Process Priority Management in Windows
Let’s talk about the priority of Windows processes. In most cases, there is no need to think about the custom process priority settings, but sometimes a qualified system administrator can help a system to better allocate the processor time between running tasks. When is it needed? For example on the application server, you can give more CPU time for application and SQL server, as the most resource-critical processes.
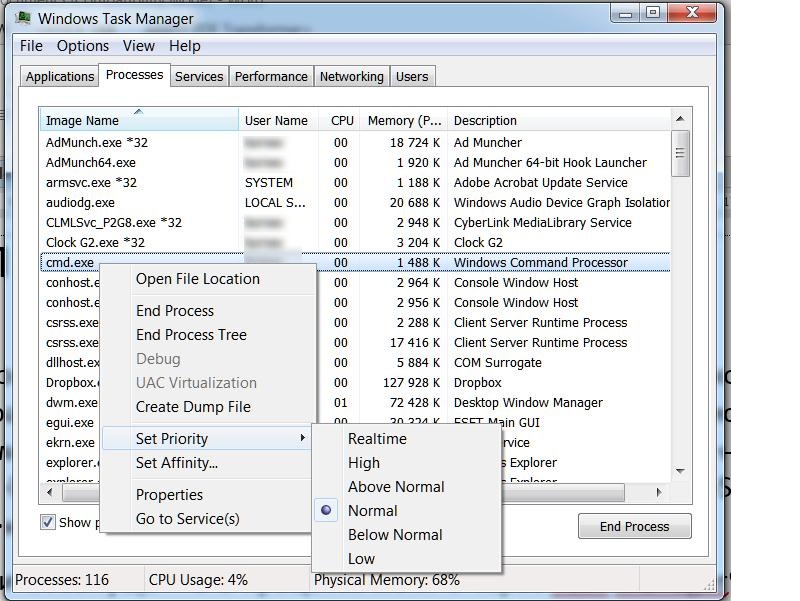
Generally, you can view and change the priority of the process using Task Manager (someprocess.exe -> Set Priority)
In Windows Server 2012, these settings are located on Details tab.
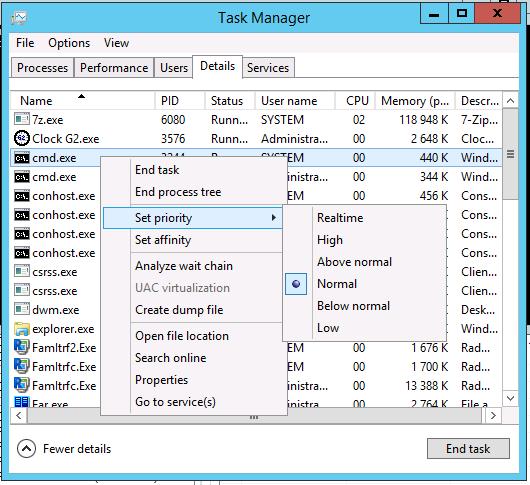
As you can see from these snapshots, only 6 priority types (as it will be explained later, these are the priority classes) are available. Is it enough? Microsoft thinks, it is. But let’s remember the epic saying by Bill Gates, who told that “640 KB of RAM will be enough for everybody”. But time has shown that it is far from the case. : )
Now let’s see, what it actually looks like.
In fact, there are 32 priority levels in Windows, from 0 to 31.
They are grouped as follows:
- 31 — 16 are real time levels
- 15 — 1 are dynamic levels
- 0 is a system level reserved for the zero-page thread
When a process is created, it is assigned one of the six priority classes:
- Real time class (value 24),
- High class (value 13),
- Above normal class (value 10),
- Normal class (value 8),
- Below normal class (value 6),
- or Idle class (value 4).
As it has been mentioned above, you can view the process priority using Task Manager.
