Installation
This section holds common questions about the way to install PHP. PHP is available for almost any OS, and almost any web server.
To install PHP, follow the instructions in Installation and Configuration.
PHP is glue. It is the glue used to build cool web applications by sticking dozens of 3rd-party libraries together and making it all appear as one coherent entity through an intuitive and easy to learn language interface. The flexibility and power of PHP relies on the stability and robustness of the underlying platform. It needs a working OS, a working web server and working 3rd-party libraries to glue together. When any of these stop working PHP needs ways to identify the problems and fix them quickly. When you make the underlying framework more complex by not having completely separate execution threads, completely separate memory segments and a strong sandbox for each request to play in, further weaknesses are introduced into PHP’s system.
If you want to use a threaded MPM, look at a FastCGI configuration where PHP is running in its own memory space.
Unix/Windows: Where should my php.ini file be located?
By default on Unix it should be in /usr/local/lib which is /lib . Most people will want to change this at compile-time with the —with-config-file-path flag. You would, for example, set it with something like:
On Windows the default path for the php.ini file is the Windows directory. If you’re using the Apache webserver, php.ini is first searched in the Apaches install directory, e.g. c:\program files\apache group\apache . This way you can have different php.ini files for different versions of Apache on the same machine.
See also the chapter about the configuration file.
Unix: I installed PHP, but every time I load a document, I get the message ‘Document Contains No Data’! What’s going on here?
This probably means that PHP is having some sort of problem and is core-dumping. Look in your server error log to see if this is the case, and then try to reproduce the problem with a small test case. If you know how to use ‘gdb’, it is very helpful when you can provide a backtrace with your bug report to help the developers pinpoint the problem. If you are using PHP as an Apache module try something like:
Stop your httpd processes
Stop your httpd processes
> run -X -f /path/to/httpd.conf
Then fetch the URL causing the problem with your browser
> run -X -f /path/to/httpd.conf
If you are getting a core dump, gdb should inform you of this now
You should include your backtrace in your bug report. This should be submitted to » https://bugs.php.net/
If your script uses the regular expression functions ( preg_match() and friends), you should make sure that you compiled PHP and Apache with the same regular expression package. This should happen automatically with PHP and Apache 1.3.x
Unix: I installed PHP using RPMS, but Apache isn’t processing the PHP pages! What’s going on here?
Assuming you installed both Apache and PHP from RPM packages, you need to uncomment or add some or all of the following lines in your httpd.conf file:
Unix: I patched Apache with the FrontPage extensions patch, and suddenly PHP stopped working. Is PHP incompatible with the Apache FrontPage extensions?
No, PHP works fine with the FrontPage extensions. The problem is that the FrontPage patch modifies several Apache structures, that PHP relies on. Recompiling PHP (using ‘make clean ; make’) after the FP patch is applied would solve the problem.
Unix/Windows: I have installed PHP, but when I try to access a PHP script file via my browser, I get a blank screen.
Do a ‘view source’ in the web browser and you will probably find that you can see the source code of your PHP script. This means that the web server did not send the script to PHP for interpretation. Something is wrong with the server configuration — double check the server configuration against the PHP installation instructions.
Unix/Windows: I have installed PHP, but when try to access a PHP script file via my browser, I get a server 500 error.
Something went wrong when the server tried to run PHP. To get to see a sensible error message, from the command line, change to the directory containing the PHP executable ( php.exe on Windows) and run php -i. If PHP has any problems running, then a suitable error message will be displayed which will give you a clue as to what needs to be done next. If you get a screen full of HTML codes (the output of the phpinfo() function) then PHP is working, and your problem may be related to your server configuration which you should double check.
Some operating systems: I have installed PHP without errors, but when I try to start Apache I get undefined symbol errors:
This has actually nothing to do with PHP, but with the MySQL client libraries. Some need —with-zlib, others do not. This is also covered in the MySQL FAQ.
Windows: I have installed PHP, but when I try to access a PHP script file via my browser, I get the error:
This error message means that PHP failed to output anything at all. To get to see a sensible error message, from the command line, change to the directory containing the PHP executable ( php.exe on Windows) and run php -i. If PHP has any problems running, then a suitable error message will be displayed which will give you a clue as to what needs to be done next. If you get a screen full of HTML codes (the output of the phpinfo() function) then PHP is working.
Once PHP is working at the command line, try accessing the script via the browser again. If it still fails then it could be one of the following:
- File permissions on your PHP script, php.exe , php5ts.dll , php.ini or any PHP extensions you are trying to load are such that the anonymous internet user ISUR_ cannot access them.
