- Отключение Credential Guard or Device Guard в Windows 10 Pro / SL
- Manage Windows Defender Credential Guard
- Enable Windows Defender Credential Guard
- Enable Windows Defender Credential Guard by using Group Policy
- Enable Windows Defender Credential Guard by using Intune
- Enable Windows Defender Credential Guard by using the registry
- Add the virtualization-based security features
- Enable virtualization-based security and Windows Defender Credential Guard
- Enable Windows Defender Credential Guard by using the HVCI and Windows Defender Credential Guard hardware readiness tool
- Review Windows Defender Credential Guard performance
- Disable Windows Defender Credential Guard
- Disable Windows Defender Credential Guard by using the HVCI and Windows Defender Credential Guard hardware readiness tool
- Disable Windows Defender Credential Guard for a virtual machine
Отключение Credential Guard or Device Guard в Windows 10 Pro / SL
Привет всем. Итак, недавно моя вторая система Windows 10 SL обновилась до сборки 1803, ну и все бы ничего, но при попытке создать и запустить новую виртуальную машину использюя VMWare Workstation 14, я обнаружил ошибку, которая сообщала мне что Credential Guard or Device Guard не позволяет мне использовать МОЮ виртуализацию, по этому я должен ее отключить и мне предлагается перейти по ссылке на сайт VMWare где подробно описано как это сделать. И все бы ничего, но инструкция предназначена для Windows 10 редакции Server и, конечно же, есть определенные отличия в плане ПО и не только, между серверной редакцией и моей десктопной. Инструкция мне не подходит.
Посетив несколько тематических забугорных форумов и почитав активные обсуждения, я обратил внимание что тем людям, которые задают такой же вопрос, обычно пишут ответ типа «ерунду несешь, данная фича — Credential Guard or Device Guard есть только в Windows редакции Server». Звучит глупо, знатоки еще те. Читая дальше и вникая в суть мне стало понятно, что в этой ошибке есть некоторая связь с Hyper-V (нативной системой виртуализации в Windows), но для десктопных Windows 10 Hyper-V доступен только в редакциях Pro и выше (типа Enterprise) как это связано с моей Single Language мне было не понятно. Данный тип редакции базово не имеет поддержки Hyper-V.
РЕШЕНИЕ.
Каким-то странным истечением обстоятельств я забрел в в установку и удаление компонентов системы и обнаружил там некоторую включенную опцию, которой ранее не было в моей системе. Опция называется Windows Hypervisor Platform. Ну вот, собственно, отключив эту опцию после перезагрузки системы, виртуальная машина под управлением VMWare Workstation начала работать без ошибок как обычно.
Если вы столкнулись с этой проблемой, попробуйте решить ее так. Отпишитесь обязательно в комментариях, у кого получилось / не получислоь.
Manage Windows Defender Credential Guard
Applies to
- Windows 10 Enterprise or Education SKUs
- Windows ServerВ 2016
- Windows Server 2019
Enable Windows Defender Credential Guard
Windows Defender Credential Guard can be enabled either by using Group Policy, the registry, or the Hypervisor-Protected Code Integrity (HVCI) and Windows Defender Credential Guard hardware readiness tool. Windows Defender Credential Guard can also protect secrets in a Hyper-V virtual machine, just as it would on a physical machine. The same set of procedures used to enable Windows Defender Credential Guard on physical machines applies also to virtual machines.
Enable Windows Defender Credential Guard by using Group Policy
You can use Group Policy to enable Windows Defender Credential Guard. This will add and enable the virtualization-based security features for you if needed.
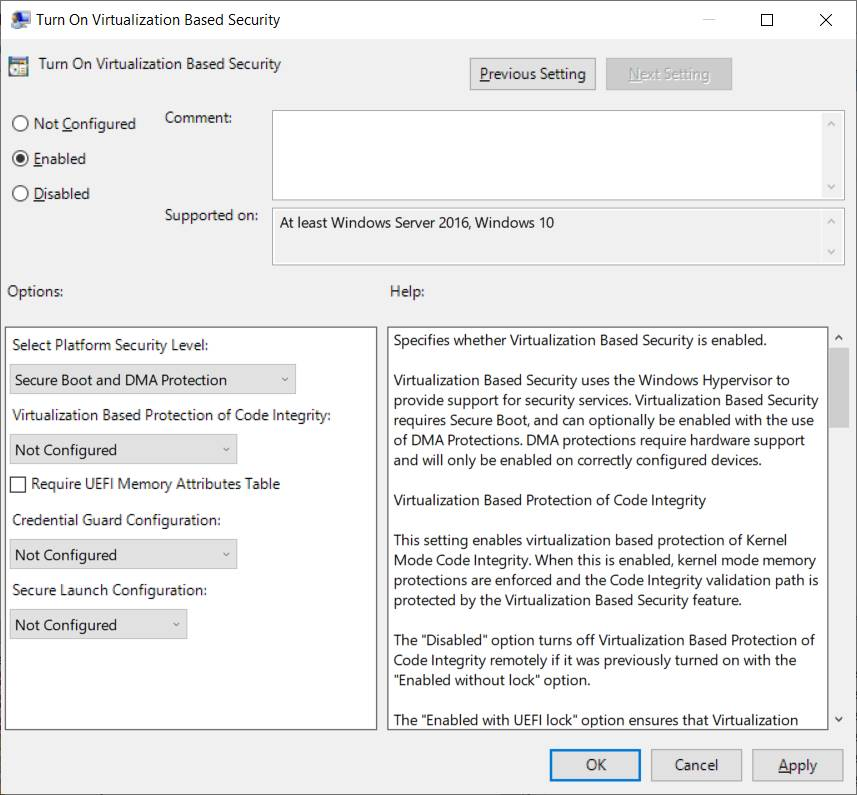
From the Group Policy Management Console, go to Computer Configuration -> Administrative Templates -> System -> Device Guard.