The priority of each thread (basic thread priority) is composed of the priority of its process and the relative priority of the thread itself. There are seven types of relative priorities of the threads:
- Normal : the same as the process has
- Above normal : +1 to the priority of the process
- Below normal : -1 from the priority of the process
- Highest : +2;
- Lowest : -2;
- Time critical : sets the current priority of a thread as 31 for the Real time class, and 15 for the rest classes
- Idle : sets the current priority of a thread as 16 for the Real time class, and 1 for the rest classes
The following table shows process priorities, relative and current priorities of a thread.
| Thread Priority | Process Class | Process Class | |||||
| Idle class | Below normal class | Normal class | Above normal class | High class | Real time class | ||
| 1 | Idle | Idle | Idle | Idle | Idle | ||
| 2 | Lowest | ||||||
| 3 | Below … | ||||||
| 4 | Idle class | Normal | Lowest | ||||
| 5 | Above … | Below … | |||||
| 6 | Below normal class | Highest | Normal | Lowest | |||
| 7 | Above … | Below … | |||||
| 8 | Normal class | Highest | Normal | Lowest | |||
| 9 | Above … | Below … | |||||
| 10 | Above normal class | Highest | Normal | ||||
| 11 | Above … | Lowest | |||||
| 12 | Highest | Below … | |||||
| 13 | High class | Normal | |||||
| 14 | Above … | ||||||
| 15 | Highest | ||||||
| 15 | Time critical | Time critical | Time critical | Time critical | Time critical | ||
| 16 | Idle | ||||||
| 17 | |||||||
| 18 | |||||||
| 19 | |||||||
| 20 | |||||||
| 21 | |||||||
| 22 | Lowest | ||||||
| 23 | Below … | ||||||
| 24 | Real time class | Normal | |||||
| 25 | Above … | ||||||
| 26 | Highest | ||||||
| 27 | |||||||
| 28 | |||||||
| 29 | |||||||
| 30 | |||||||
| 31 | Time critical | ||||||
How to start a process with a non-standard priority or change it?
Method 1. Start a task/process and change its priority using Task Manager
- Only 6 types of priorities are available
- The priorities are changes with your mouse and you cannot make it automatic.
Method 2. You can use START command with the corresponding keys
The available keys responsible for priorities are as follows (I deliberately omit the keys of the START command, which are not related to the process of setting priorities being described):
C:\>start /?
Starts a separate window to run a specified program or command.
START [“title”] [/D path] [/I] [/MIN] [/MAX] [/SEPARATE | /SHARED]
[/LOW | /NORMAL | /HIGH | /REALTIME | /ABOVENORMAL | /BELOWNORMAL]
[/NODE ] [/AFFINITY ] [/WAIT] [/B]
[command/program] [parameters]
LOW Start application in the IDLE priority class.
NORMAL Start application in the NORMAL priority class.
HIGH Start application in the HIGH priority class.
REALTIME Start application in the REALTIME priority class.
ABOVENORMAL Start application in the ABOVENORMAL priority class.
BELOWNORMAL Start application in the BELOWNORMAL priority class.
As we can see, the START command allows to run a process with the same 6 priorities available in the Task Manager
- Only 6 types of priorities are available
Method 3. Using wmic.exe utility
As shown above, Task Manager and START command are quite awkward in assigning priorities. Let’s see how to do it more flexibly. We’ll use wmic.exe.
The command prompt:
wmic process where name=»AppName» CALL setpriority ProcessIDLevel
wmic process where name=»calc.exe» CALL setpriority 32768
wmic process where name=»calc.exe» CALL setpriority «above normal»
- idle: 64
- below normal: 16384
- normal: 32
- above normal: 32768
- high priority: 128
- real time: 256
Here is a short example of running wmic.exe to get the necessary information.