- The script file does not exist (or possibly isn’t where you think it is relative to your web root directory). Note that for IIS you can trap this error by ticking the ‘check file exists’ box when setting up the script mappings in the Internet Services Manager. If a script file does not exist then the server will return a 404 error instead. There is also the additional benefit that IIS will do any authentication required for you based on the NTLanMan permissions on your script file.
Windows: I’ve followed all the instructions, but still can’t get PHP and IIS to work together!
Make sure any user who needs to run a PHP script has the rights to run php.exe ! IIS uses an anonymous user which is added at the time IIS is installed. This user needs rights to php.exe . Also, any authenticated user will also need rights to execute php.exe . And for IIS4 you need to tell it that PHP is a script engine. Also, you will want to read this faq.
When running PHP as CGI with IIS, PWS, OmniHTTPD or Xitami, I get the following error: Security Alert! PHP CGI cannot be accessed directly. .
You must set the cgi.force_redirect directive to 0 . It defaults to 1 so be sure the directive isn’t commented out (with a ; ). Like all directives, this is set in php.ini
Because the default is 1 , it’s critical that you’re 100% sure that the correct php.ini file is being read. Read this faq for details.
How do I know if my php.ini is being found and read? It seems like it isn’t as my changes aren’t being implemented.
To be sure your php.ini is being read by PHP, make a call to phpinfo() . Near the top, there will be a listing called Configuration File (php.ini) . This will tell you where PHP is looking for php.ini and whether or not it’s being read. If just a directory PATH exists, then it’s not being read, and you should put your php.ini in that directory. If php.ini is included within the PATH , it is being read.
If php.ini is being read and you’re running PHP as a module, then be sure to restart your web server after making changes to php.ini
How do I add my PHP directory to the PATH on Windows?
Go to Control Panel and open the System icon (Start → Control Panel)
Go to the Advanced tab
Click on the ‘Environment Variables’ button
Look into the ‘System Variables’ pane
Find the Path entry (you may need to scroll to find it)
Double click on the Path entry
Enter your PHP directory at the end, including ‘;’ before (e.g. ;C:\php )
Note: Be sure to reboot after following the steps above to ensure that the PATH changes are applied.
There are several ways of doing this. If you are using Apache, read their installation specific instructions (Apache 1, Apache 2), otherwise you must set the PHPRC environment variable:
Go to Control Panel and open the System icon (Start → Settings → Control Panel → System, or just Start → Control Panel → System)
Go to the Advanced tab
Click on the ‘Environment Variables’ button
Look into the ‘System variables’ pane
Click on ‘New’ and enter ‘PHPRC’ as the variable name and the directory where php.ini is located as the variable value (e.g. C:\php )
Press OK and restart your computer
Is it possible to use Apache content negotiation (MultiViews option) with PHP?
If links to PHP files include extension, everything works perfect. This FAQ is only for the case when links to PHP files don’t include extension and you want to use content negotiation to choose PHP files from URL with no extension. In this case, replace the line AddType application/x-httpd-php .php with:
Is PHP limited to process GET and POST request methods only?
Настройка файла php.ini
PHP — это один из самых популярных языков программирования для создания сайтов и веб-приложений. На нем разработано множество готовых систем управления контентом для блогов, сайтов фирм или даже интернет-магазинов. Несмотря на то что у этого языка есть свои недостатки, он достаточно прост в освоении и поэтому очень часто используется для разработки новых сайтов.
Интерпретатор php может поставляться в виде модуля для Apache, выполнять скрипты из командной строки или в виде отдельного сервиса php-fpm. Эти сервисы отличаются своими возможностями, и предназначением, но для любого вида интерпретатора нужно задать базовые настройки, например, рабочая папка, включенные расширения, отображение ошибок и так далее. Все эти настройки задаются через файл php.ini. В этой инструкции мы рассмотрим как выполняется настройка файла php.ini в операционных системах Linux, хотя все информация подойдет и для Windows.
Если у вас еще не установлен интерпретатор языка программирования php, то вы можете ознакомиться со статьей установка lamp в Ubuntu 16.04.
