- How to Fix: Sound Delays,Lags and Audio Latency in Windows 10
- Audio problems under Windows 10
- April 2021 Update:
- Run Sound Playback Troubleshooter
- Restart the Windows audio service
- Change the Audio Properties
- Reinstalling or resetting audio drivers
- Windows 10: What’s New for Audio Drivers
- Feature Summary
- Low Latency Audio Improvements
- Signal Processing Modes and Audio Categories
- Signal Processing Modes
- Audio Categories
- Hardware Offloaded APO Effects
- Cortana Voice Activation — Wake on Voice
- Windows Universal Drivers for Audio
- Resource Management for Audio Drivers
- PNP Rebalance for Audio Drivers
How to Fix: Sound Delays,Lags and Audio Latency in Windows 10
Almost all Windows 10 actions are accompanied by sound, especially on laptops. What if you notice a noticeable delay in this sound? I am not talking about a one-minute delay, but a remarkable delay that could last one to two seconds. If this is the case, in this post, we offer you a solution that allows you to correct sound delays on a Windows 10 PC.
Audio problems under Windows 10
There are a number of symptoms, but the most common and annoying audio problems that can be solved with this manual are:
- After a period of silence, it takes up to one to two seconds for the sound to be reproduced. A good example of this is the Windows 10 UAC prompt, where the message box can be displayed but the corresponding thing is not read until a second later. This can be easily verified by clicking on the audio icon in the taskbar and changing the volume: If it takes more than 100 ms for the audio notification that indicates the volume level to be played, you are probably affected by this problem.
- Garbling the first half second of the audio output after a period of silence.
- Audio and video are not synchronized in any application or video clip.
п»ї
April 2021 Update:
We now recommend using this tool for your error. Additionally, this tool fixes common computer errors, protects you against file loss, malware, hardware failures and optimizes your PC for maximum performance. You can fix your PC problems quickly and prevent others from happening with this software:
- Step 1 : Download PC Repair & Optimizer Tool (Windows 10, 8, 7, XP, Vista – Microsoft Gold Certified).
- Step 2 : Click “Start Scan” to find Windows registry issues that could be causing PC problems.
- Step 3 : Click “Repair All” to fix all issues.
Run Sound Playback Troubleshooter
Let’s start with the execution of the integrated sound problem search. Windows 10 comes with a number of special problem solvers, one of which deals with audio problems. These include reading problems that so many users have experienced, such as sound distortion, delays or even the complete absence of its system.
After its execution, the troubleshooter should either solve the problem or at least show you what causes the audio delay.
To troubleshoot audio playback in Windows 10:
- Right-click Start, then open Settings.
- Select Update and Security.
- In the left pane, select Troubleshooting.
- Expand the convenience store for audio playback, then click Run convenience store.
Restart the Windows audio service
One of the reasons you experience sound delays is a problem with the Windows audio service. You can try restarting it to solve the problem. To do this, proceed as follows:
- Press Windows + R on your keyboard. This should open the Run dialog box.
- Now type “services.msc” (without quotation marks). Click on OK.
- When prompted to allow the application, click Yes.
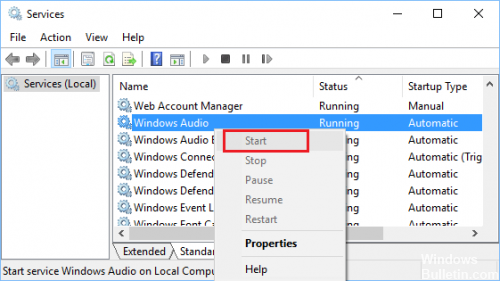
- Scroll down until you find Windows Audio. Right-click and select Properties from the options.
- Go to the General tab.
- If you notice that the service is not running, click the Start button to activate it.
- Then click on the drop-down list next to Startup Type, and select Automatically from the list.
- Click on the Restoration tab.
- Select Restart Service from the drop-down list next to First Failure.
- Save the changes by clicking on OK.
- In the Services window, search for the creator of Windows audio devices. Repeat the same steps until you reach this entry.
- Restart your computer.
Change the Audio Properties
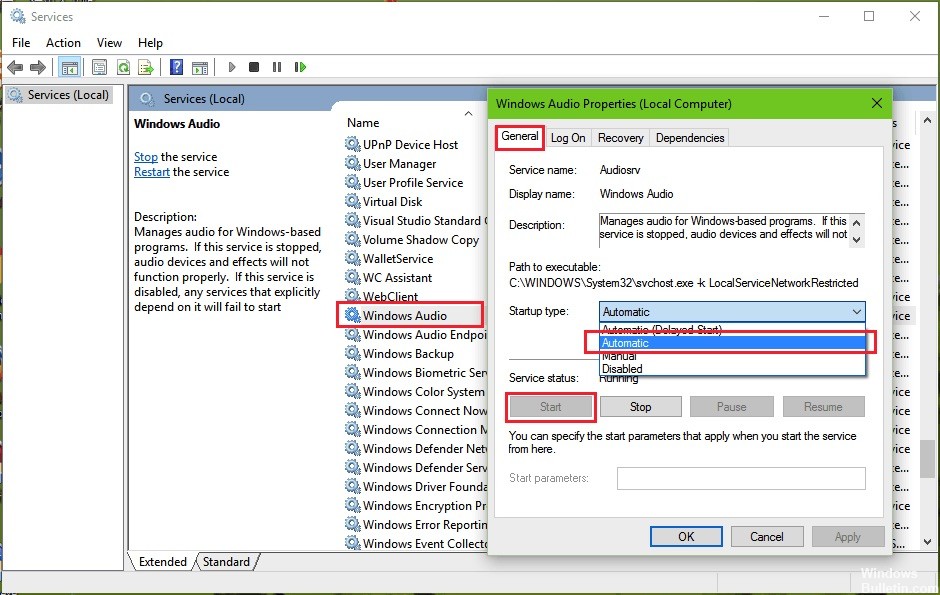
- Scroll down and find Windows Audio in the list.
- Double-click to display the Windows Audio Properties dialog box.
- Select the General tab.
- If the service is disabled, click the Start button to activate it.
- In the list of start types, select Automatic.
- Select the Restore tab.
- Select Restart service from the list of first errors. The same applies to the following two lists.
- Click on the OK button.
Reinstalling or resetting audio drivers
I suggest you follow the following steps to uninstall the audio driver.
- Right-click the Start button, then click Device Manager.
- Expand the sound, video and game controllers from the window.
- Right-click on the Realtek High Definition Audio driver and select Properties.
- Click on the Drivers tab, then click on Uninstall.
- Restart your computer and the drivers will be automatically installed on your Windows 10.
If the problem persists, I recommend that you download and install the latest audio drivers in compatibility mode for the manufacturer’s website and check that they are compatible with your computer.
CCNA, Web Developer, PC Troubleshooter
I am a computer enthusiast and a practicing IT Professional. I have years of experience behind me in computer programming, hardware troubleshooting and repair. I specialise in Web Development and Database Design. I also have a CCNA certification for Network Design and Troubleshooting.
Windows 10: What’s New for Audio Drivers
This topic provides a high level summary of what’s new in audio for WindowsВ 10.
Feature Summary
Here are the new audio features in WindowsВ 10.
Low Latency Audio Improvements
Audio latency is the delay between that time that sound is created and when it is heard. Having low audio latency is very important for several key scenarios, such as the following.
- Pro Audio
- Music Creation and Mixing
- Communications such as Skype
- Virtual and Augmented Reality
- Games
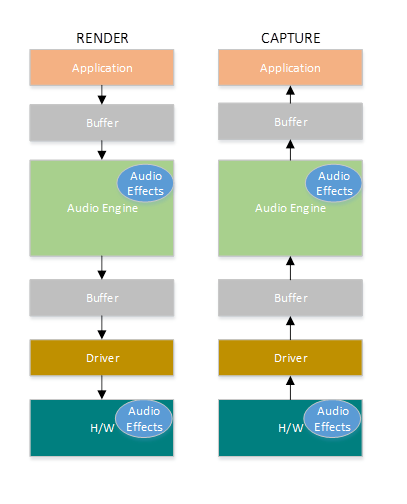
The total latency of a device is the sum of the latencies of the following components:
- Operating System
- Audio Processing Objects
- Audio Driver
- Audio Hardware
In WindowsВ 10 work was done to reduce the latency in the OS. Without any driver changes, applications in Windows 10 will experience 4.5-16ms lower latency. In addition, if the driver has been updated to take advantage of the new low latency DDIs that use small buffers to process audio data, then the latency will be reduced even more. If a driver supports 3ms audio buffers, then the roundtrip latency is
The audio stack supports multiple packet sizes and dynamic packet resizing, in order to optimize the tradeoff between latency and power based on the user’s scenario. In addition, streams will be prioritized, in order to ensure that high priority streams (e.g. phone calls) have dedicated resources.
In order for audio drivers to support low latency, WindowsВ 10 provides the following 3 new features:
- [Mandatory] Declare the minimum buffer size that is supported in each mode.
- [Optional, but recommended] Improve the coordination for the data flow between the driver and the OS.
- [Optional, but recommended] Register the driver resources (interrupts, threads), so that they can be protected by the OS in low latency scenarios. For more information, see Low Latency Audio.
Signal Processing Modes and Audio Categories
Signal Processing Modes
Drivers declare the supported audio signal processing modes for each device.