Use this command:
wmic process list brief
You’ll get the list of processes run on your local computer. Now run this command:
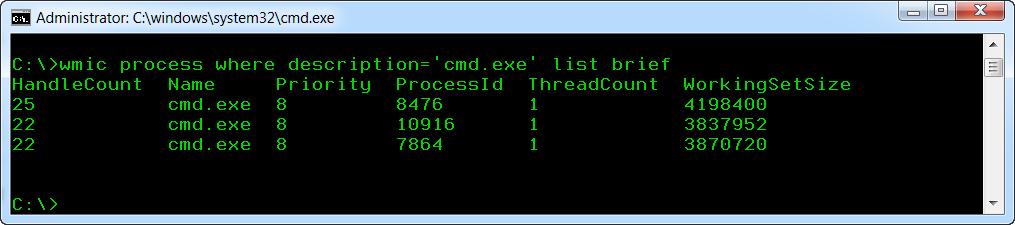
wmic process list brief | find «cmd.exe»
Here is the result:
I have deliberately started several copies of cmd.exe, to make it more demonstrative.
Now the list of processes is limited to those having “cmd.exe” in their name. Pay attention to the PID of the process(es).
Now let’s try to select the necessary processes using WMI. To do it, just enter:
wmic process where description=’cmd.exe’ list brief
Here is the result:
Compare the results. Remember the PID of CMD.EXE.
The command string to start wmic.exe
wmic process where processid=’XXXX’ CALL setpriority ProcessIDLevel
Now we can change the priority of a specific process (e. g., PID=8476):
wmic process where processid=’8476′ CALL setpriority 32768
wmic process where processid=’8476′ CALL setpriority «above normal»
What next? Think, try, select and manage your priorities to improve the performance of services and processes, together with the end user experience.
Управление приоритетами процессов в Windows
Давайте поговорим о приоритетах Windows процессов. В большинстве случаев «играться» с настройкой приоритетов нет необходимости, но, иногда, грамотный системный администратор может помочь системе более правильно распределить процессорное время между запущенными задачами. Единого рецепта нет, но путем «подбора и перебора» это вполне реализуемо. Где это может понадобиться? Например, в связке 1С-SQL можно дать больше процессорного времени 1С и SQL, как наиболее критичным к ресурсам процессам.
В общем случае, посмотреть и изменить приоритет запущенного процесса можно через Task Manager
Windows NT/2000/7/2008
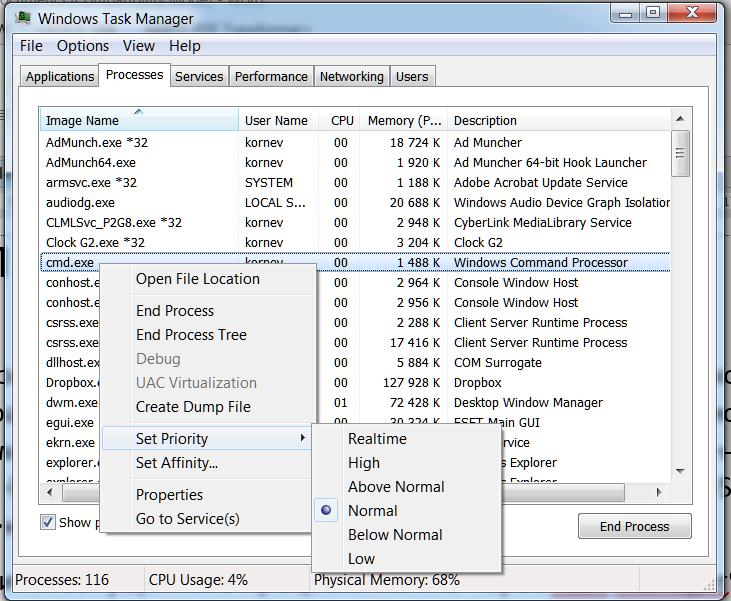
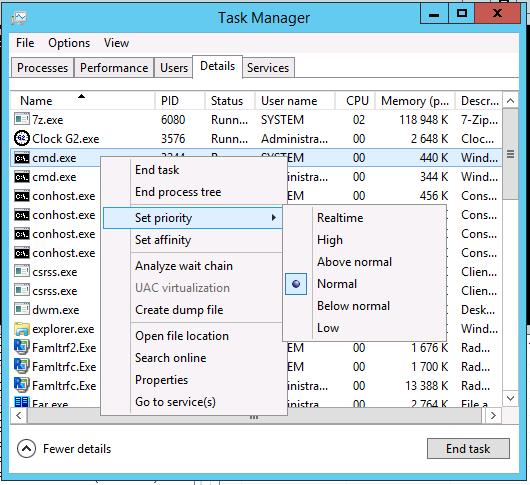
А теперь давайте разберемся, как это есть на самом деле.