Расположение и синтаксис php.ini
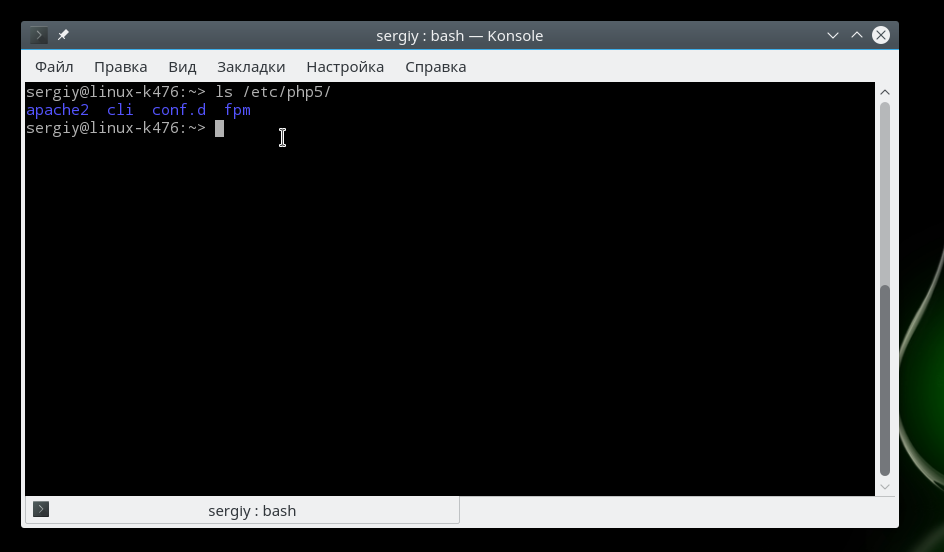
Для каждой версии интерпретатора конфигурационный файл php.ini находится в отдельной папке. Но все конфигурационные файлы находятся в папке /etc/php, например, /etc/php5:
Папка conf.d содержит общие настройки для различных расширений и модулей, они не будут нас сейчас интересовать. Более интересны следующие три папки — apache, cli и fpm. В них содержатся конфигурационные файлы php.ini для каждого из этих интерпретаторов.
Если вы собираетесь использовать несколько из этих интерпретаторов, то вам придется указывать настройки для каждого из них отдельно. Вы можете убедиться, что в каждой из папок лежит файл php.ini.
Что касается синтаксиса файла, то он разделен на секции, сначала идет секция настройки php, которая разделена на подсекции в зависимости от типа настроек, дальше идут секции настройки разных модулей. Синтаксис самих настроек очень прост, он соответствует привычному синтаксису ini файлов. Строка начинается с имени настройки, затем следует знак равно, а за ним значение:
имя_настройки = значение_параметра
Символами [] обозначается имя секции, например, [PHP], а символ ; означает комментарий, он и все символы после него не читаются интерпретатором. А теперь рассмотрим как выполняется настройка php.ini и переберем самые важные параметры.
Настройка файла php.ini
Для удобства ориентирования мы разобьем все параметры по категориях в зависимости от их назначения. Вам будет достаточно найти нужный параметр и изменить его значение. А теперь откройте файл настроек php, например, для модуля apache и перейдем к настройке. Чтобы избежать ошибок не добавляйте новые строки, а ищите уже существующие и изменяйте значения на нужные:
sudo gedit /etc/php5/apache/php.ini
Сначала идет немного информации о самом файле в виде комментариев, затем интересующие нас настройки.