Audio categories (selected by applications) are mapped to audio modes (defined by drivers). Windows defines seven audio signal processing modes. OEMs and IHVs can determine which modes they want to implement. The modes are summarized in the table shown below.
| Mode | Render/Capture | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Raw | Both | Raw mode specifies that there should not be any signal processing applied to the stream. An application can request a raw stream that is completely untouched and perform its own signal processing. |
| Default | Both | This mode defines the default audio processing. |
| Movies* | Render | Movie audio playback |
| Media* | Both | Music audio playback (default for most media streams) |
| Speech* | Capture | Human voice capture (e.g. input to Cortana) |
| Communications* | Both | VOIP render and capture (e.g. Skype, Lync) |
| Notification* | Render | Ringtones, alarms, alerts, etc. |
Audio device drivers need to support at least the Raw or Default mode. Supporting additional modes is optional.
Dedicated modes for speech, movie, music and communications. Audio drivers will be able to define different type of audio formats and processing, based on the stream type.
Audio Categories
The following table shows the audio categories in WindowsВ 10.
In order to inform the system about the usage of an audio stream, applications have the option to tag the stream with a specific audio stream category. In Windows 10 there are nine audio stream categories.
| Category | Description |
|---|---|
| Movie* | Movies, video with dialog (Replaces ForegroundOnlyMedia) |
| Media* | Default category for media playback (Replaces BackgroundCapableMedia) |
| Game Chat* | In-game communication between users (New category in Windows 10) |
| Speech* | Speech input (e.g. personal assistant) and output (e.g. navigation apps) (New category in Windows 10) |
| Communications | VOIP, real-time chat |
| Alerts | Alarm, ring tone, notifications |
| Sound Effects | Beeps, dings, etc |
| Game Media | In game music |
| Game Effects | Balls bouncing, car engine sounds, bullets, etc. |
| Other | Uncategorized streams |
* New in WindowsВ 10.
Hardware Offloaded APO Effects
WindowsВ 10 supports hardware offloaded APO effects. APOs can be loaded on top of the offload pin. This allows for the audio processing to be done in both software and hardware. In addition, the processing can change dynamically. Some or all of the processing can be moved from the software APO to the DSP when there are enough hardware resources and then moved back to the software APO when the load in the DSP increases.
Cortana Voice Activation — Wake on Voice
Cortana, the personal assistant technology was first demonstarted at the Microsoft BUILD Developer Conference in 2013. Voice activation is a feature that enables users to invoke a speech recognition engine from various device power states by saying a specific phrase — «Hey Cortana». The «Hey Cortana» Voice Activation (VA) feature allows users to quickly engage an experience (e.g., Cortana) outside of their active context (i.e., what is currently on screen) by using their voice. The feature is targeted for scenarios when the screen is off, idle or when it is fully active. If the hardware supports buffering, users can then chain the key phrase and command phrase together. This improves the end to end wake on voice experience for the user. For more information, see Voice Activation.
Windows Universal Drivers for Audio
Windows 10 supports one driver model that works for PC and 2:1’s and Windows 10 for phones and small screen tablets. This means that IHVs can develop their driver in one platform and that driver works in all devices (desktops, laptops, tablets, phones). The result is reduced development time and cost.
In order to develop Universal Audio Drivers, use the following tools:
- Visual Studio 2015: New driver settings allow the “Target Platform” to be set to “Universal” to create a multi-platform driver.
- APIValidator: This is a WDK tool that checks whether driver is universal and highlights calls that need to be updated.
- Audio samples in GitHub: The sysvad and SwapAPO have been converted to be Universal Drivers. For more information and pointers to GitHub sample code, see Universal Windows Drivers for Audio.
Resource Management for Audio Drivers
One challenge with creating a good audio experience on a low cost mobile device, is that some devices have various concurrency constraints. For example, it is possible that the device can only play up to 6 audio streams concurrently and supports only 2 offload streams. When there is an active phone call on a mobile device, it is possible that the device supports only 2 audio streams. When the device is capturing audio, the device can only play up to 4 audio streams.
WindowsВ 10 includes a mechanism to express concurrency constraints to insure that high-priority audio streams and cellular phone calls will be able to play. If the system does not have enough resources, then low priority streams are terminated. This mechanism is only available in phones and tablets not on desktops or laptops.
PNP Rebalance for Audio Drivers
PNP rebalancing is used in certain PCI scenarios where memory resources need to be reallocated. In that case, some drivers are unloaded, and then reloaded at different memory locations, in order to create free contiguous memory space. Rebalance can be triggered in two main scenarios:
- PCI hotplug: A user plugs in a device and the PCI bus does not have enough resources to load the driver for the new device. Some examples of devices that fall into this category include Thunderbolt, USB-C and NVME Storage. In this scenario, memory resources need to be rearranged and consolidated (rebalanced) to support the additional devices being added.
- PCI resizeable BARs: After a driver for a device is successfully loaded in memory, it requests additional resources. Some examples of devices include high-end graphics cards and storage devices. For more information, see Implement PnP Rebalance for PortCls Audio Drivers.
—>