На самом деле в Windows существует 32 уровня приоритета, от 0 до 31.
Они группируются так:
- 31 — 16 уровни реального времени;
- 15 — 1 динамические уровни;
- 0 — системный уровень, зарезервированный для потока обнуления страниц (zero-page thread).
При создании процесса, ему назначается один из шести классов приоритетов:
- Real time class (значение 24),
- High class (значение 13),
- Above normal class (значение 10),
- Normal class (значение 8),
- Below normal class (значение 6),
- или Idle class (значение 4).
Посмотреть приоритет процесса, как писалось выше, можно, используя Task Manager.
Приоритет каждого потока (базовый приоритет потока) складывается из приоритета его процесса и относительного приоритета самого потока. Есть семь относительных приоритетов потоков:
- Normal : такой же как и у процесса;
- Above normal : +1 к приоритету процесса;
- Below normal : -1;
- Highest : +2;
- Lowest : -2;
- Time critical : устанавливает базовый приоритет потока для Real time класса в 31, для остальных классов в 15.
- Idle : устанавливает базовый приоритет потока для Real time класса в 16, для остальных классов в 1.
В следующей таблице показаны приоритеты процесса, относительный и базовый приоритеты потока.
| Приоритет потока | Класс процесса | Класс процесса | |||||
| Idle class | Below normal class | Normal class | Above normal class | High class | Real time class | ||
| 1 | Idle | Idle | Idle | Idle | Idle | ||
| 2 | Lowest | ||||||
| 3 | Below … | ||||||
| 4 | Idle class | Normal | Lowest | ||||
| 5 | Above … | Below … | |||||
| 6 | Below normal class | Highest | Normal | Lowest | |||
| 7 | Above … | Below … | |||||
| 8 | Normal class | Highest | Normal | Lowest | |||
| 9 | Above … | Below … | |||||
| 10 | Above normal class | Highest | Normal | ||||
| 11 | Above … | Lowest | |||||
| 12 | Highest | Below … | |||||
| 13 | High class | Normal | |||||
| 14 | Above … | ||||||
| 15 | Highest | ||||||
| 15 | Time critical | Time critical | Time critical | Time critical | Time critical | ||
| 16 | Idle | ||||||
| 17 | |||||||
| 18 | |||||||
| 19 | |||||||
| 20 | |||||||
| 21 | |||||||
| 22 | Lowest | ||||||
| 23 | Below … | ||||||
| 24 | Real time class | Normal | |||||
| 25 | Above … | ||||||
| 26 | Highest | ||||||
| 27 | |||||||
| 28 | |||||||
| 29 | |||||||
| 30 | |||||||
| 31 | Time critical | ||||||
Теперь, когда мы все это узнали, что же с этим всем можно сделать? Ну, например, начать использовать.
Как еще можно запустить процесс с «нестандартным» приоритетом или изменить?
Метод 1. Запустить задачу/процесс и изменить приоритет через Task Manager.
- Доступно только 6 приоритетов
- Переключение приоритетов производится мышкой, не автоматизируется.
Метод 2. Можно воспользоваться командой START с соответствующими ключами
Доступные ключи, отвечающие за приоритеты, следующие (я умышленно опускаю ключи командной строки команды START не имеющие отношения к описываемому процессу работы с приоритетами):
C:\>start /?
Starts a separate window to run a specified program or command.
START [«title»] [/D path] [/I] [/MIN] [/MAX] [/SEPARATE | /SHARED]
[/LOW | /NORMAL | /HIGH | /REALTIME | /ABOVENORMAL | /BELOWNORMAL]
[/NODE ] [/AFFINITY ] [/WAIT] [/B]
[command/program] [parameters]
LOW Start application in the IDLE priority class.
