (whichever is larger, but no more than one-eighth of the volume size) when the system commit charge reaches 90 percent of the system commit limit. This assumes that enough free disk space is available to accommodate the growth.
How to increase Page File size or Virtual Memory in Windows 10
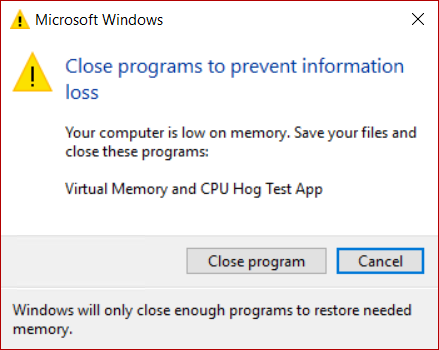
If you get a message Your system is low on virtual memory; when you try to start any memory-intensive application, like Microsoft Office, Corel, etc., then you may want to consider the option to increase Page File on Windows. The steps are the same for Windows 10, Windows 8.1 as well as Windows 7.
Increase Page File size on Windows 10
In case you get such an error message, you may have to increase the size of your virtual memory or page file or paging file – although for most users, leaving the Page File size at its default value should be good enough.
To increase Page File size via System Properties in Windows 10, follow these steps:
- In the Taskbar Search, type “Advanced System“. You will see View Advanced System Settings. Click on it.
- Or you can navigate to it via Control Panel
- In System Properties, click Advanced tab
- In Performance section click Settings button
- Performance Options will open. Click Advanced tab
- Here, under Virtual memory, select Change
- Uncheck Automatically manage paging file size for all drives
- Highlight your Windows system drive
- Select Custom size
- Change the Initial size value and the Maximum size value to a higher value
- Click Set
- Finally, Click Apply/OK all the way.
Page File location
The page file or swap file is also known as Virtual memory, and is situated on your system drive; e.,g. C:\pagefile.sys. In addition to physical memory or RAM, Windows and its applications use it as and when required.
Date: June 22, 2020 Tags: Memory, Page File
How to Change Pagefile Size and Location in Windows
Every now and then, you will see a suggestion in the Internet telling you to change the location and/or the size of the pagefile file in your Windows PC. Changing pagefile isn’t anything hard, but it is buried deep inside Windows settings as to avoid any unwanted changes. Let’s check out the way to change the location and size of pagefile in Windows.
Note: Even though it is easy to change pagefile settings, it is not recommended that you change these settings unless you know what you are doing. Any misconfiguration may result in your system not working as it should. Also, this procedure is the same for all the Windows versions.
What is Pagefile
Pagefile is like a virtual memory in your Windows PC. Whenever Windows runs low on the physically installed memory (RAM), it creates a hidden file named “pagefile.sys” and dumps all the least-used memory bits into that file. That way, Windows can clear up the physical RAM for any excess work.
Change Pagefile Size
1. To change pagefile size, we need to access Windows Advanced System Settings. To do that, press the Windows start button, search for “System” and then click on the “System” item displayed under the Control Panel in the results. If you are using Windows 8, press “Win + X” and then select “System” from the power user menu.
2. In this screen, click on the link “Advanced System Settings” displayed in the left pane. This will open the Advanced System Properties window.
3. Click on the “Settings” button under the Performance section. This action will open the Performance Options window.
4. Navigate to the “Advanced” tab and click on the “Change” button under Virtual Memory.
5. The above action will open the “Virtual Memory” window. Here uncheck the check box “Automatically manage paging file size for all drives,” select the paging file drive and again select the radio button “custom size.” Enter the initial size and maximum size for your pagefile and click on the “Ok” button to save the changes.
That’s all there is to do. Once you are done, close all the windows and restart your system to apply the changes.
Change Pagefile Location
To change the pagefile location, first follow the steps 1 through 4 above. Here in this window, uncheck the check box “Automatically manage paging file size for all drives.” Now select the default paging file drive, select the radio button “No Paging File” and click on the “Set” button. This action will effectively disable the paging file feature.
Select the drive where you want to store the paging file, select the radio button “System managed size” and click on the button “Set” to apply the changes. Once you are done, click on the “Ok” button and close all the windows.
That’s all there is to do. Just restart your system and you have successfully changed the paging file location in Windows.
In fact, if you head over to the drive you just selected, you will see the paging file with the name “Pagefile.sys.” Make sure that you have changed the Folder Options to show the protected operating system files.
Changing paging file settings is fairly easy in Windows, and it is particularly helpful when you are using SSD. That being said, only change the paging file settings if you are hundred percent sure.
Hopefully that helps, and do comment below with any suggestions and thoughts.
Vamsi is a tech and WordPress geek who enjoys writing how-to guides and messing with his computer and software in general. When not writing for MTE, he writes for he shares tips, tricks, and lifehacks on his own blog Stugon.
What is the best Page File size for 64-bit versions of Windows 10?
64-bit versions of Windows and Windows Server support more physical memory (RAM) than 32-bit versions support. However, the reason to configure or increase page file size has not changed. It has always been about supporting a system crash dump, if it is necessary, or extending the system commit limit if it is needed.
For example, when a lot of physical memory is installed, a page file might not be required to back the system commit charge during peak usage. The available physical memory alone might be large enough to do this. However, a page file or a dedicated dump file might still be required to back a system crash dump.
Best Page File size for 64-bit versions of Windows 10
That brings up the question of how much pagefile.sys size should be allocated? For the regular users, it is best to leave the Page File size to its default value, by letting the Windows OS decide.
Most of the Windows PCs have started moving towards SSDs and NVMe, and they are costly. So let’s take a look at the factors which can help you determine the appropriate size:
- Crash dump setting
- Peak system commit charge
- Quantity of infrequently accessed pages
Page File management is set to Automatic by Windows. It is located at C:\pagefile.sys and is a hidden file. If you want to configure it manually, then you can use this calculation. Also, to get this done, you should have a clear understanding of Pagefile and how it works with admin account privilege.
1] Crash dump setting
Below is the calculation Microsoft recommends to use the following calculations:
| System crash dump setting | Minimum page file size requirement |
|---|---|
| Small memory dump (256 KB) | 1 MB |
| Kernel memory dump | Depends on kernel virtual memory usage |
| Complete memory dump | 1 x RAM plus 257 MB* |
| Automatic memory dump | Depends on kernel virtual memory usage. For details, see the Automatic memory dump. |
* 1 MB of header data and device drivers can total 256 MB of secondary crash dump data.
Windows keeps all dump files at %SystemRoot%\Minidump and manages them automatically. If you want to enable the dedicated, DedicatedDumpFile then you need to change a Registry entry.
- Open the Registry Editor and browse to the following key:
- Right-click on the CrashControl and create a new String Value and name it DedicatedDumpFile
- Double click on it, and set the value to :\ . Where Drive is the partition like “D, E” and so on.
- Next, create a DWORD DumpFileSize and set the value which defines the size in megabytes (MB).
You can also set size and other factors. You can read more about it on the official page.
2] Peak system commit charge
Commit charge describes the total amount of virtual memory guaranteed for all processes to fit in physical memory and the page file. When you say Peak, it is the highest amount that the total commit charge has reached since the operating system was last started.
3] Quantity of infrequently accessed pages+
Follow this method to find out the quantity of infrequently accessed pages+ for minimum and maximum page file size.
| Minimum page file size | Maximum page file size |
|---|---|
| Varies based on-page file usage history, amount of RAM (RAM ÷ 8, max 32 GB), and crash dump settings. | 3 × RAM or 4 GB, whichever is larger. This is then limited to the volume size ÷ 8. However, it can grow to within 1 GB of free space on the volume if required for crash dump settings. |
I hope you were able to determine the appropriate page file size for 64-bit versions of Windows 10.