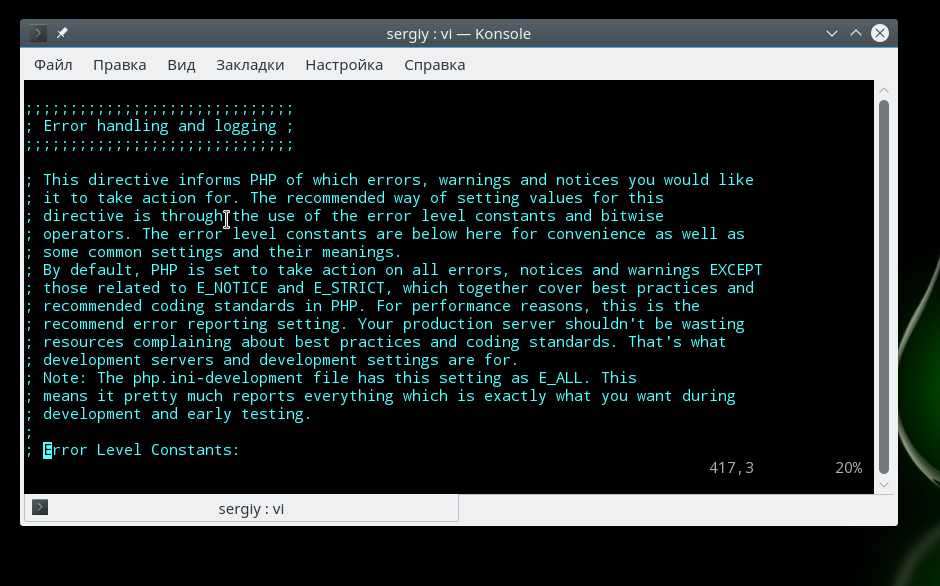
Вывод ошибок в php
Настройка php 7 обычно начинается с конфигурации вывода ошибок. Все настройки вывода ошибок находятся в разделе Error handling and logging. По умолчанию вывод ошибок на экран во время выполнения скрипта отключен. Это сделано для того, чтобы пользователи не смогли увидеть ничего лишнего. Вместо этого, все ошибки записываются в лог файл. Если вы используете php на домашнем компьютере, то такие меры не нужны и вы можете сразу выводить все на экран:
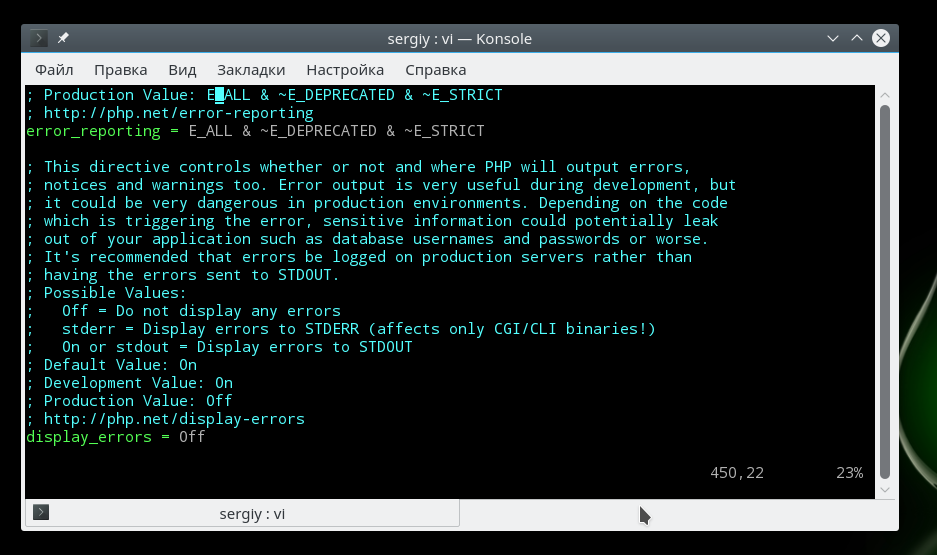
Замените off на on. В php используются различные типы ошибок, например, критические, предупреждения, ошибки синтаксиса, с помощью строки error_reporting вы можете включить вывод только определенных типов ошибок:
Если нужно объединить несколько типов ошибок, то используйте символ &, а для отключения отображения поставьте перед типом знак
. Приведенный выше пример отображает все ошибки (E_ALL), кроме сообщений об устаревших функциях (E_DEPRECATED). Вы можете отключить все типы использовав 0:
Включите запись ошибок php в лог файл, если не выводите их на экран:
Чтобы не засорять лог однотипными сообщениями можно игнорировать повторяющиеся ошибки в пределах одного исполнения:
Ограничения ресурсов
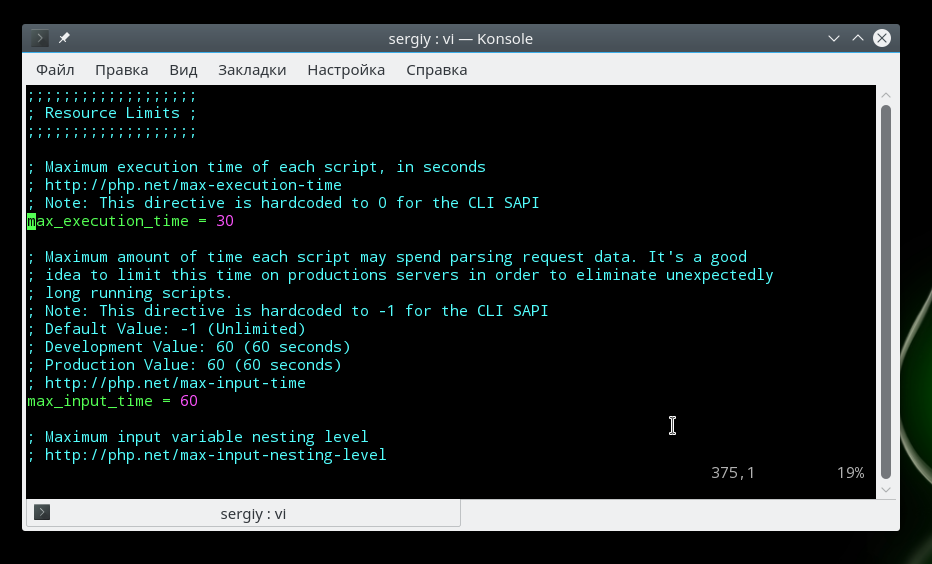
Если бы скрипты php никак не ограничивались в ресурсах, то они запросто могли бы перегрузить сервер и не дать ему нормально работать. Поэтому, по умолчанию php устанавливает жесткие ограничения, но, возможно, вам нужно будет их немного ослабить.