Double-click Turn On Virtualization Based Security, and then click the Enabled option.
In the Select Platform Security Level box, choose Secure Boot or Secure Boot and DMA Protection.
In the Credential Guard Configuration box, click Enabled with UEFI lock, and then click OK. If you want to be able to turn off Windows Defender Credential Guard remotely, choose Enabled without lock.
In the Secure Launch Configuration box, choose Not Configured, Enabled or Disabled. Check this article for more details.
Close the Group Policy Management Console.
To enforce processing of the group policy, you can run gpupdate /force .
Enable Windows Defender Credential Guard by using Intune
From Home, click Microsoft Intune.
Click Device configuration.
Click Profiles > Create Profile > Endpoint protection > Windows Defender Credential Guard.
It will enable VBS and Secure Boot and you can do it with or without UEFI Lock. If you will need to disable Credential Guard remotely, enable it without UEFI lock.
You can also configure Credential Guard by using an account protection profile in endpoint security. See Account protection policy settings for endpoint security in Intune.
Enable Windows Defender Credential Guard by using the registry
If you don’t use Group Policy, you can enable Windows Defender Credential Guard by using the registry. Windows Defender Credential Guard uses virtualization-based security features which have to be enabled first on some operating systems.
Add the virtualization-based security features
Starting with Windows 10, version 1607 and Windows Server 2016, enabling Windows features to use virtualization-based security is not necessary and this step can be skipped.
If you are using Windows 10, version 1507 (RTM) or Windows 10, version 1511, Windows features have to be enabled to use virtualization-based security. You can do this by using either the Control Panel or the Deployment Image Servicing and Management tool (DISM).
If you enable Windows Defender Credential Guard by using Group Policy, the steps to enable Windows features through Control Panel or DISM are not required. Group Policy will install Windows features for you.
Add the virtualization-based security features by using Programs and Features
Open the Programs and Features control panel.
Click Turn Windows feature on or off.
Go to Hyper-V -> Hyper-V Platform, and then select the Hyper-V Hypervisor check box.
Select the Isolated User Mode check box at the top level of the feature selection.
Click OK.
Add the virtualization-based security features to an offline image by using DISM
Open an elevated command prompt.
Add the Hyper-V Hypervisor by running the following command:
Add the Isolated User Mode feature by running the following command:
In Windows 10, version 1607 and later, the Isolated User Mode feature has been integrated into the core operating system. Running the command in step 3 above is therefore no longer required.
You can also add these features to an online image by using either DISM or Configuration Manager.
Enable virtualization-based security and Windows Defender Credential Guard
Open Registry Editor.
Enable virtualization-based security:
Go to HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\DeviceGuard.
Add a new DWORD value named EnableVirtualizationBasedSecurity. Set the value of this registry setting to 1 to enable virtualization-based security and set it to 0 to disable it.
Add a new DWORD value named RequirePlatformSecurityFeatures. Set the value of this registry setting to 1 to use Secure Boot only or set it to 3 to use Secure Boot and DMA protection.
Enable Windows Defender Credential Guard:
Go to HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\LSA.
Add a new DWORD value named LsaCfgFlags. Set the value of this registry setting to 1 to enable Windows Defender Credential Guard with UEFI lock, set it to 2 to enable Windows Defender Credential Guard without lock, and set it to 0 to disable it.
Close Registry Editor.
You can also enable Windows Defender Credential Guard by setting the registry entries in the FirstLogonCommands unattend setting.
Enable Windows Defender Credential Guard by using the HVCI and Windows Defender Credential Guard hardware readiness tool
You can also enable Windows Defender Credential Guard by using the HVCI and Windows Defender Credential Guard hardware readiness tool.
When running the HVCI and Windows Defender Credential Guard hardware readiness tool on a non-English operating system, within the script, change $OSArch = $(gwmi win32_operatingsystem).OSArchitecture to be $OSArch = $((gwmi win32_operatingsystem).OSArchitecture).tolower() instead, in order for the tool to work.
This is a known issue.
Review Windows Defender Credential Guard performance
Is Windows Defender Credential Guard running?
You can view System Information to check that Windows Defender Credential Guard is running on a PC.
Click Start, type msinfo32.exe, and then click System Information.
Click System Summary.