NORMAL Start application in the NORMAL priority class.
HIGH Start application in the HIGH priority class.
REALTIME Start application in the REALTIME priority class.
ABOVENORMAL Start application in the ABOVENORMAL priority class.
BELOWNORMAL Start application in the BELOWNORMAL priority class.
Как видим, команда START дает возможность запустить процесс все с теми же 6-ю приоритетами, которые доступны через Task Manager
- Доступно только 6 приоритетов
Метод 3. Использование утилиты wmic.exe
Как было показано выше, Task Manager, и команда START достаточно неуклюжи для задачи назначения приоритетов. Посмотрим, как это применять более гибко. Будем использовать утилиту wmic.exe.
wmic process where name=»AppName» CALL setpriority ProcessIDLevel
wmic process where name=»calc.exe» CALL setpriority 32768
wmic process where name=»calc.exe» CALL setpriority «above normal»
- idle: 64
- below normal: 16384
- normal: 32
- above normal: 32768
- high priority: 128
- real time: 256
Вот короткий пример запуска wmic.exe для получения необходимой информации
wmic process list brief
Вы получите список процессов, запущенных на вашем локальном компьютере. Теперь выполните команду:
wmic process list brief | find «cmd.exe»
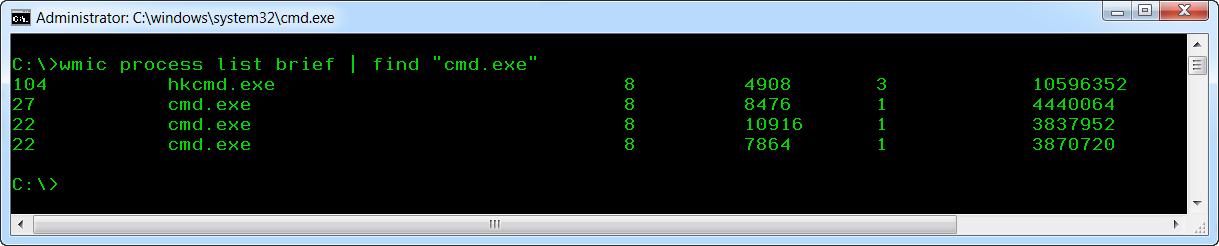
Теперь список процессов ограничен только теми процессами, в имени исполняемого модуля которых присутствует строка «cmd.exe». Обратите внимание на PID процесса(ов).
Теперь давайте попробуем отобрать интересующие нас процессы, используя непосредственно WMI и не прибегая к стандартным средствам командной строки. Для этого просто напишите:
wmic process where description=’cmd.exe’ list brief
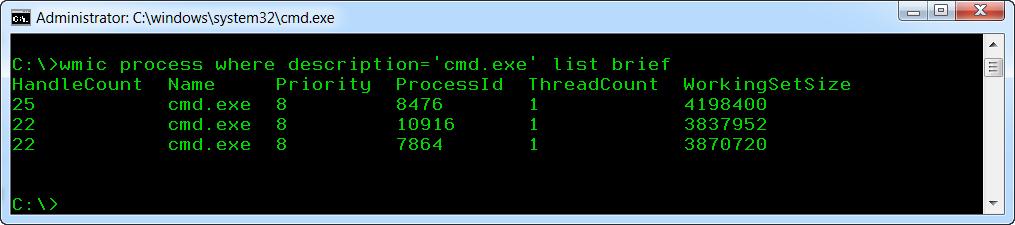
Командная строка для запуска wmic.exe
wmic process where processid=’XXXX’ CALL setpriority ProcessIDLevel
Ну а теперь можем изменить приоритет конкретного процесса (например с PID=8476):
wmic process where processid=’8476′ CALL setpriority 32768
wmic process where processid=’8476′ CALL setpriority «above normal»
А что дальше? Прикидывать, пробовать, подбирать и тонко регулировать приоритеты. Улучшая работу сервисов и процессов, а также работу конечных пользователей.