По умолчанию максимальное время выполнения скрипта — 30 секунд, сделаем минуту:
Если указать 0, то скрипт может выполняться бесконечно. Вы также можете ограничить время, на протяжении которого скрипт будет загружать данные, 60 секунд:
Максимальное количество переменных в GET и POST:
Следующий параметр задает максимальное количество памяти, которую может использовать один скрипт во время своего выполнения, в мегабайтах:
Максимальный размер данных, передаваемых в POST запросе тоже ограничивается, размер по умолчанию — 8 Мегабайт:
Вы можете ограничить область действия php в системе с помощью опции openbase_dir, она указывает папку, выше которой скрипт не может получить доступ к файловой системе:
С помощью директив disable_functions и disable_classes вы можете отключить использование в скриптах определенных функций или классов, например, это может быть полезно для веб-хостингов. В этом примере мы отключаем использование функции ini_set, которая позволяет менять настройки php из скрипта:
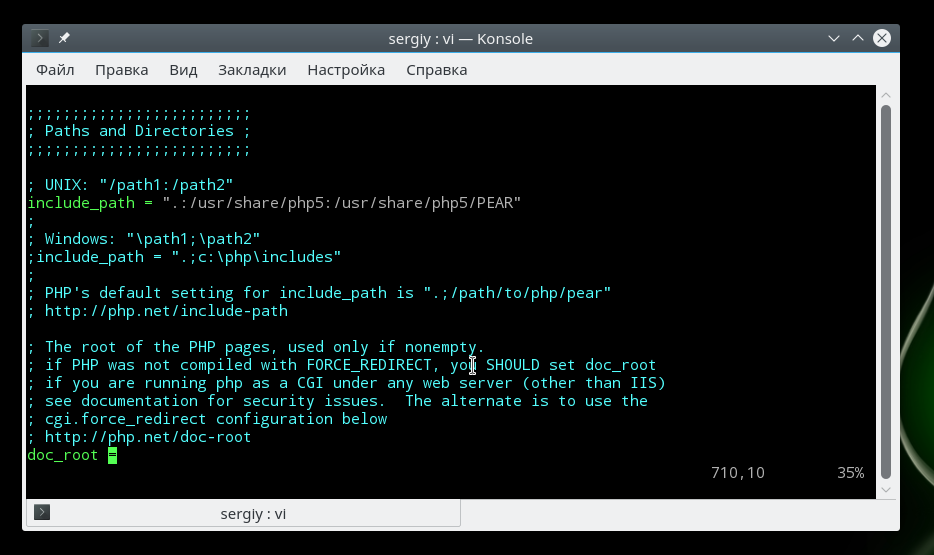
Директории по умолчанию
Файл настройки php.ini позволяет указать пути в файловой системе по умолчанию для различных действий. Вы можете задать папки где система будет искать скрипты, если вы попытаетесь подключить их с помощью инструкции include:
Папка с модулями php:
Папка для записи временных файлов:
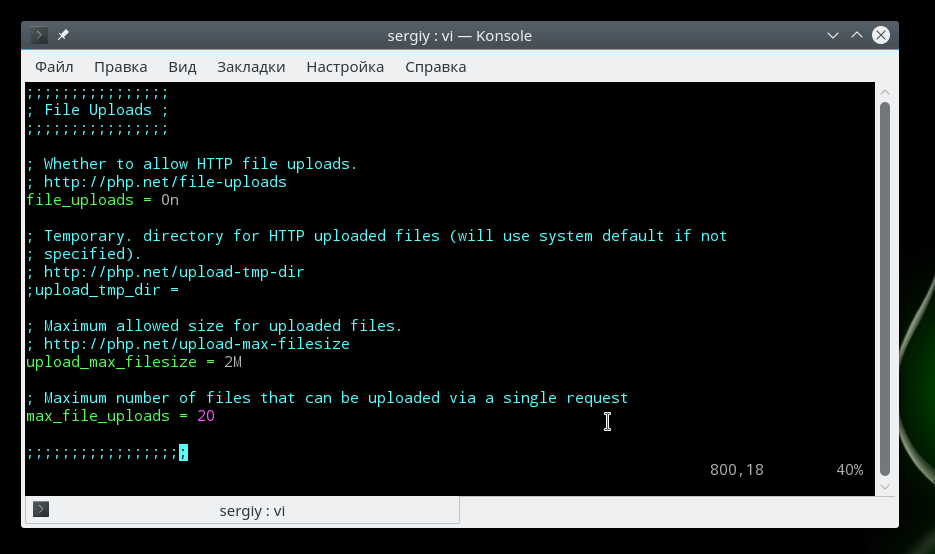
Загрузка файлов
Для того чтобы пользователи могли загружать свои файлы на сервер, например, фото, нужно включить эту функцию в php:
Максимальный размер загружаемого файла:
Максимальное количество файлов, которые может загрузить один скрипт:
Настройка php.ini практически завершена, нам остались лишь расширения.
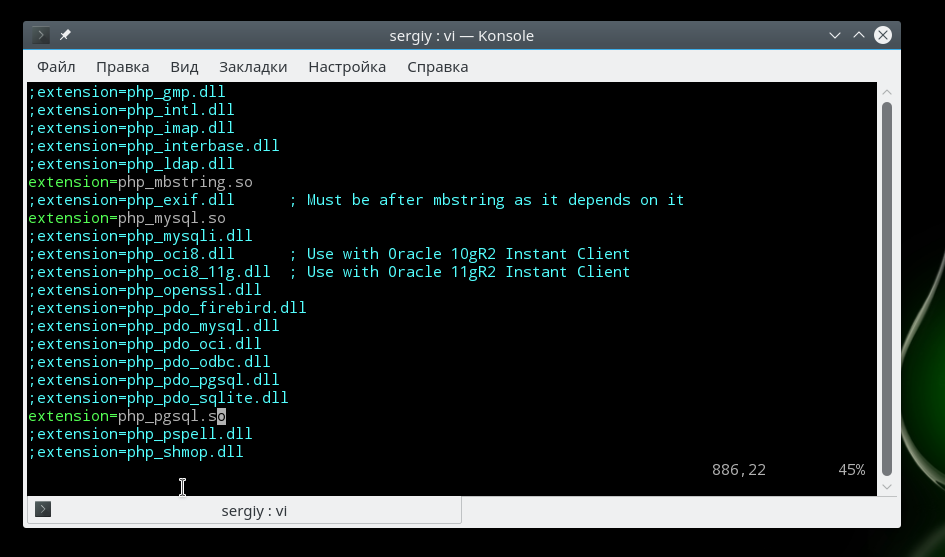
Настройка расширений
Расширения позволяют очень сильно увеличить функциональность php. Например, благодаря расширениям вы можете использовать в своих скриптах базы данных mysql, postgresql, mysqli, sqlite, графическую библиотеку gd и многое другое. Все это включается в этом разделе.
Для включения расширения достаточно убрать комментарий перед строкой с его командой, например:
extension=php_mysql.so
extension=php_mbstring.so
extension=php_pgsql.so
Обратите внимание, что для windows расширение будет иметь формат dll, но для linux нужно использовать so. В следующих секциях идет настройка каждого из расширений, но мы их рассматривать не будем потому что они обычно не требуют настройки.
Выводы
В этой статье мы рассмотрели как выполняется настройка php на сервере или обычном компьютере для разработки веб-сайтов. Файл настроек php имеет довольно простую структуру и с ним довольно не сложно справиться. После завершения всех настроек и сохранения изменений не забудьте перезагрузить веб-сервер или сервис php-fpm.
Вообще говоря, php-fpm это отдельная тема, потому что там есть много дополнительных настроек, и, возможно, мы рассмотрим его в одной из следующих статей. Если у вас остались вопросы, спрашивайте в комментариях!