Confirm that Credential Guard is shown next to Virtualization-based security Services Running.
Here’s an example:
You can also check that Windows Defender Credential Guard is running by using the HVCI and Windows Defender Credential Guard hardware readiness tool.
When running the HVCI and Windows Defender Credential Guard hardware readiness tool on a non-English operating system, within the script, change *$OSArch = $(gwmi win32_operatingsystem).OSArchitecture to be $OSArch = $((gwmi win32_operatingsystem).OSArchitecture).tolower() instead, in order for the tool to work.
This is a known issue.
For client machines that are running Windows 10 1703, LsaIso.exe is running whenever virtualization-based security is enabled for other features.
We recommend enabling Windows Defender Credential Guard before a device is joined to a domain. If Windows Defender Credential Guard is enabled after domain join, the user and device secrets may already be compromised. In other words, enabling Credential Guard will not help to secure a device or identity that has already been compromised, which is why we recommend turning on Credential Guard as early as possible.
You should perform regular reviews of the PCs that have Windows Defender Credential Guard enabled. This can be done with security audit policies or WMI queries. Here’s a list of WinInit event IDs to look for:
Event ID 13 Windows Defender Credential Guard (LsaIso.exe) was started and will protect LSA credentials.
Event ID 14 Windows Defender Credential Guard (LsaIso.exe) configuration: [0x0 | 0x1 | 0x2], 0
The first variable: 0x1 or 0x2 means that Windows Defender Credential Guard is configured to run. 0x0 means that it’s not configured to run.
The second variable: 0 means that it’s configured to run in protect mode. 1 means that it’s configured to run in test mode. This variable should always be 0.
Event ID 15 Windows Defender Credential Guard (LsaIso.exe) is configured but the secure kernel is not running; continuing without Windows Defender Credential Guard.
Event ID 16 Windows Defender Credential Guard (LsaIso.exe) failed to launch: [error code]
Event ID 17 Error reading Windows Defender Credential Guard (LsaIso.exe) UEFI configuration: [error code]
You can also verify that TPM is being used for key protection by checking Event ID 51 in the Microsoft -> Windows -> Kernel-Boot event source. If you are running with a TPM, the TPM PCR mask value will be something other than 0.
Event ID 51 VSM Master Encryption Key Provisioning. Using cached copy status: 0x0. Unsealing cached copy status: 0x1. New key generation status: 0x1. Sealing status: 0x1. TPM PCR mask: 0x0.
You can use Windows PowerShell to determine whether credential guard is running on a client computer. On the computer in question, open an elevated PowerShell window and run the following command:
This command generates the following output:
0: Windows Defender Credential Guard is disabled (not running)
1: Windows Defender Credential Guard is enabled (running)
Checking the task list or Task Manager to see if LSAISO.exe is running is not a recommended method for determining whether Windows Defender Credential Guard is running.
Disable Windows Defender Credential Guard
To disable Windows Defender Credential Guard, you can use the following set of procedures or the Device Guard and Credential Guard hardware readiness tool. If Credential Guard was enabled with UEFI Lock then you must use the following procedure as the settings are persisted in EFI (firmware) variables and it will require physical presence at the machine to press a function key to accept the change. If Credential Guard was enabled without UEFI Lock then you can turn it off by using Group Policy.
If you used Group Policy, disable the Group Policy setting that you used to enable Windows Defender Credential Guard (Computer Configuration -> Administrative Templates -> System -> Device Guard -> Turn on Virtualization Based Security).
Delete the following registry settings:
If you also wish to disable virtualization-based security delete the following registry settings:
If you manually remove these registry settings, make sure to delete them all. If you don’t remove them all, the device might go into BitLocker recovery.
Delete the Windows Defender Credential Guard EFI variables by using bcdedit. From an elevated command prompt, type the following commands:
Accept the prompt to disable Windows Defender Credential Guard.
Alternatively, you can disable the virtualization-based security features to turn off Windows Defender Credential Guard.
The PC must have one-time access to a domain controller to decrypt content, such as files that were encrypted with EFS. If you want to turn off both Windows Defender Credential Guard and virtualization-based security, run the following bcdedit commands after turning off all virtualization-based security Group Policy and registry settings:
For more info on virtualization-based security and HVCI, see Enable virtualization-based protection of code integrity.
Credential Guard and Device Guard are not supported when using Azure Gen 1 VMs. These options are available with Gen 2 VMs only.
Disable Windows Defender Credential Guard by using the HVCI and Windows Defender Credential Guard hardware readiness tool
You can also disable Windows Defender Credential Guard by using the HVCI and Windows Defender Credential Guard hardware readiness tool.
When running the HVCI and Windows Defender Credential Guard hardware readiness tool on a non-English operating system, within the script, change *$OSArch = $(gwmi win32_operatingsystem).OSArchitecture to be $OSArch = $((gwmi win32_operatingsystem).OSArchitecture).tolower() instead, in order for the tool to work.
This is a known issue.
Disable Windows Defender Credential Guard for a virtual machine
From the host, you can disable Windows Defender Credential Guard for a virtual machine: